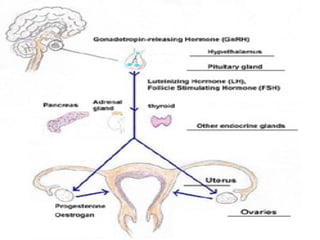
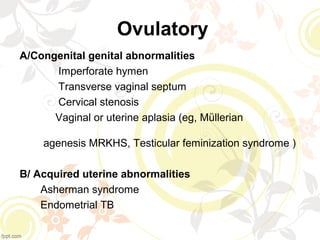
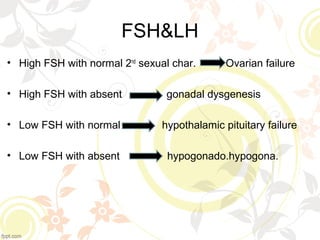
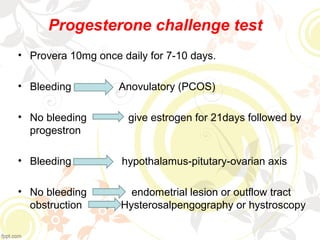
Primary amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation by age 16, while secondary amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation for three or more months. Amenorrhea can be caused by ovulatory issues like genetic abnormalities or acquired uterine issues, or by anovulatory issues involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, or excess androgen levels. Evaluating a patient for amenorrhea involves taking a medical history and performing an examination and lab tests to diagnose the underlying cause. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, minimizing long-term health effects, and inducing ovulation if desired for pregnancy.