Embed presentation
Downloaded 58 times

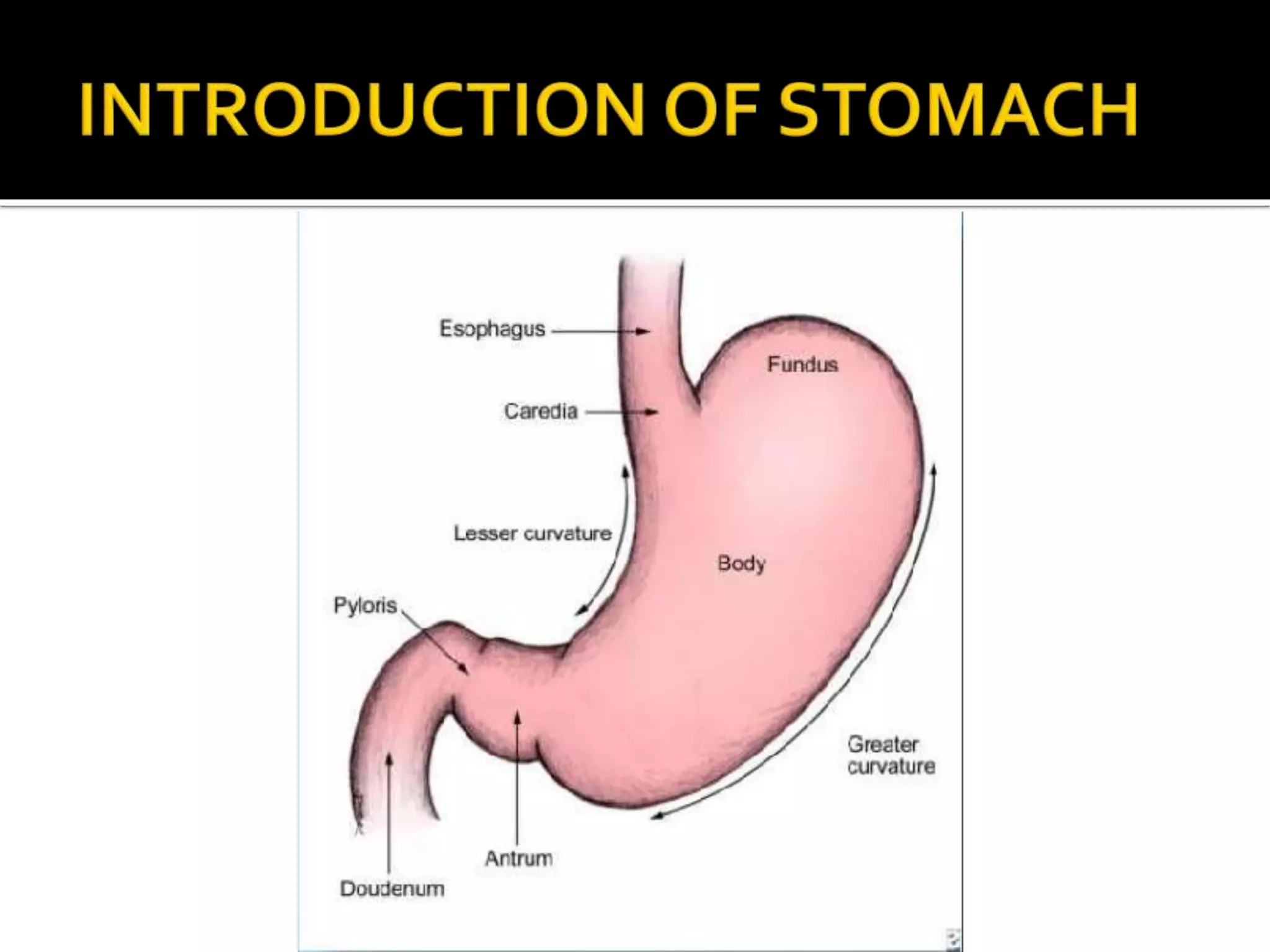
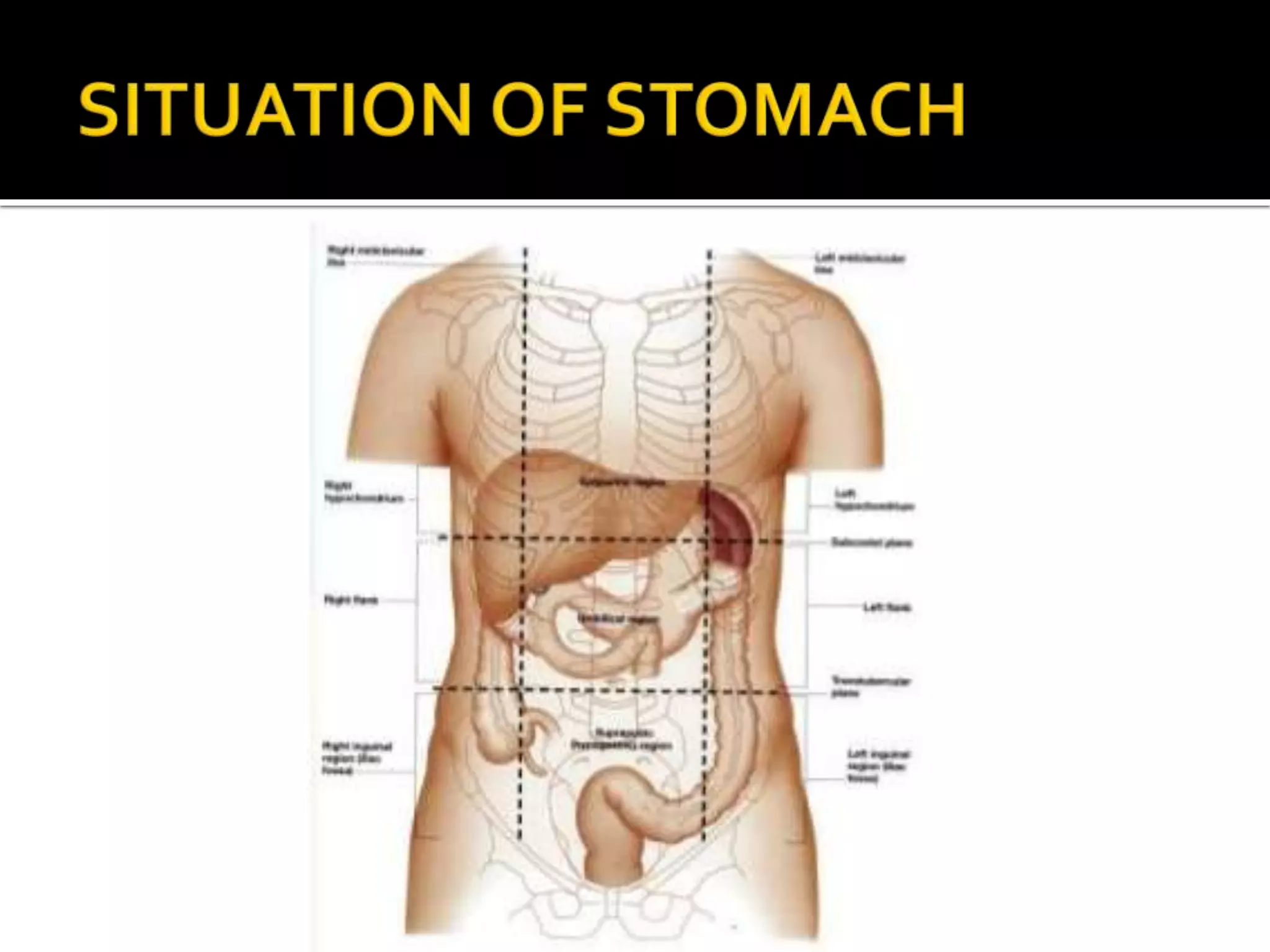
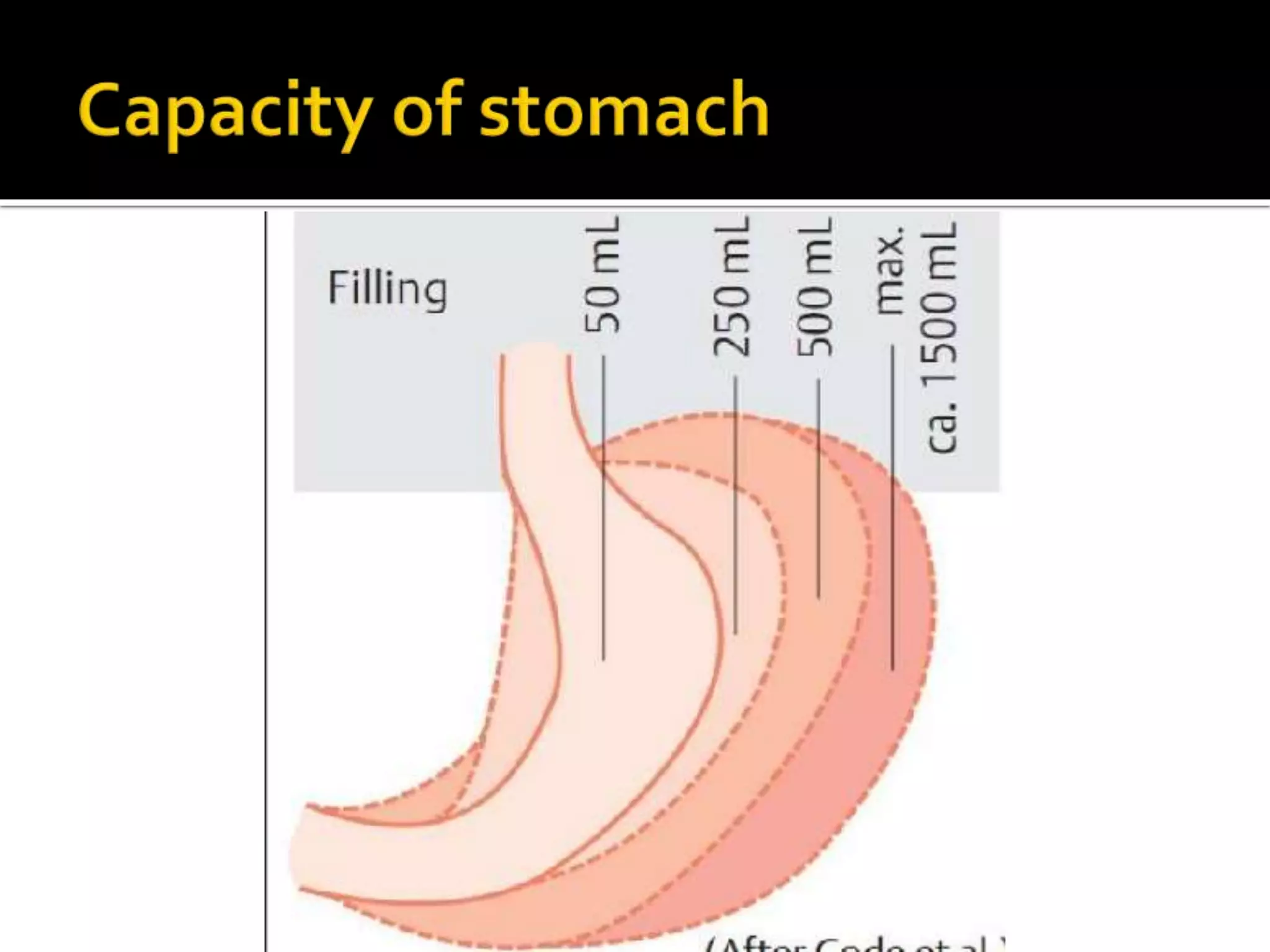

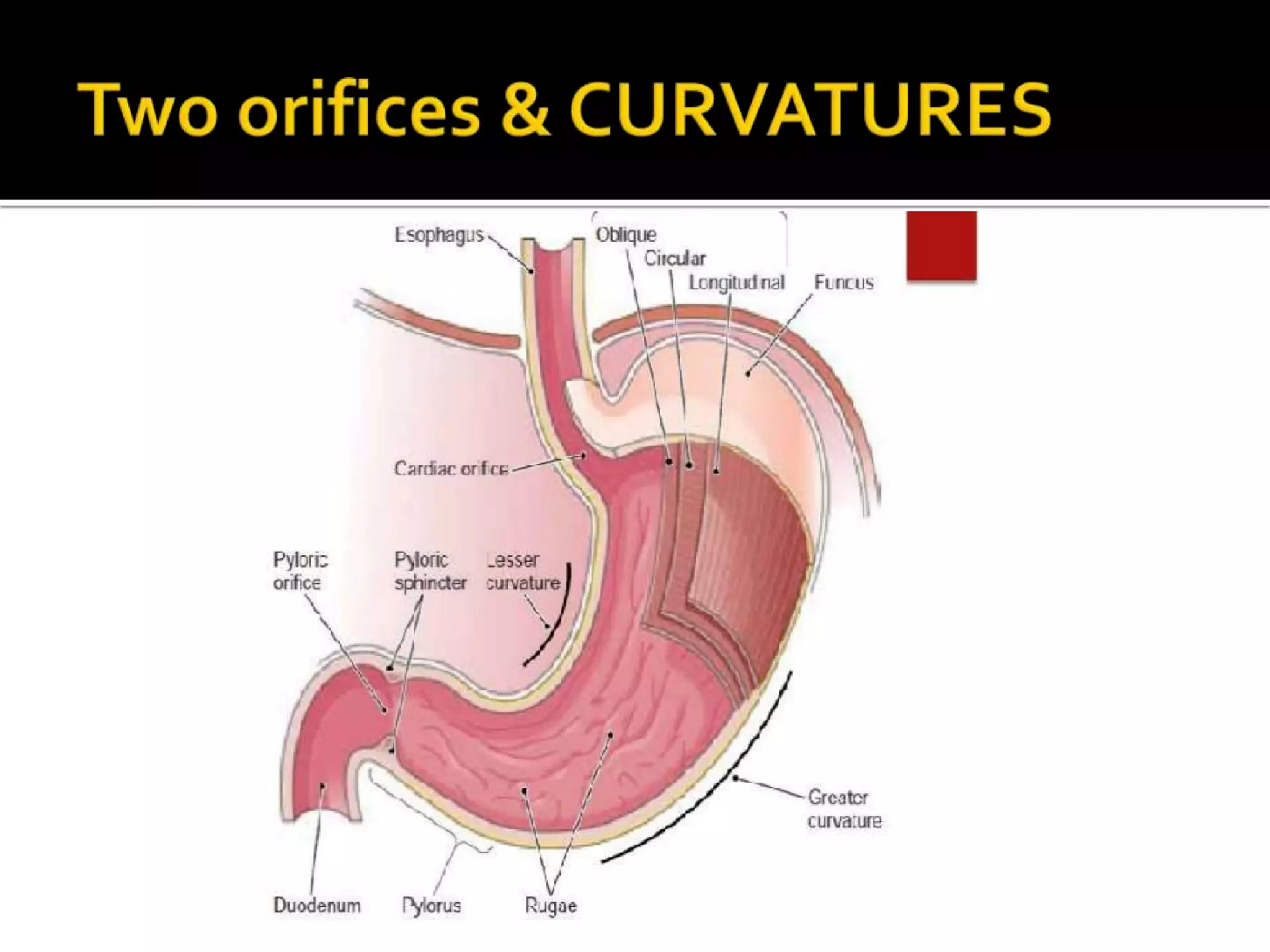
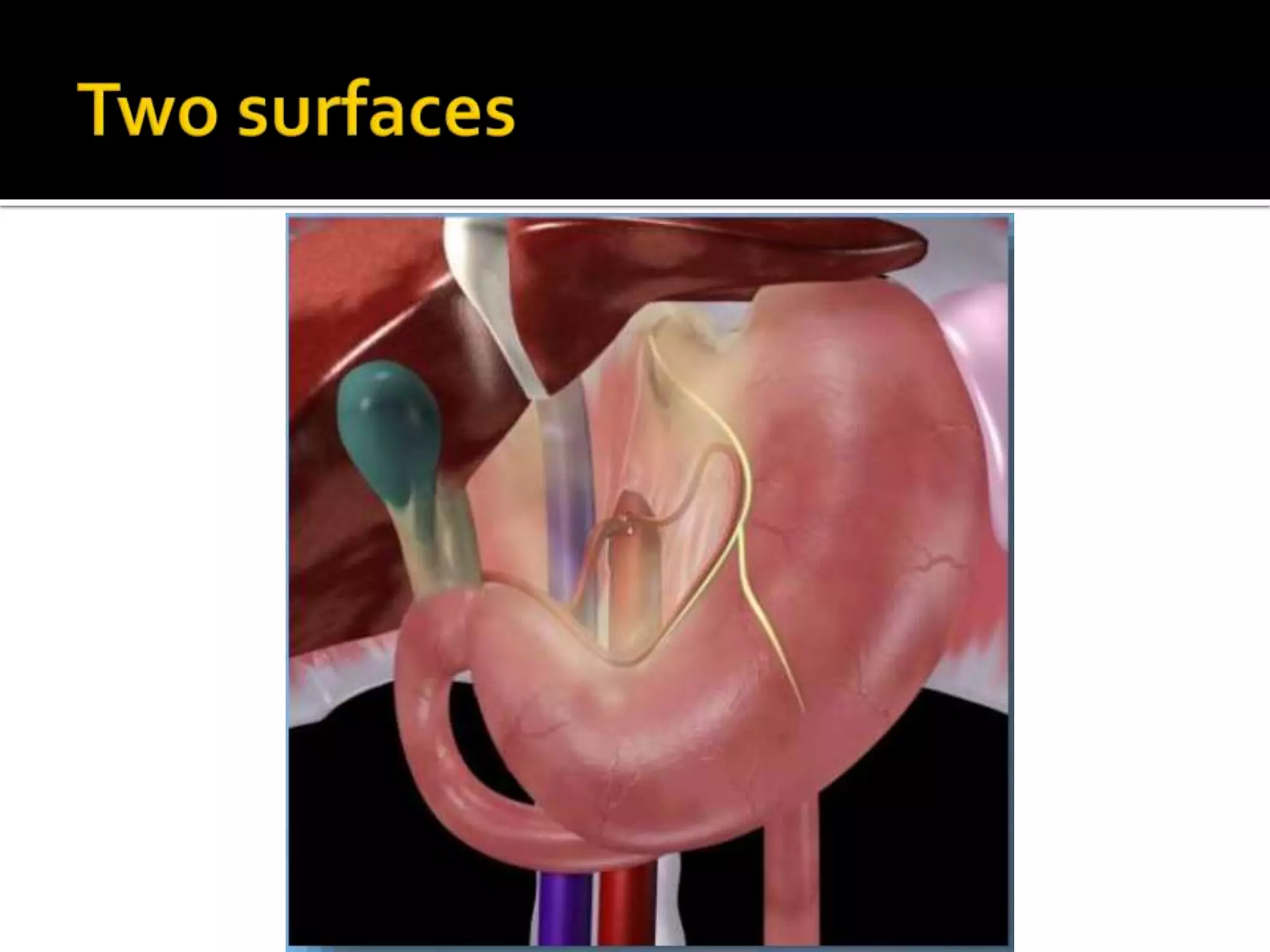
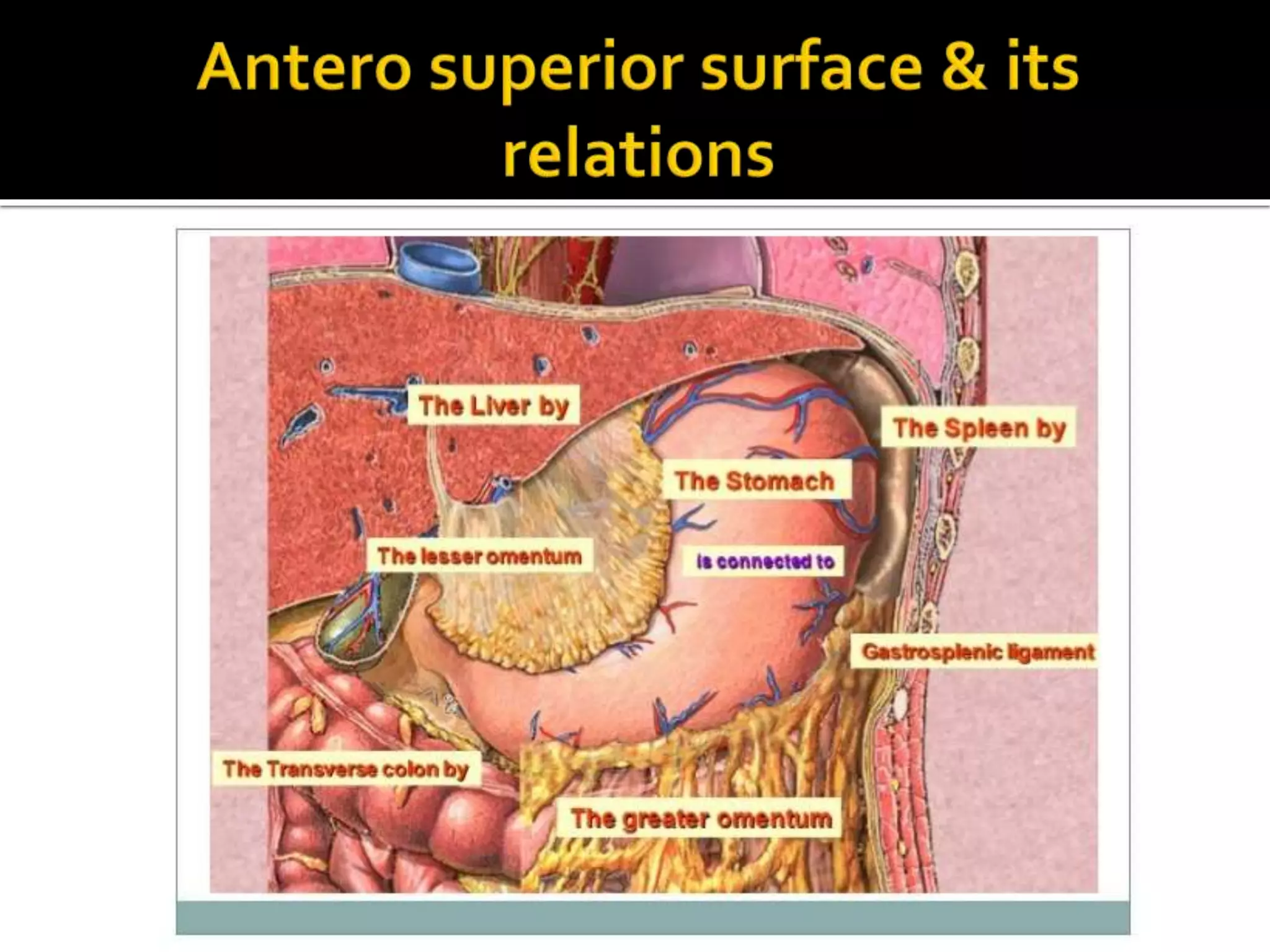
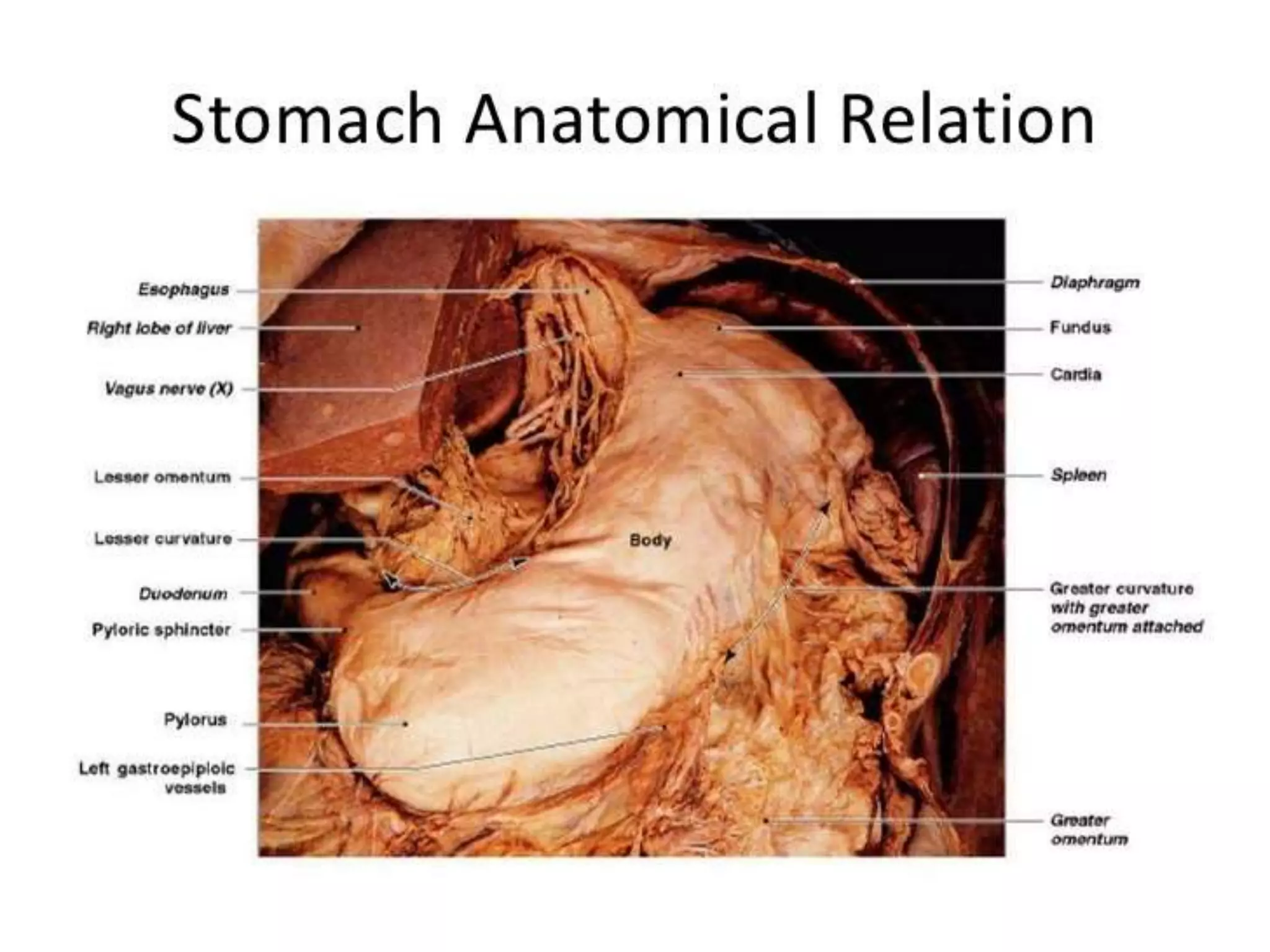
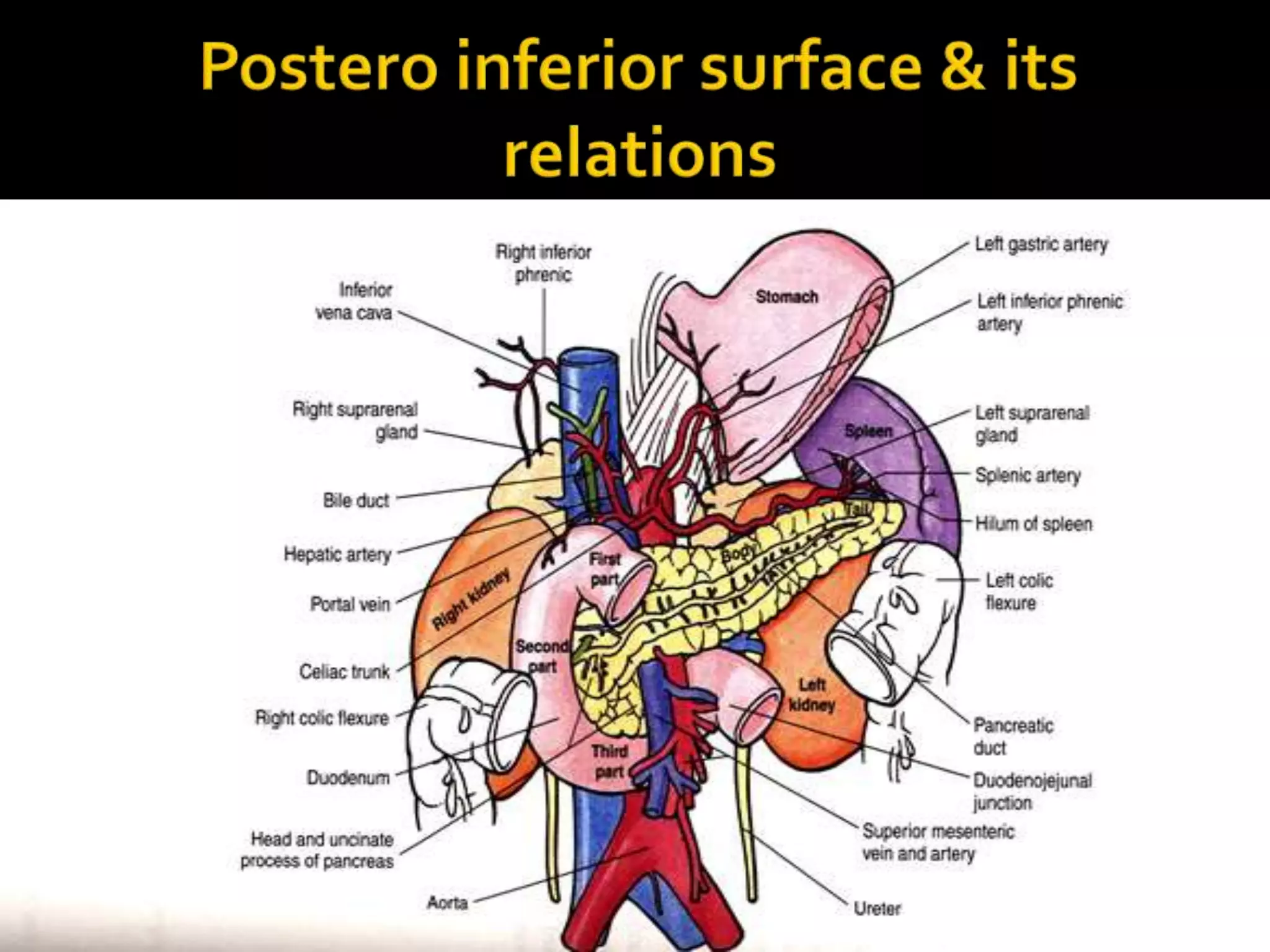
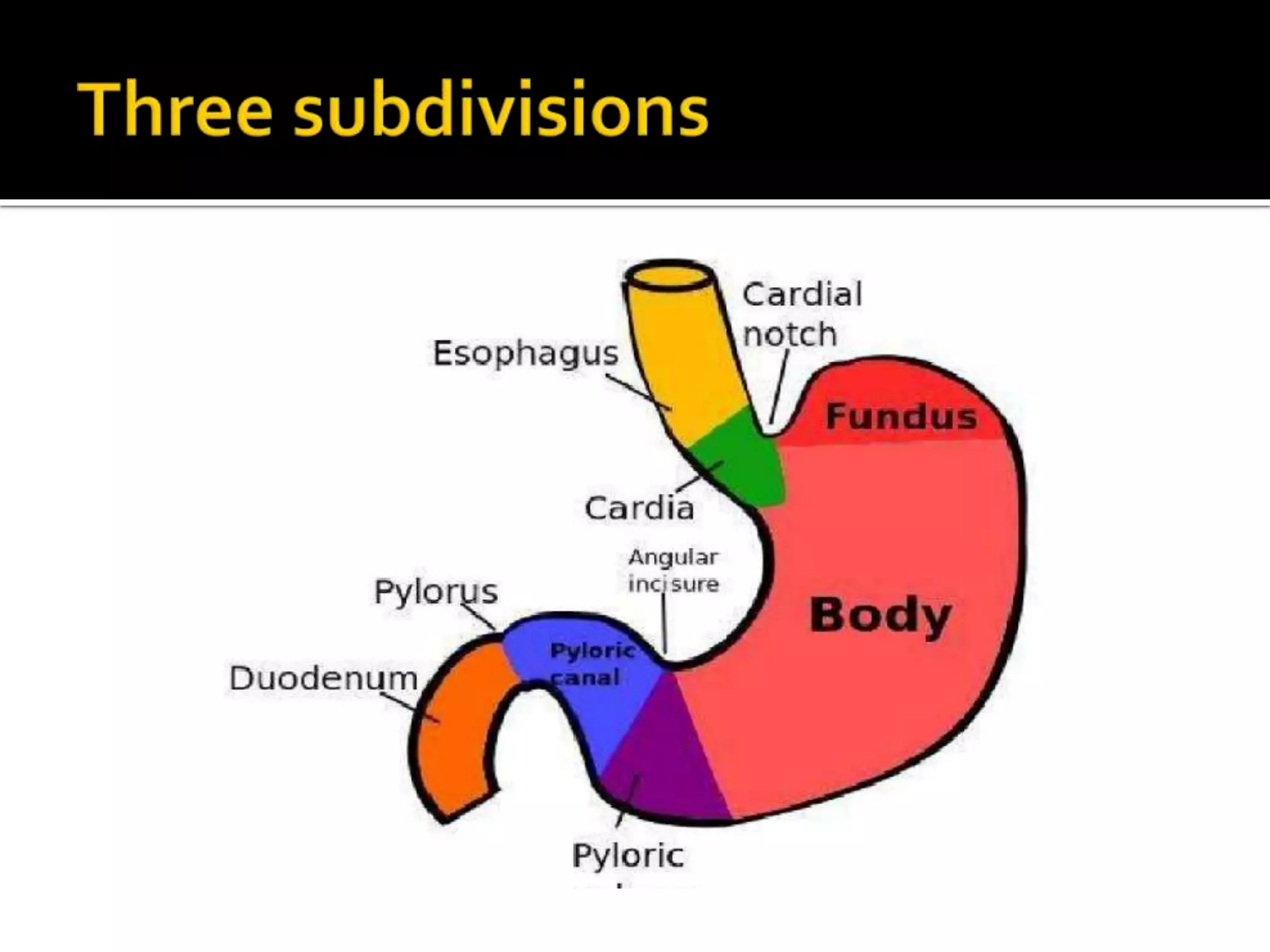

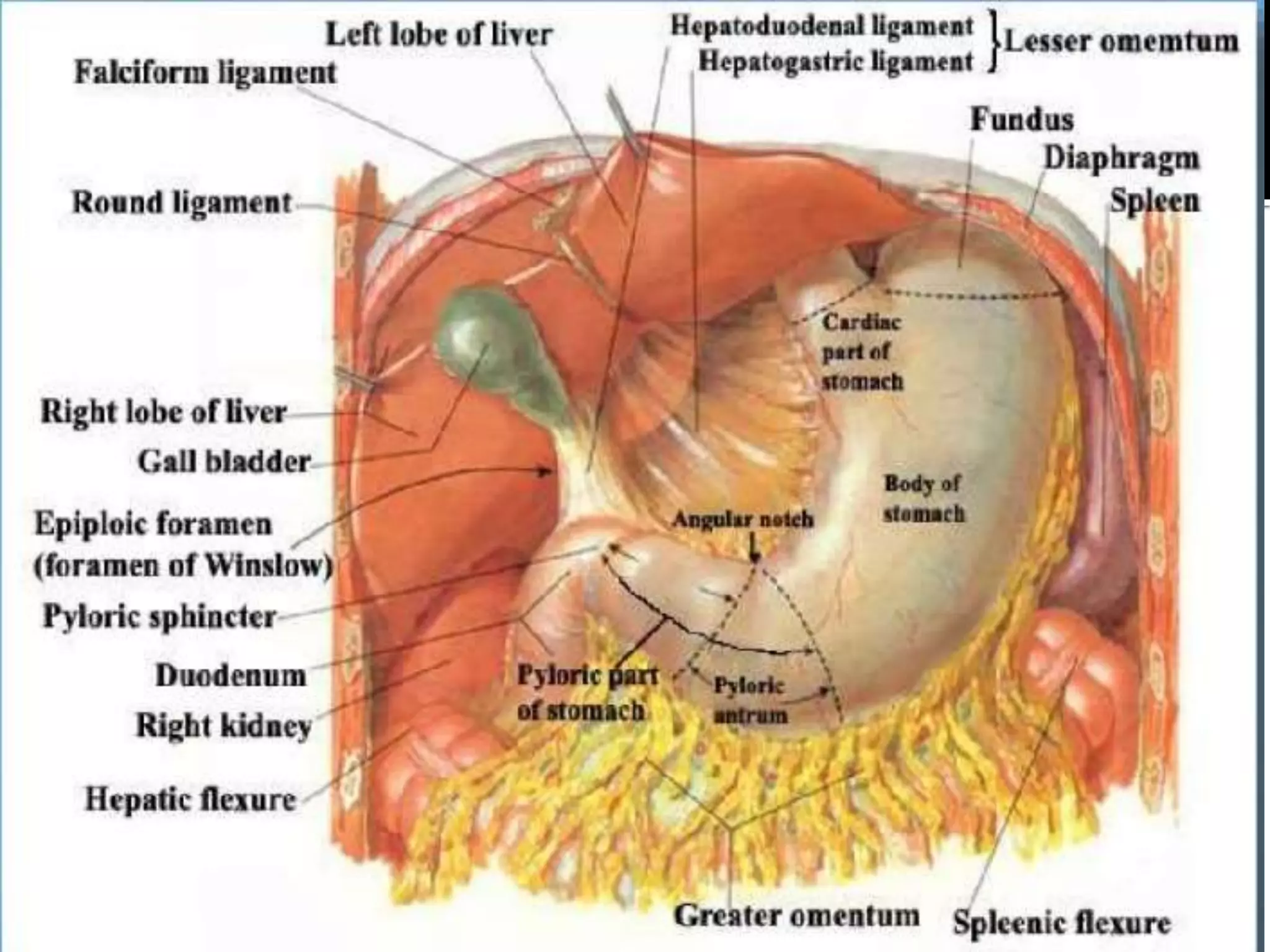
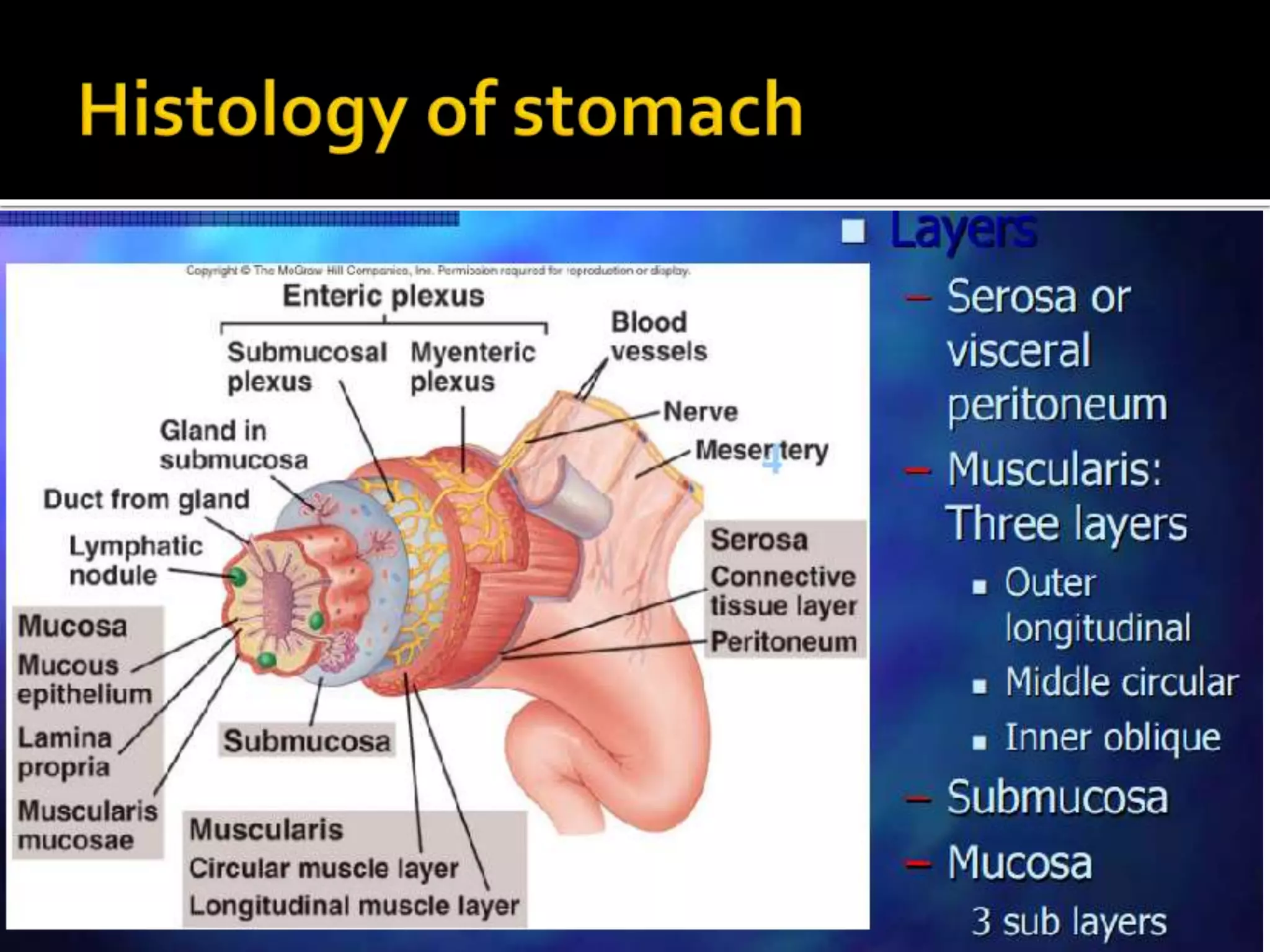
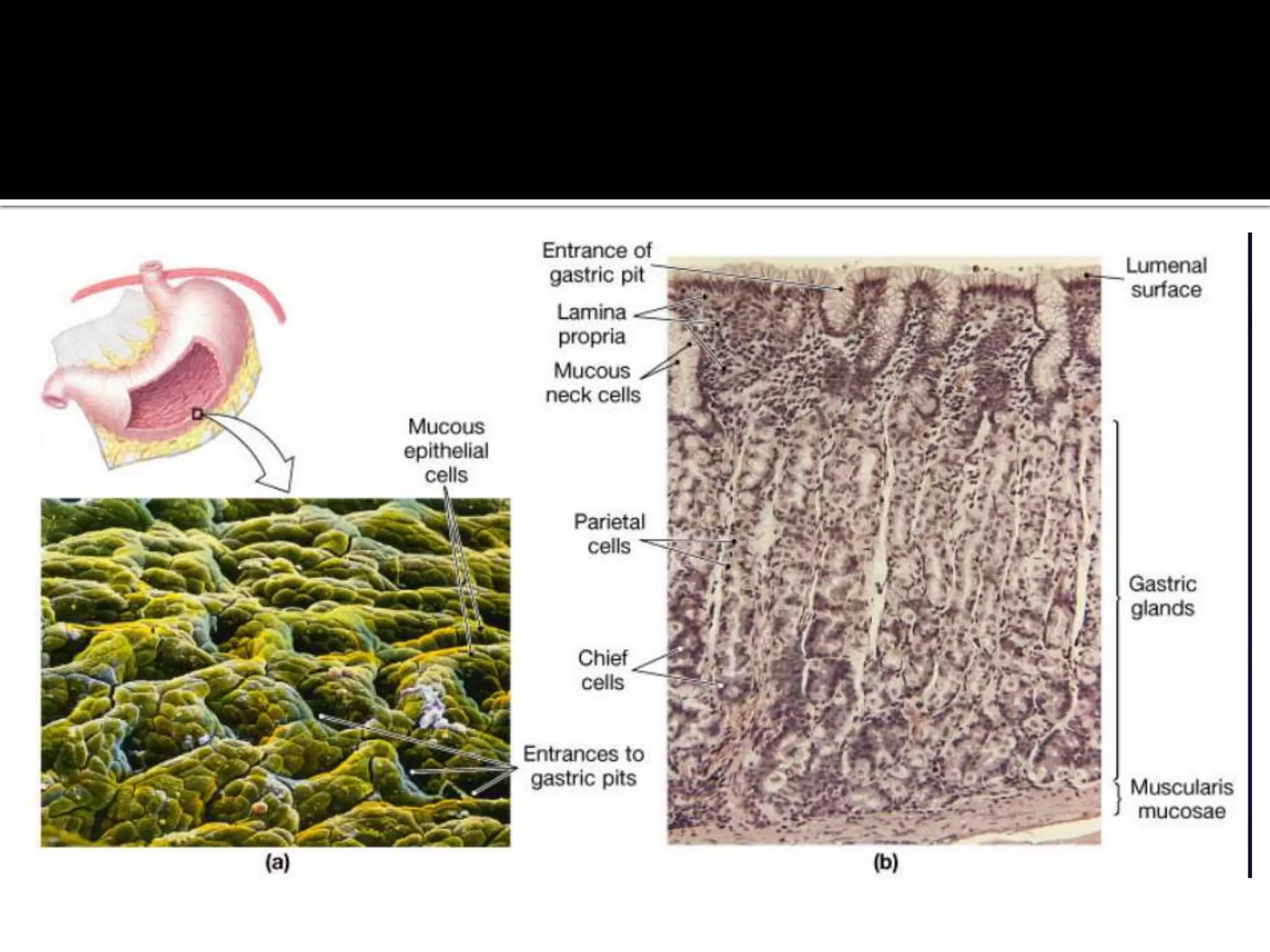
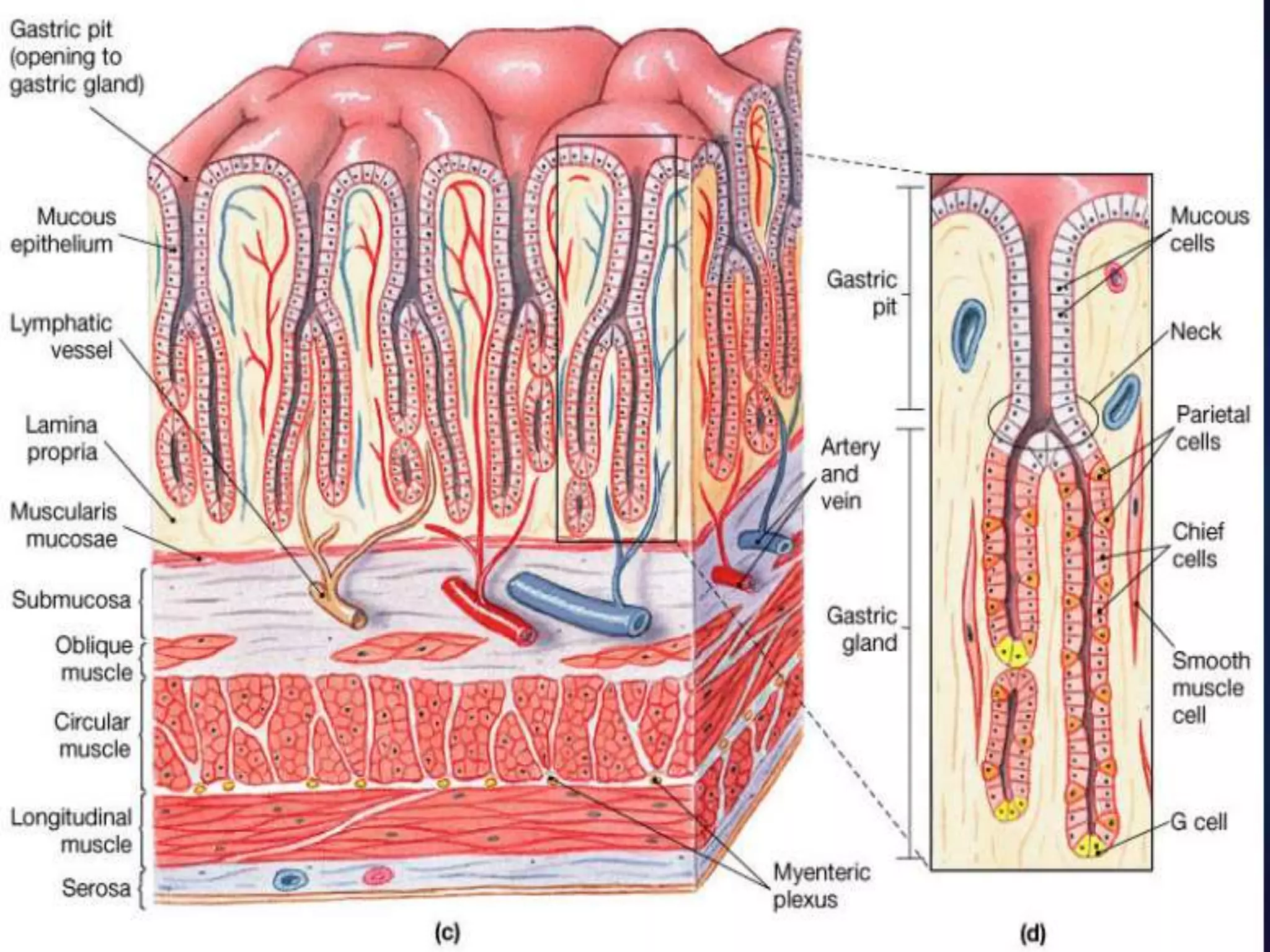
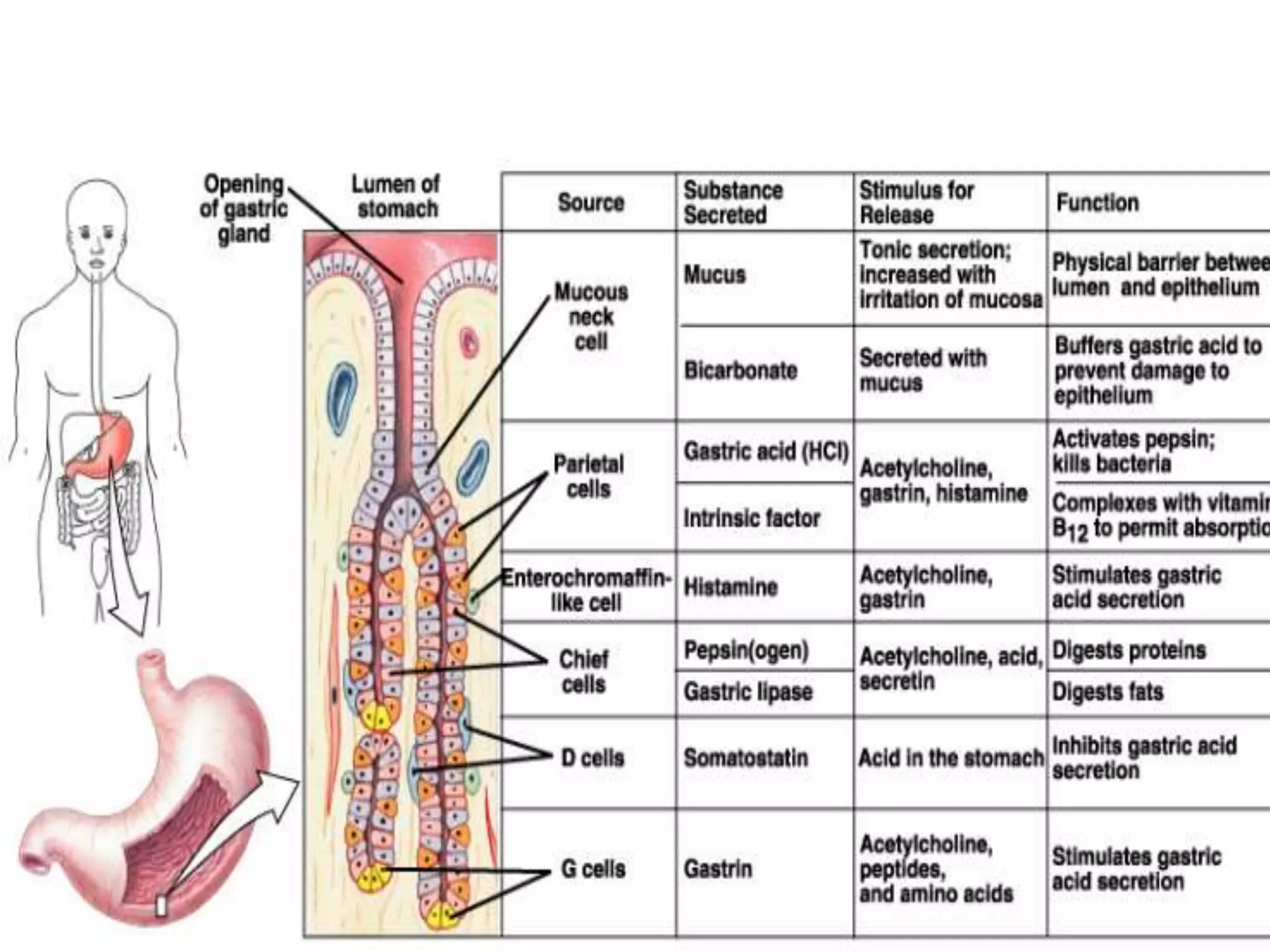
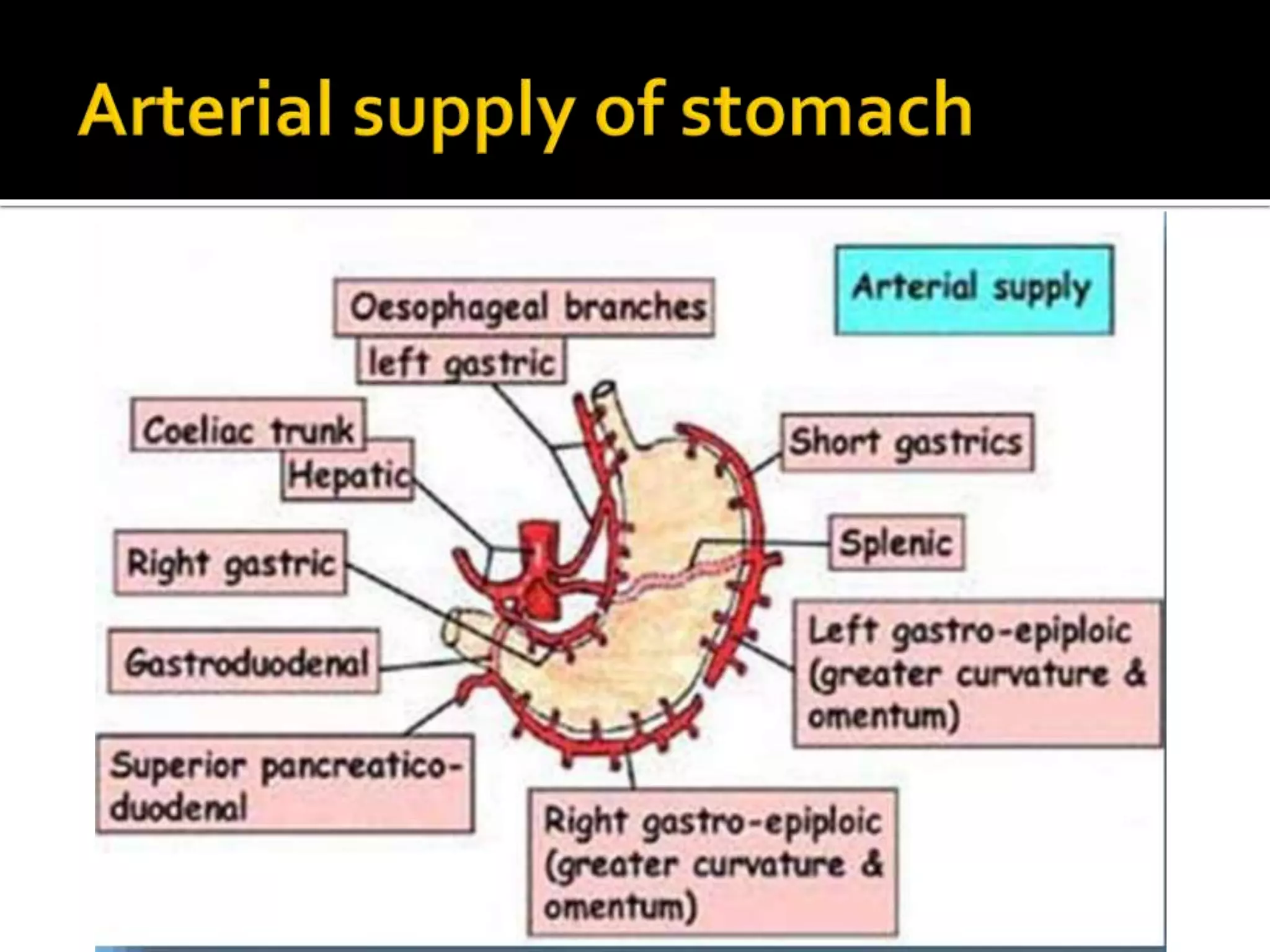
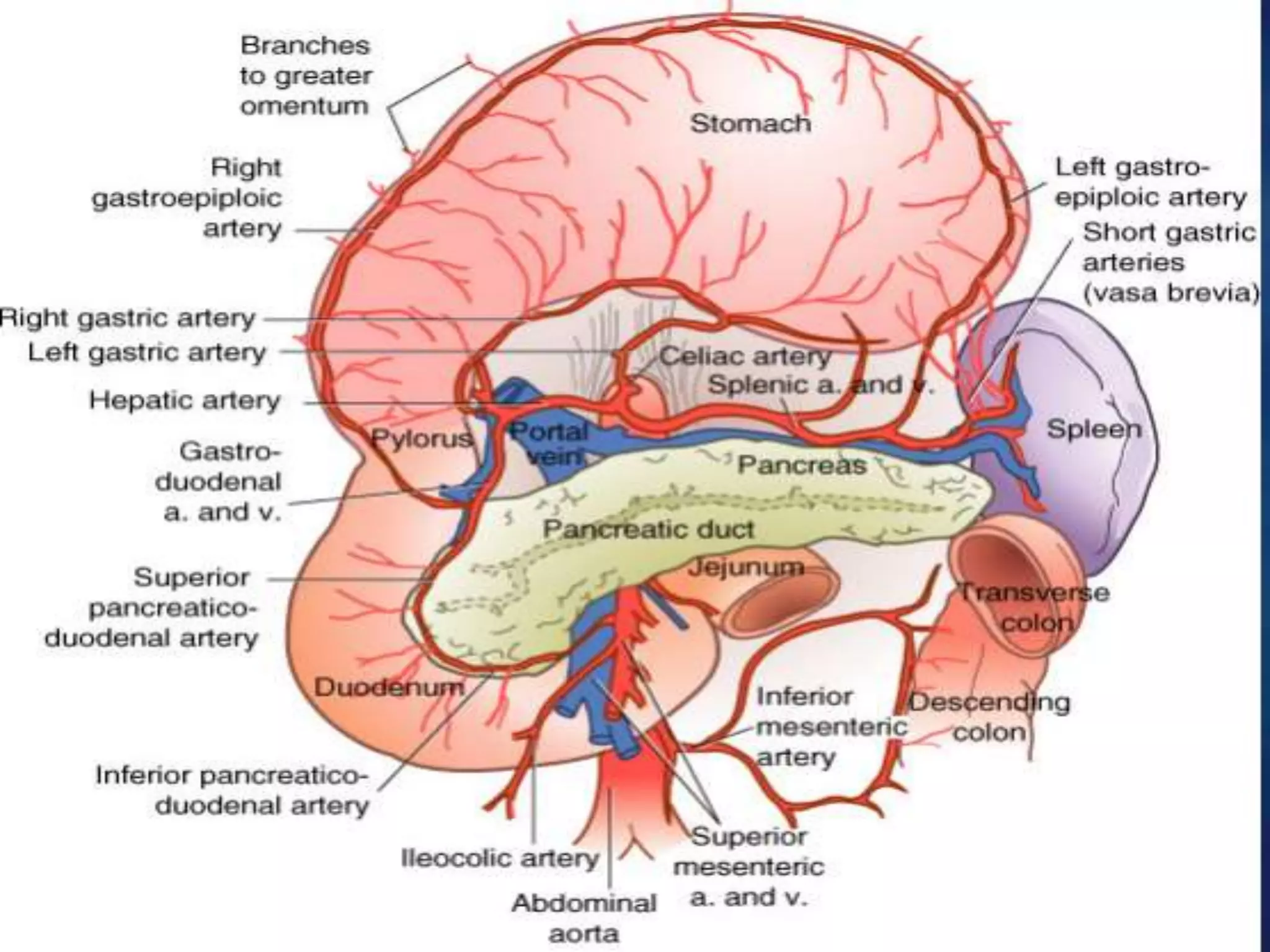
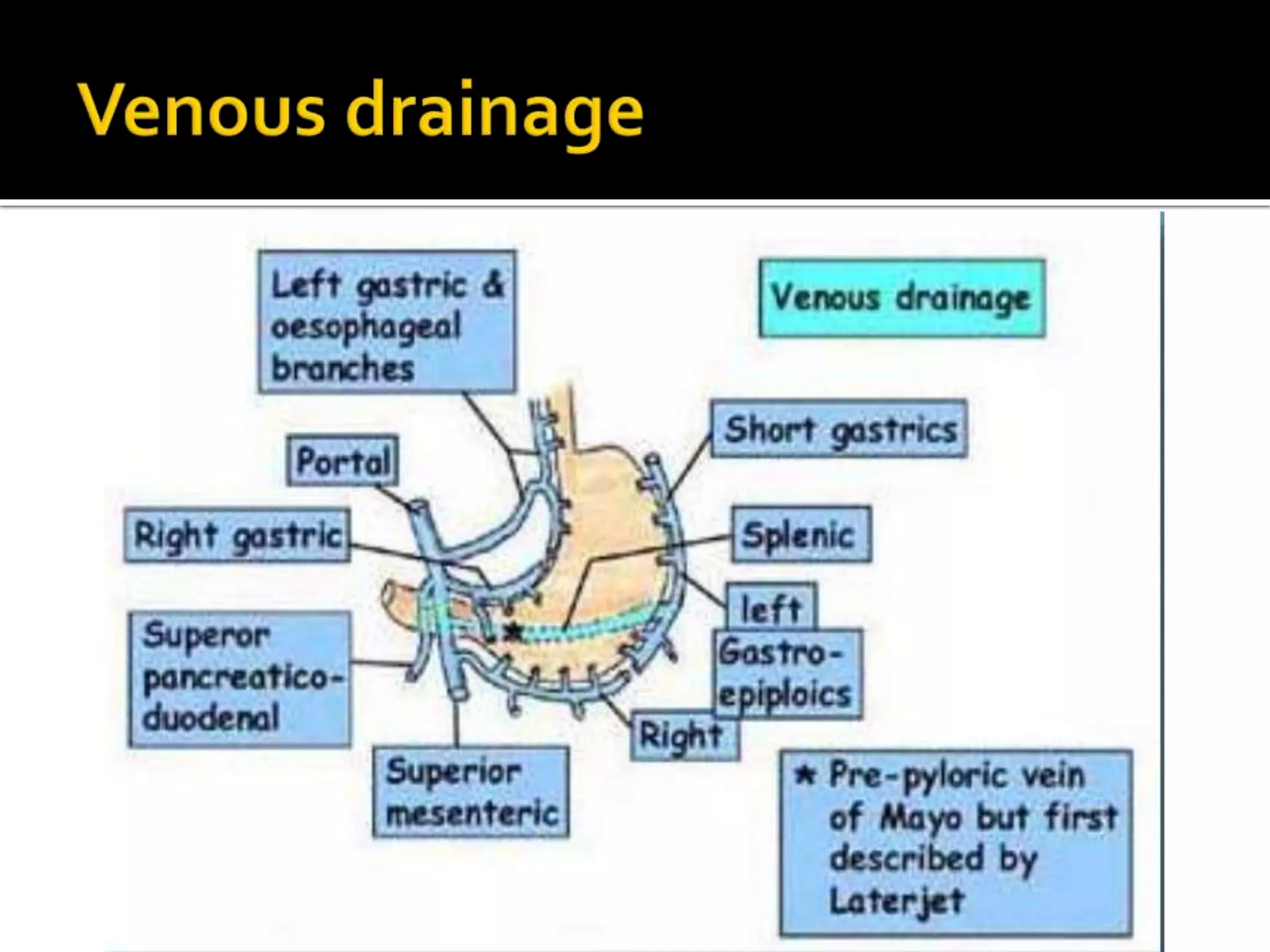
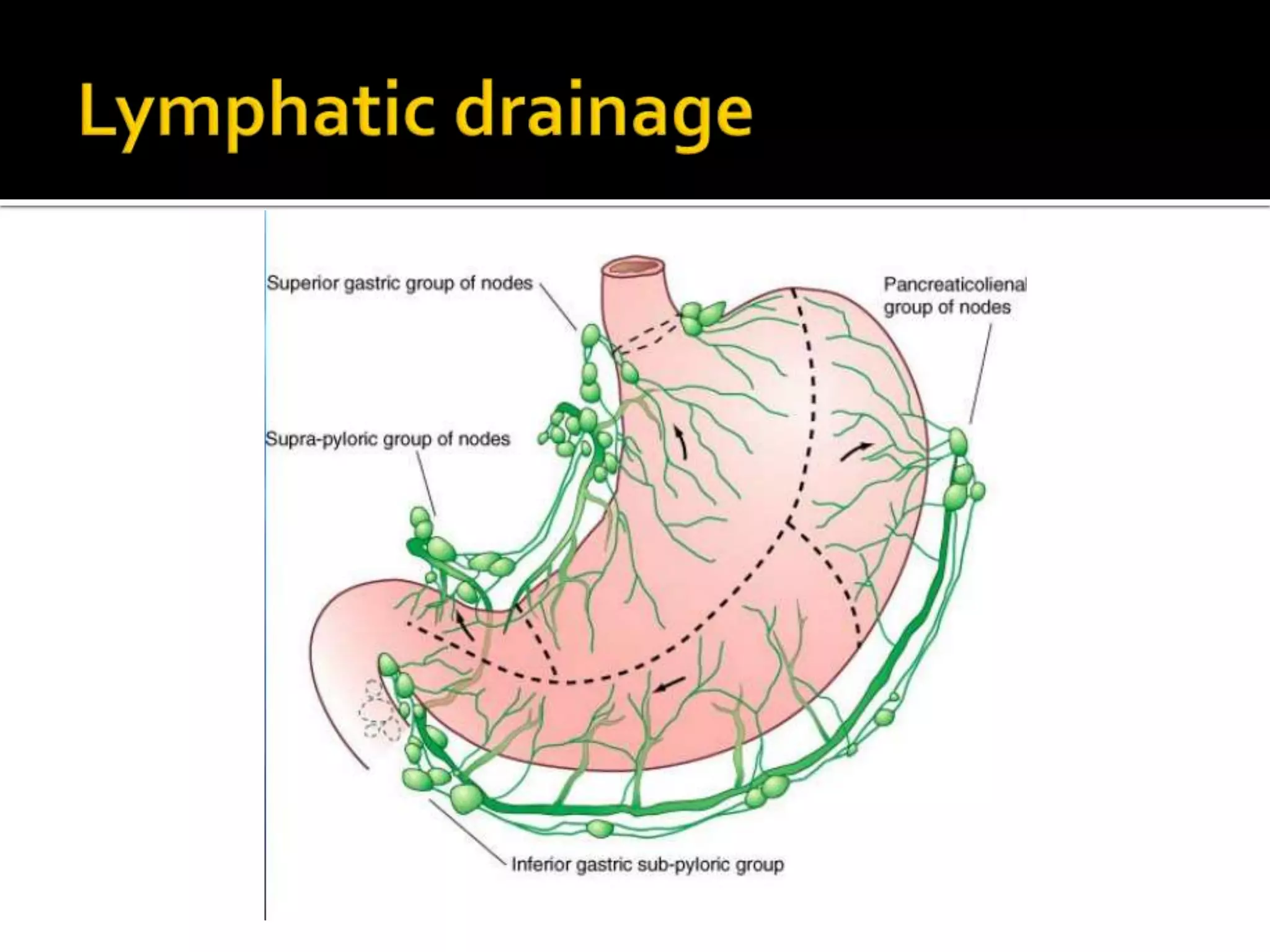
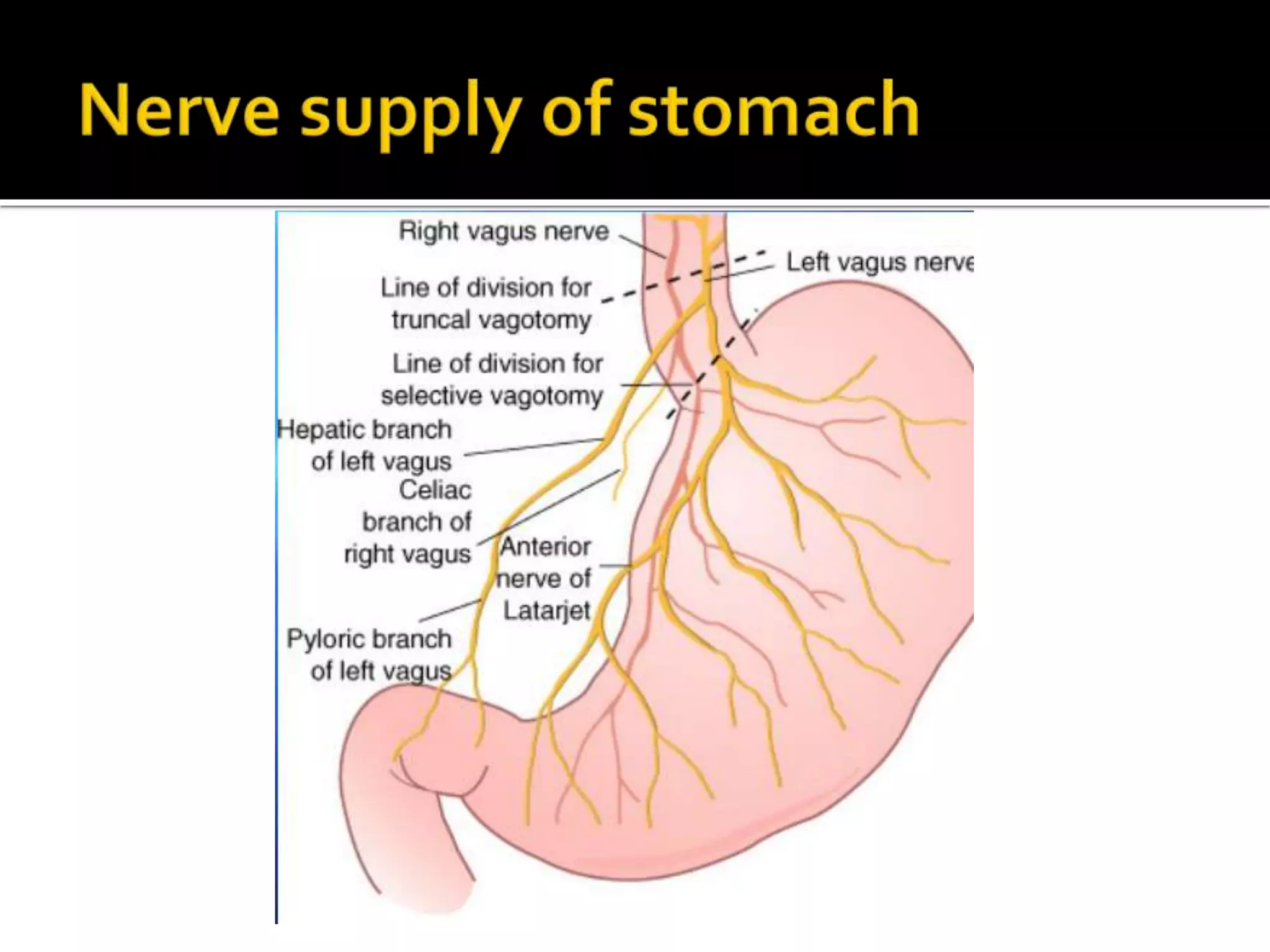

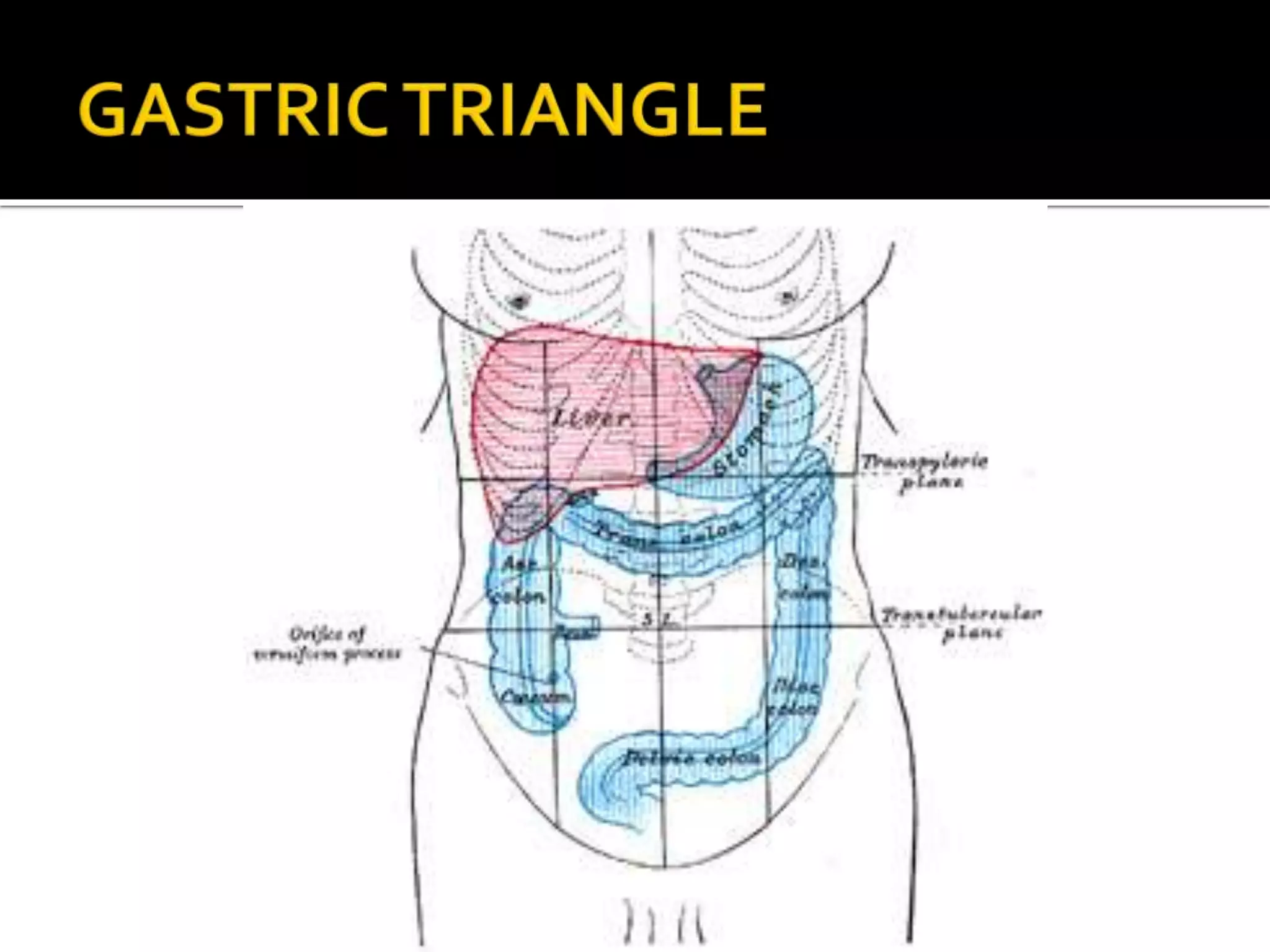
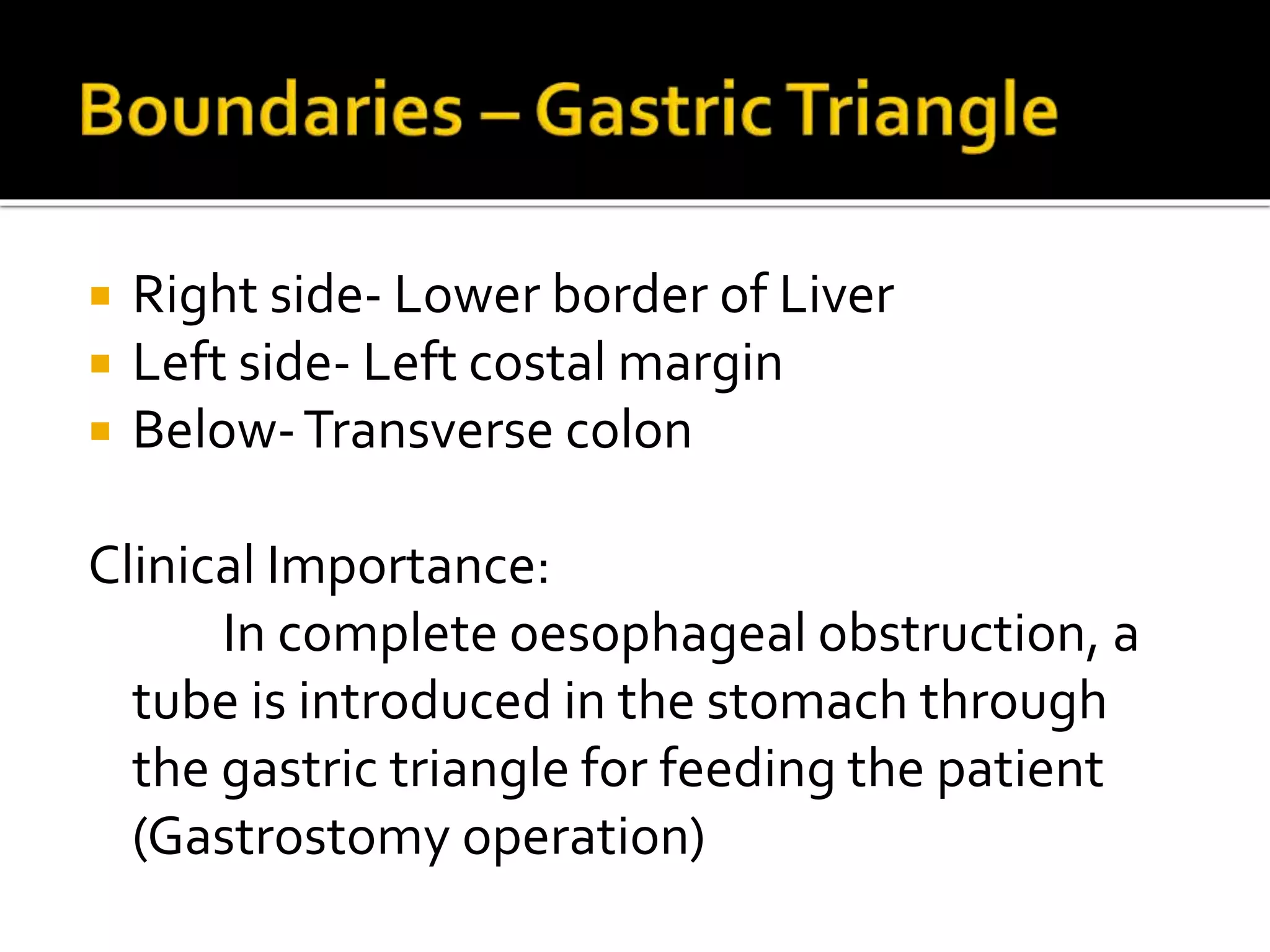
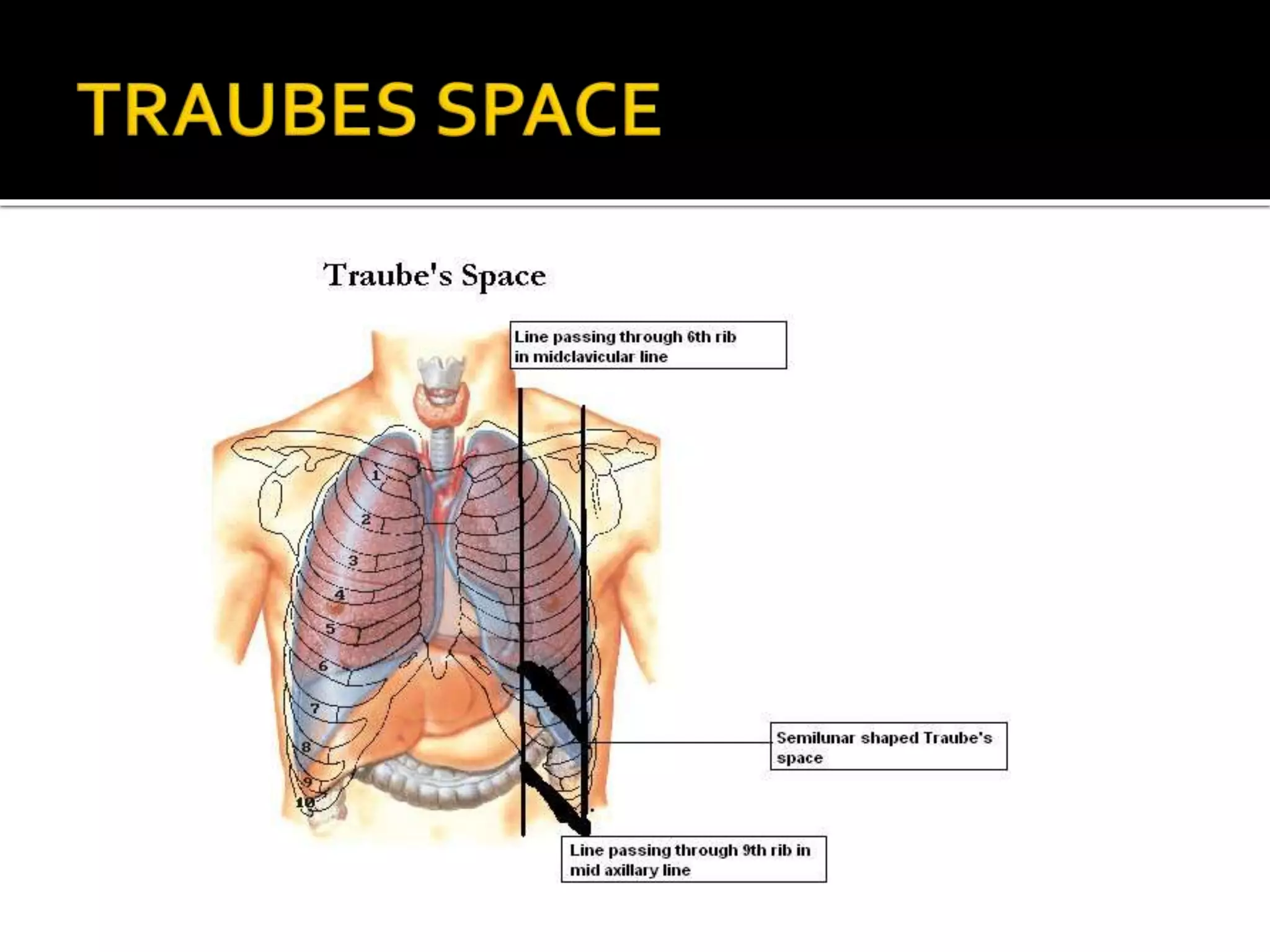
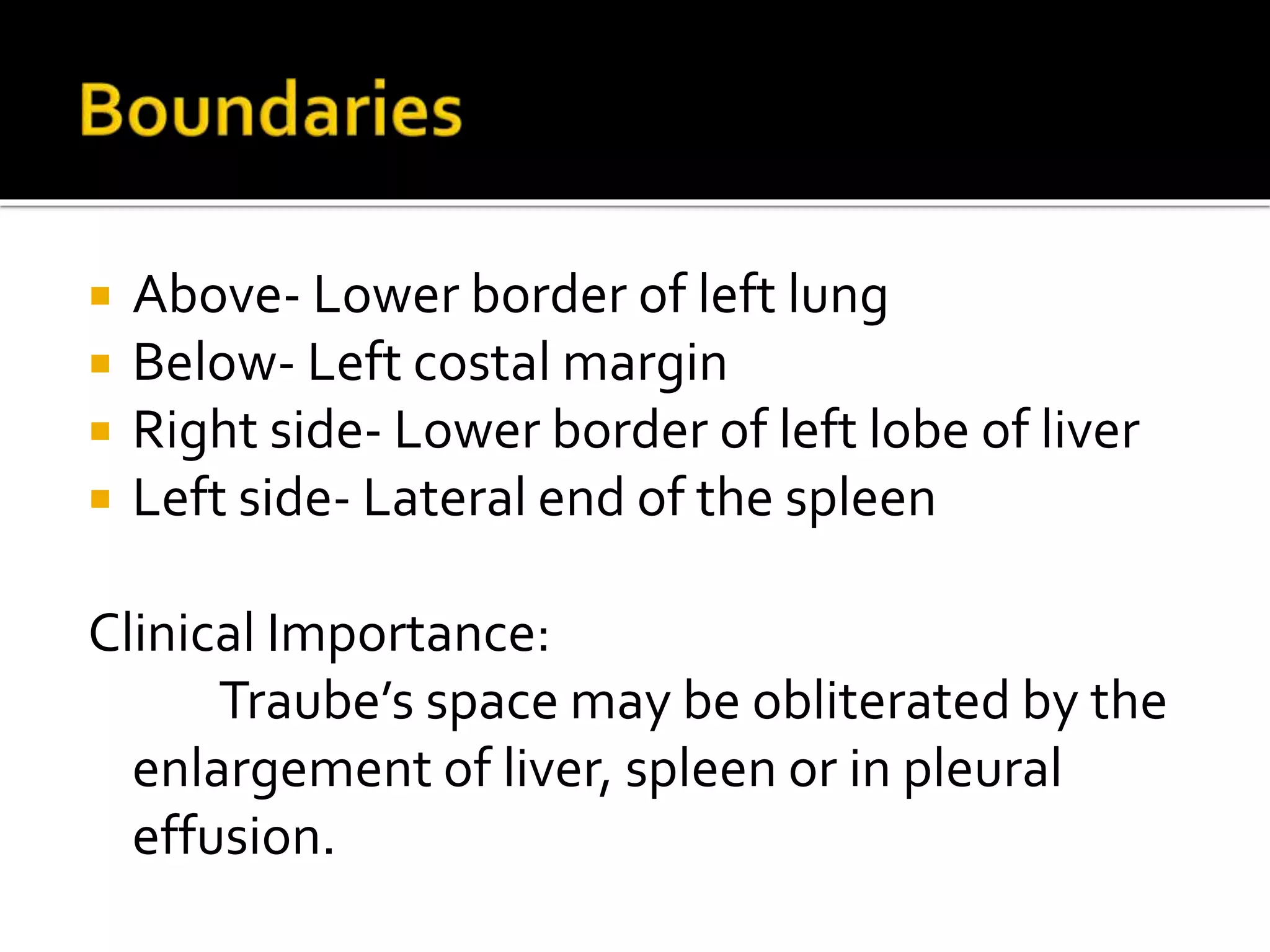

The document describes the anatomy and clinical importance of the stomach. It notes that the stomach has two orifices, two curvatures, two surfaces, and three subdivisions. It lists the various ligaments associated with the stomach and some common stomach conditions. It provides details on the borders and clinical importance of the gastric triangle and Traube's space, including how they are used in certain medical procedures and how they can be affected by other anatomical structures.



























