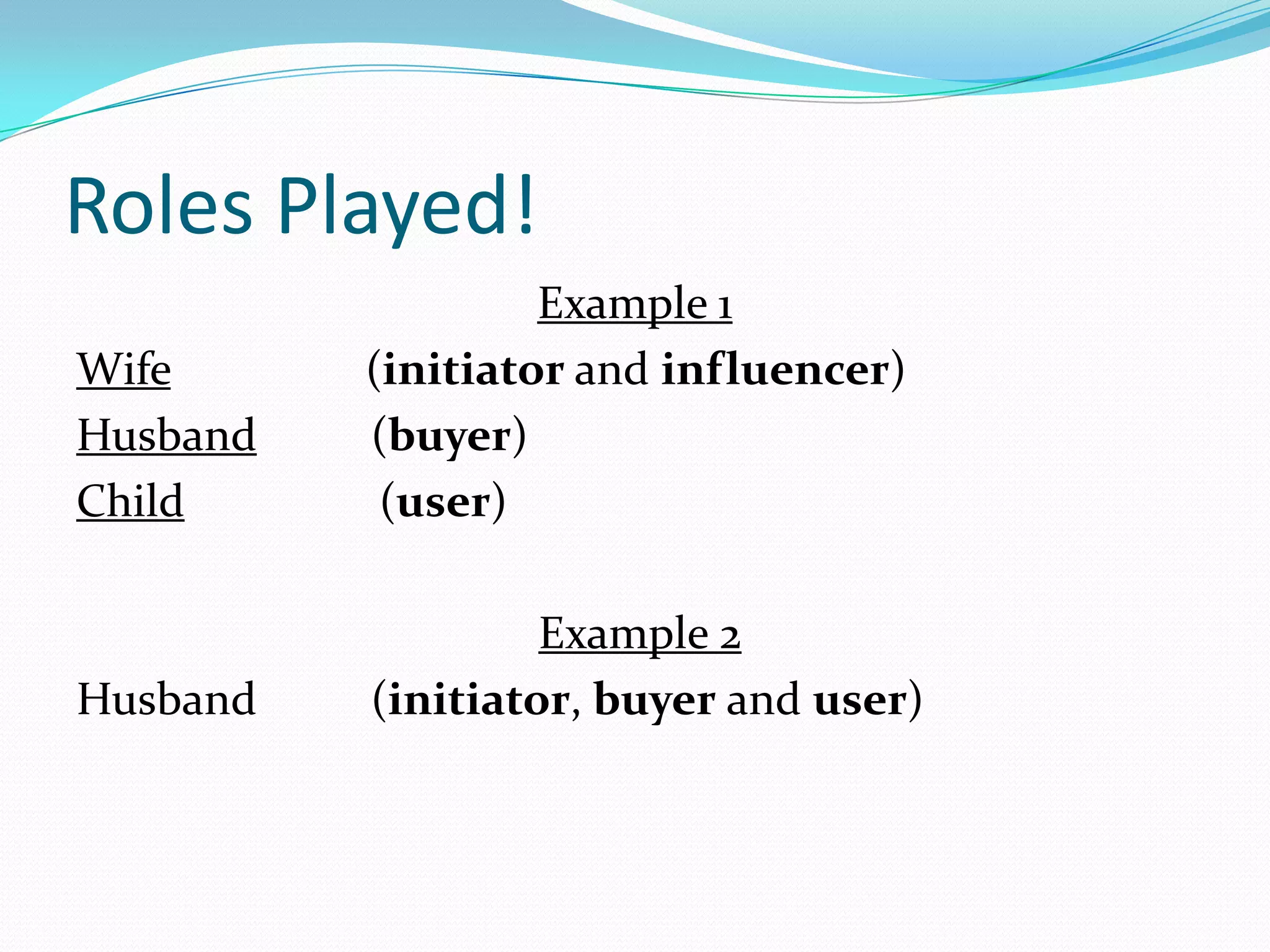
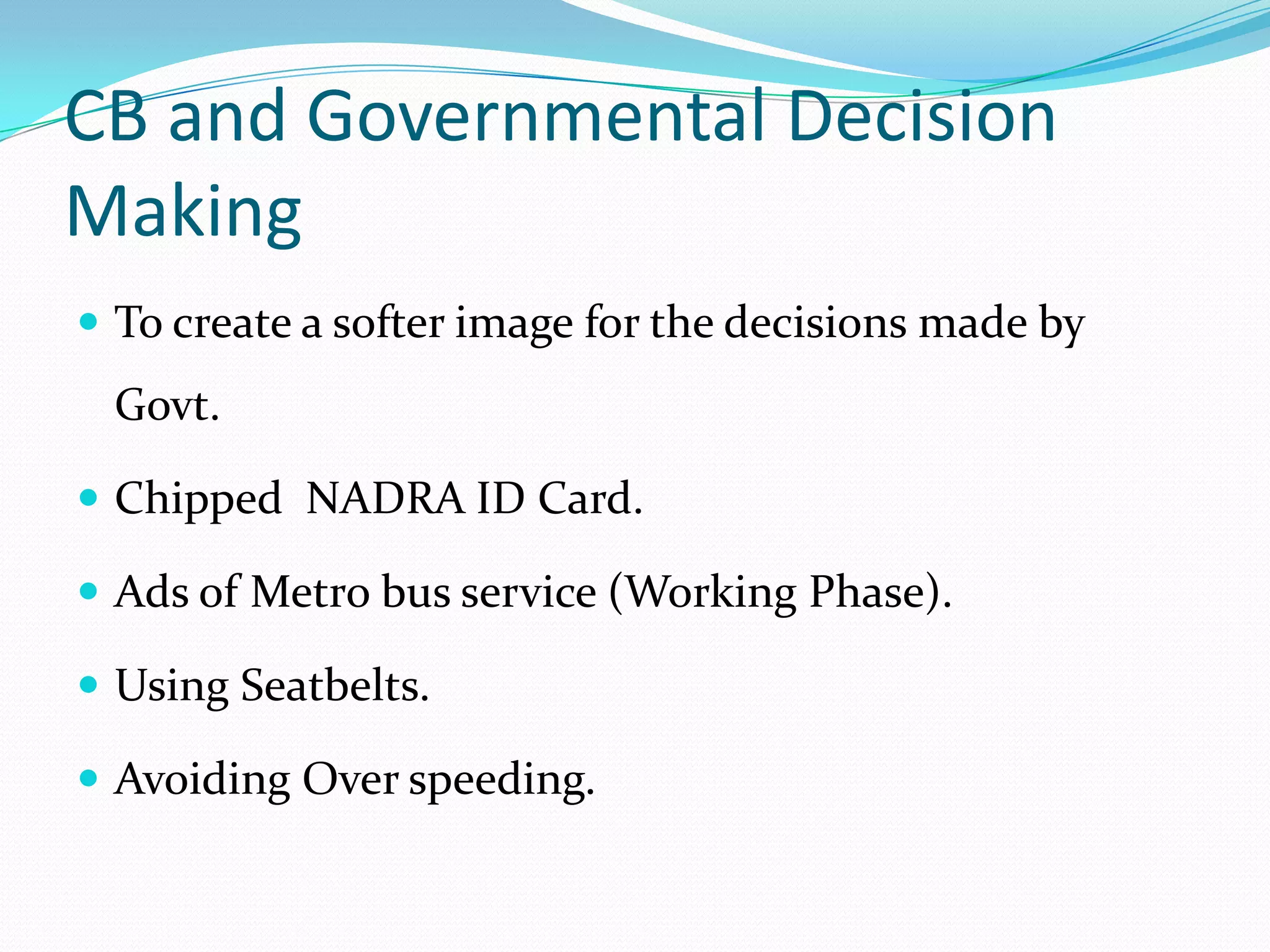
Consumer behavior involves the mental and physical activities individuals engage in when buying and using products and services. It is influenced by psychological, social, and economic factors. Understanding consumer behavior is important for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies. It helps businesses identify target markets, determine the marketing mix of product, price, place, and promotion, and create integrated strategies to satisfy consumer needs and achieve business objectives. Studying consumer behavior is also important for non-profit organizations, governments, and consumer education programs.