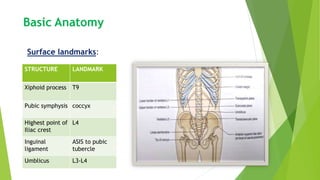
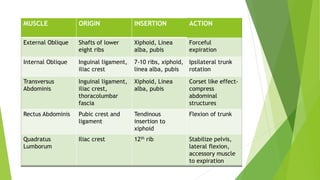
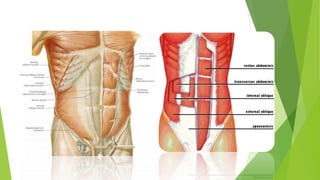
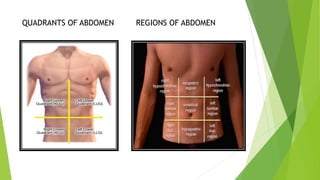
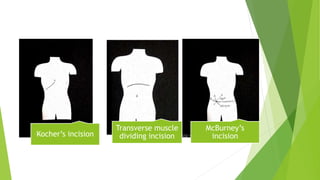
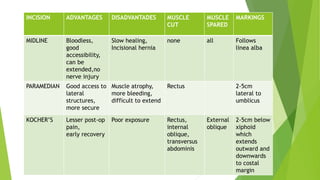
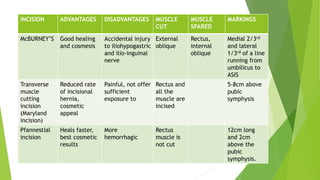
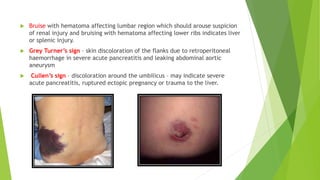
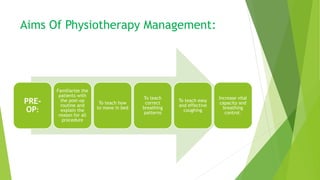
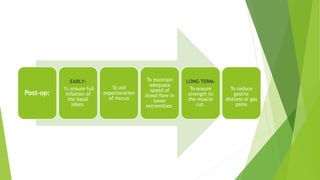
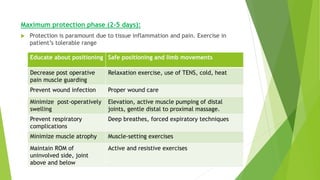
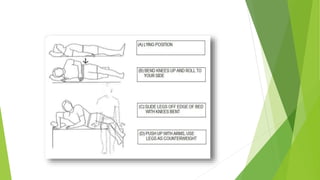
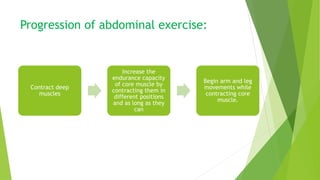
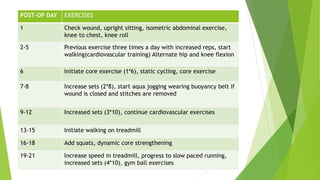
This document provides an overview of physiotherapy management for abdominal surgeries. It begins with basic anatomy including surface landmarks of the abdominal structures. It then discusses the different types of abdominal incisions and their advantages and disadvantages. The document outlines the process for history taking and physical examination for abdominal surgeries, including inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation of the abdomen. It notes potential postoperative complications from abdominal surgeries and how prehabilitation can help reduce postoperative complications. In summary, the document provides essential information on anatomy, surgical procedures, examination techniques and postoperative management related to physiotherapy for abdominal surgeries.