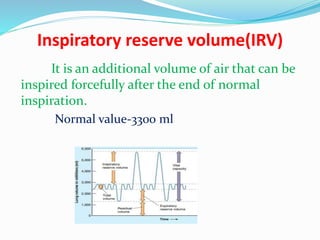
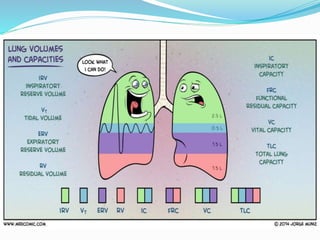
This document discusses lung volumes and capacities. It defines four lung volumes: tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. It also defines four lung capacities that are combinations of the volumes: inspiratory capacity, vital capacity, functional residual capacity, and total lung capacity. It provides the normal values for each volume and capacity. Lung function tests measure these volumes and capacities to evaluate lung health and detect respiratory diseases. Spirometry uses a device called a spirometer to measure the volumes expired and inspired.