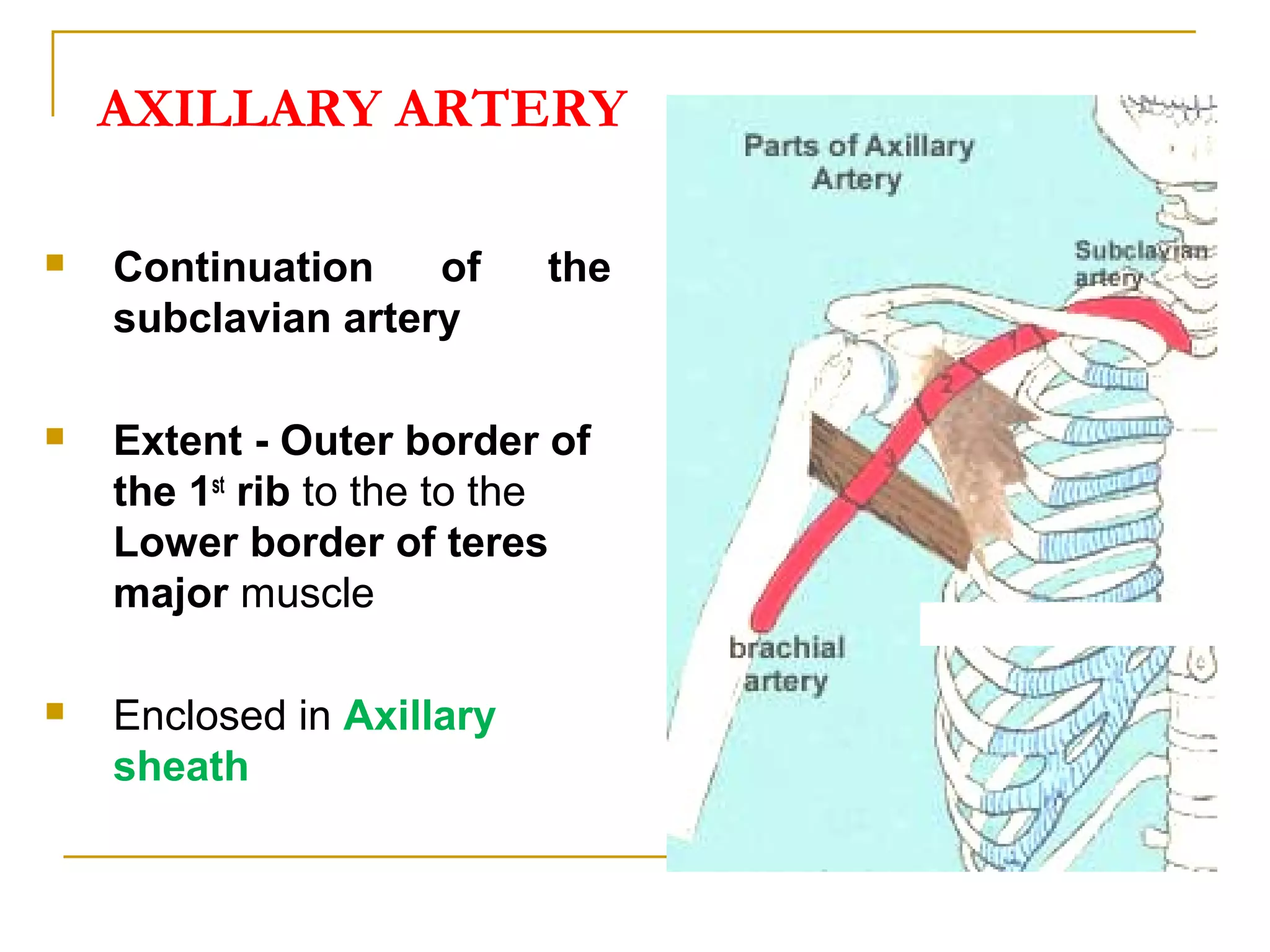
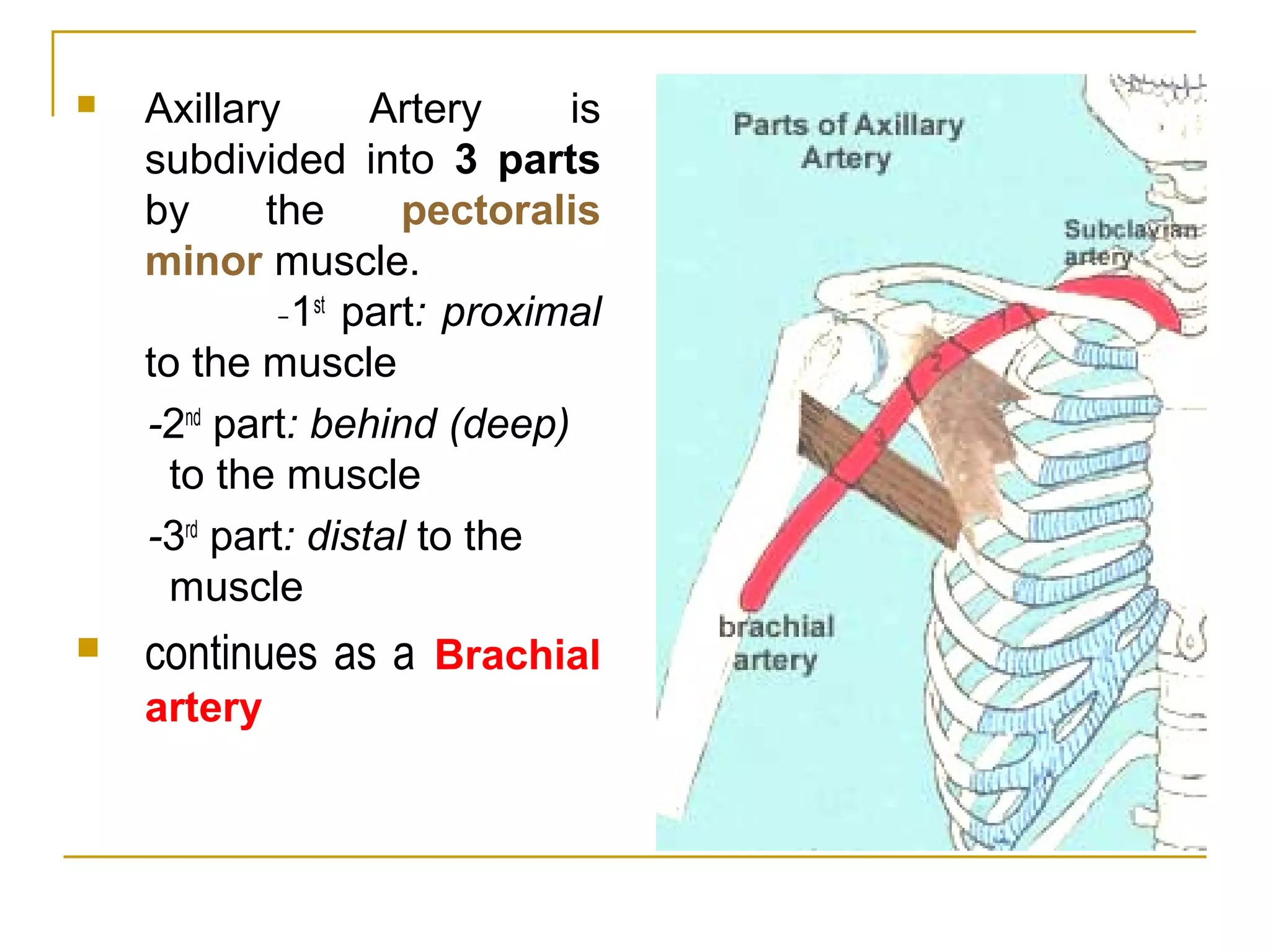
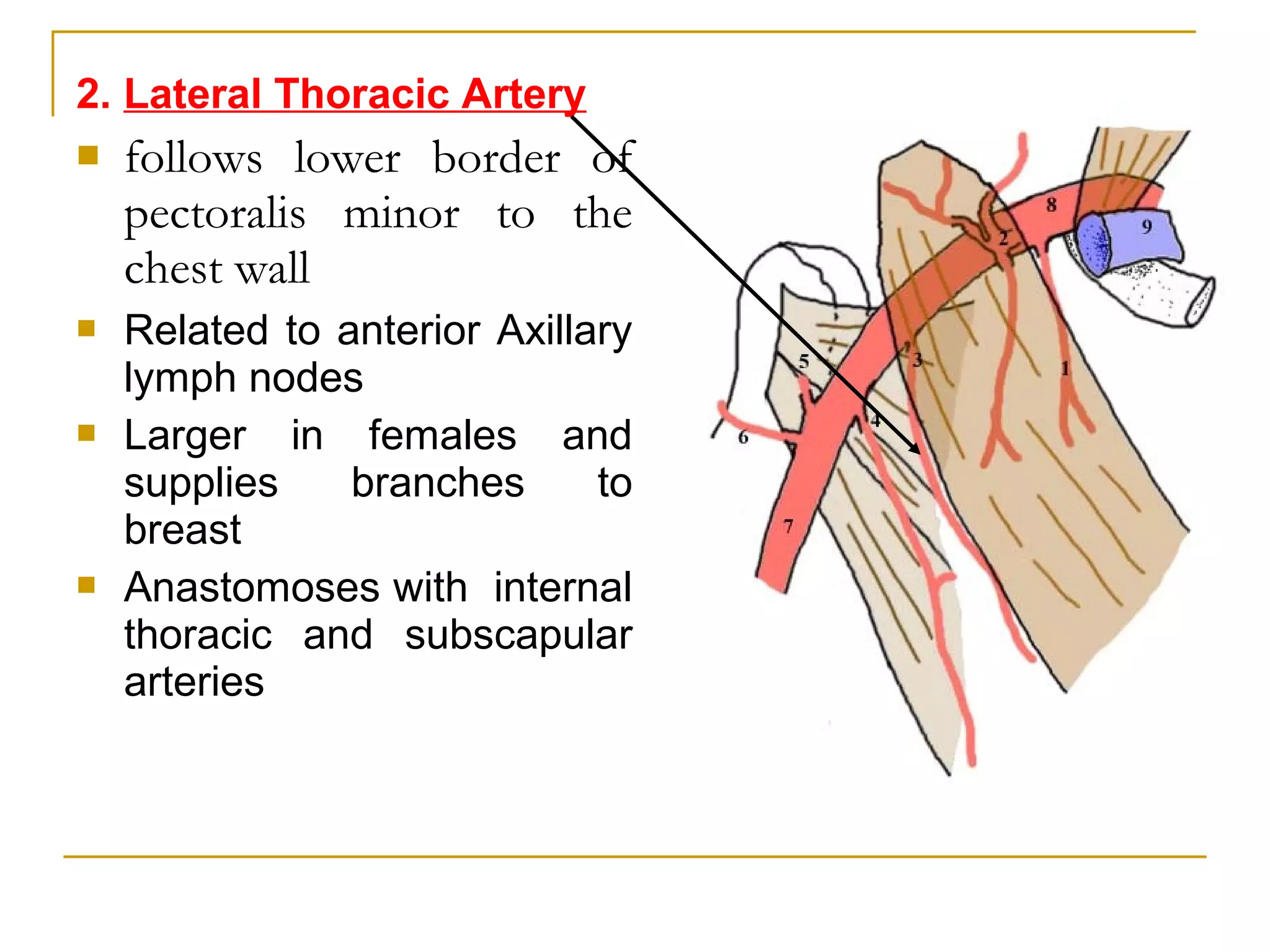
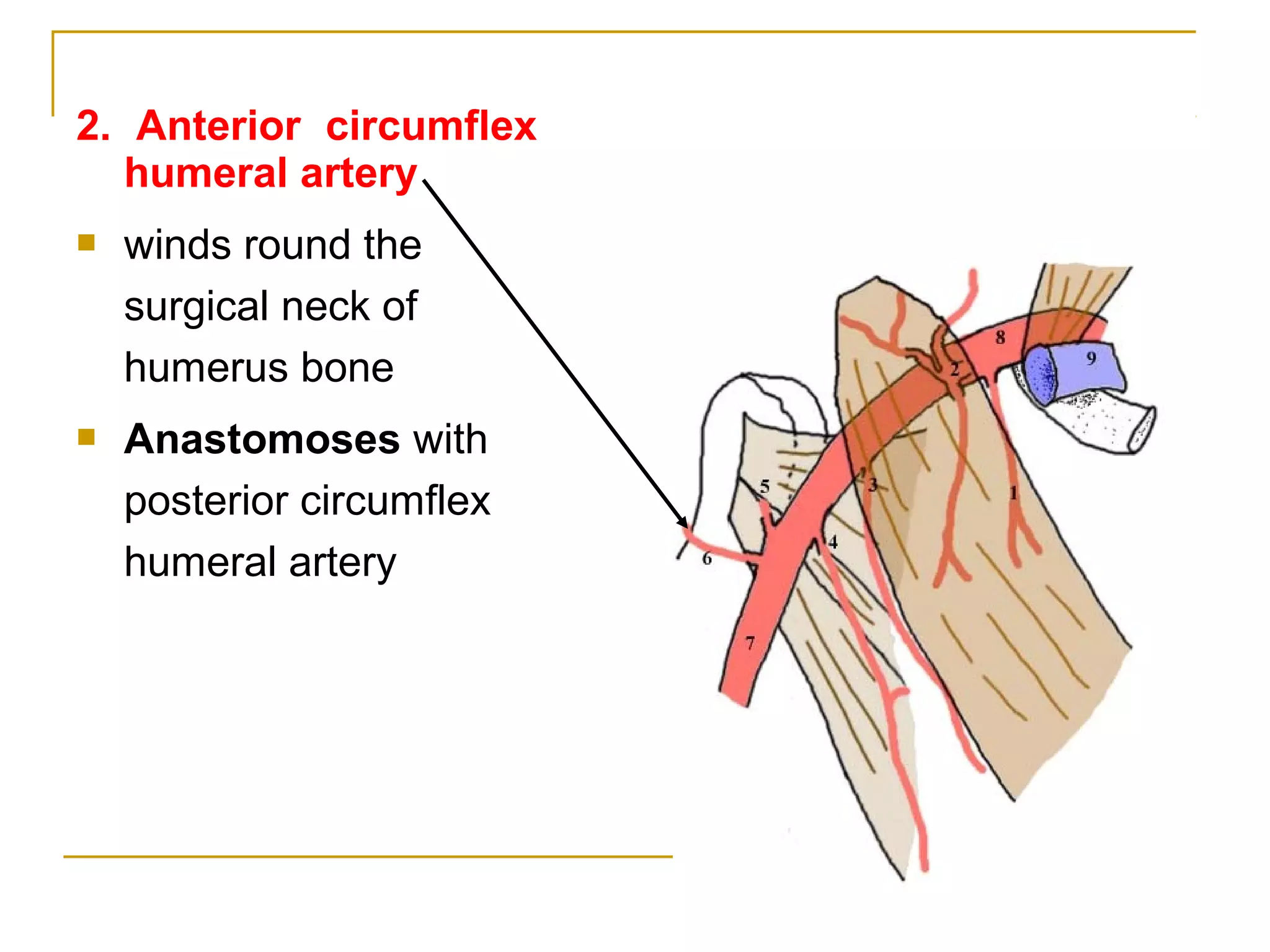
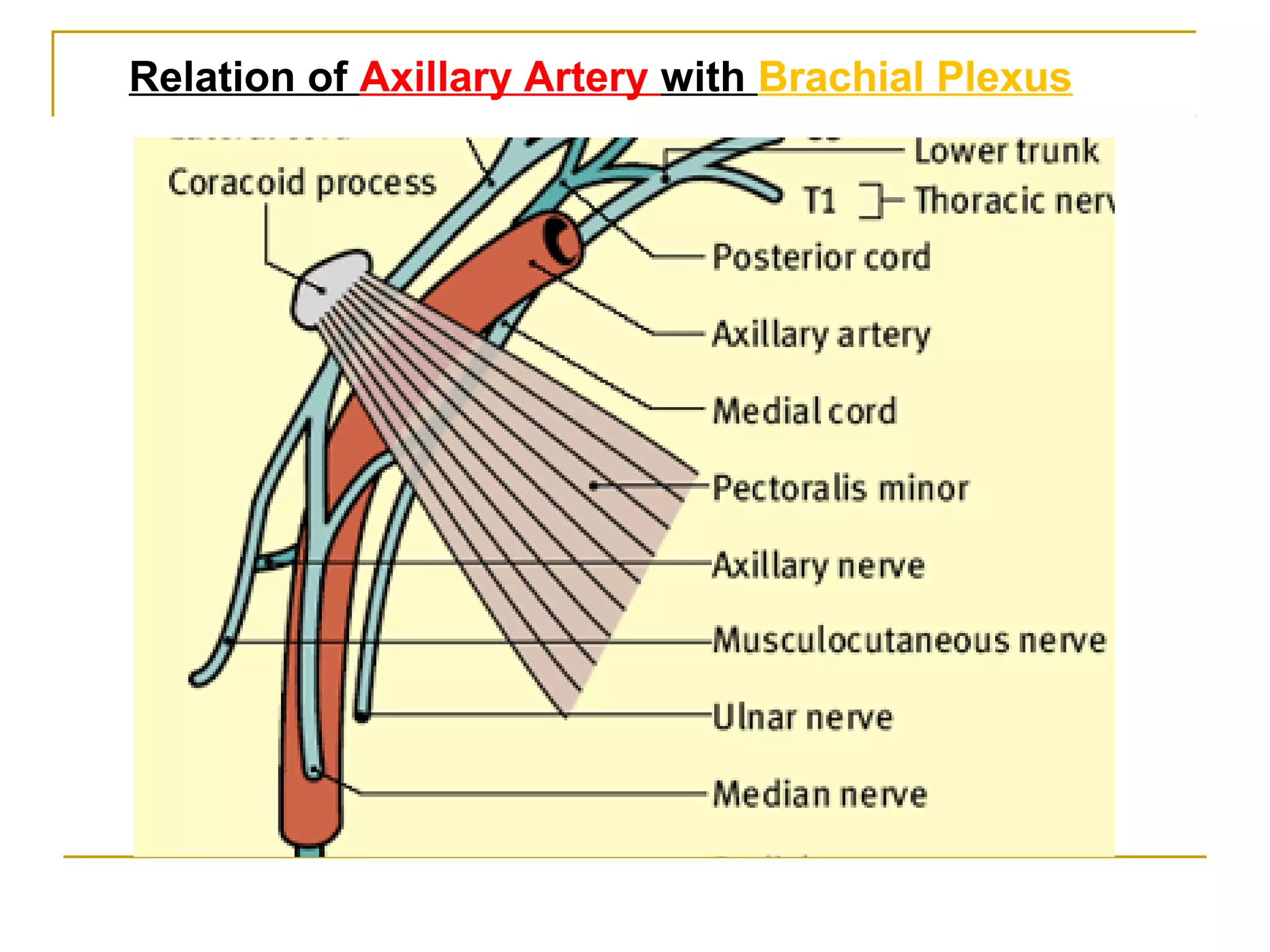
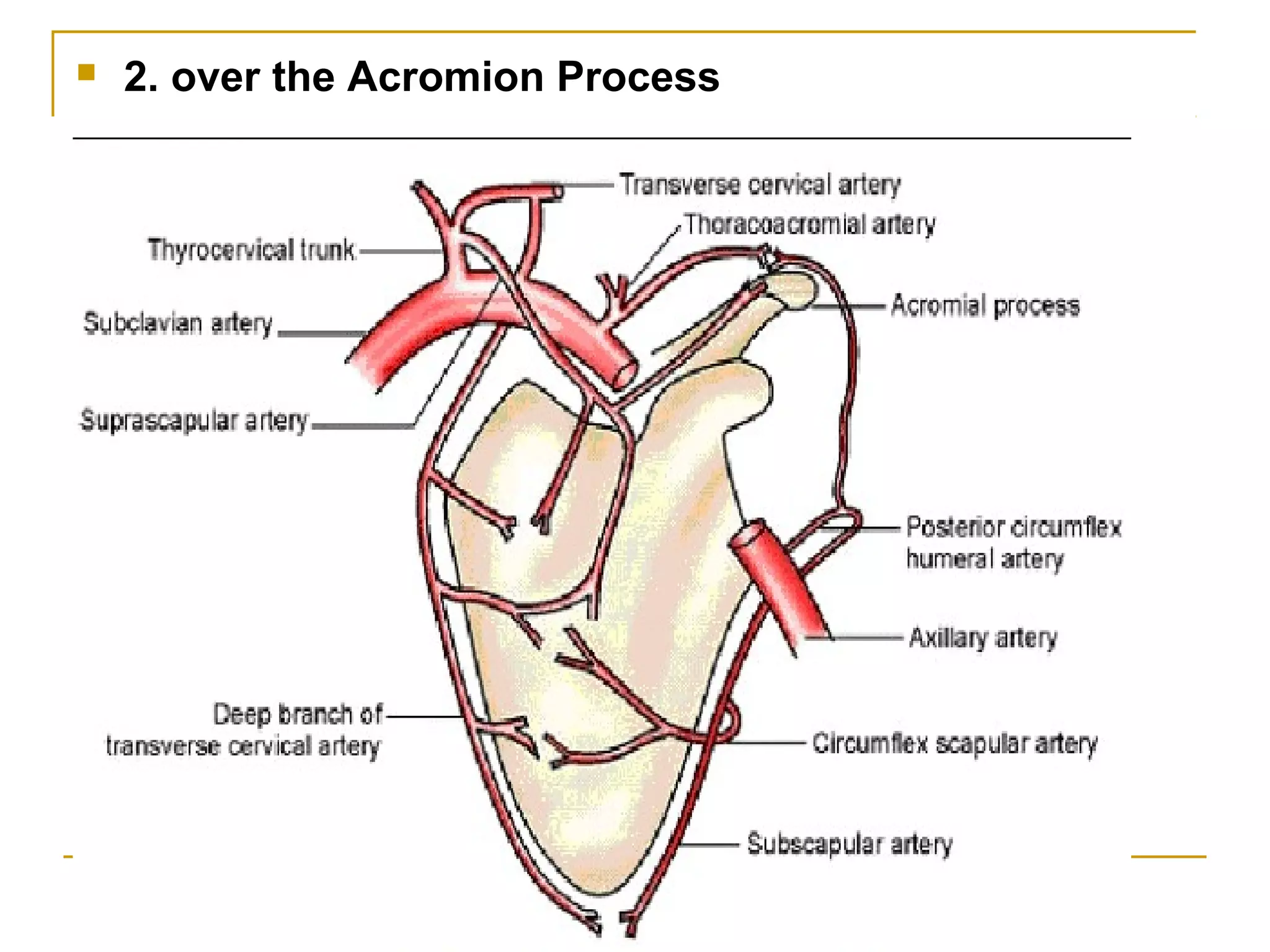
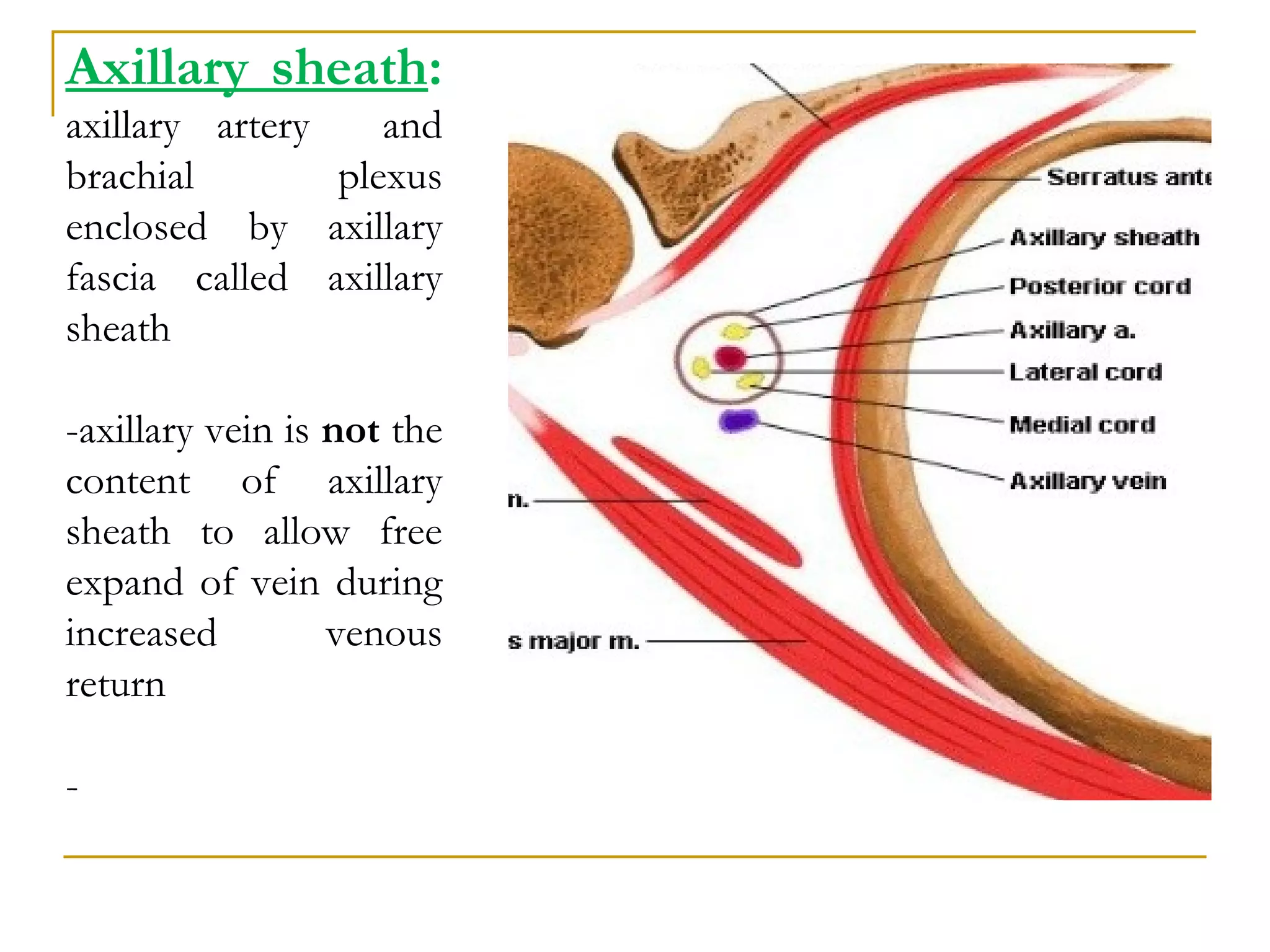
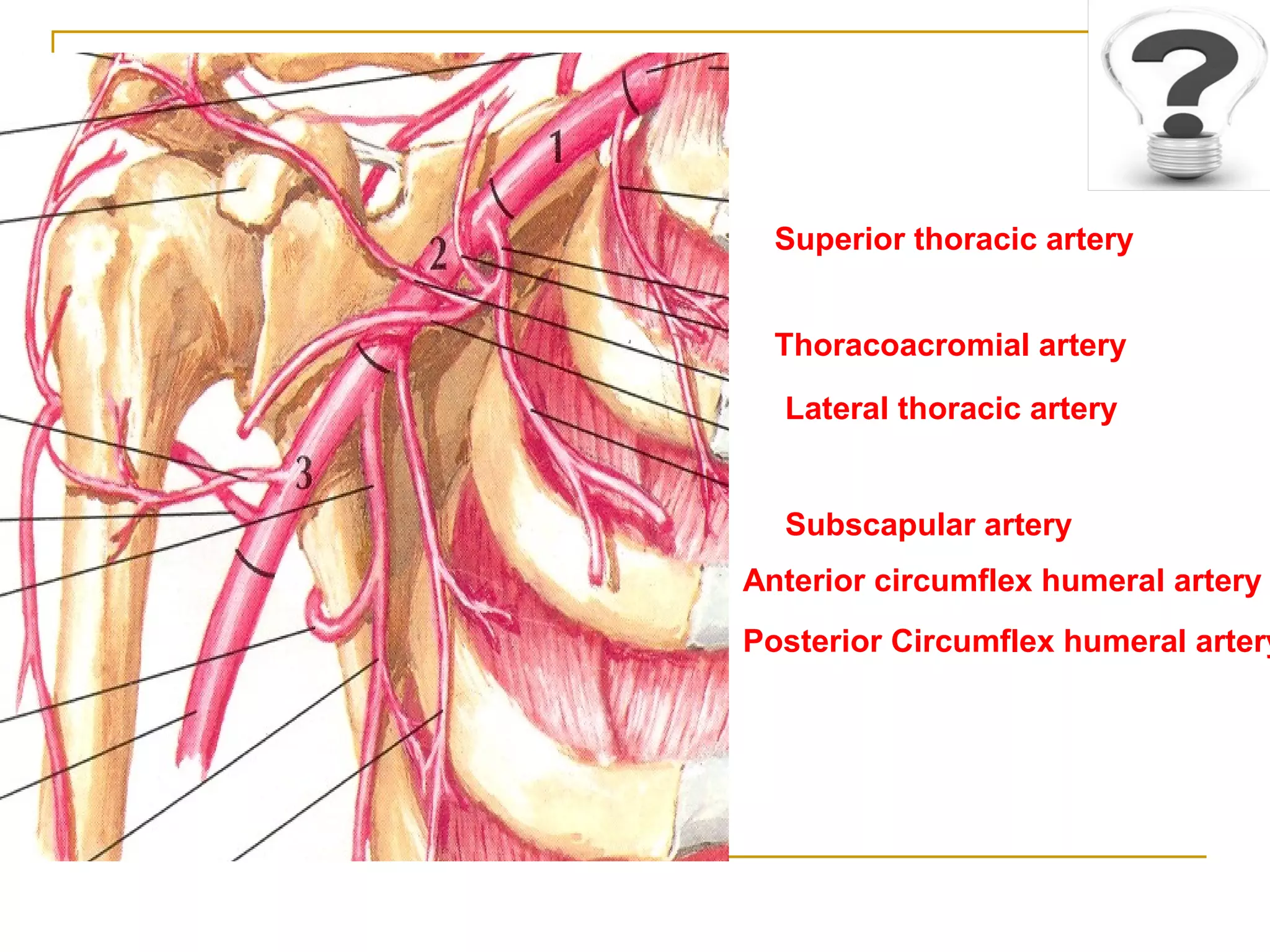
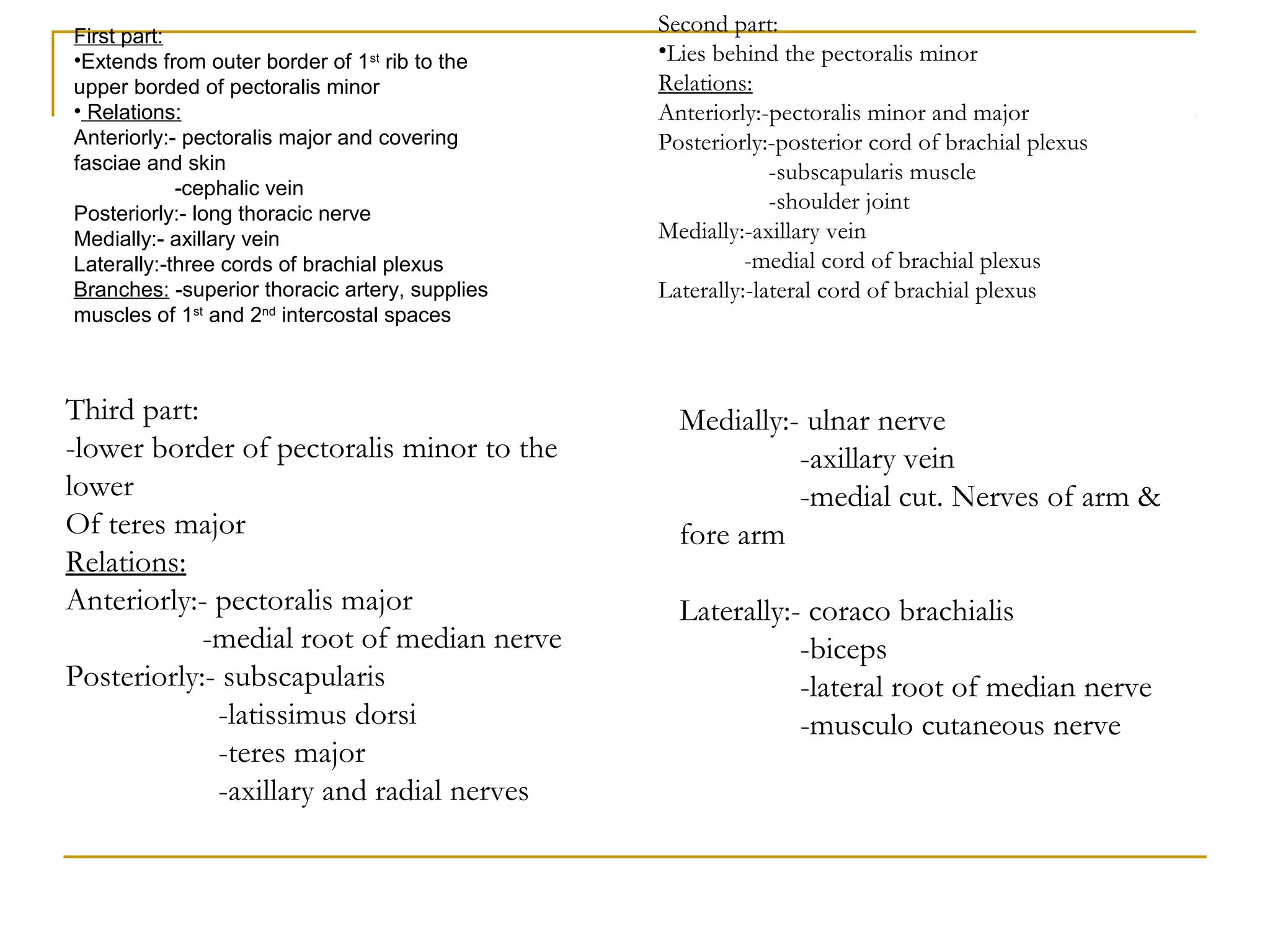
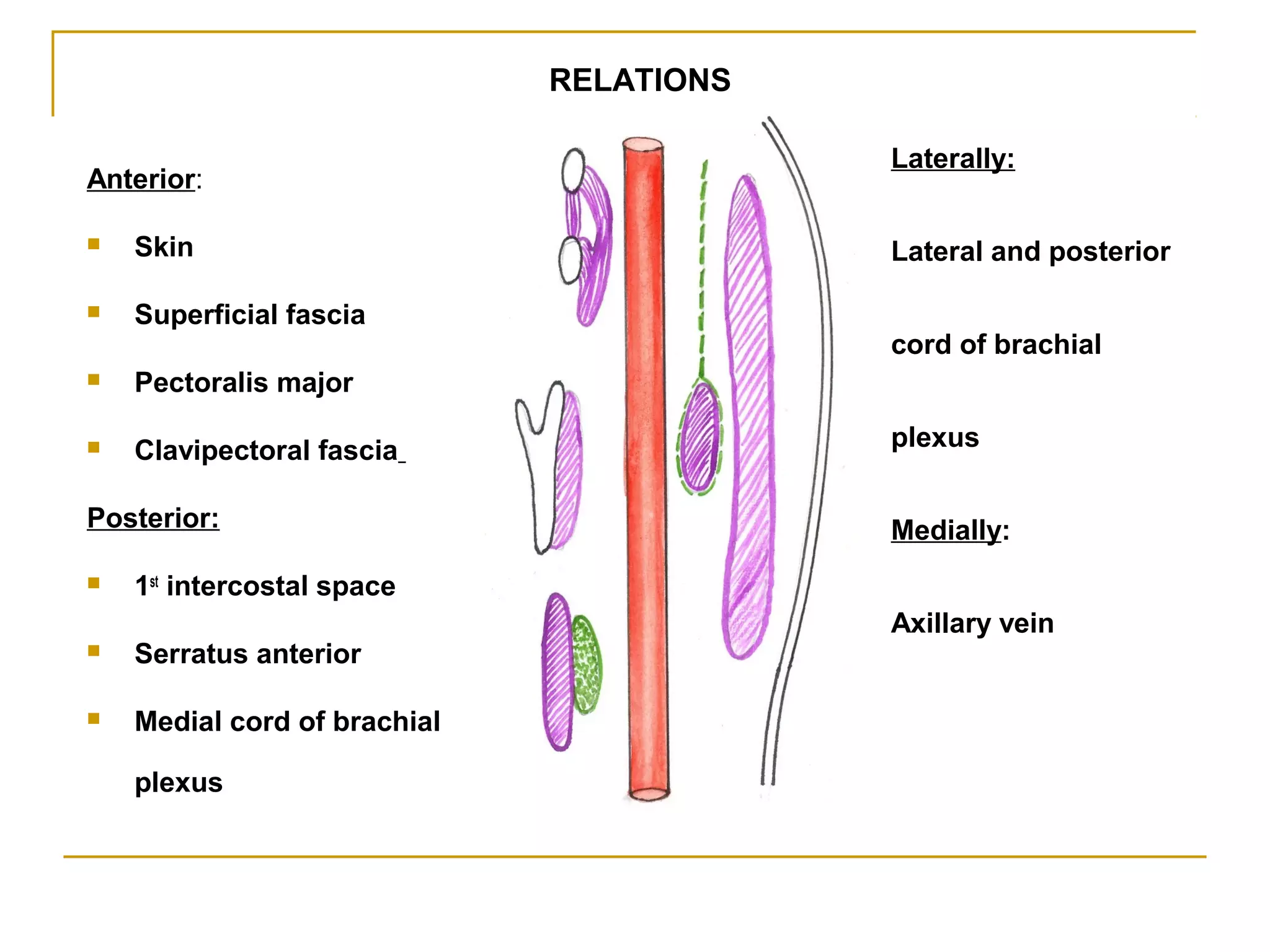
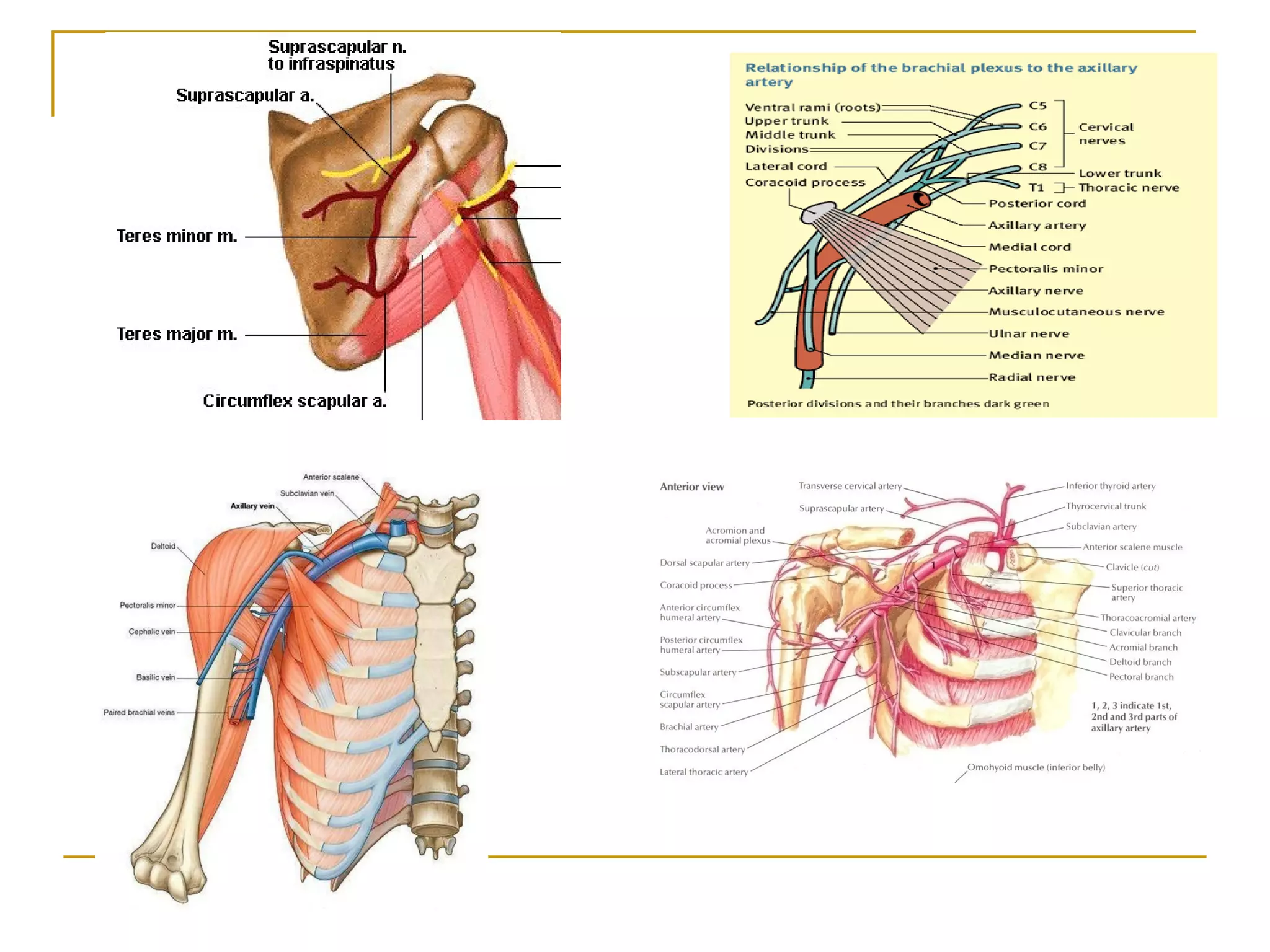
The axillary artery continues as the subclavian artery and extends from the outer border of the first rib to the lower border of teres major muscle. It has three parts separated by the pectoralis minor muscle and gives off several important branches that supply structures in the axilla and upper limb. These branches include the superior thoracic artery, thoracoacromial artery, lateral thoracic artery, subscapular artery, anterior circumflex humeral artery, and posterior circumflex humeral artery. The axillary vein runs medially and accompanies the artery, draining blood from the upper limb into the subclavian vein.