This document discusses pulmonary and alveolar ventilation, dead space, and ventilation-perfusion ratio.
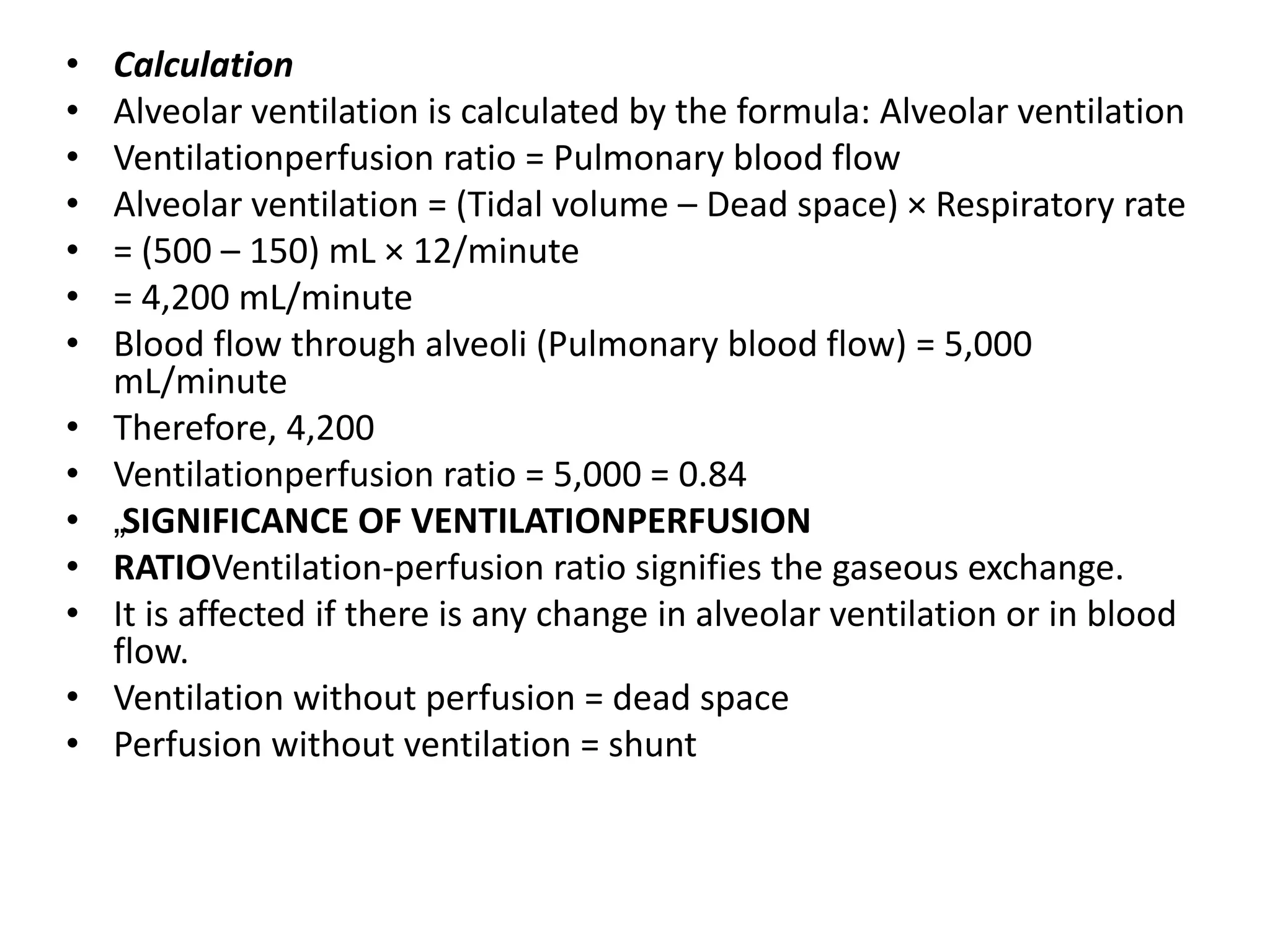
It defines pulmonary ventilation as the volume of air moving in and out of the respiratory tract per minute during normal breathing, which is normally 6 L/minute. Alveolar ventilation is the amount of air used for gas exchange, normally 4.2 L/minute, which accounts for tidal volume minus dead space.
Dead space refers to the part of the respiratory tract where gas exchange does not occur, which is normally 150mL. The ventilation-perfusion ratio signifies gas exchange efficiency, with a normal value of 0.84.