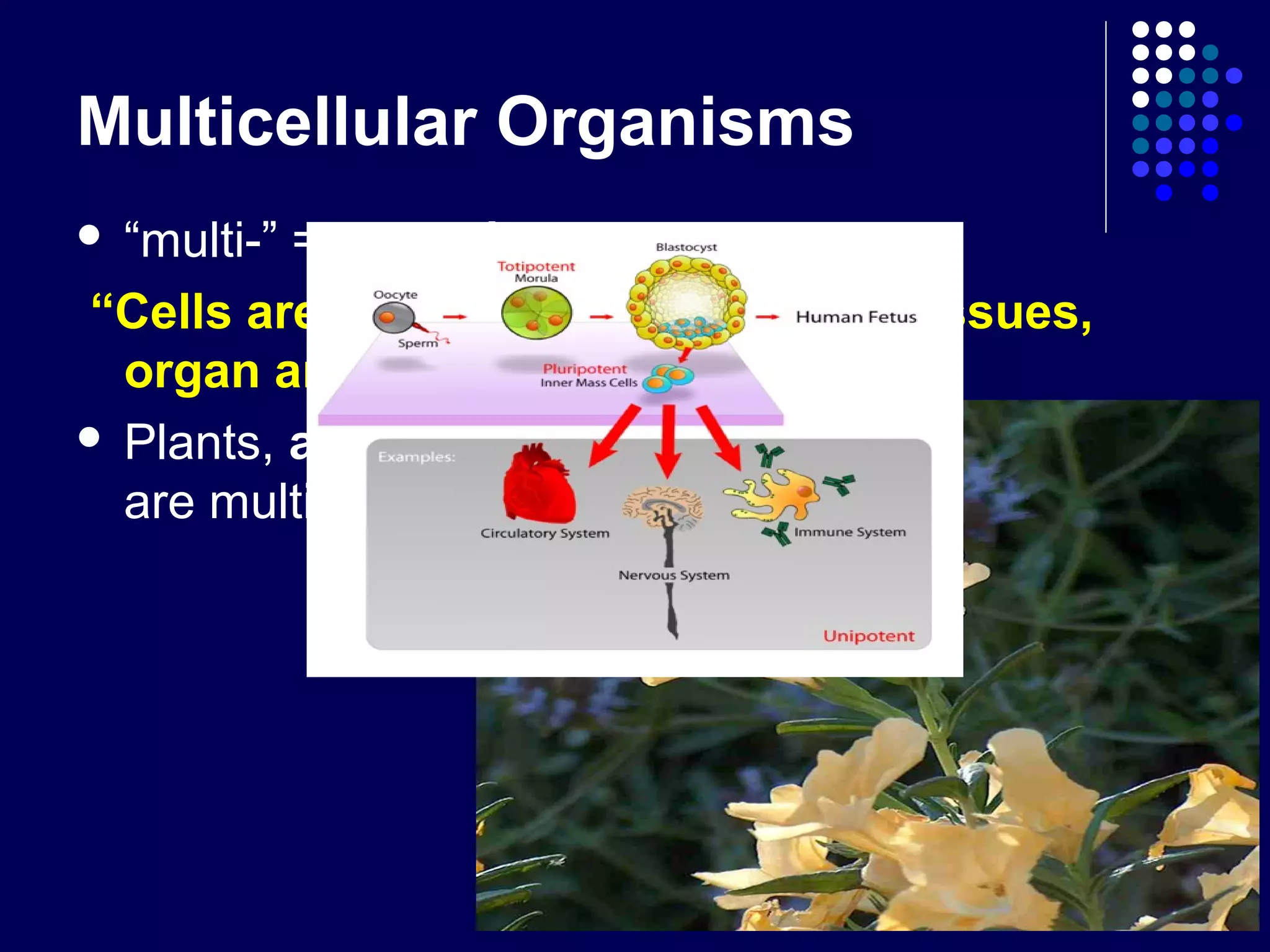
Cells organize in three main ways: unicellular, colonial, and multicellular. Unicellular organisms like prokaryotes consist of a single cell. Colonial organisms like Volvox live together in colonies but cells do not specialize. Multicellular organisms like plants and animals have cells that are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems, allowing for larger size, longer life, and division of labor.