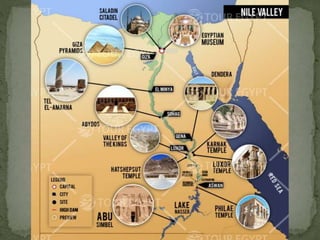
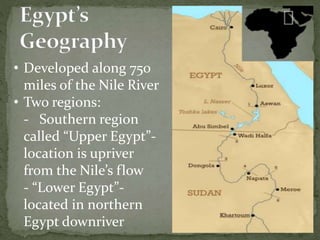
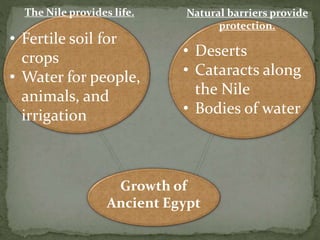
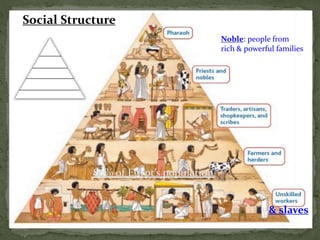
The ancient Egyptians developed a great civilization along the fertile banks of the Nile River around 3200 BC. The Nile provided water for irrigation and its annual flooding deposited rich silt on the land. Egypt was divided into Upper and Lower Egypt, and was unified under King Menes around 3100 BC. Egyptian society was stratified, with kings, nobles, priests, skilled workers, peasants, and slaves. The Egyptians built large pyramids and temples and also achieved advancements in art, architecture, mathematics, and writing in hieroglyphics. Egyptian religion was closely tied to the pharaoh and centered around beliefs about the afterlife.