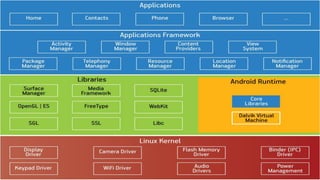
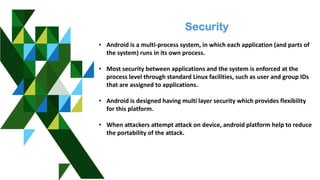
The presentation by Umang Vyas provides an overview of Android, covering its history, architecture, security features, advantages, and disadvantages. Android, developed by Google and based on the Linux kernel, is an open-source operating system that has evolved through various versions, becoming the most widely used smartphone OS globally. The document highlights Android's customizable nature, rich feature set, and ongoing security improvements while also acknowledging issues like malware and battery drain.


![History Of Android
• Android Inc. founded in Palo Alto, California, United
States in October 2003.
• Android Develop By:-
• Andy Rubin [Co-Founder of Danger]
• Rich Miner[Co-Founder of Wildfire
Communication Inc.]
• Nick Sears[Once VP at T-mobile]
• Chris White[Headed Design & Interface
Development at Web TV]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonandroid-170119170319/85/Presentation-On-Android-3-320.jpg)