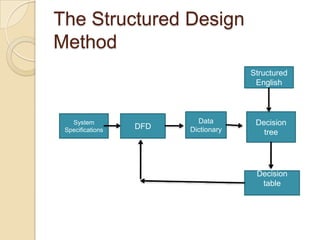
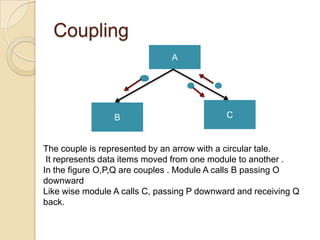
The document discusses the process of system design, which goes through logical and physical design phases. Logical design involves data flow diagrams and defining user needs, while physical design specifies design details for programmers. Structured design uses tools like data flow diagrams, data dictionaries, and structure charts to decompose the system into modules. A key part of design is structured walkthroughs where peers review and provide feedback on the design. User involvement is also important throughout the design process.