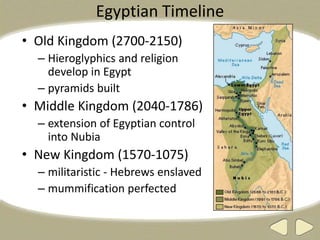
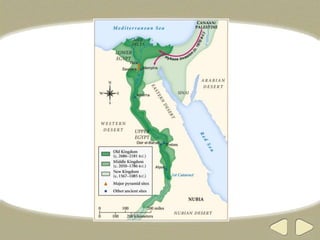
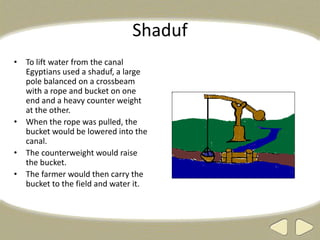
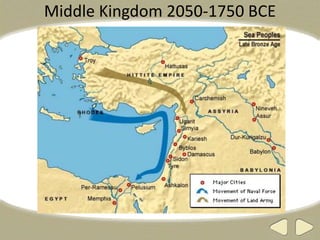
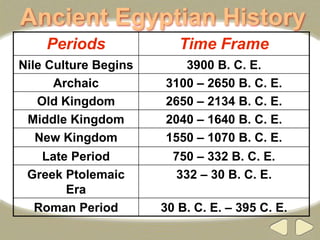
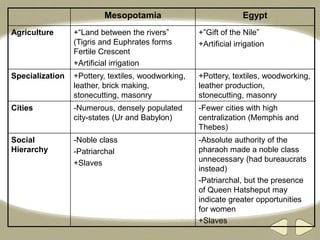
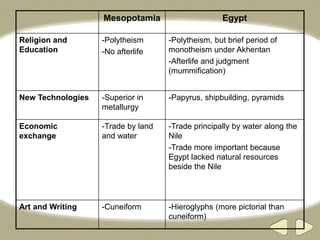
The document provides an overview of ancient Egyptian history and culture from around 3000 BCE to 400 CE. It describes the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms, highlighting developments like the building of pyramids, expansion of Egyptian control, and the rise and fall of powerful pharaohs. Key aspects of Egyptian society discussed include the central role of the Nile River, polytheistic religion, the absolute power of pharaohs, and a social hierarchy topped by pharaohs and bureaucrats and including peasants, slaves, and artisans. Hieroglyphics, mummification, and an early calendar are noted as important achievements of ancient Egyptian civilization.