This document discusses key concepts in managerial accounting, including:
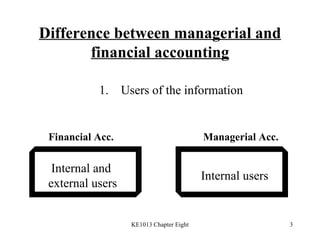
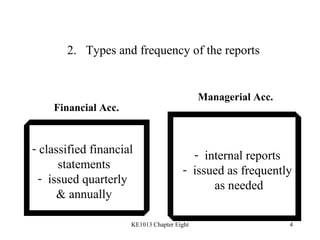
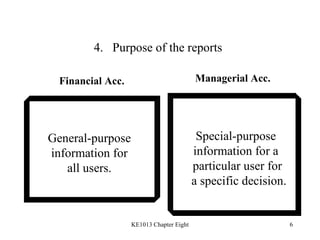
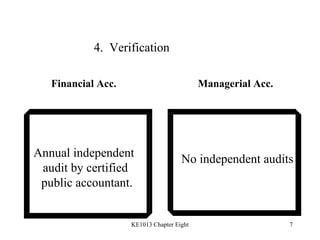
1. The differences between managerial and financial accounting in terms of users, reports, purposes, and verification.
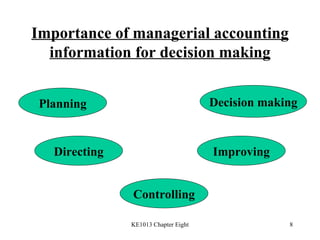
2. The importance of managerial accounting information for decision making through planning, directing, and controlling.
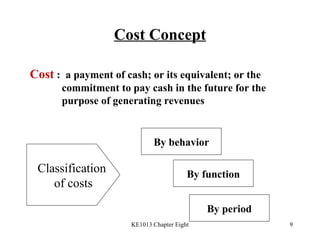
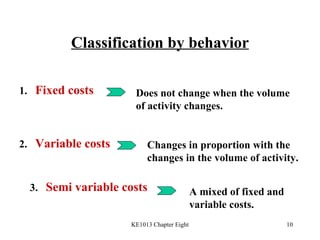
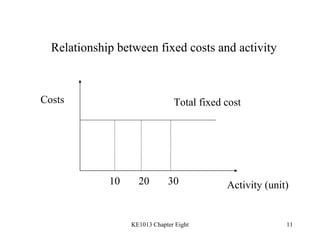
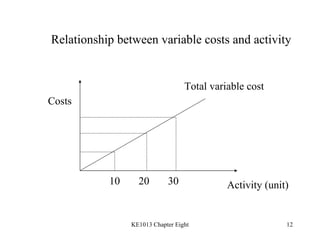
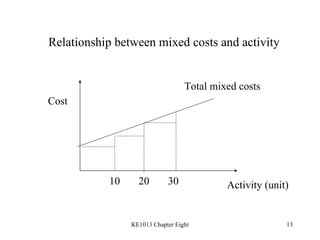
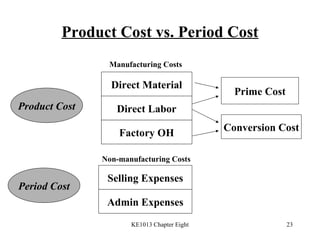
3. Key cost concepts like classifications of costs by behavior, function, and period.
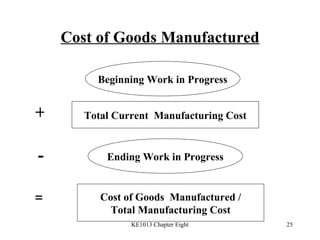
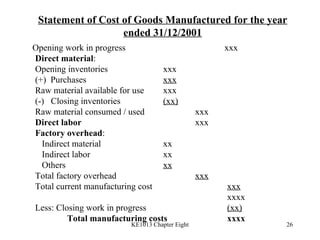
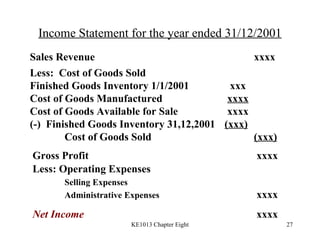
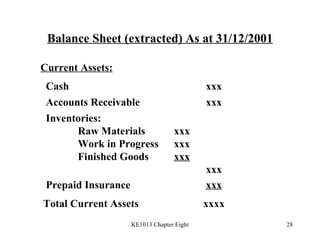
4. Preparing key statements for manufacturing companies including the statement of cost of goods manufactured, income statement, and balance sheet.