Embed presentation
Download to read offline

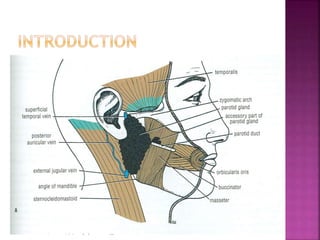
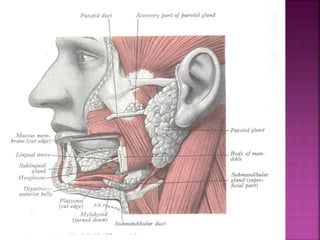
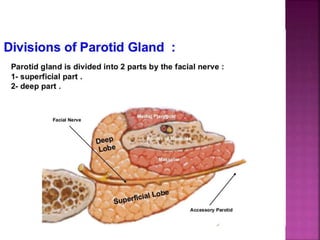
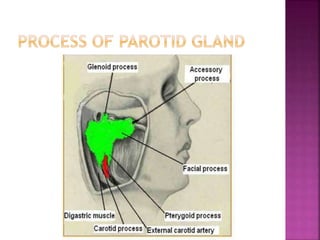
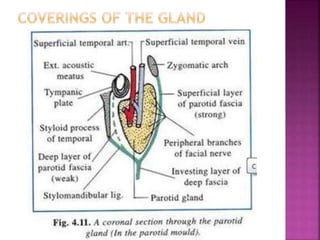
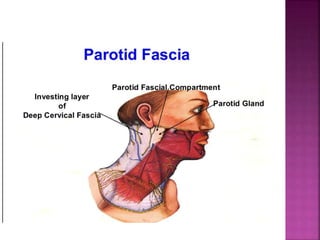

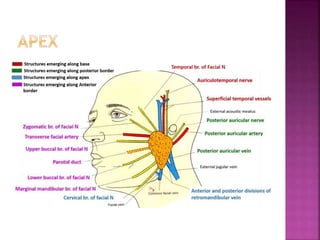
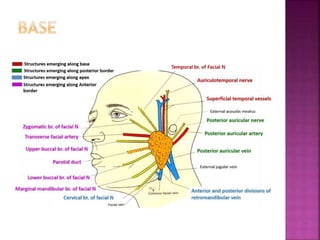
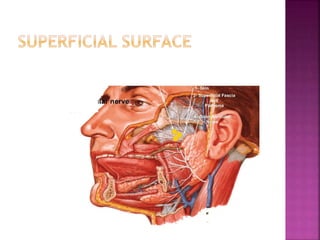
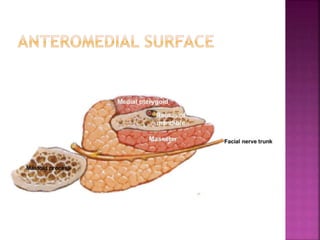
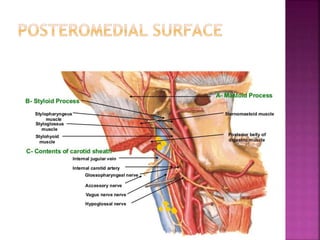

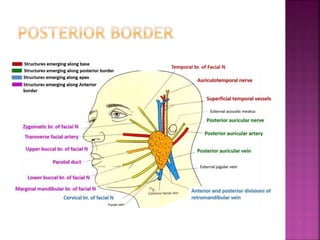

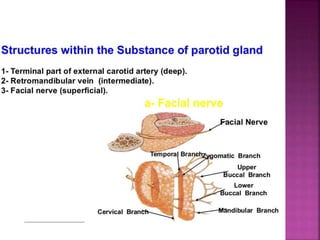
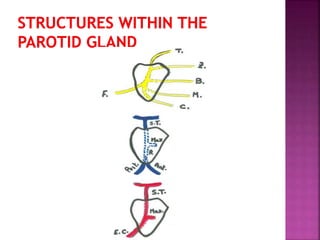
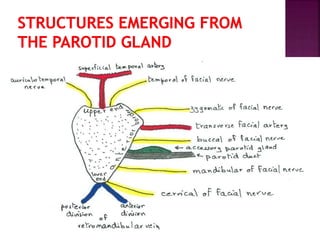
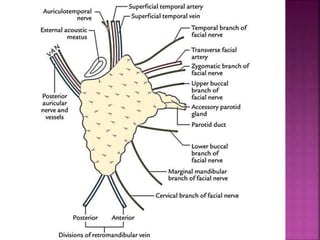

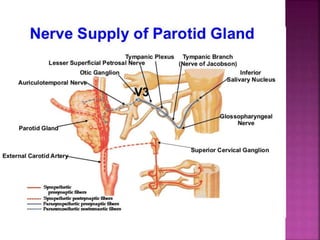
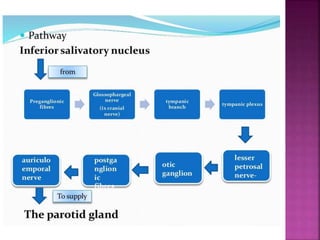
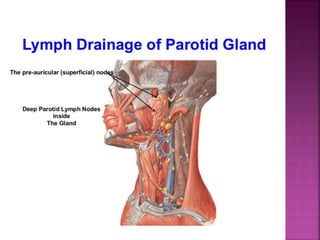


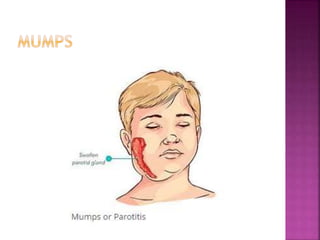
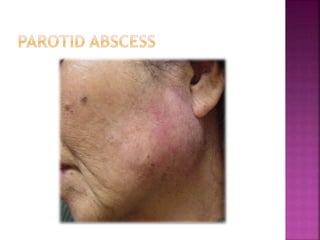




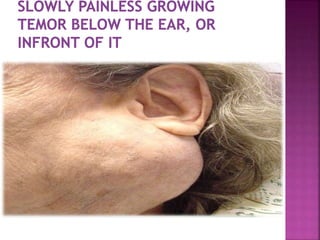
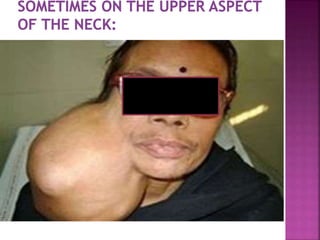
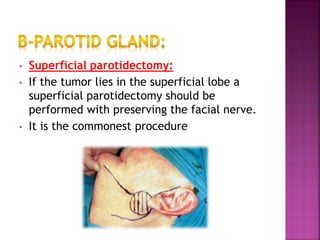

The parotid gland has three surfaces and borders and is located below and in front of the ear. Stensen's duct, which carries saliva from the parotid gland to the mouth, is 5 cm long and opens opposite the second upper molar tooth. Inflammatory swelling of the parotid gland is painful due to the inflexible fascial capsule surrounding it. Mumps is a viral infection of the salivary glands that causes fever and malaise in children ages 3-6 and lasts 3-7 days. Superficial parotidectomy is commonly used to remove tumors from the superficial lobe of the parotid gland while preserving the facial nerve.


































