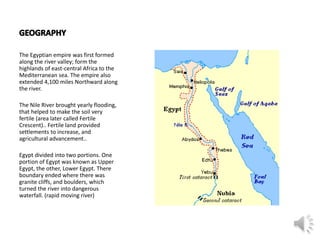
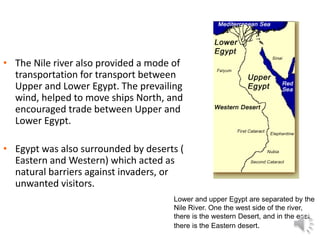
The document provides information about ancient Egypt, including its location along the Nile River valley, the development of Egyptian civilization by around 3000 BC, and key details about Upper and Lower Egypt. Important aspects of Egyptian culture discussed include religion and beliefs, math and scientific advancements, architecture, farming techniques, irrigation systems, calendars, and hieroglyphic writing. Key figures mentioned are priests, scribes, farmers, and different social classes.