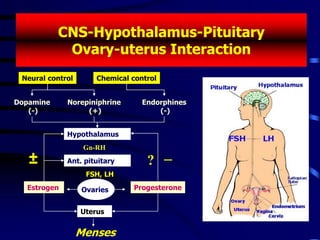
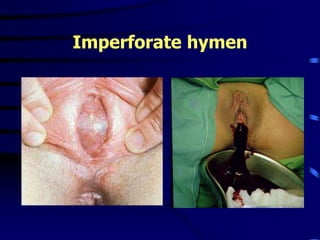
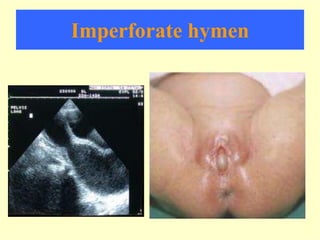
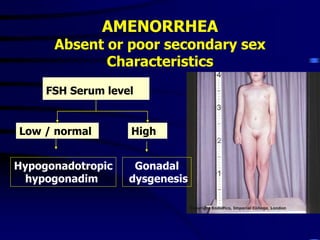
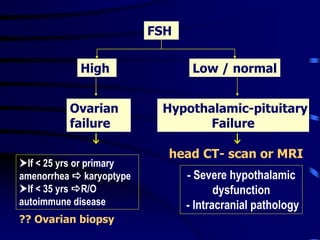
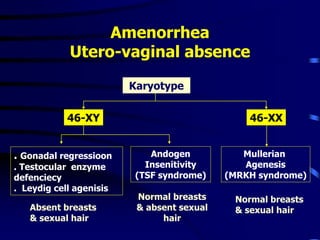
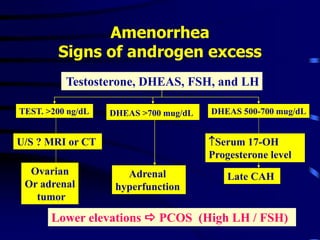
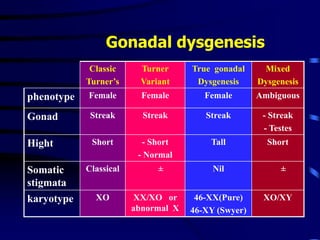
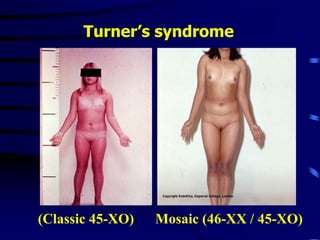
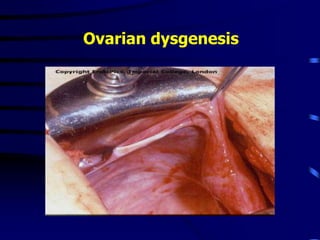
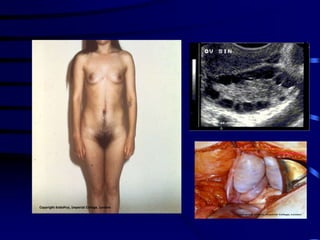
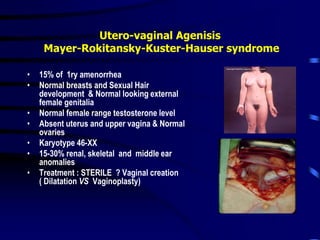
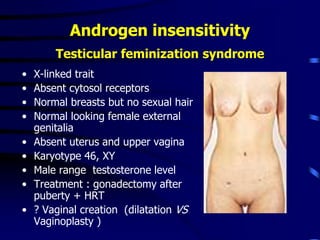
This document discusses amenorrhea, including definitions, pathophysiology, diagnostic approach, and management. Primary amenorrhea is defined as the absence of menarche by age 16 with pubertal development or by age 14 without pubertal development. Secondary amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation for 3 or more months in a previously menstruating woman. The diagnostic approach involves obtaining a thorough history, physical exam, and ultrasound to rule out pregnancy and cryptomenorrhea before classifying the patient based on endocrine abnormalities. Management aims to restore ovulatory cycles if possible or replace estrogen when deficient, with periodic progestogen to protect the endometrium.