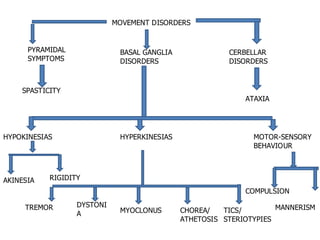
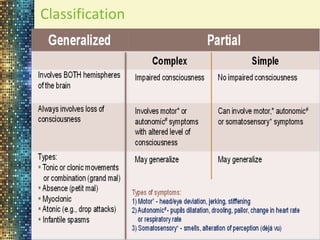
Movement disorders are diseases that affect control of bodily movements. They result from abnormalities in the extrapyramidal system or basal ganglia. This document categorizes and describes different types of involuntary movements including chorea, athetosis, dystonia, tremor, myoclonus, tics, ataxia, and stereotypies. It also discusses convulsions, epilepsy, febrile seizures, status epilepticus, and the approach to evaluating and managing a child presenting with abnormal movements or seizures.