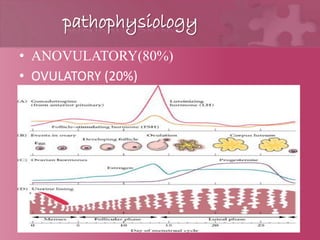
This document discusses dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB), which refers to abnormal uterine bleeding that has no identifiable structural or medical cause. It describes the various types of abnormal bleeding patterns seen in DUB, including menorrhagia, polymenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, metrorrhagia, and menometrrhagia. The causes of DUB are divided into structural (identified by PALM-COEIN classification) and non-structural categories. DUB is further characterized as anovulatory or ovulatory, depending on whether ovulation is occurring normally. Anovulatory DUB is more common and results from irregularities in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis leading to unopposed



![CLINICAL TYPES
1. Menorrhagia (hypermenorrhea): prolonged (>7
days) and/or excessive (>80ml) uterine bleeding
occurring at REGULAR intervals.
[Fibroids,hematological problems]
2. Polymenorrhea: shortened cycles- uterine
bleeding at regular intervals of <21
days.[Endometriosis, PID]
3. Oligomenorrhea: uterine bleeding at regular
intervals from 6weeks to 6 months.[hormonal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dysfunctionaluterinebleeding-130927074636-phpapp02/85/Dysfunctional-uterine-bleeding-4-320.jpg)
![CLINICAL TYPES….
4. Metorrhagia: acyclical and intermenstrual
uterine bleeding.[surface lesions-cervical
polyps,erosions,cervical ca]
5. Menometorrhagia: uterine bleeding that is
prolonged and occurs at completely irregular
intervals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dysfunctionaluterinebleeding-130927074636-phpapp02/85/Dysfunctional-uterine-bleeding-5-320.jpg)


![In adolescents and in perimenopausal women,
the bleeding may be triggered by estrogen
withdrawal
• Threshold bleeding-low estrogen and atropic
endometrium[lactation,menopause]
• Metropathia hemorrhagica-periods of
amenorrhoea followed by prolonged heavy
bleeding[hyperestrogenism]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dysfunctionaluterinebleeding-130927074636-phpapp02/85/Dysfunctional-uterine-bleeding-9-320.jpg)
![Ovulatory DUB:
• Presents as menorrhagia
• A less common cause of DUB
• caused by a defect in local endometrial
hemostasis
• Absence of progesterone Alterations in
prostaglandin production, with more PGE2 PGI2
[vasodilation and antiplatelet] and less
PGF2[vasoconstriction] , increased
fibrinolytic activity bleeding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dysfunctionaluterinebleeding-130927074636-phpapp02/85/Dysfunctional-uterine-bleeding-10-320.jpg)




