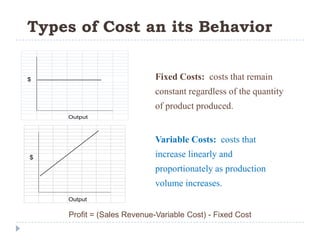
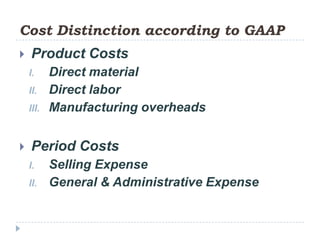
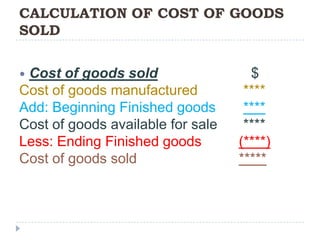
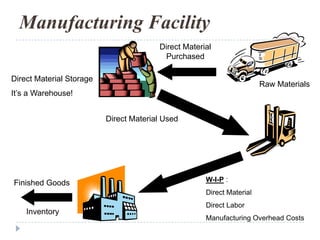
This document provides an introduction to accounting concepts related to cost. It defines cost accounting as recording and summarizing financial transactions and events in terms of money. It also discusses the different types of accounting, including financial accounting which publishes reports for external users, and management accounting which provides information to managers for decision making. Finally, it outlines the key steps in calculating cost of goods manufactured and cost of goods sold.