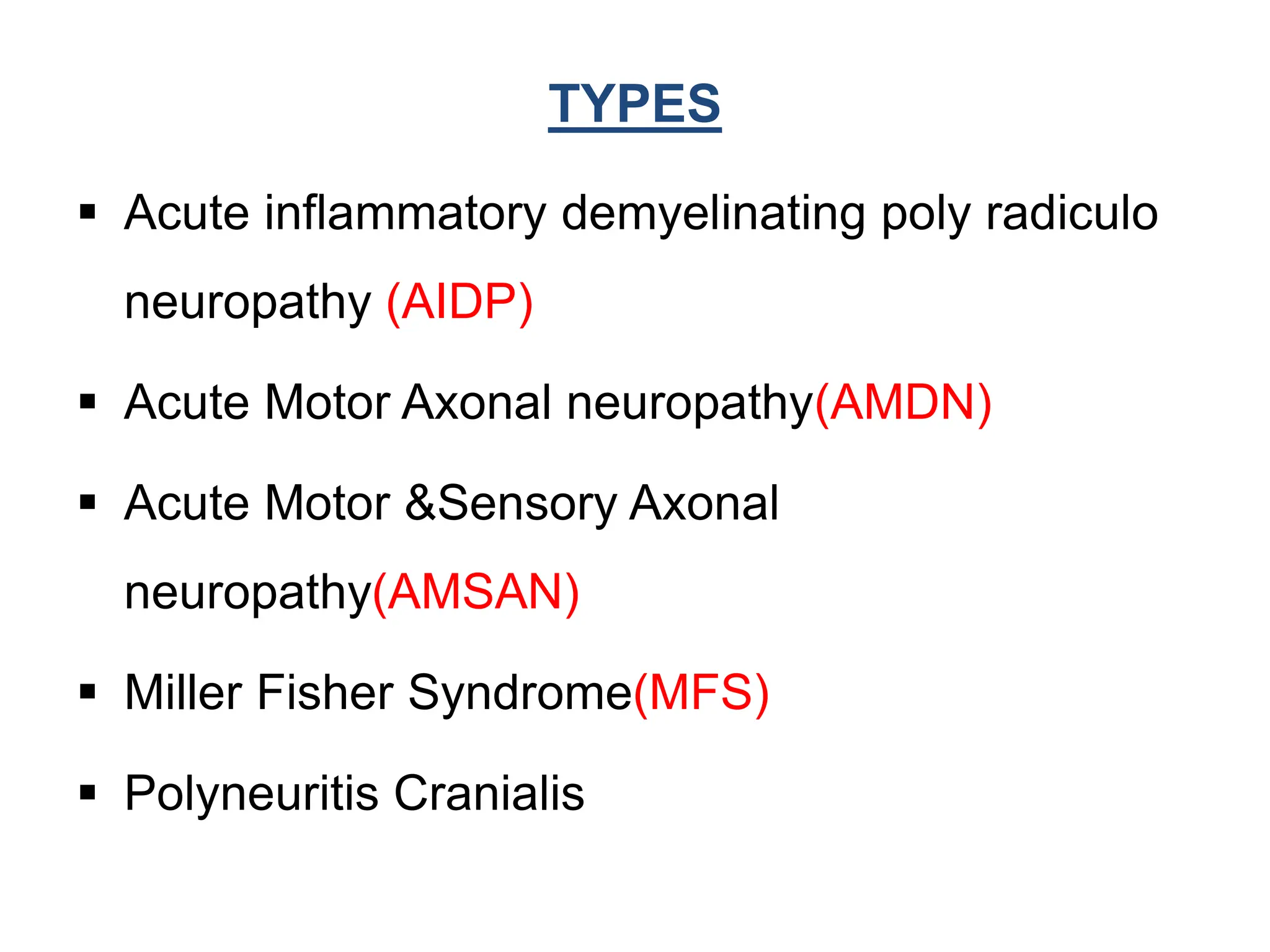
This document discusses Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), an acute immune-mediated polyneuropathy that results in rapid progressive motor paralysis. GBS is characterized by acute onset muscle weakness that spreads throughout the body. It is caused by an autoimmune response triggered by bacterial or viral infections. Diagnosis involves neurological exams, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, electromyography, and nerve conduction studies. Treatment aims to prevent complications through respiratory support, physical therapy, intravenous immunoglobulins, and plasma exchange. Nursing care focuses on monitoring respiratory function, range of motion exercises, and managing symptoms like pain and impaired communication.