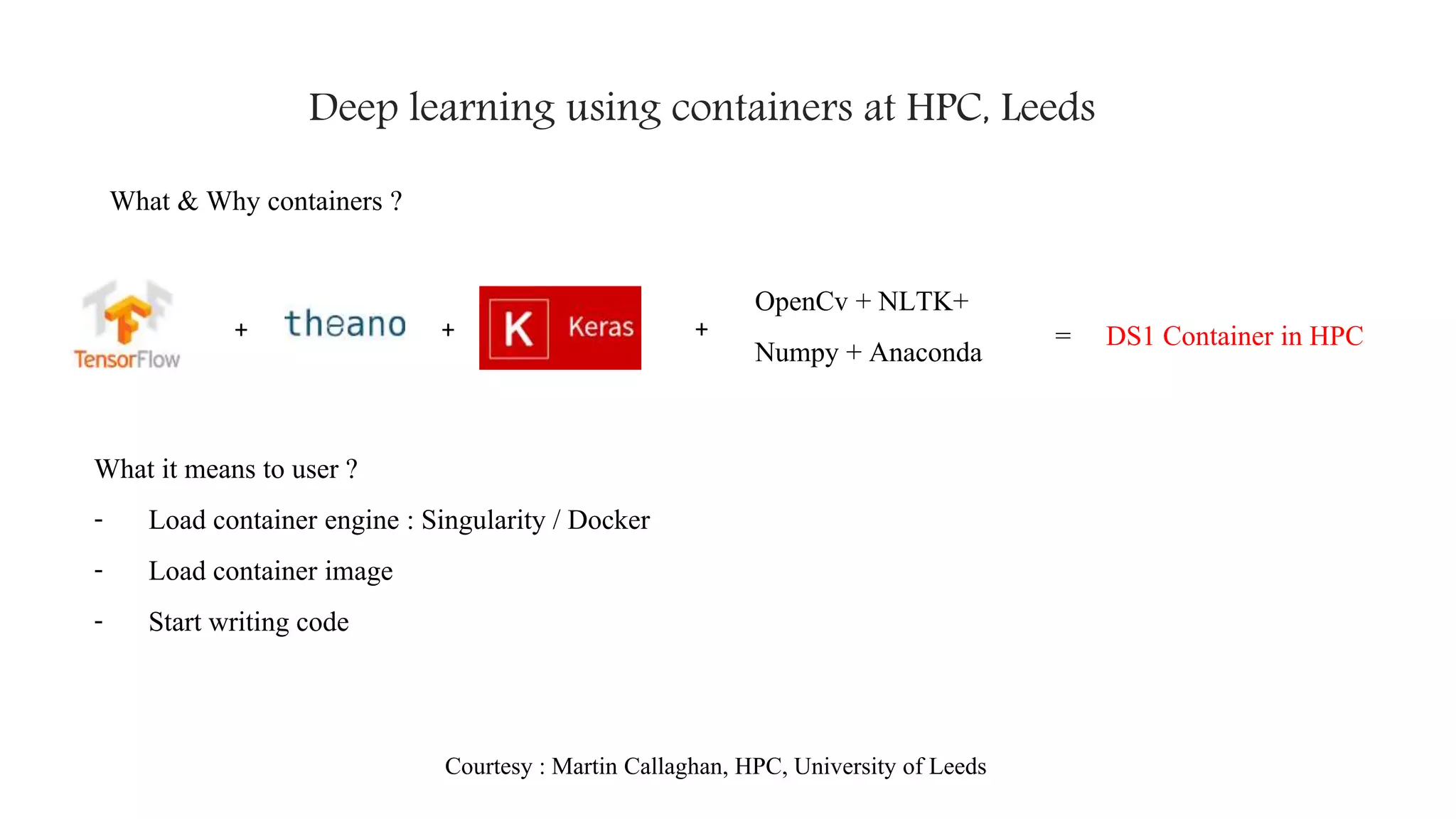
The document provides an introduction to deep learning, covering its history, key concepts like convolutional neural networks, and research focuses in image segmentation. It discusses various applications of deep learning across fields such as computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics, as well as current activities at the University of Leeds. The text emphasizes the evolution of deep learning, addressing challenges and advancements including containerization for high-performance computing.


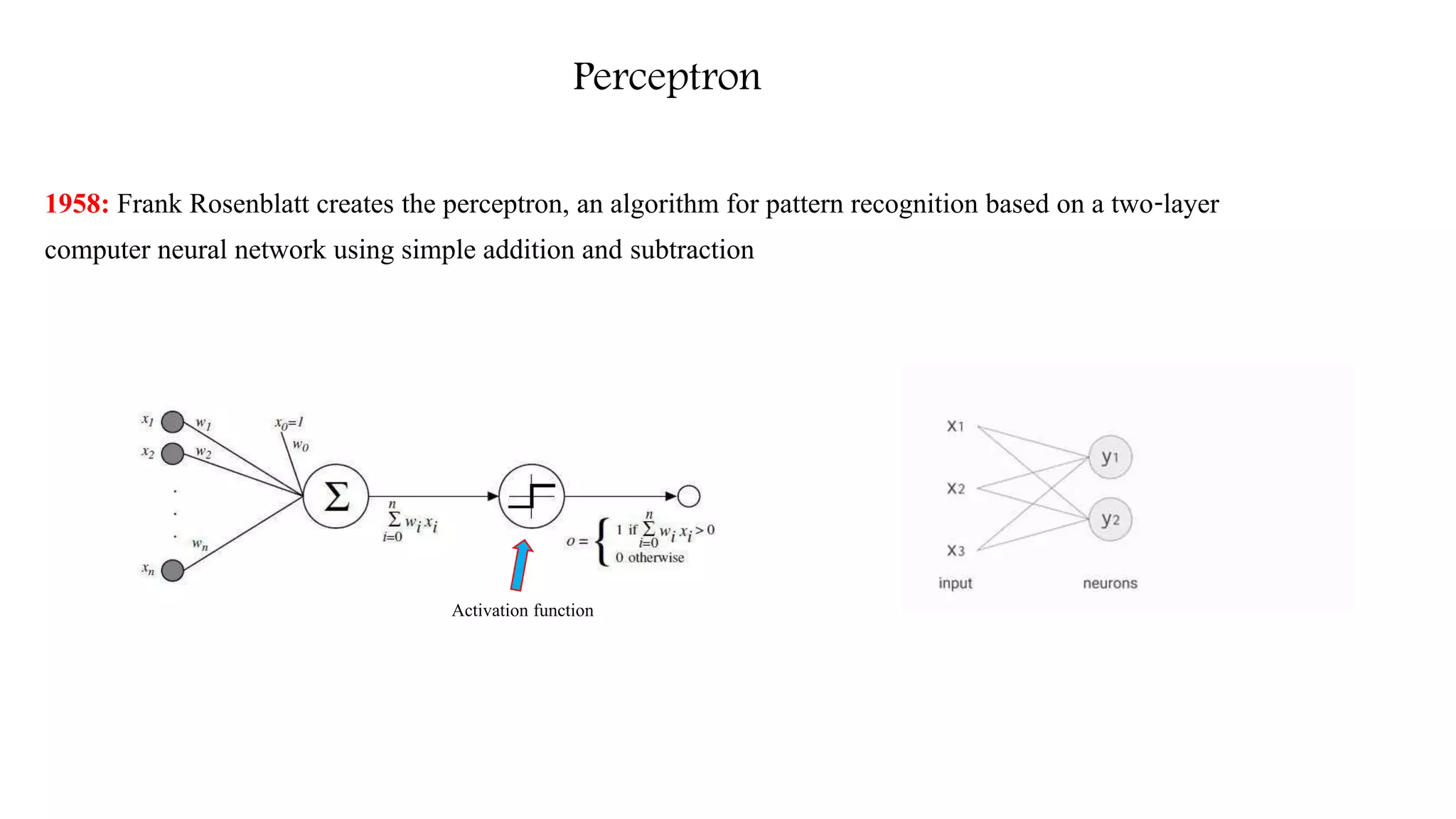
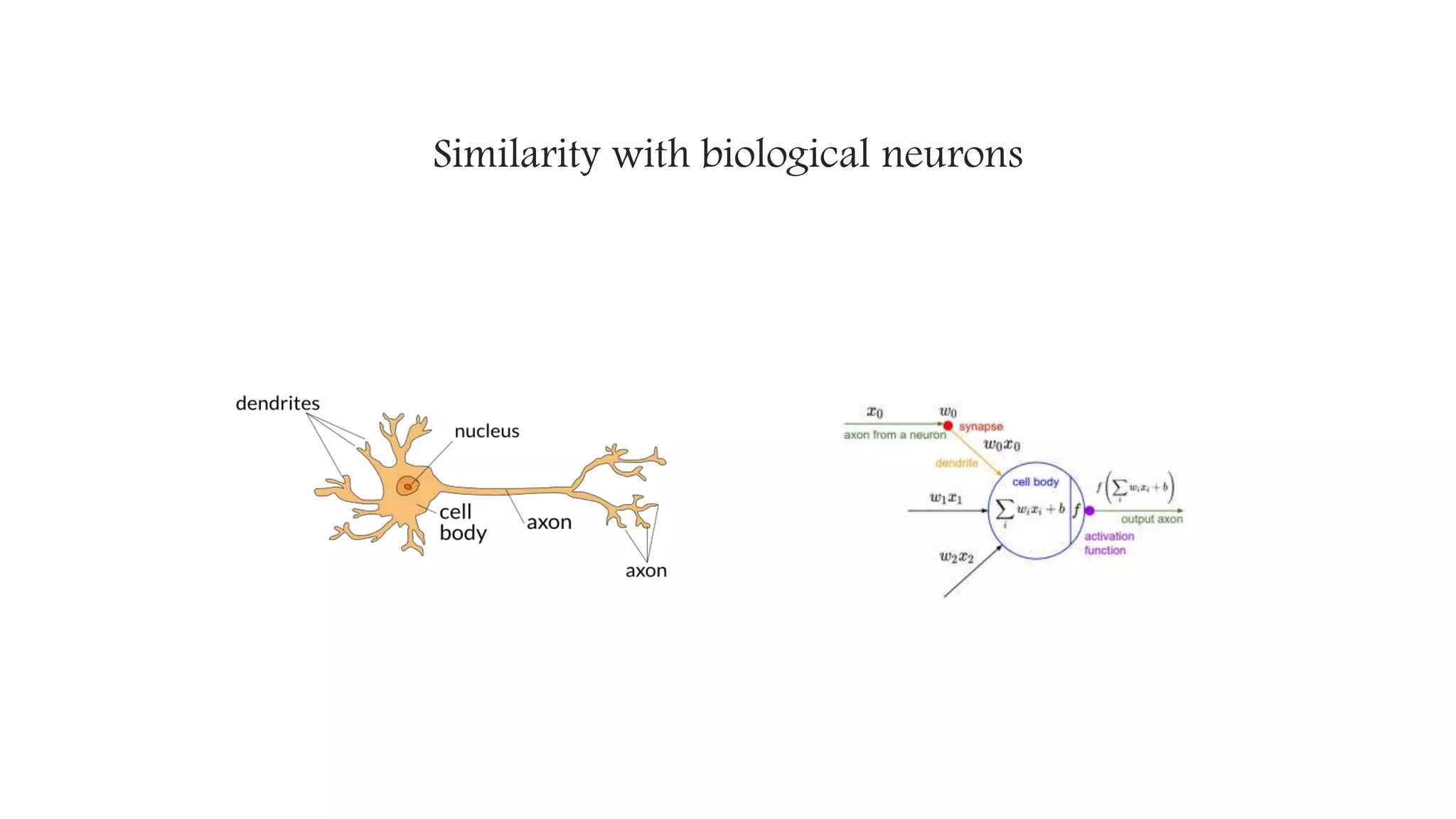


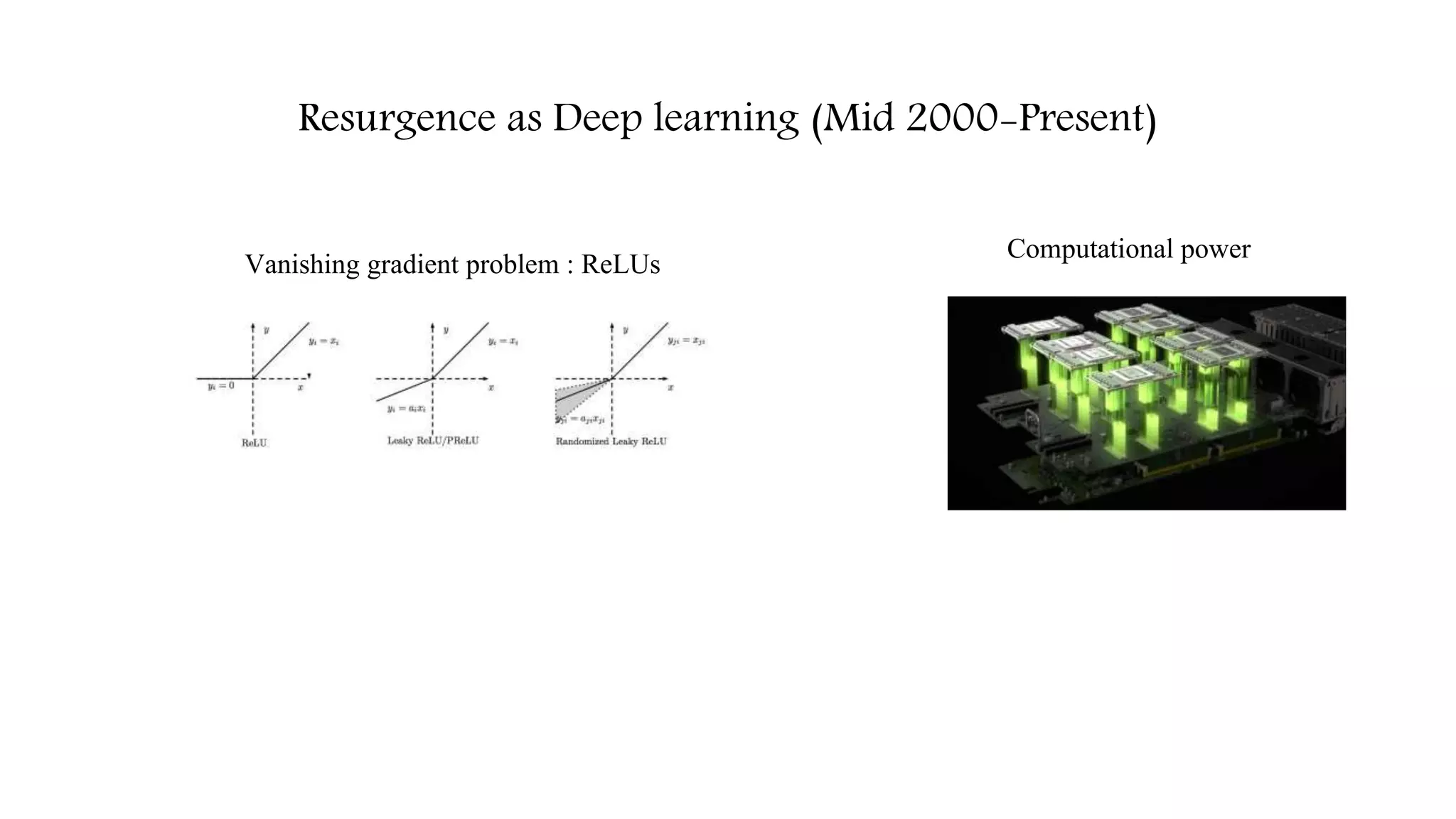
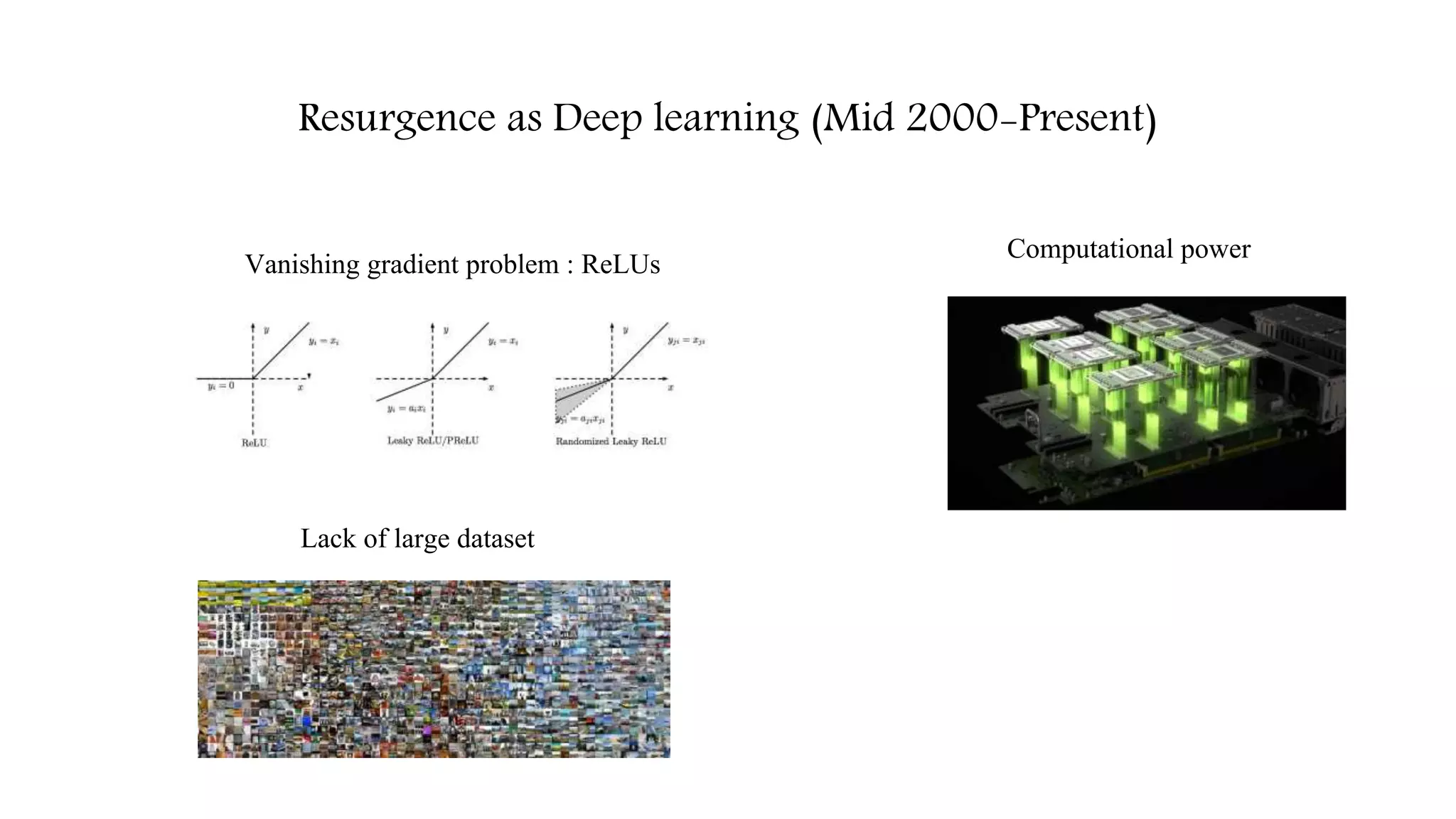
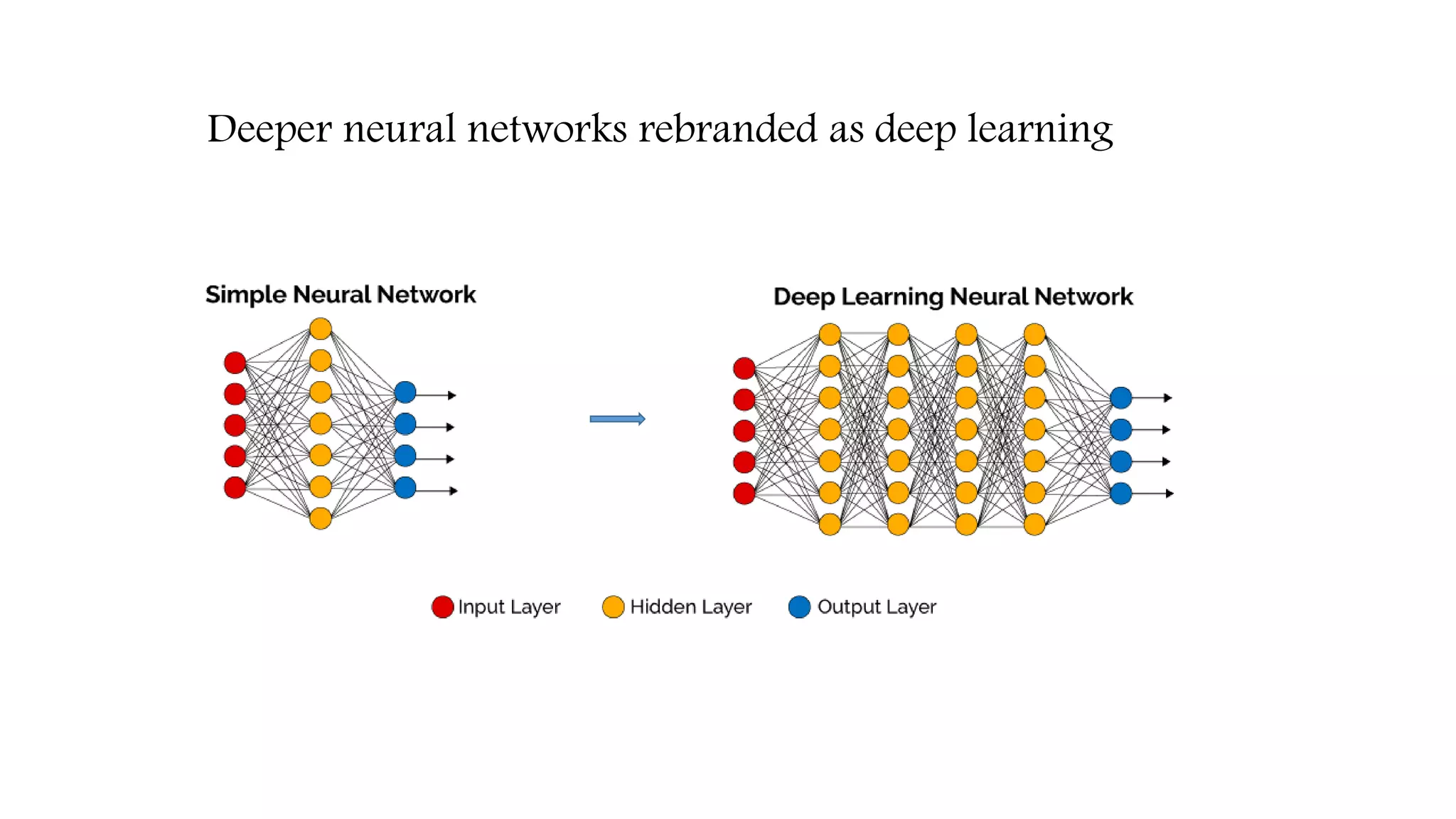
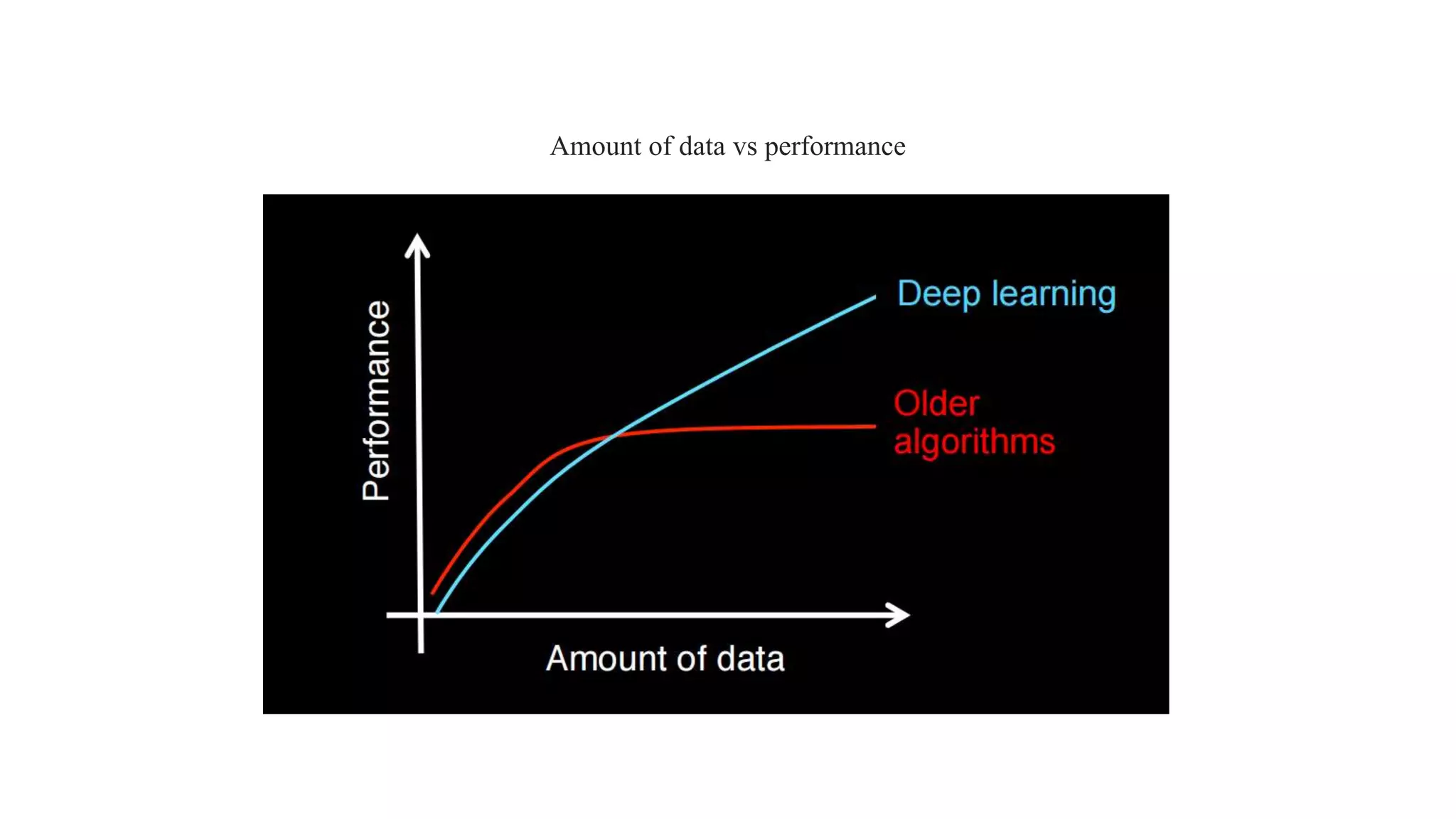
![Resurgence as Deep learning (Mid 2000-Present)
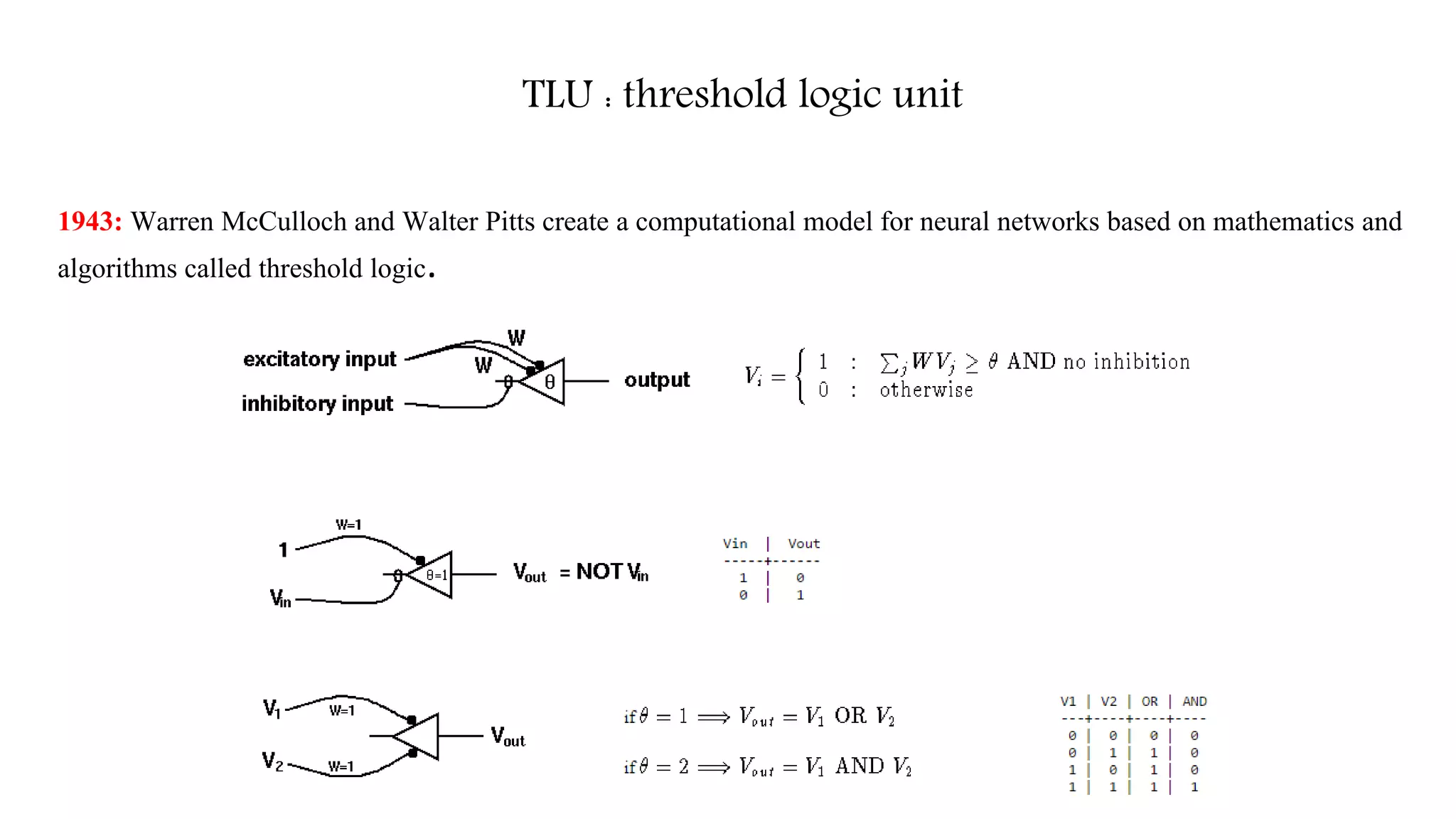
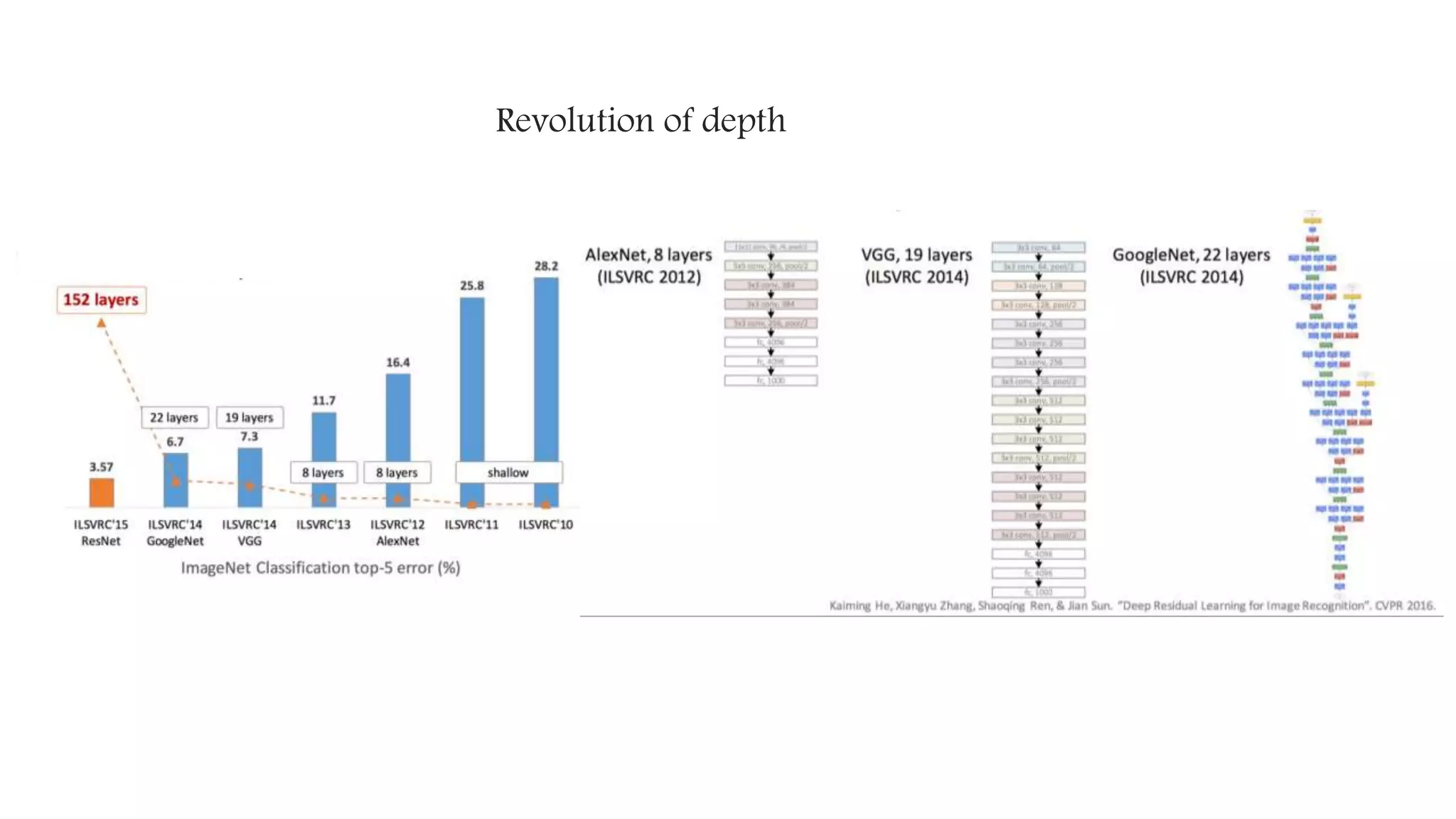
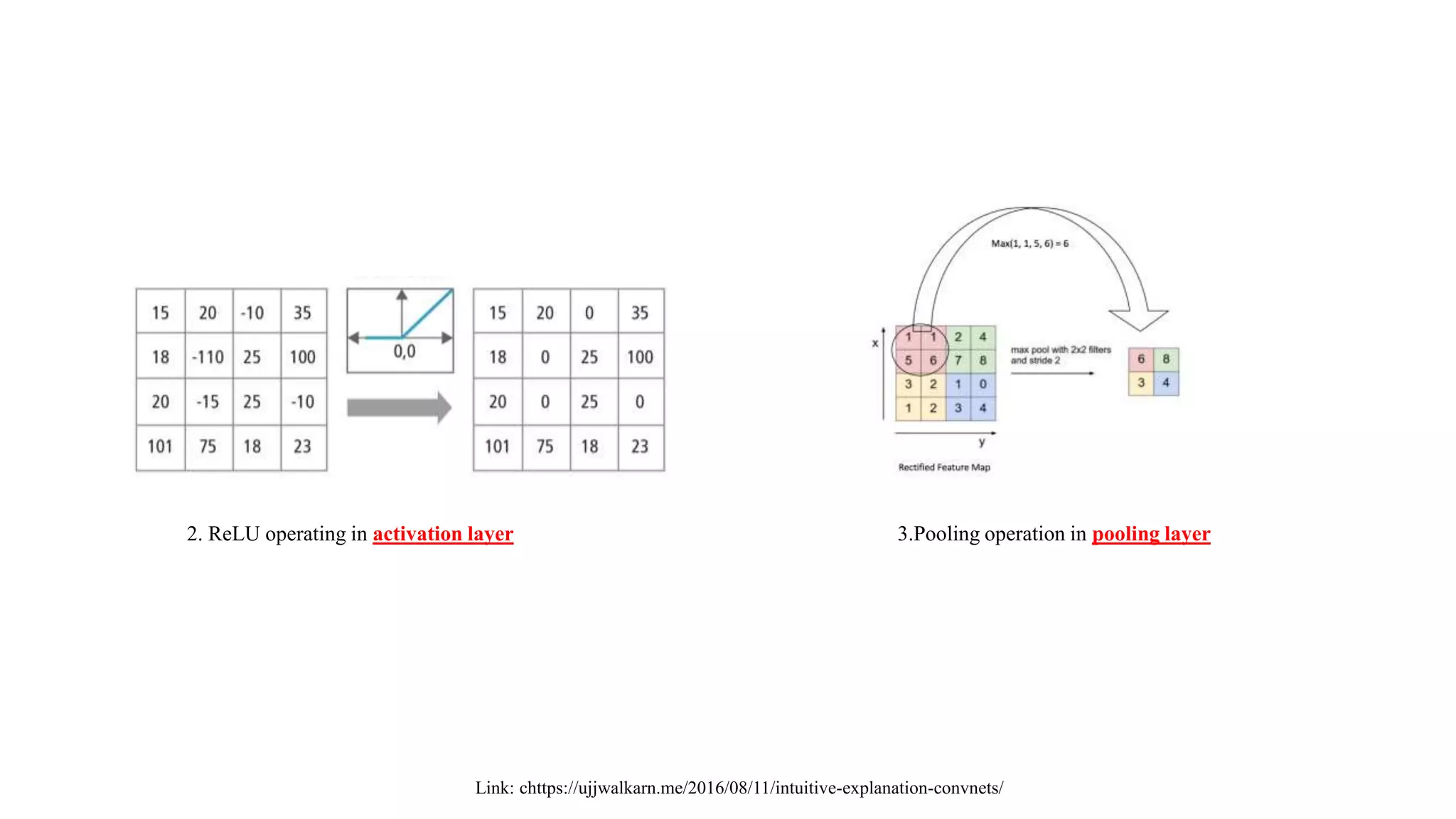
Vanishing gradient problem : ReLUs [1]
[1] Nair, Vinod, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. "Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines." Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10). 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningintrobyleopauly-170618123413/75/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-10-2048.jpg)



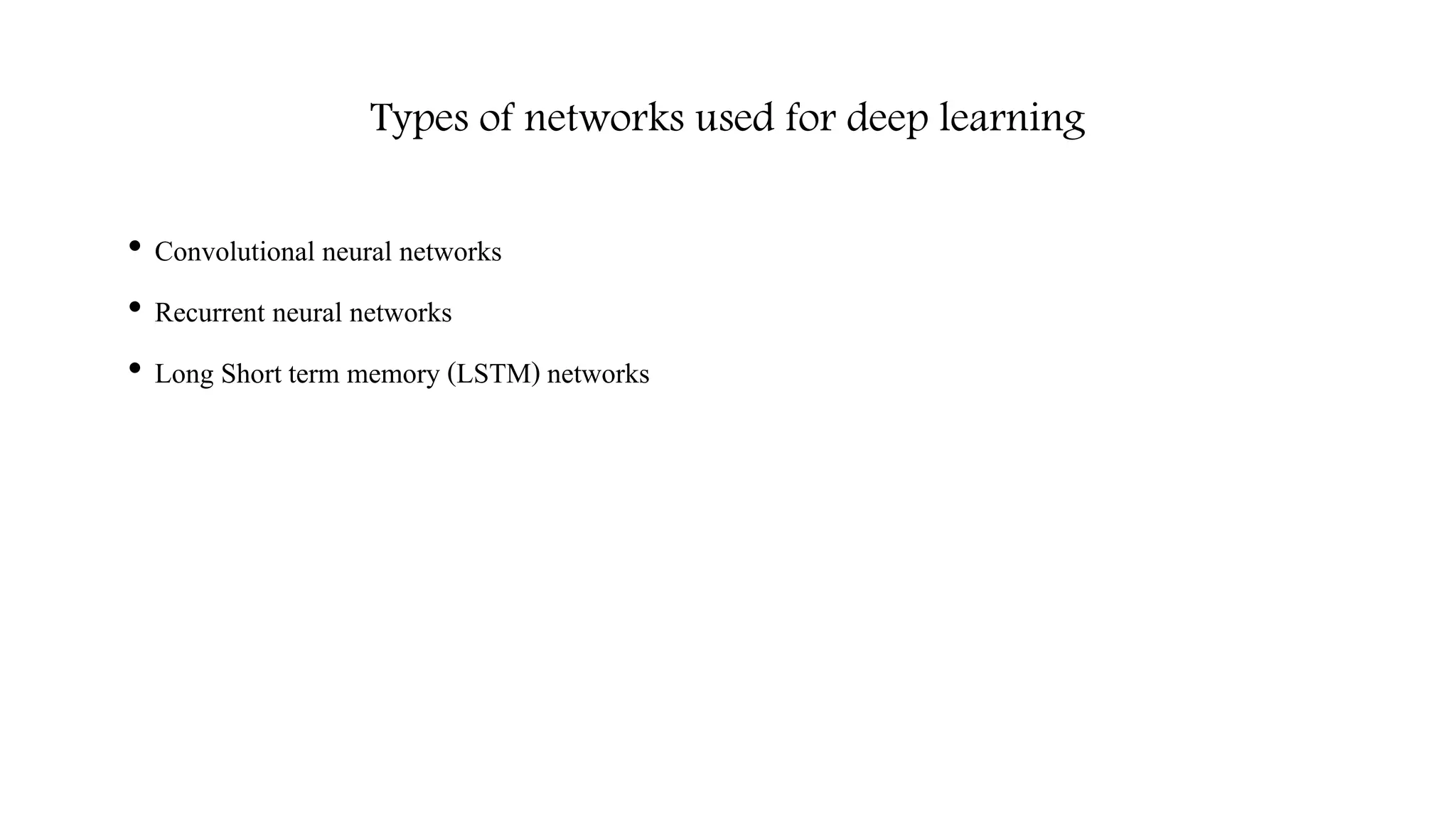
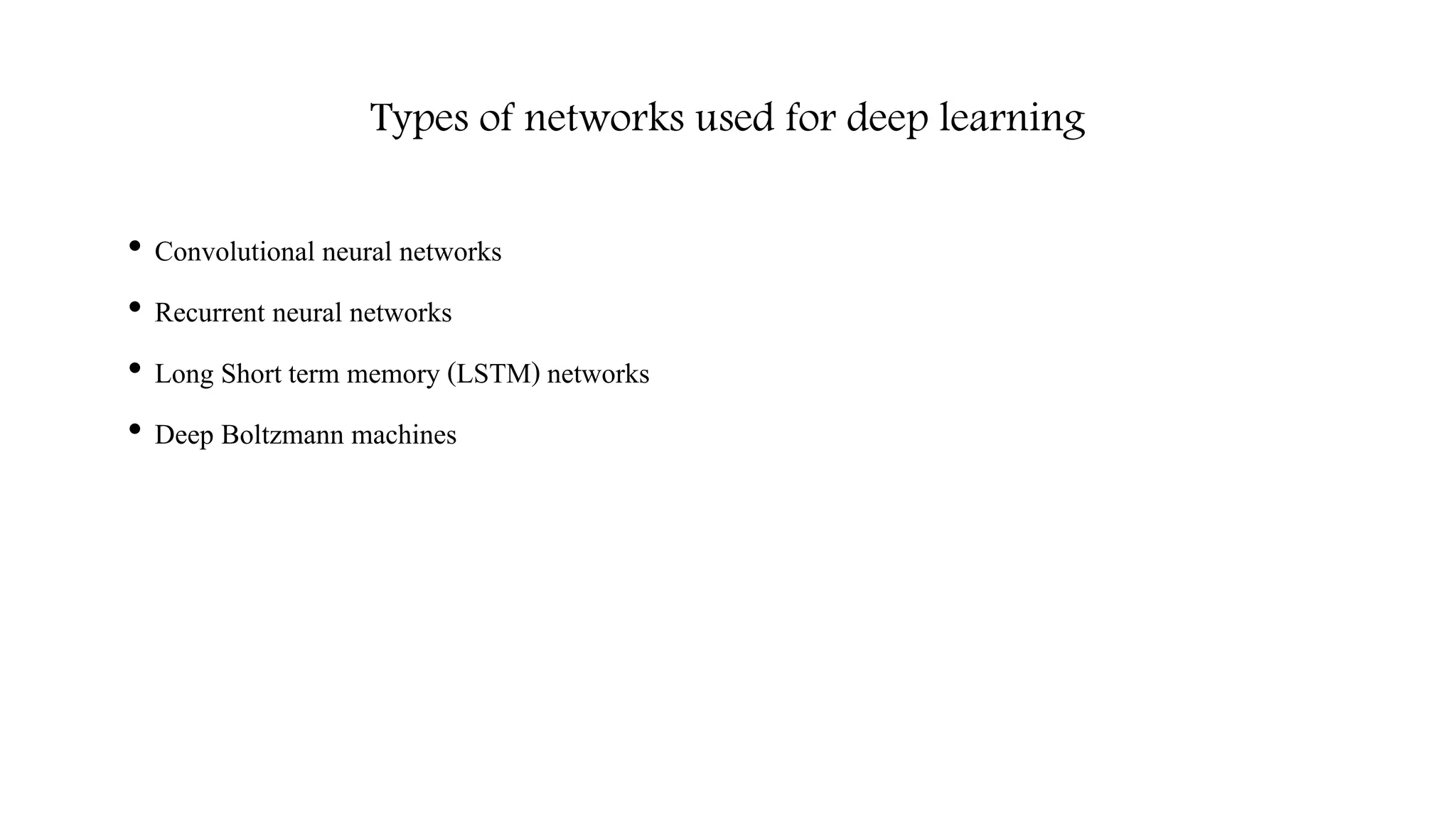
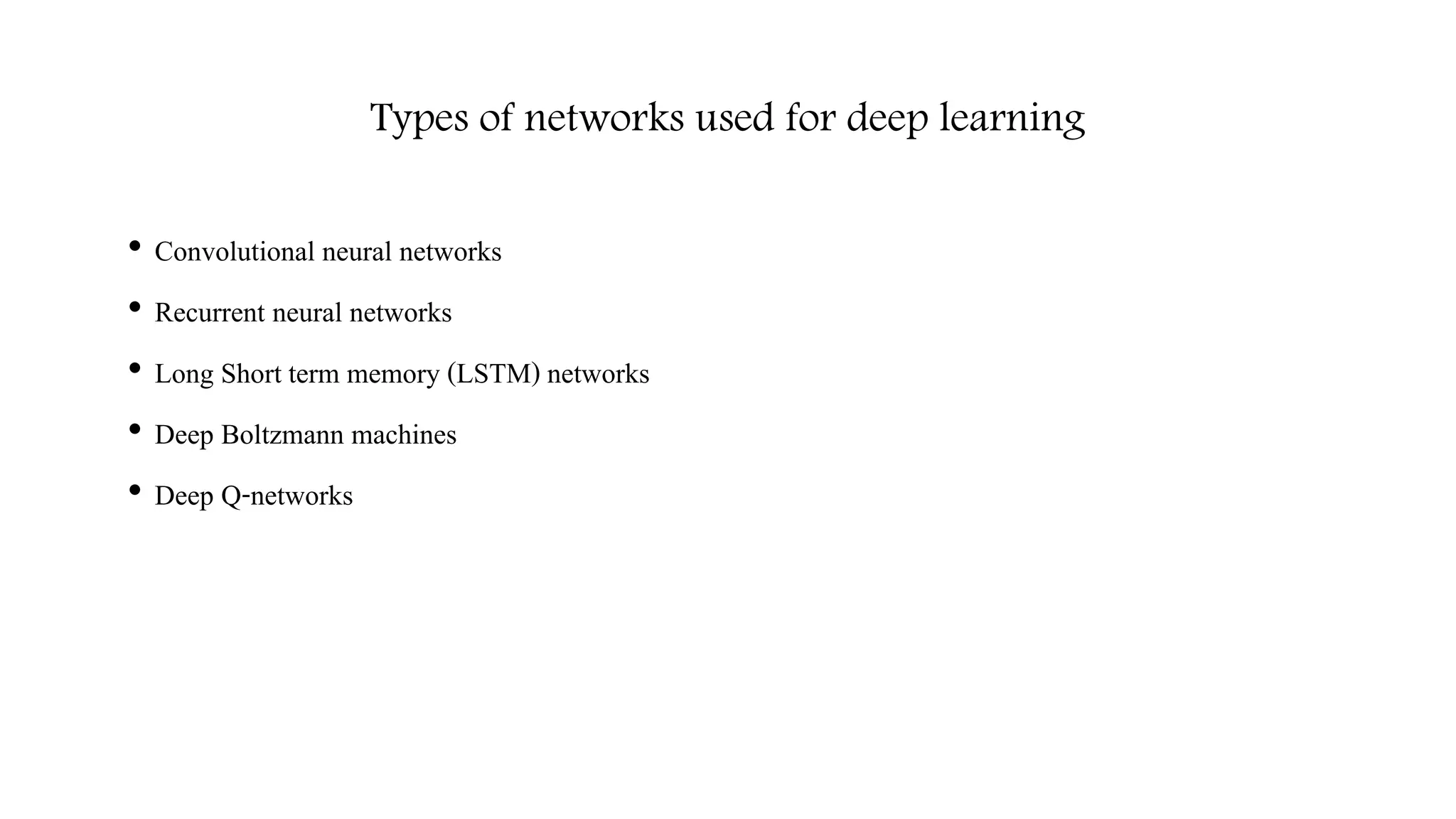
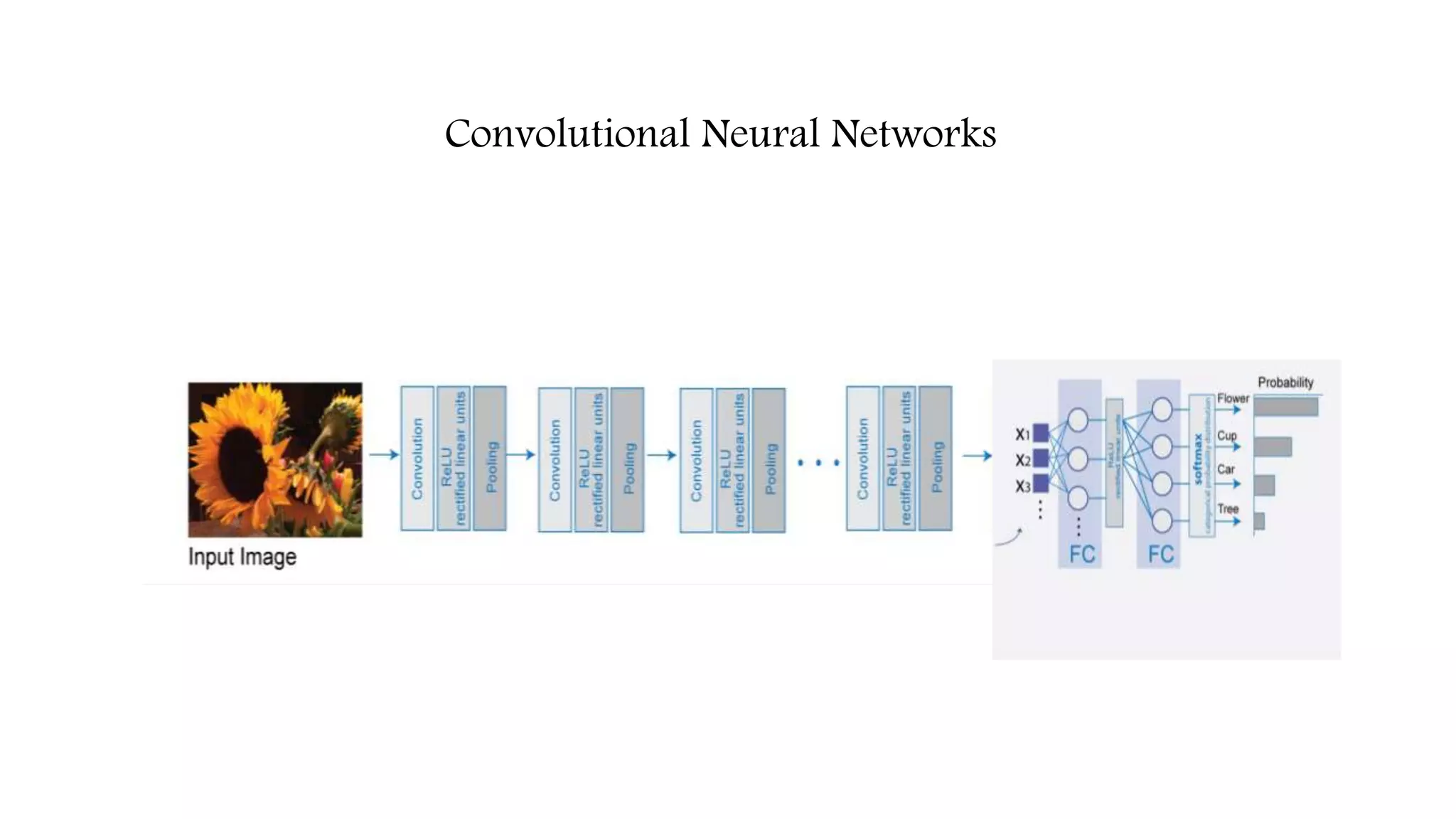
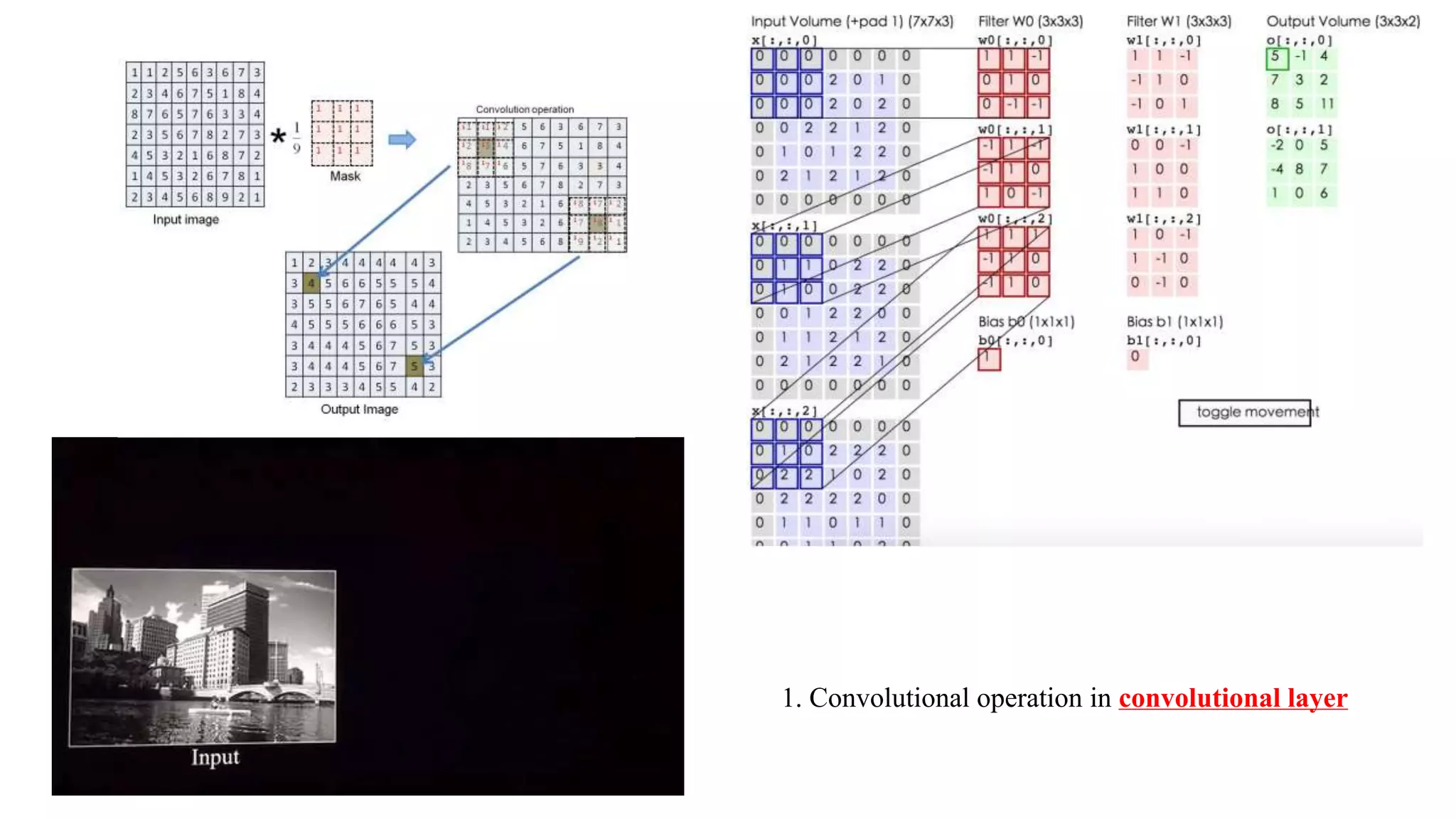


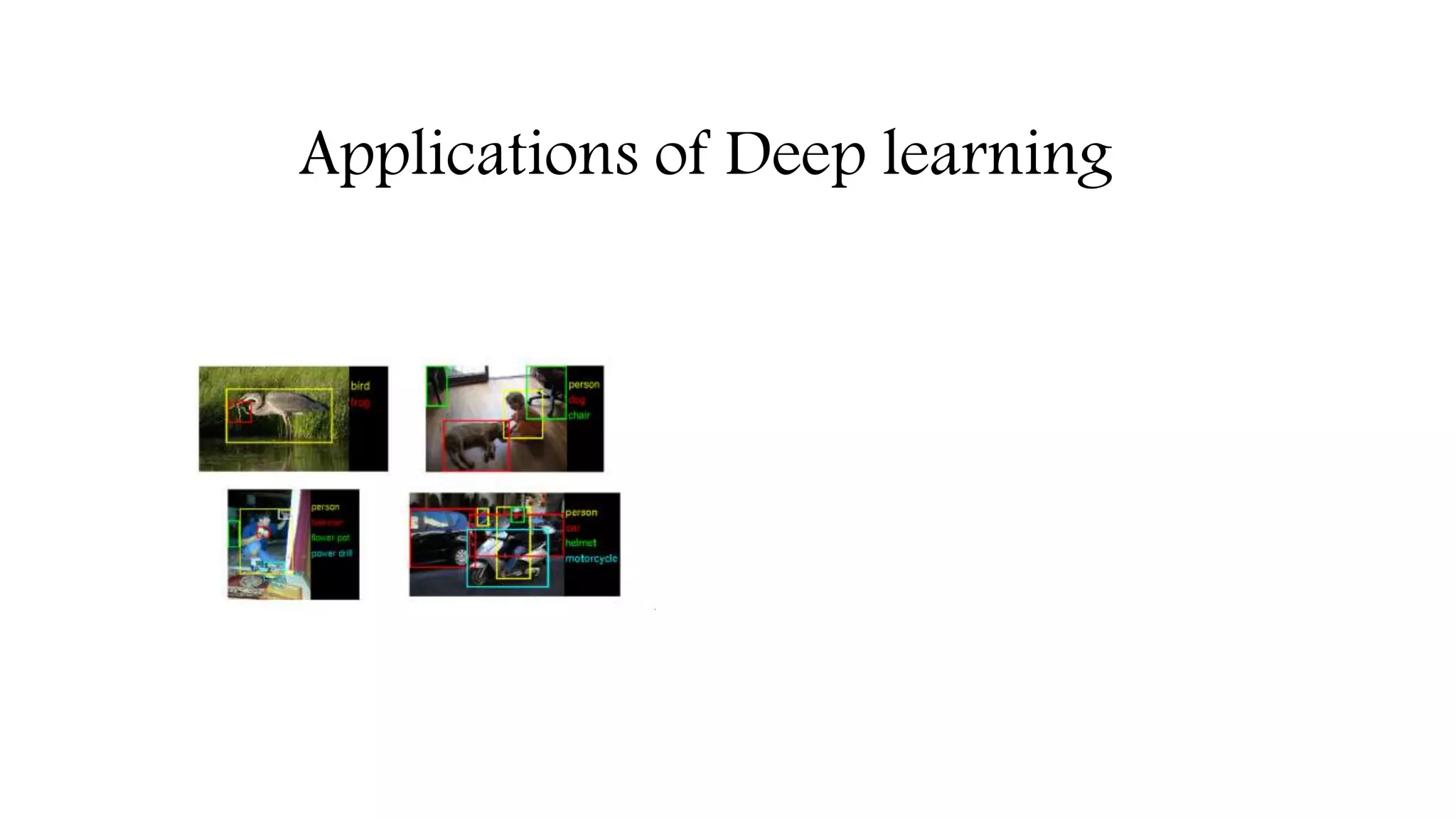





![Computer Vision
Object detection [2]
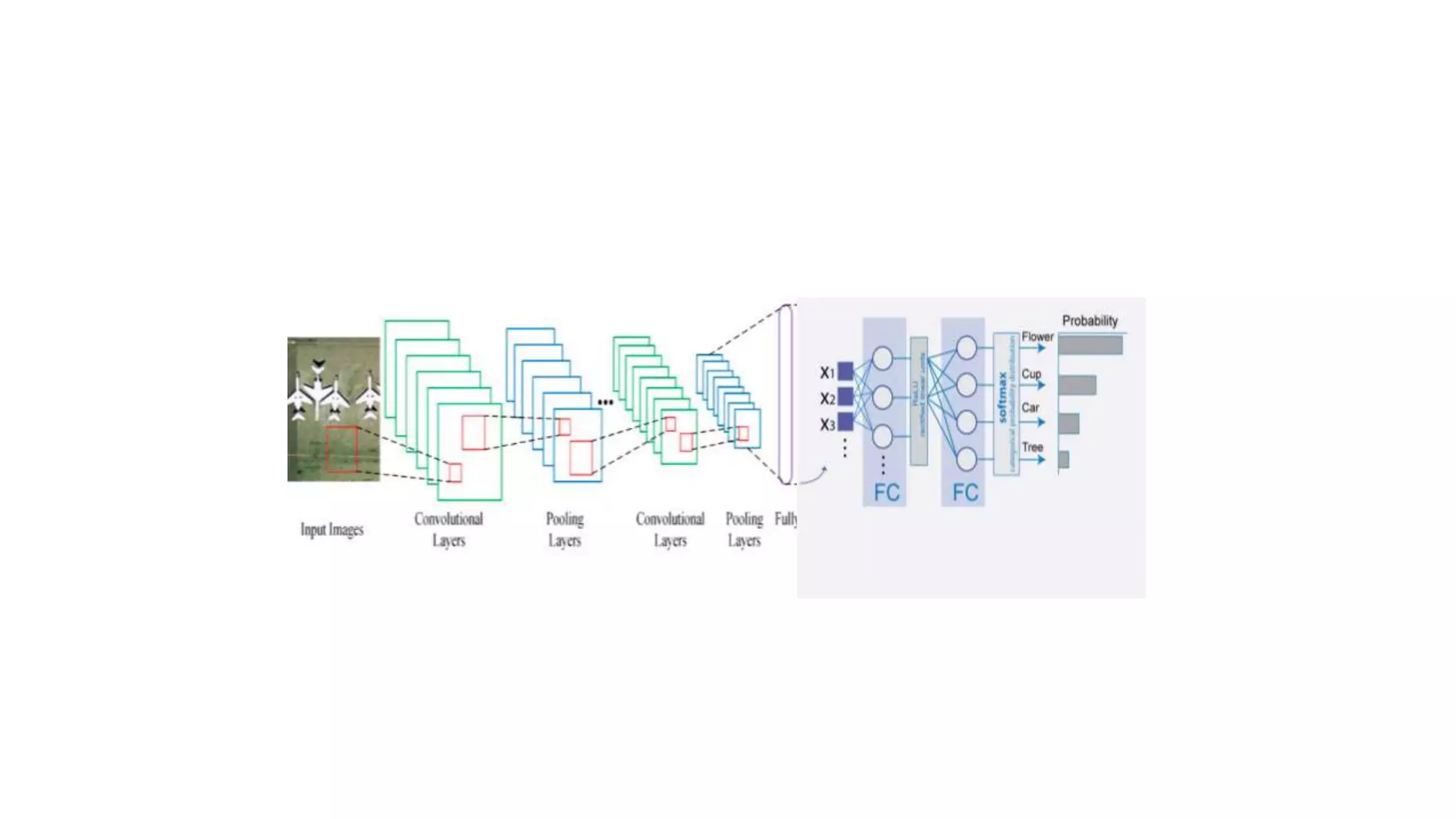
Image classification [1]
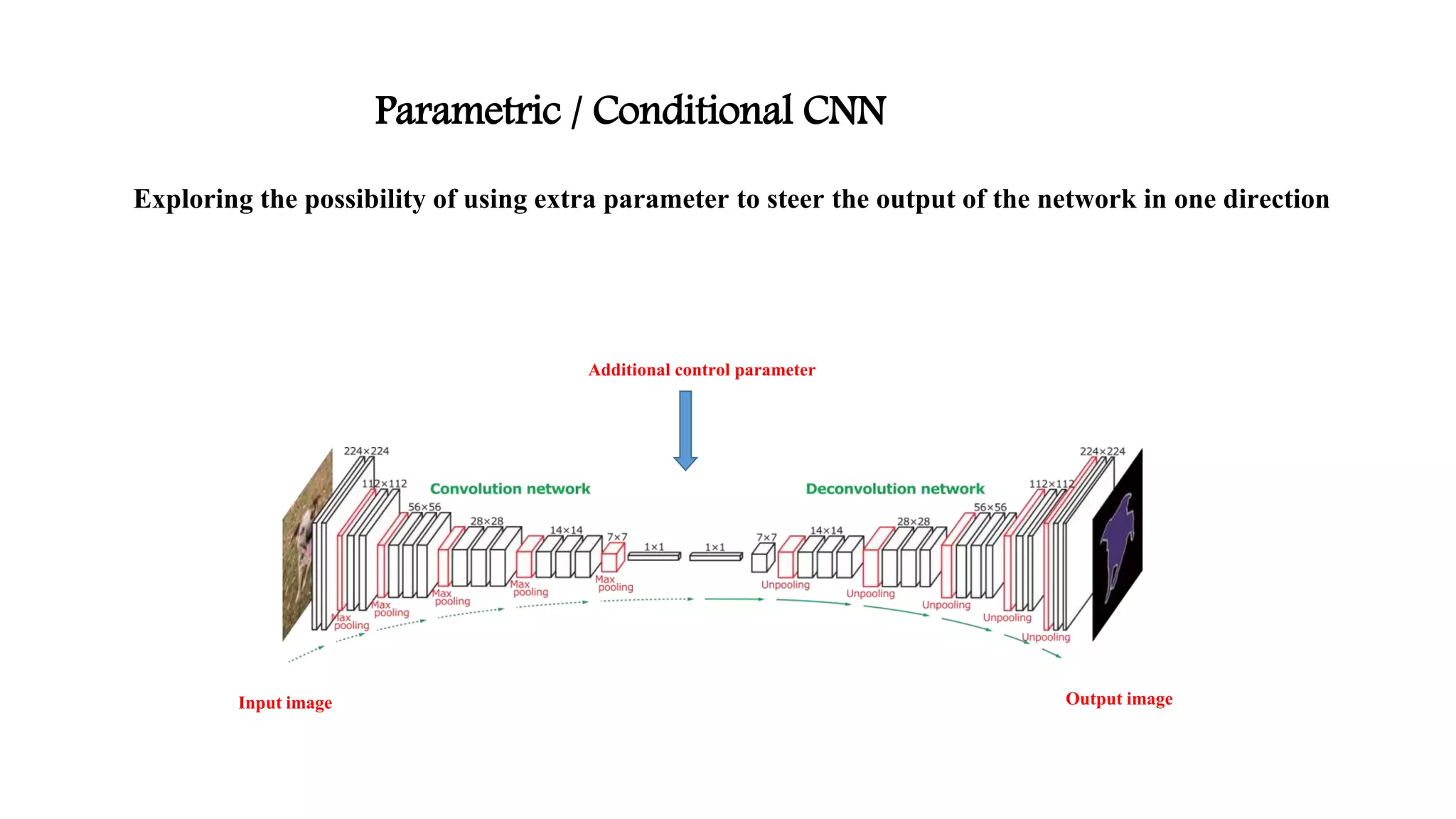
Image segmentation [3]
Edge detection [4]
[1] Krizhevsky, Alex, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks." Advances in neural information processing systems. 2012.
[2] Girshick, Ross. "Fast r-cnn." Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.
[3] Zheng, Shuai, et al. "Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks." Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.
[4] Xie, Saining, and Zhuowen Tu. "Holistically-nested edge detection." Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningintrobyleopauly-170618123413/75/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-40-2048.jpg)
![[1]Kafle, Kushal, and Christopher Kanan. "Visual Question Answering: Datasets, Algorithms, and Future Challenges." arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.01465 (2016).
Natural Language processing
Visual question answering [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningintrobyleopauly-170618123413/75/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-41-2048.jpg)
![[1] Levine, Sergey, et al. "Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection." arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.02199 (2016).
[2] Chen, Chenyi, et al. "Deepdriving: Learning affordance for direct perception in autonomous driving." Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer
Vision. 2015.
Robotics
Grasping objects[1]
Autonomous driving[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningintrobyleopauly-170618123413/75/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-42-2048.jpg)
![[1] Esteva, Andre, et al. "Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks." Nature 542.7639 (2017): 115-118.
[2] Maninis, Kevis-Kokitsi, et al. "Deep retinal image understanding." International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer International
Publishing, 2016.
[3] Ramsundar, Bharath, et al. "Massively multitask networks for drug discovery." arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.02072 (2015).
Medicine
Skin cancer classification[1]
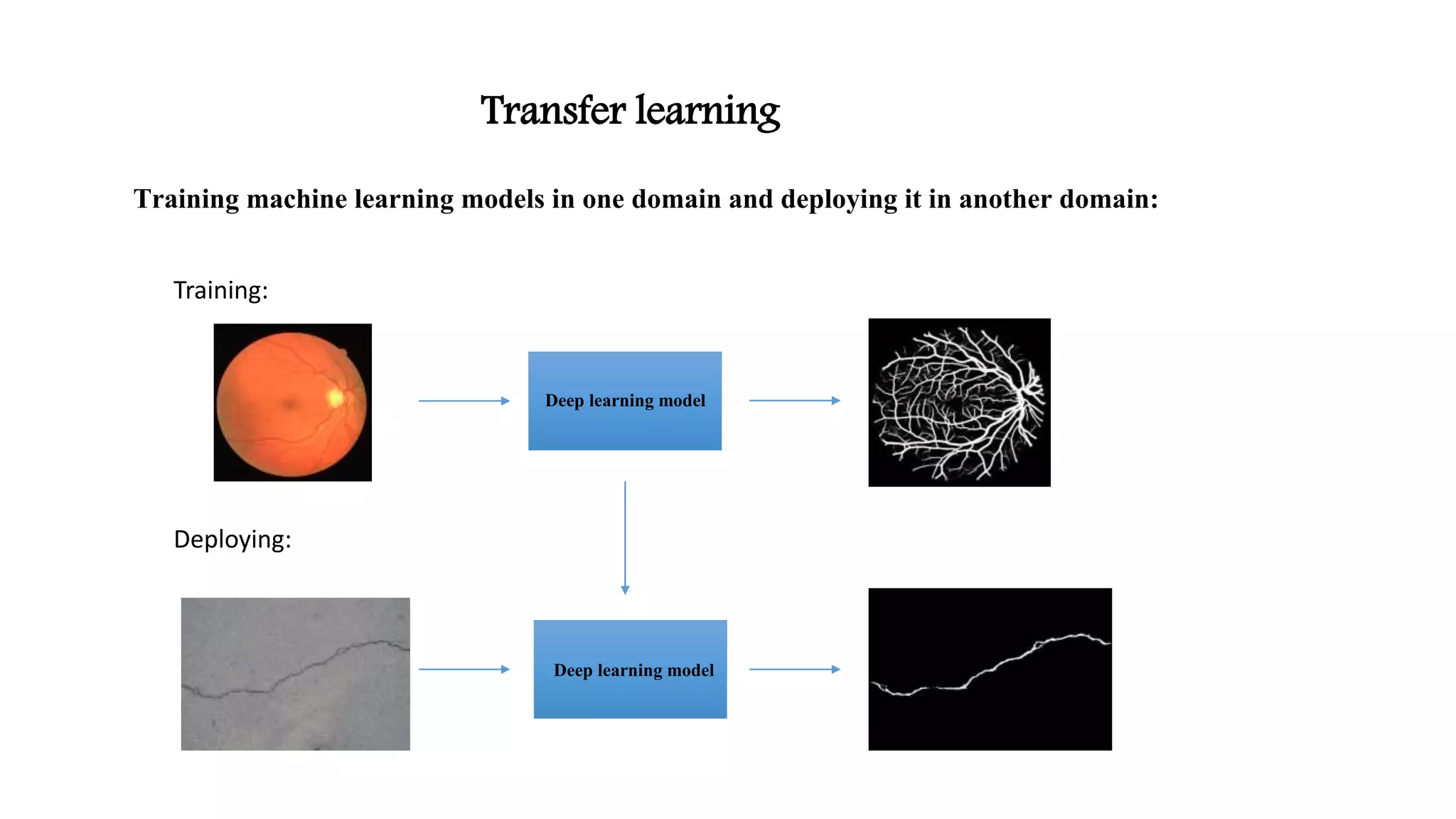
Retinal vessel segmentation[2]
Drug Discovery[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningintrobyleopauly-170618123413/75/Introduction-to-Deep-learning-43-2048.jpg)