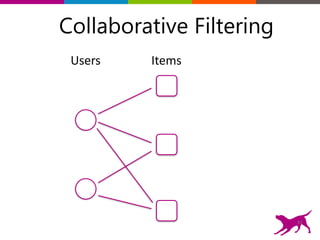
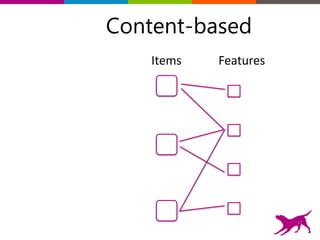
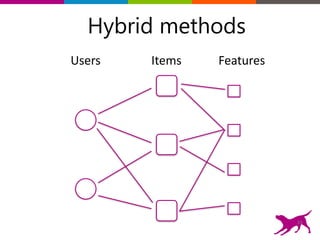
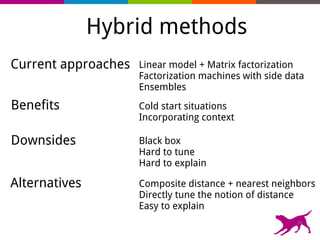
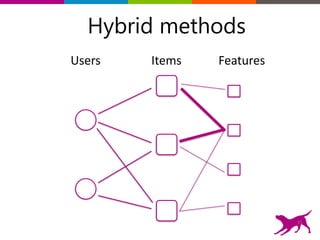
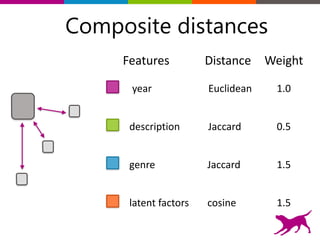
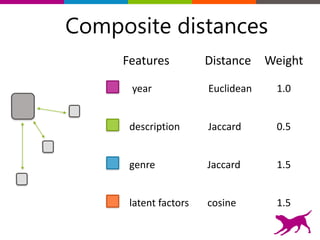
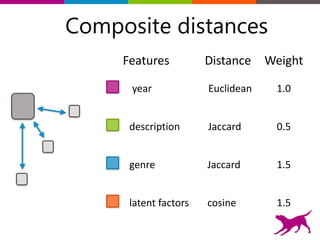
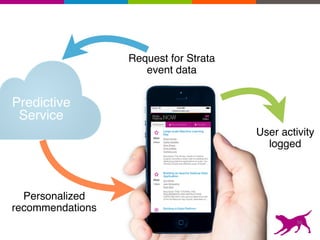
The document is an introductory tutorial on recommender systems presented at the Strata + Hadoop World in NYC, 2015. It covers the fundamentals of collaborative filtering, content-based recommendations, and hybrid methods, emphasizing their applications in platforms like Netflix and Spotify. Additionally, it discusses practical considerations for feedback, evaluation, and tuning in deploying such systems.



















![recs = sim_model.recommend()
>>> nn_model
Class : NearestNeighborsModel
Distance : jaccard
Method : brute force
Number of examples : 195
Number of feature columns : 1
Number of unpacked features : 5170
Total training time (seconds) : 0.0318
talks[‘bow’] = gl.text_analytics.count_words(talks[‘abstract’])
talks[‘tfidf’] = gl.text_analytics.tf_idf(talks[‘bow’])
nn_model = gl.nearest_neighbors.create(talks, ‘id’, features=[‘tfidf’])
nbrs = nn_model.query(talks, label=‘id’, k=50)
sim_model = gl.item_similarity_recommender.create(historical, nearest=nbrs)
>>> historical
+------------+----------+------------------+---------+------------+
| date | time | user | item_id | event_type |
+------------+----------+------------------+---------+------------+
| 2015-02-12 | 07:05:37 | 809c0dc2548cbbc3 | 38825 | like |
| 2015-02-12 | 07:05:39 | 809c0dc2548cbbc3 | 38825 | like |
>>> talks
+------------+------------+-------------------------------+--------------------------------+
| date | start_time | title | tech_tags |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------+--------------------------------+
| 02/20/2015 | 10:40am | The IoT P2P Backbone | [MapReduce, Storm, Docker,... |
| 02/20/2015 | 10:40am | Practical Problems in Dete... | [Storm, Docker, Impala, R,... |
| 02/19/2015 | 1:30pm | From MapReduce to Programm... | [MapReduce, Spark, Apache,... |
| 02/19/2015 | 2:20pm | Drill into Drill: How Prov... | [JAVA, Docker, R, Hadoop, SQL] |
| 02/19/2015 | 4:50pm | Maintaining Low Latency wh... | [Apache, Hadoop, HBase, YA... |
| 02/20/2015 | 4:00pm | Top Ten Pitfalls to Avoid ... | [MapReduce, Hadoop, JAVA, ... |
| 02/20/2015 | 4:00pm | Using Data to Help Farmers... | [MapReduce, Spark, Storm, ... |
| 02/19/2015 | 1:30pm | Sears Hometown and Outlet... | [Hadoop, Spark, Docker, R,... |
| 02/20/2015 | 11:30am | Search Evolved: Unraveling... | [Docker, R, Hadoop, SQL, R... |
| 02/19/2015 | 4:00pm | Data Dexterity: Immediate ... | [Hadoop, NoSQL, Spark, Sto... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------+--------------------------------+
[195 rows x 4 columns]
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strata-nyc-2015-recommendation-systems-150928235216-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-Recommender-Systems-26-320.jpg)
![recs = sim_model.recommend()
>>> si
Class
Schema
------
User I
Item I
Target
Additi
Number
Number
Statis
------
Number
Number
Number
Traini
------
Traini
Settin
>>> nn_model
Class : NearestNeighborsModel
Distance : jaccard
Method : brute force
Number of examples : 195
Number of feature columns : 1
Number of unpacked features : 5170
Total training time (seconds) : 0.0318
talks[‘bow’] = gl.text_analytics.count_words(talks[‘abstract’])
talks[‘tfidf’] = gl.text_analytics.tf_idf(talks[‘bow’])
nn_model = gl.nearest_neighbors.create(talks, ‘id’, features=[‘tfidf’])
nbrs = nn_model.query(talks, label=‘id’, k=50)
sim_model = gl.item_similarity_recommender.create(historical, nearest=nbrs)
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strata-nyc-2015-recommendation-systems-150928235216-lva1-app6891/85/Introduction-to-Recommender-Systems-27-320.jpg)