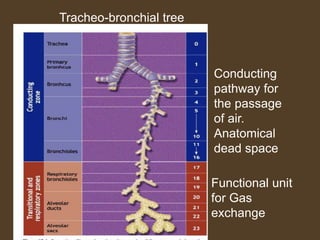
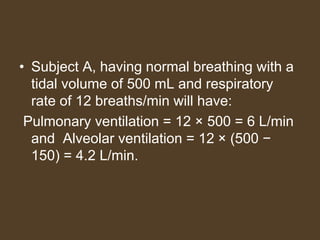
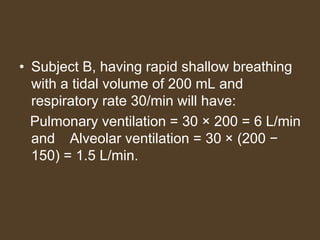
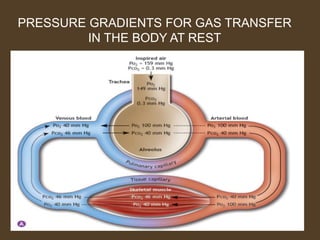
1) Alveolar ventilation refers to the volume of fresh air that reaches the gas exchange areas of the lungs per minute. It is calculated as respiratory rate multiplied by tidal volume minus dead space volume.
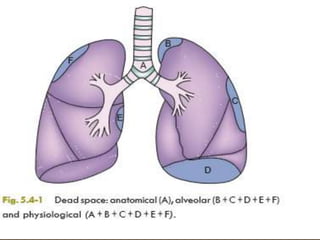
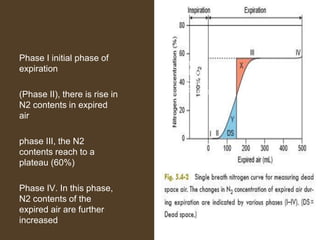
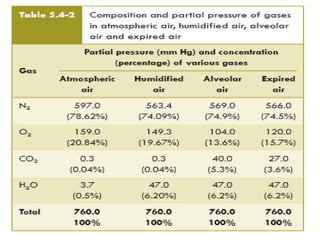
2) Dead space includes anatomical dead space in the conducting airways and alveolar dead space from non-functioning alveoli. Physiological dead space is the total dead space measured using Bohr's equation.
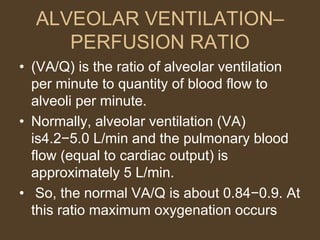
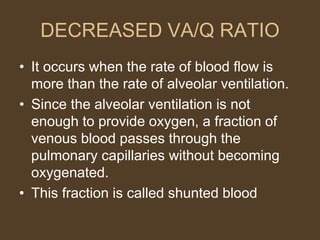
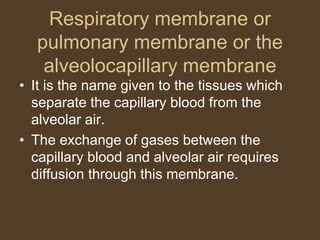
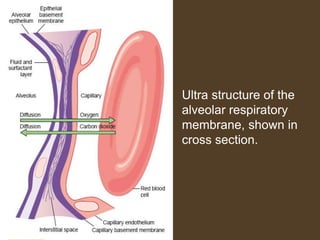
3) Uneven ventilation and perfusion can cause alterations in the alveolar ventilation to perfusion (VA/Q) ratio, leading to inefficient gas exchange and hypoxemia. Conditions like asthma and pulmonary embolism can cause these imbalances.