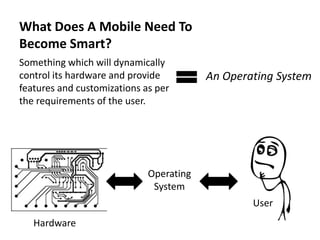
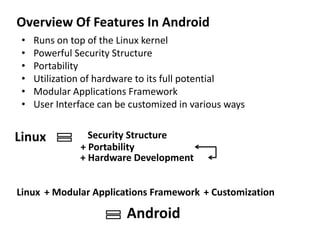
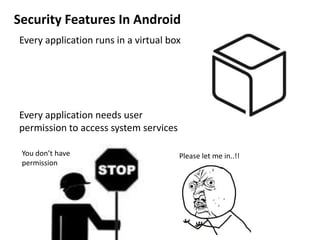
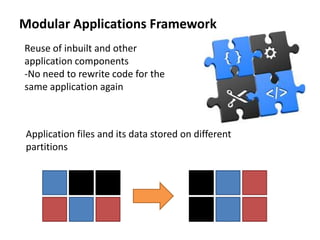
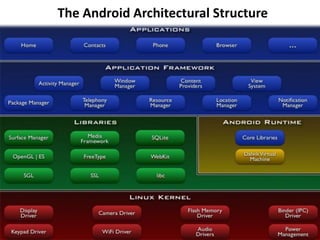
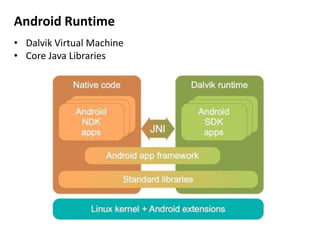
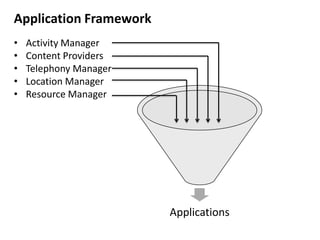
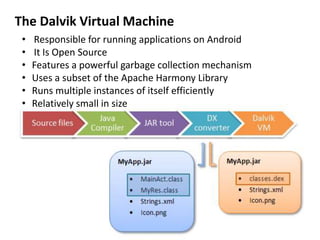
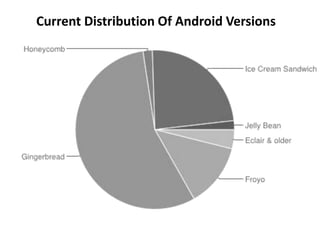
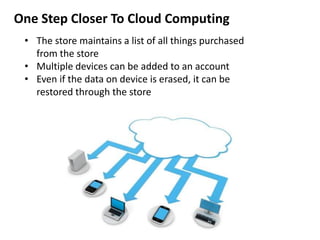
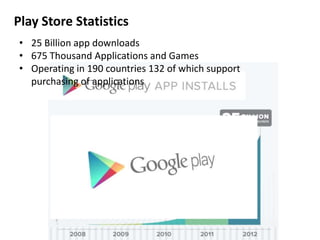
Android is an open source operating system developed by the Open Handset Alliance led by Google. It allows manufacturers to customize the OS for their devices and provides developers with an open platform to create applications. Some key points about Android include that it is built on top of the Linux kernel, uses the Dalvik virtual machine, and has a modular structure with core applications and system libraries. The open nature of Android has made it highly customizable and scalable, contributing to its rapid growth and adoption worldwide across various device types.