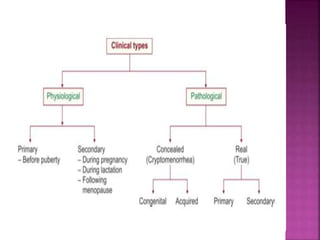
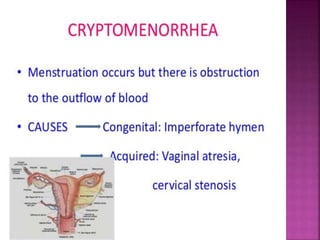
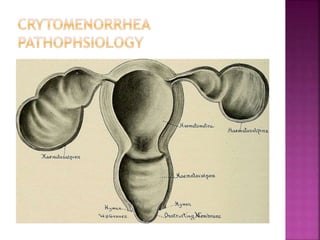
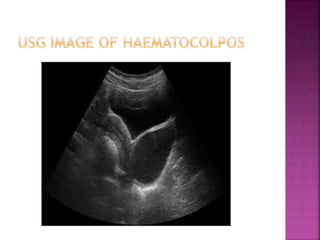
1. Amenorrhea is defined as the absence of menstruation and can be classified as physiological, pathological, primary, or secondary.
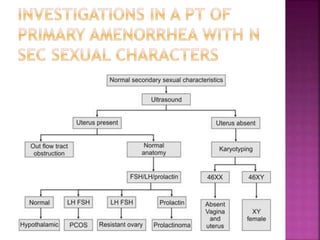
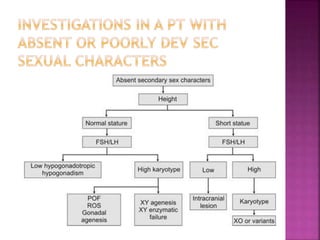
2. Causes of amenorrhea include developmental defects of the genital tract, abnormalities of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, chromosomal abnormalities, and diseases of the thyroid or adrenal glands.
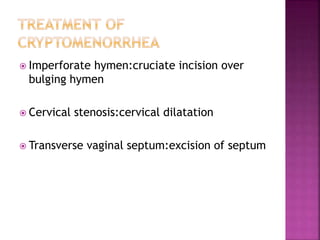
3. Treatment depends on the underlying cause, and may include vaginoplasty or gonadectomy for developmental anomalies, hormone replacement therapy for chromosomal or hormonal issues, and treatment of underlying diseases in metabolic or systemic illness cases.