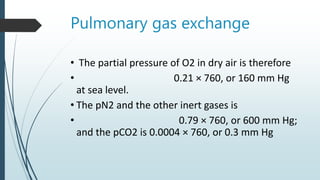
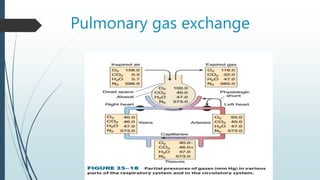
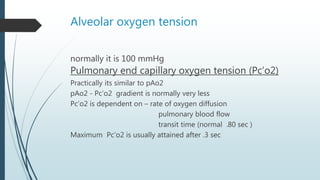
Pulmonary gas exchange involves the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli in the lungs and blood in the pulmonary capillaries. The partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide drive this diffusion according to Henry's Law. Oxygen diffuses into the blood down its partial pressure gradient from the alveoli to the pulmonary capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction from blood to alveoli. The partial pressures, rates of diffusion, and blood flow influence the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the arterial blood leaving the lungs.