Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times

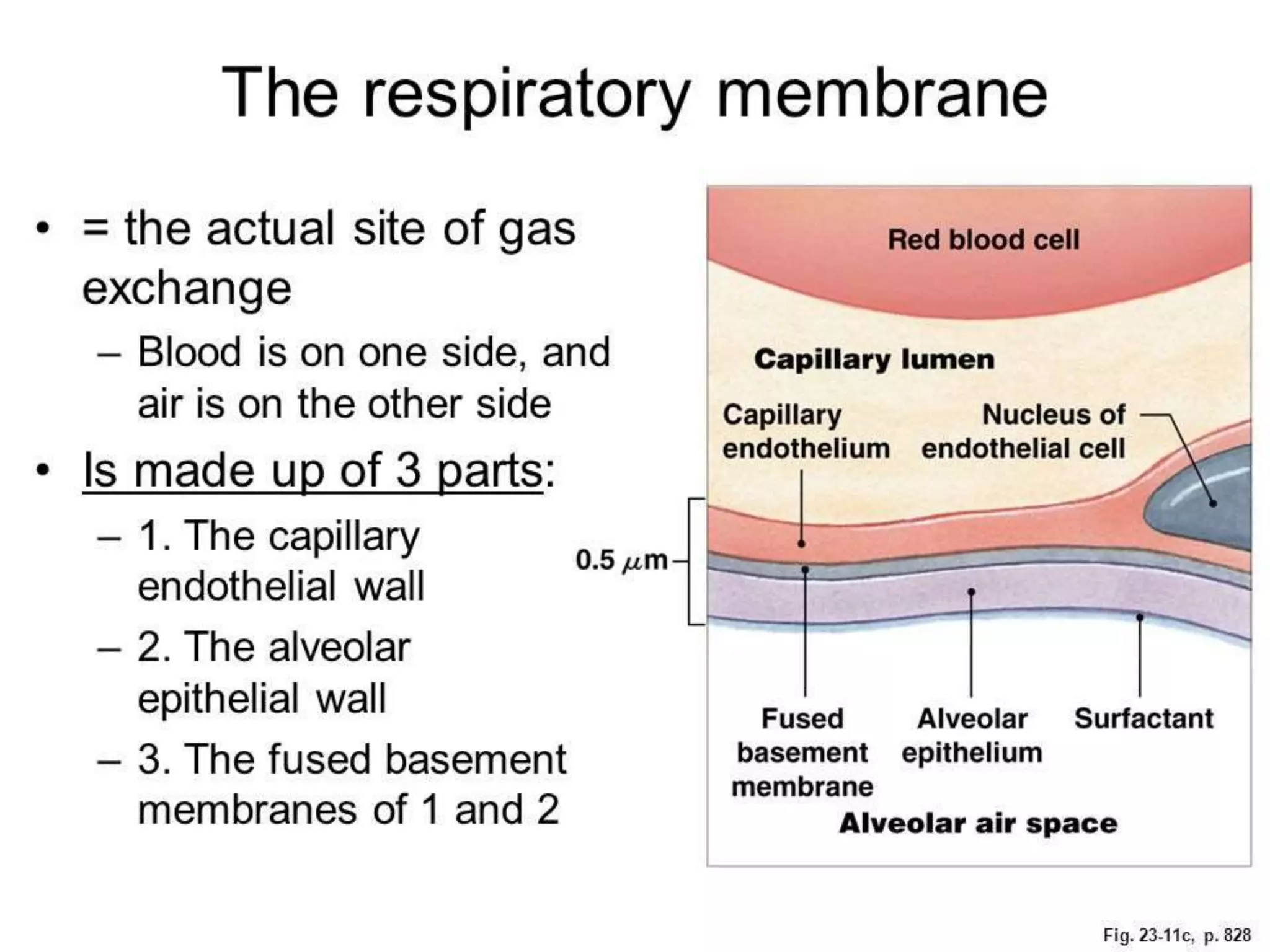








The document discusses gas exchange through the respiratory membrane. It describes how oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream in the alveoli and capillaries while carbon dioxide diffuses out. This process is facilitated by the thin alveolar membranes and large surface area of the lungs, allowing gases to rapidly move across based on partial pressure differences. Several factors like membrane thickness, surface area, gas diffusion coefficient, and partial pressure gradients determine the rate of gas diffusion through the respiratory membrane.













Discusses the function of the respiratory system, emphasizing gas exchange and the role of the respiratory membrane.
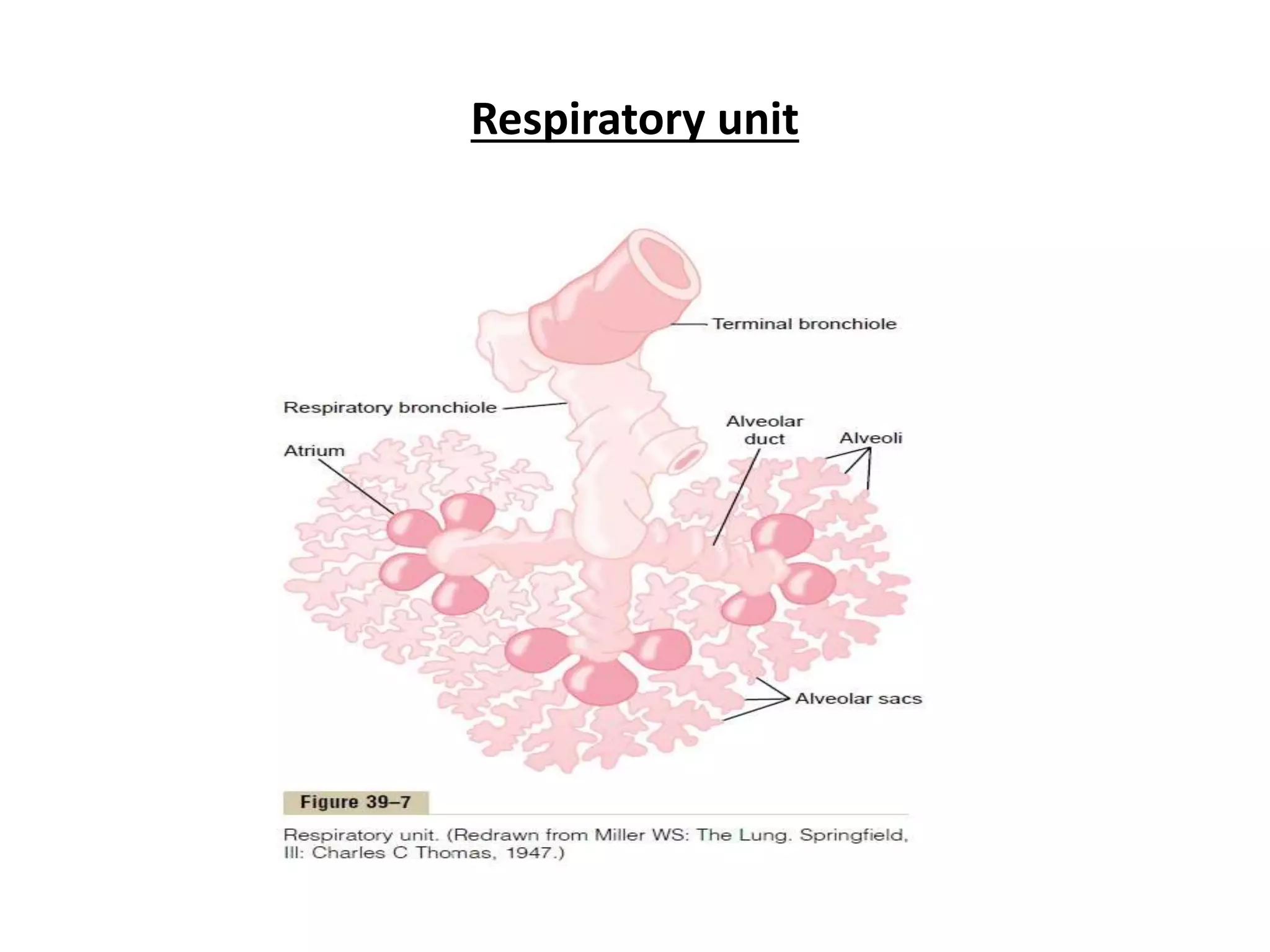
Describes the composition and structure of the respiratory unit including alveoli and capillaries.
Explains oxygen diffusion into the blood, the role of partial pressures, and the effectiveness during exercise.
Details carbon dioxide diffusion from blood to alveoli, pressure differences, and transport mechanisms.
Identifies factors affecting gas diffusion rate through the respiratory membrane including thickness and surface area.
Introduces clinical relevance by mentioning emphysema and its relation to gas exchange.