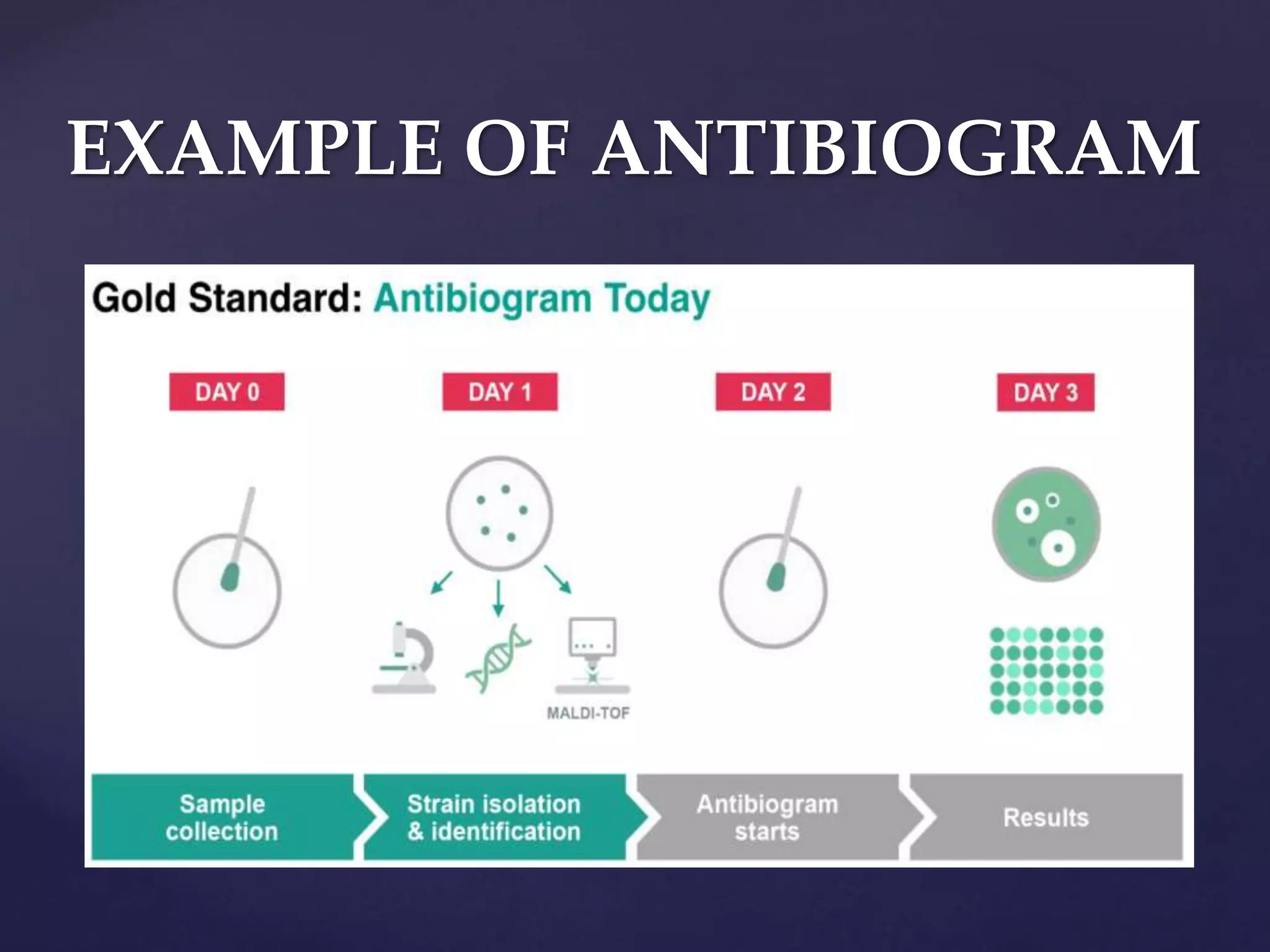
An antibiogram is a summary of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results for a specific microorganism against a range of antimicrobial drugs. It provides the percentages of organisms tested that were susceptible to each drug. Antibiograms help clinicians select appropriate empirical antimicrobial treatment and allow healthcare facilities to monitor antimicrobial resistance trends over time. They have limitations as they do not show subtle resistance trends below thresholds or account for synergistic drug combinations.