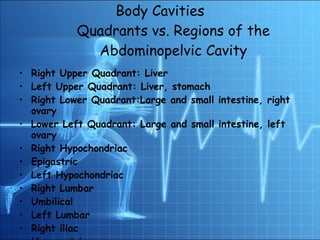
The document provides an overview of human anatomy and physiology, describing the following key points:
1. Anatomy is the study of the structure and relationship between body parts, while physiology is the study of how the body and its parts function.
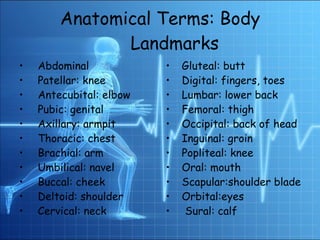
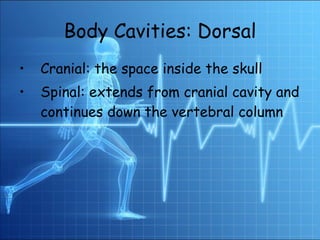
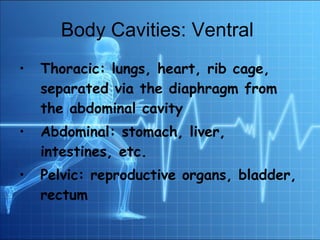
2. The human body is composed of several levels of organization from atoms to organ systems.
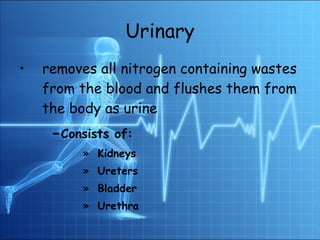
3. The major organ systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
4. All organ systems work together to carry out essential life functions like maintaining homeostasis.