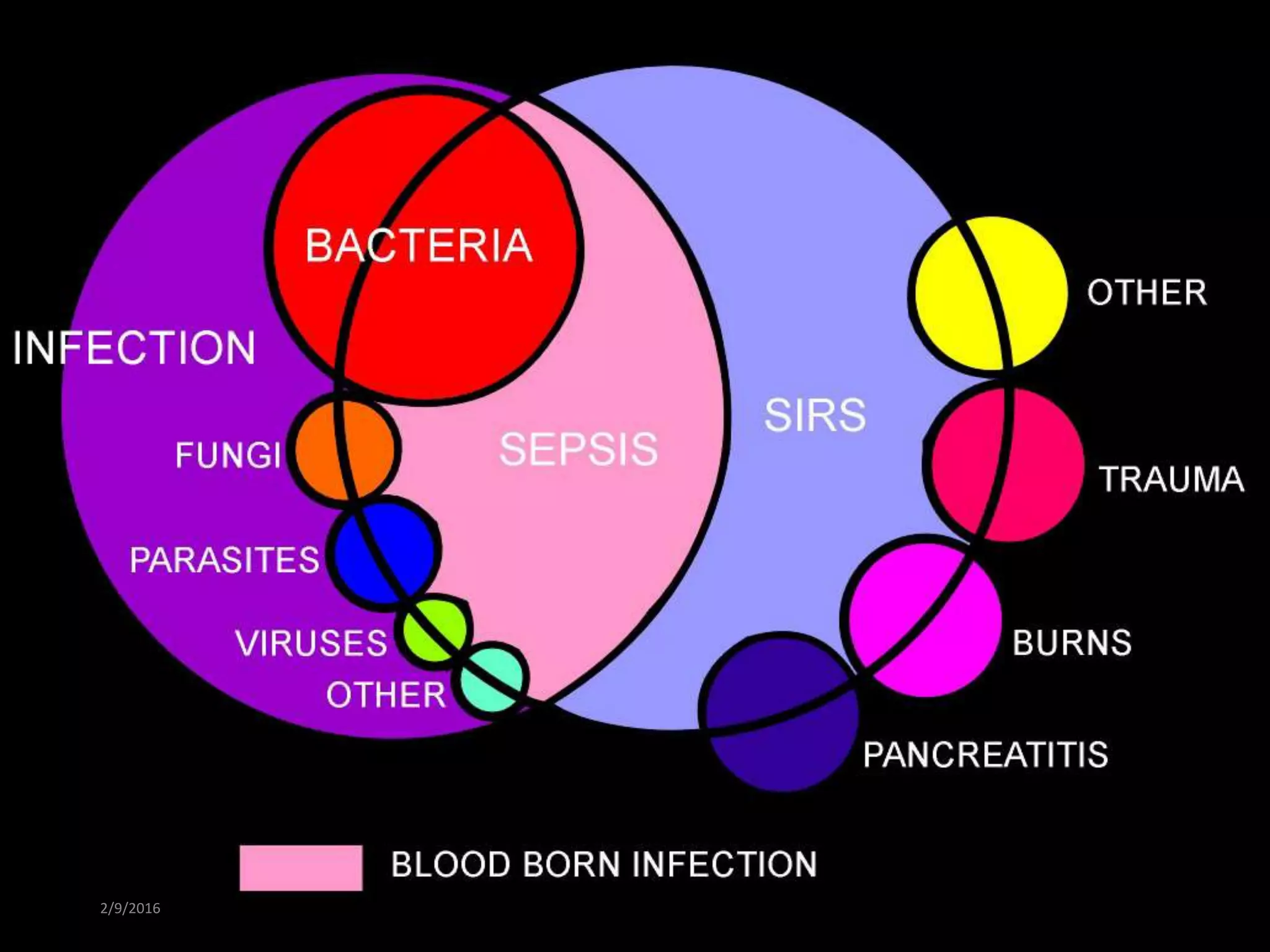
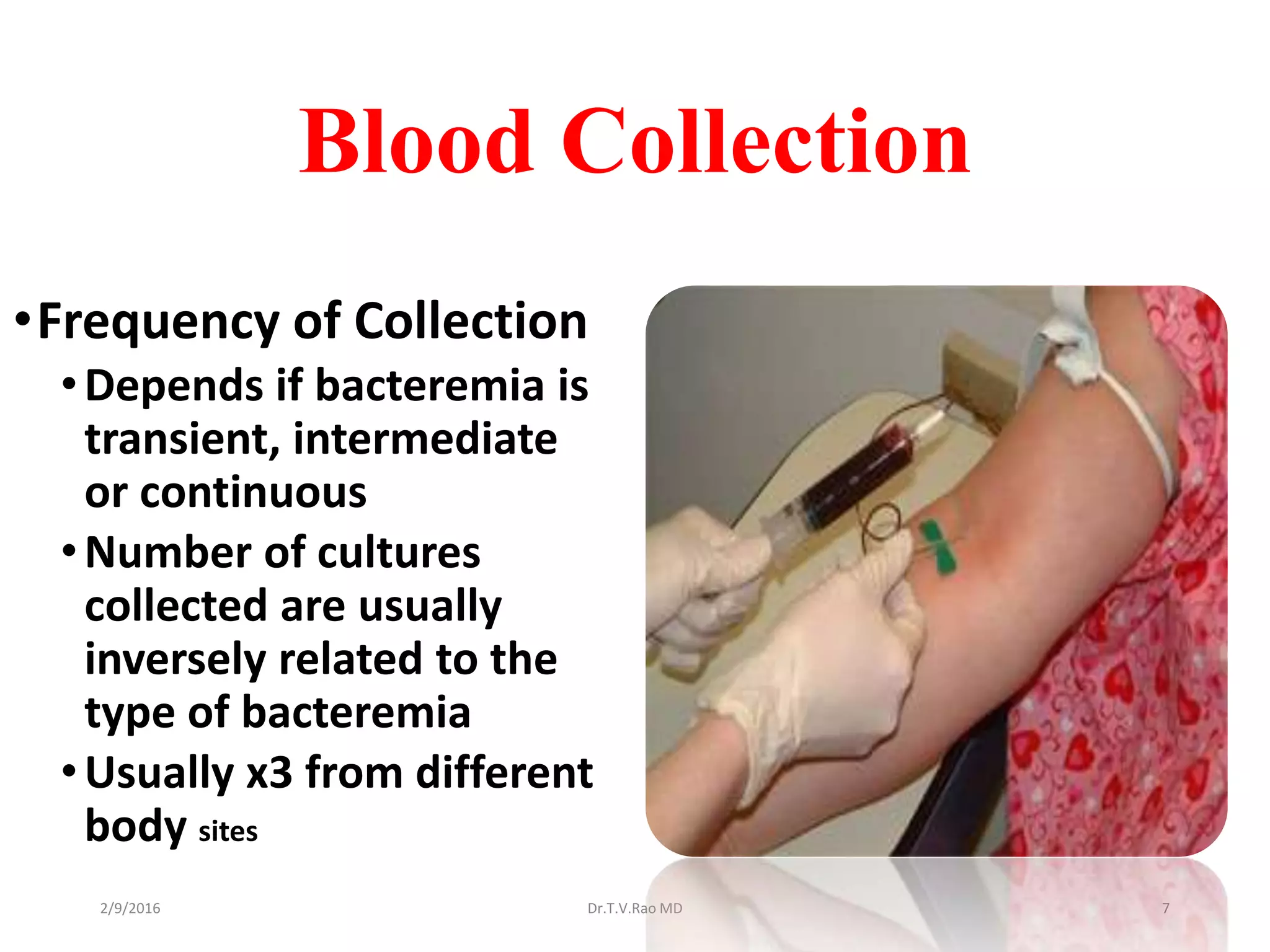
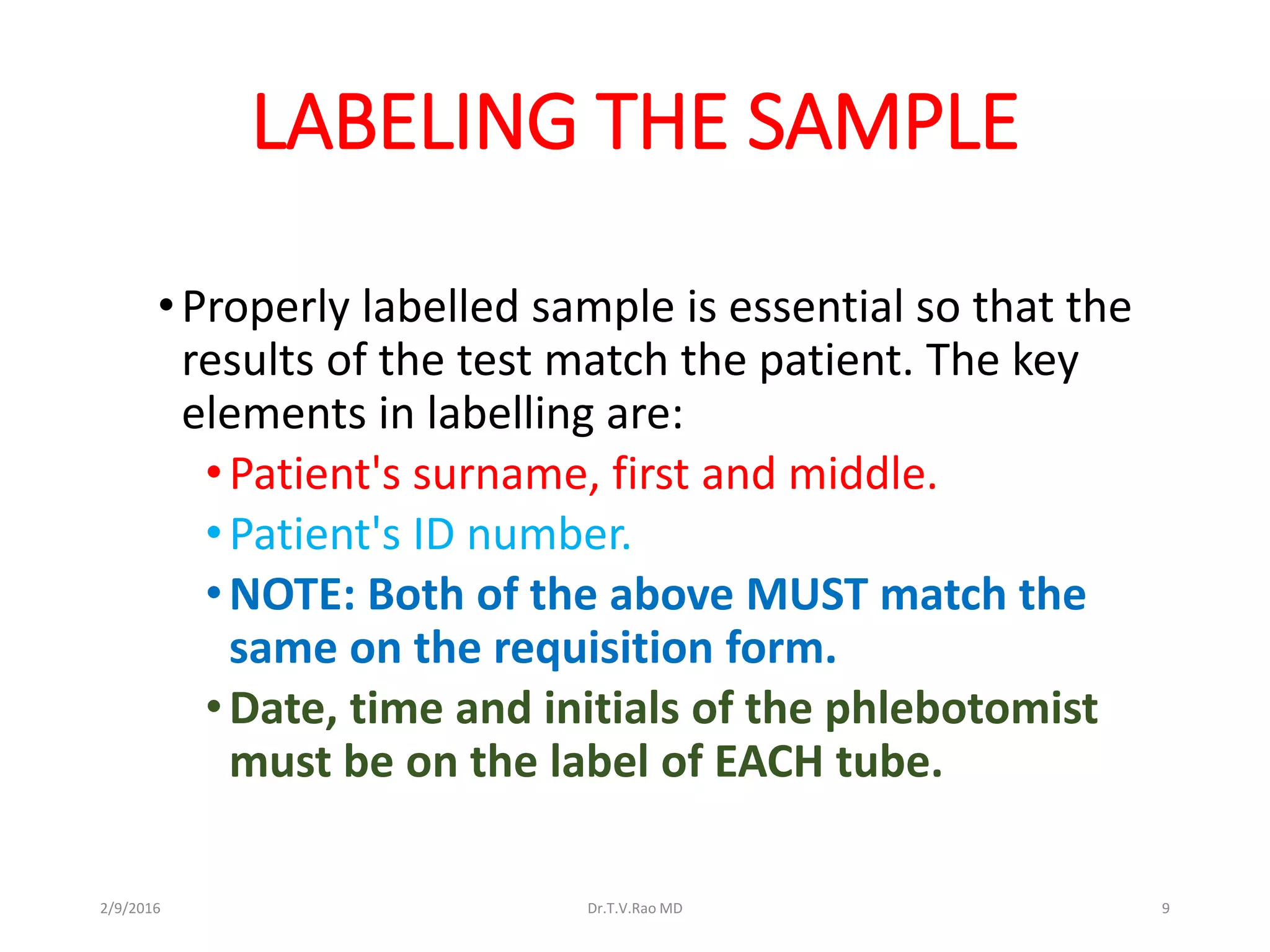
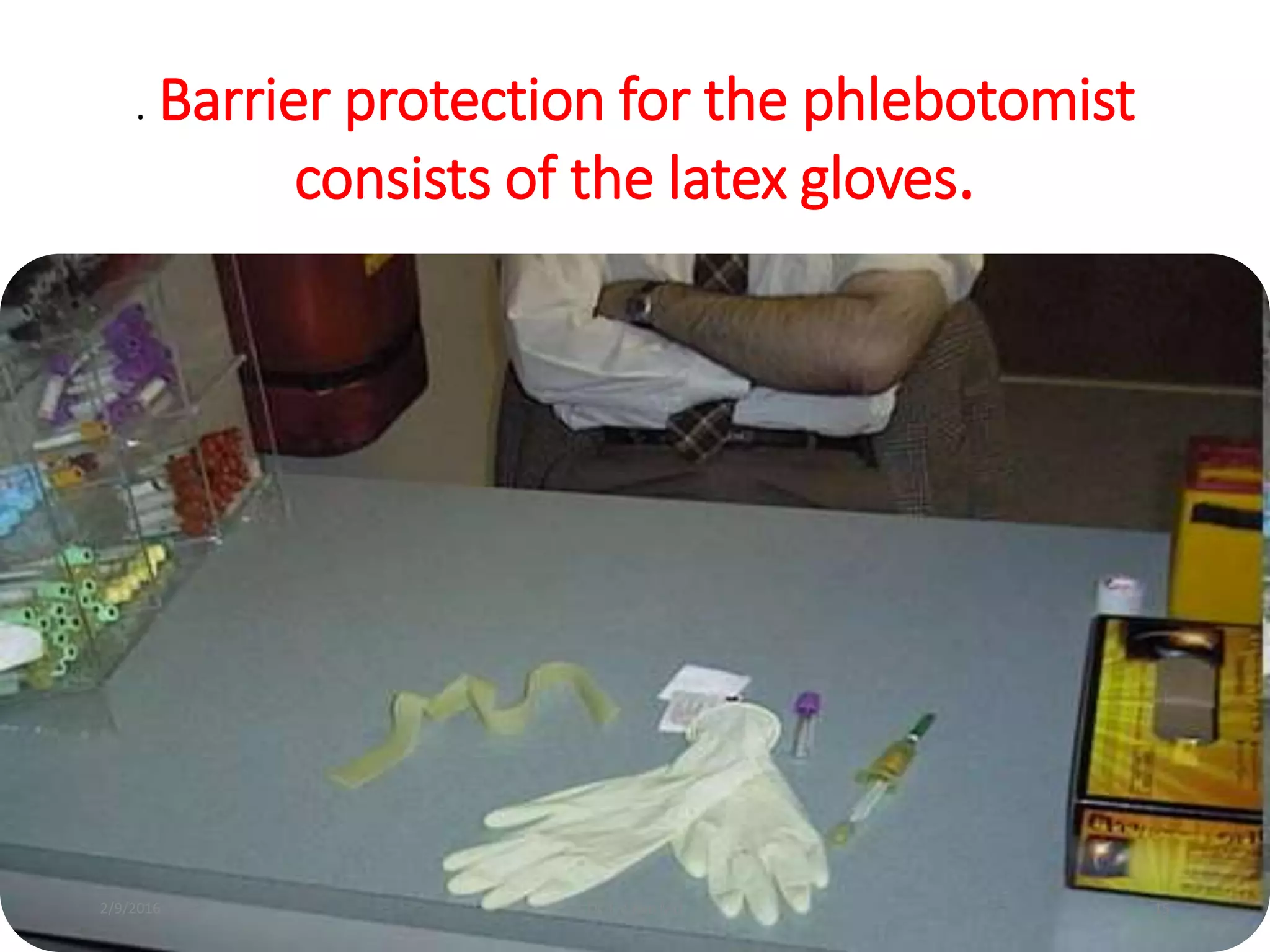
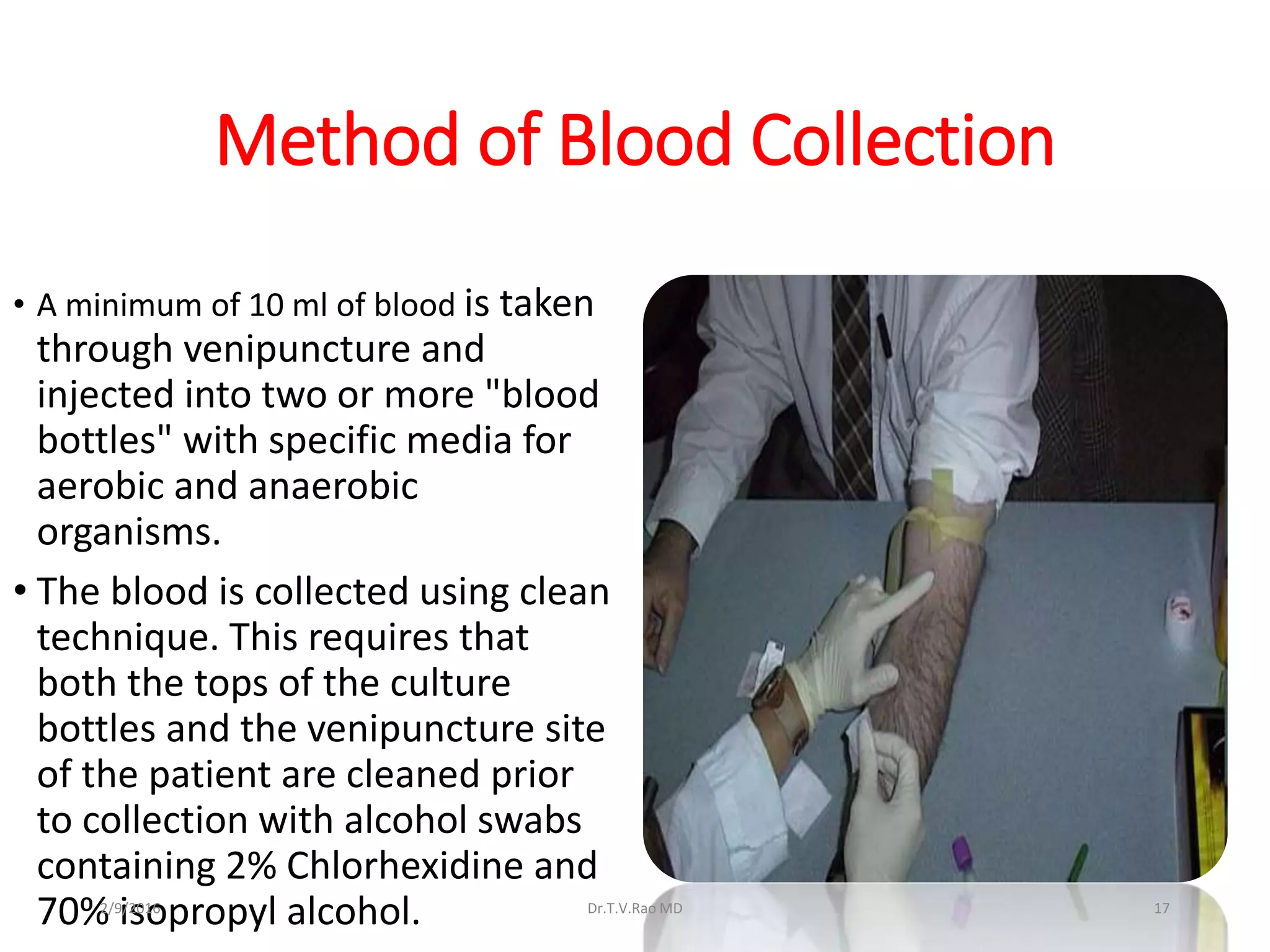
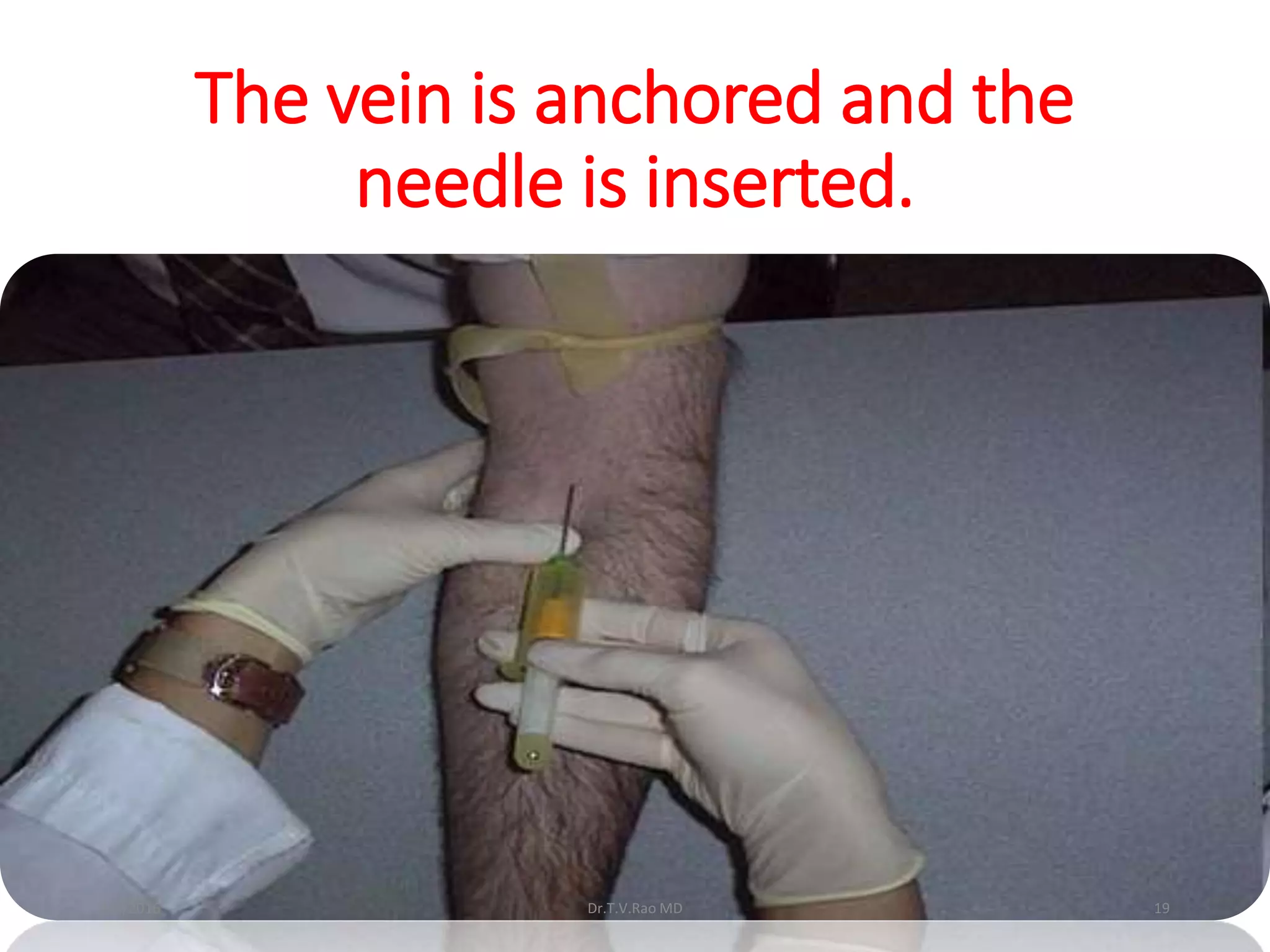
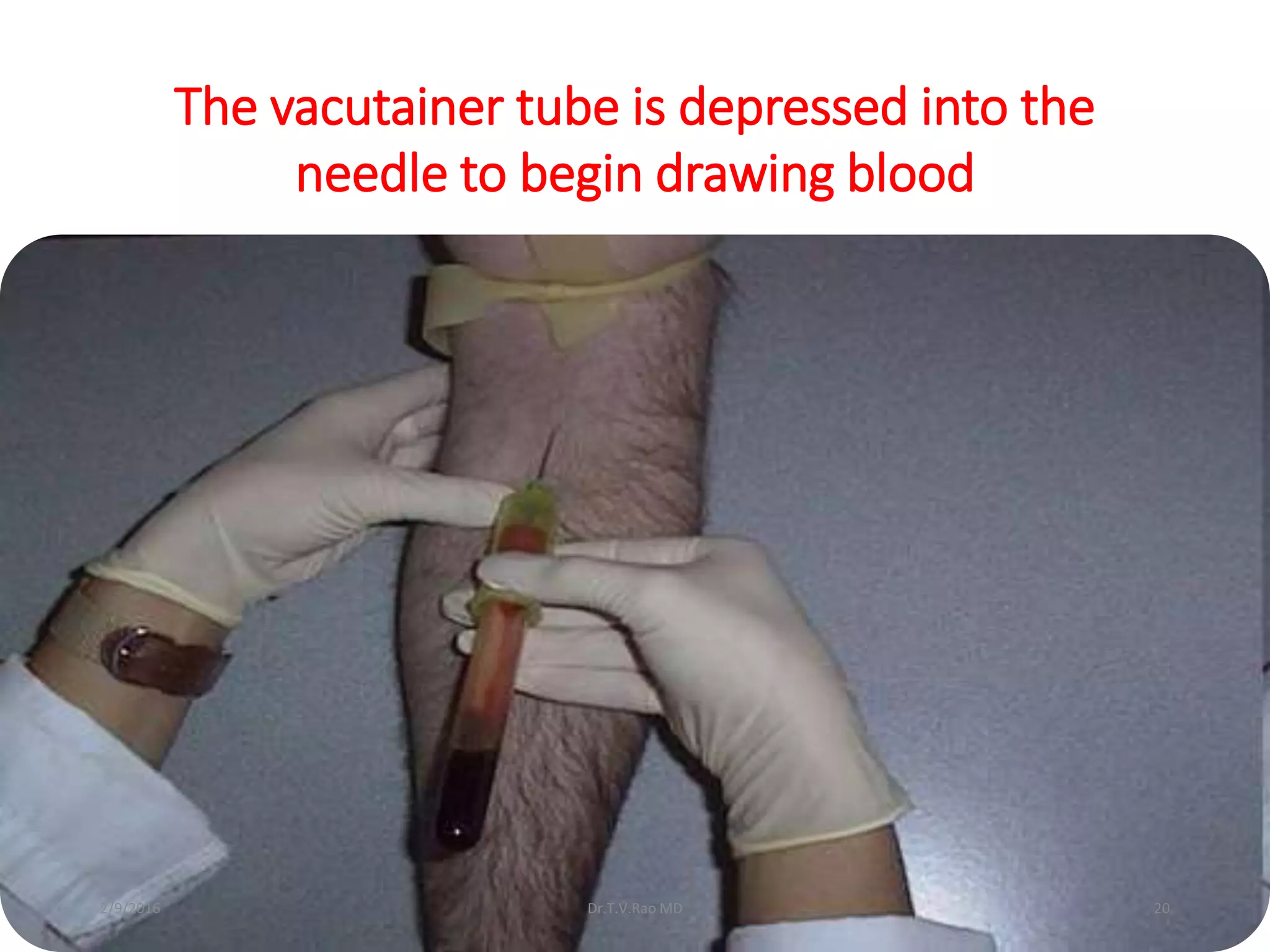
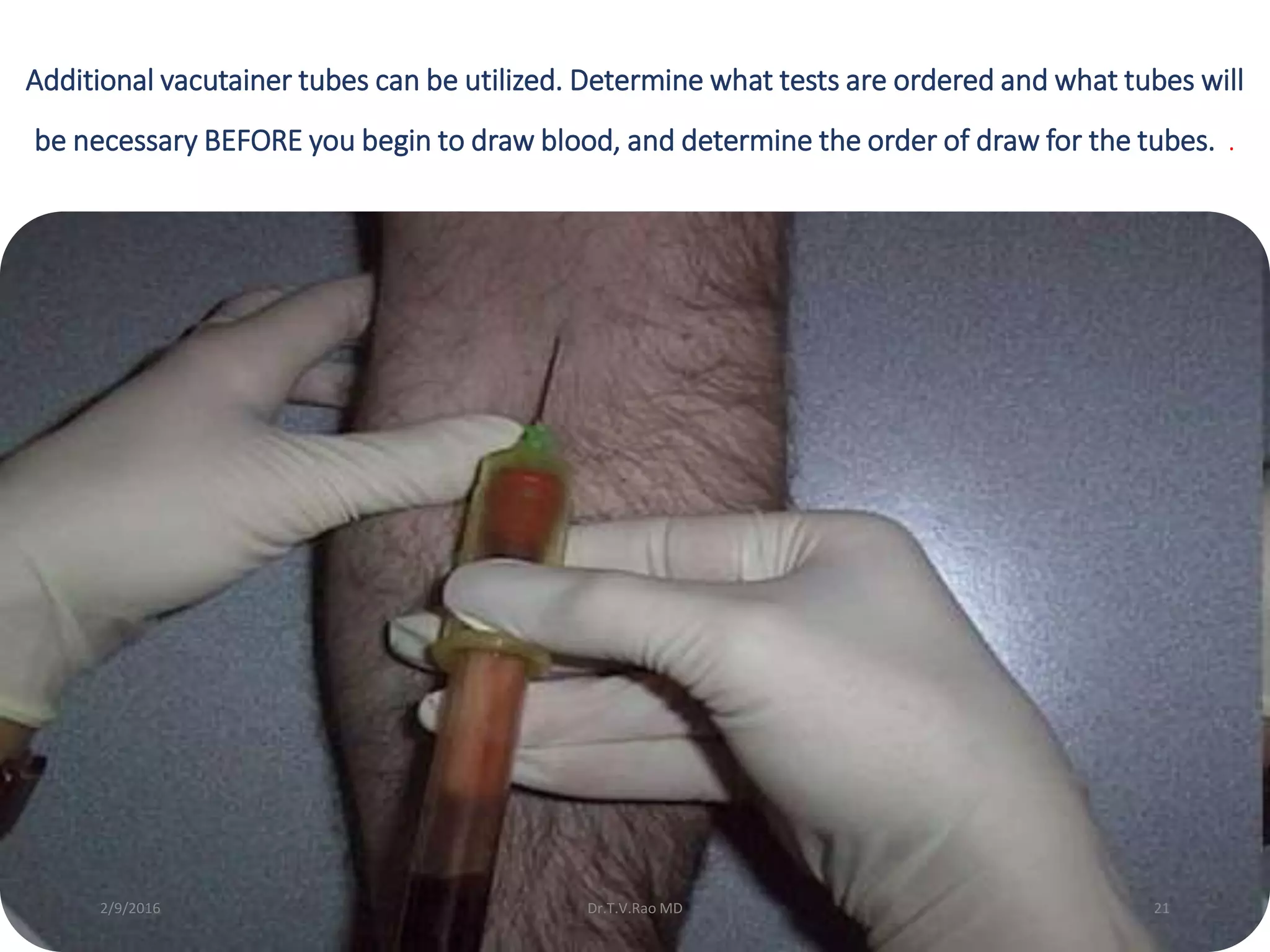
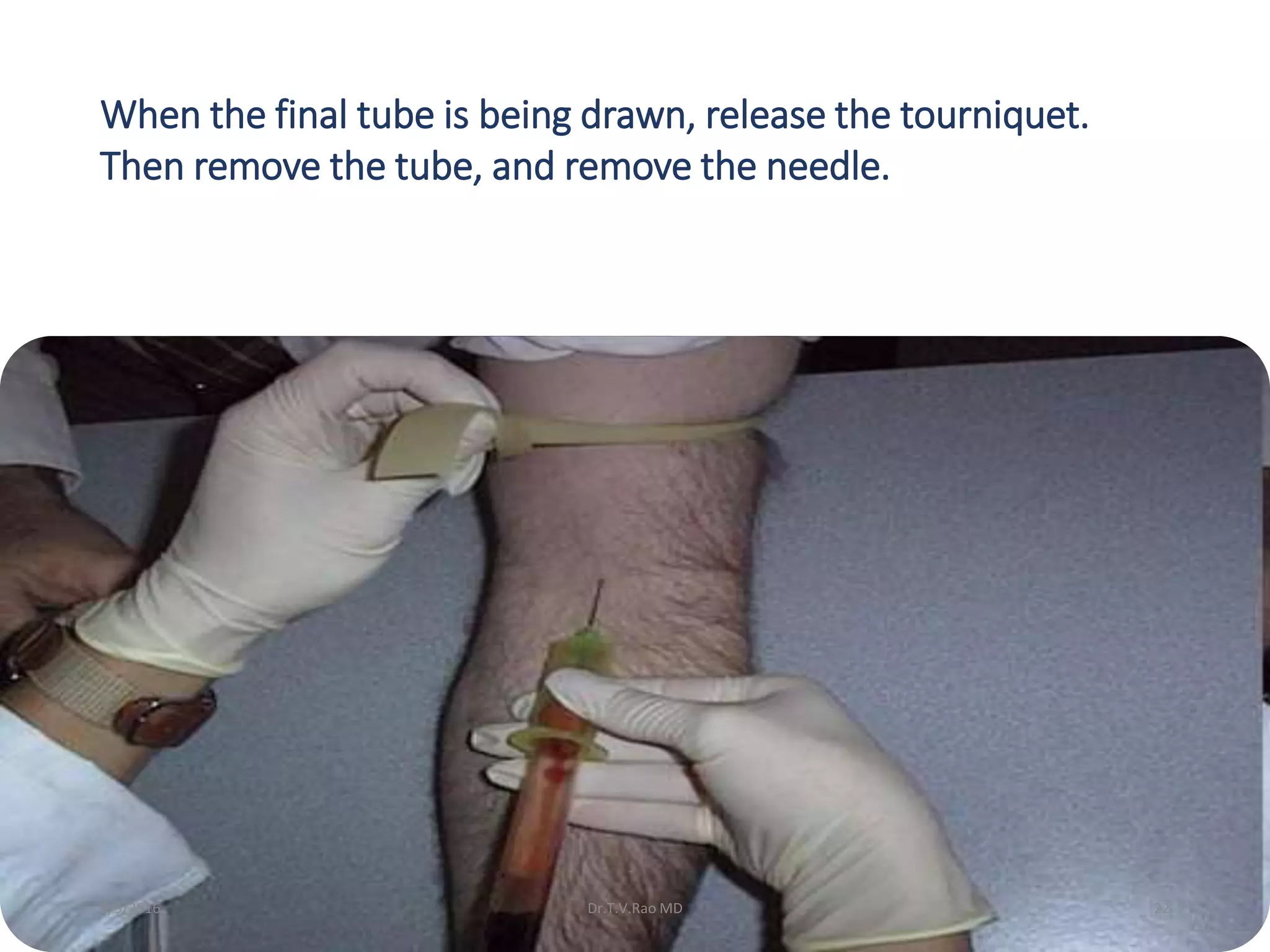
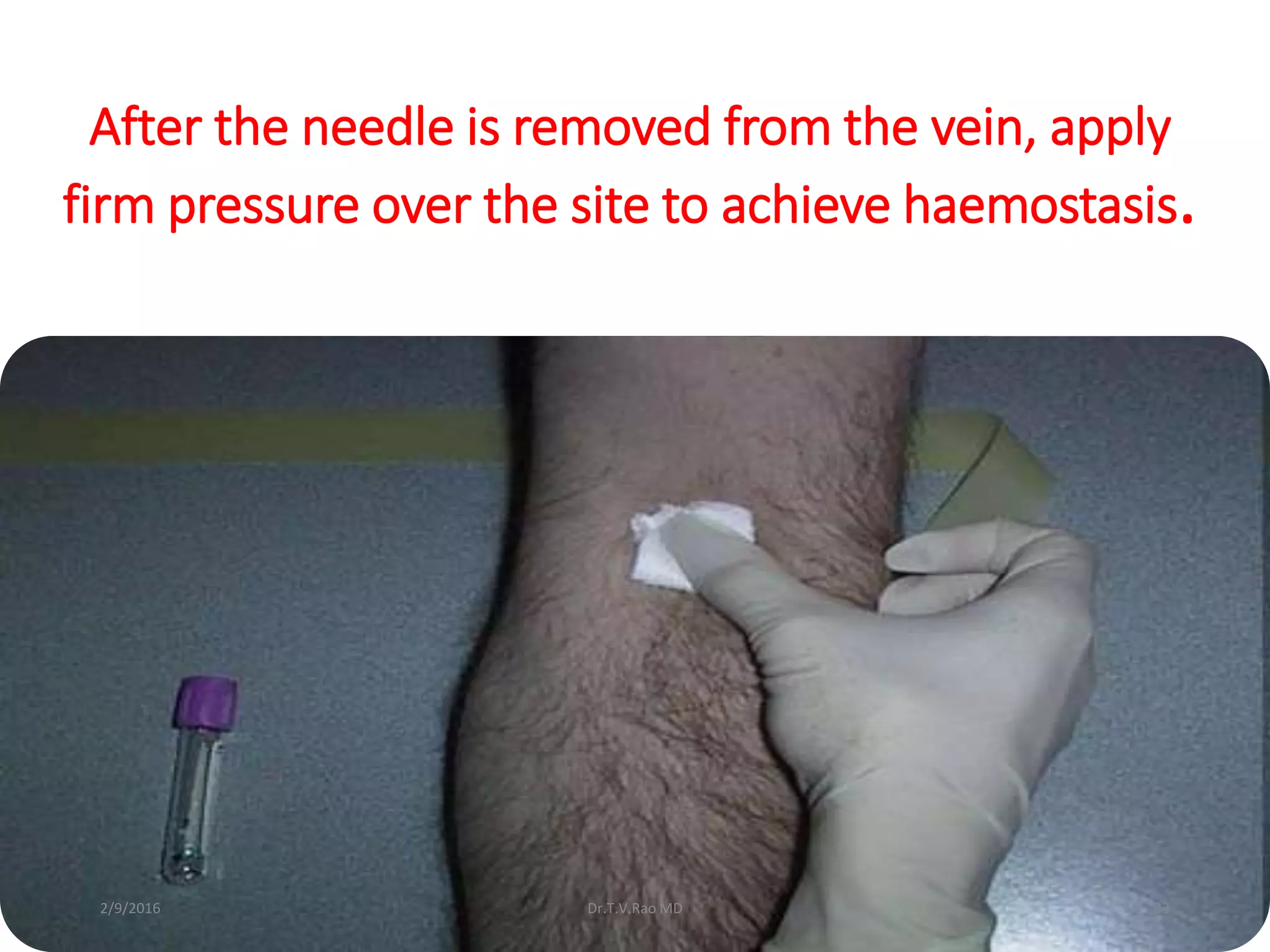
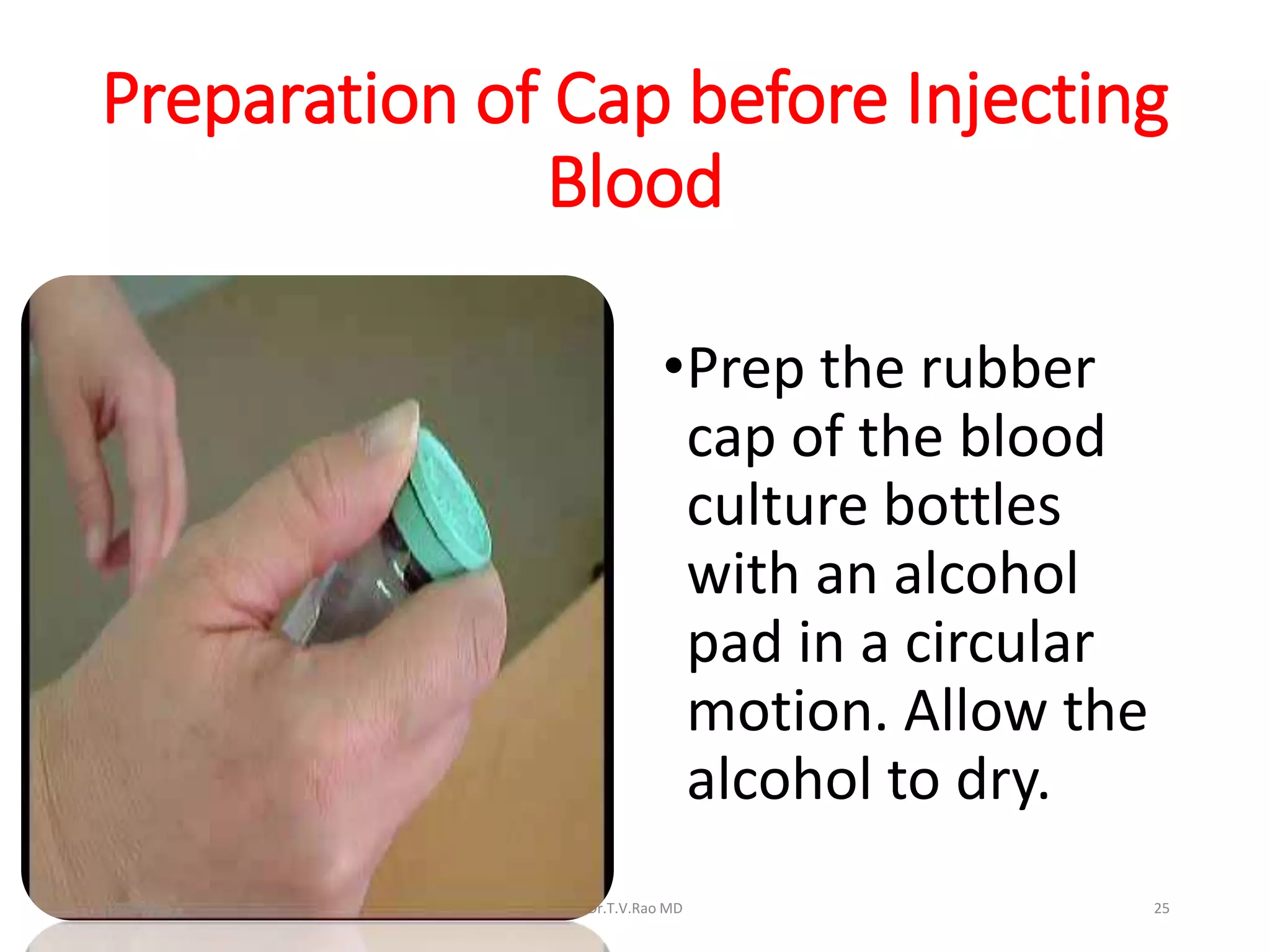
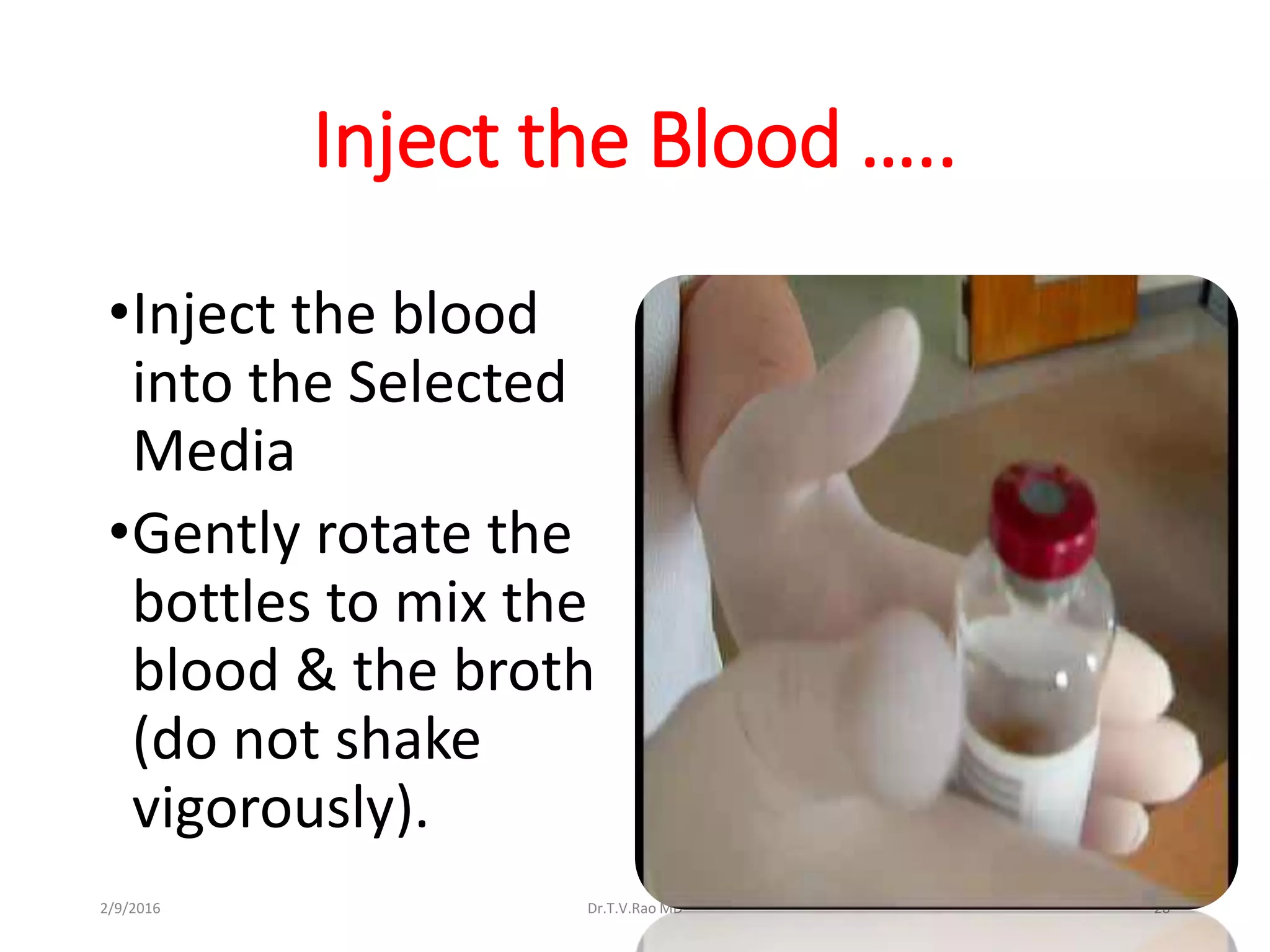
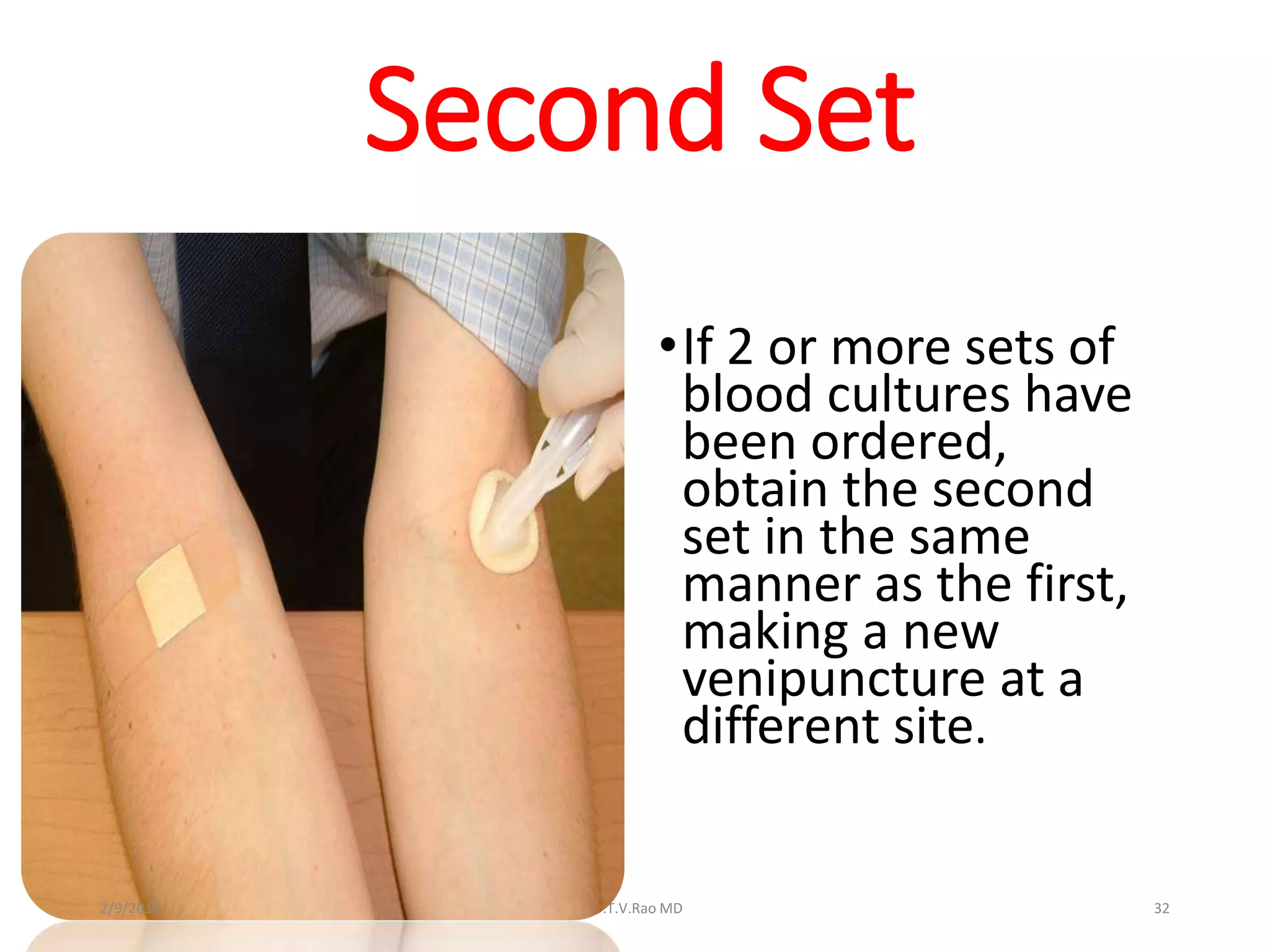
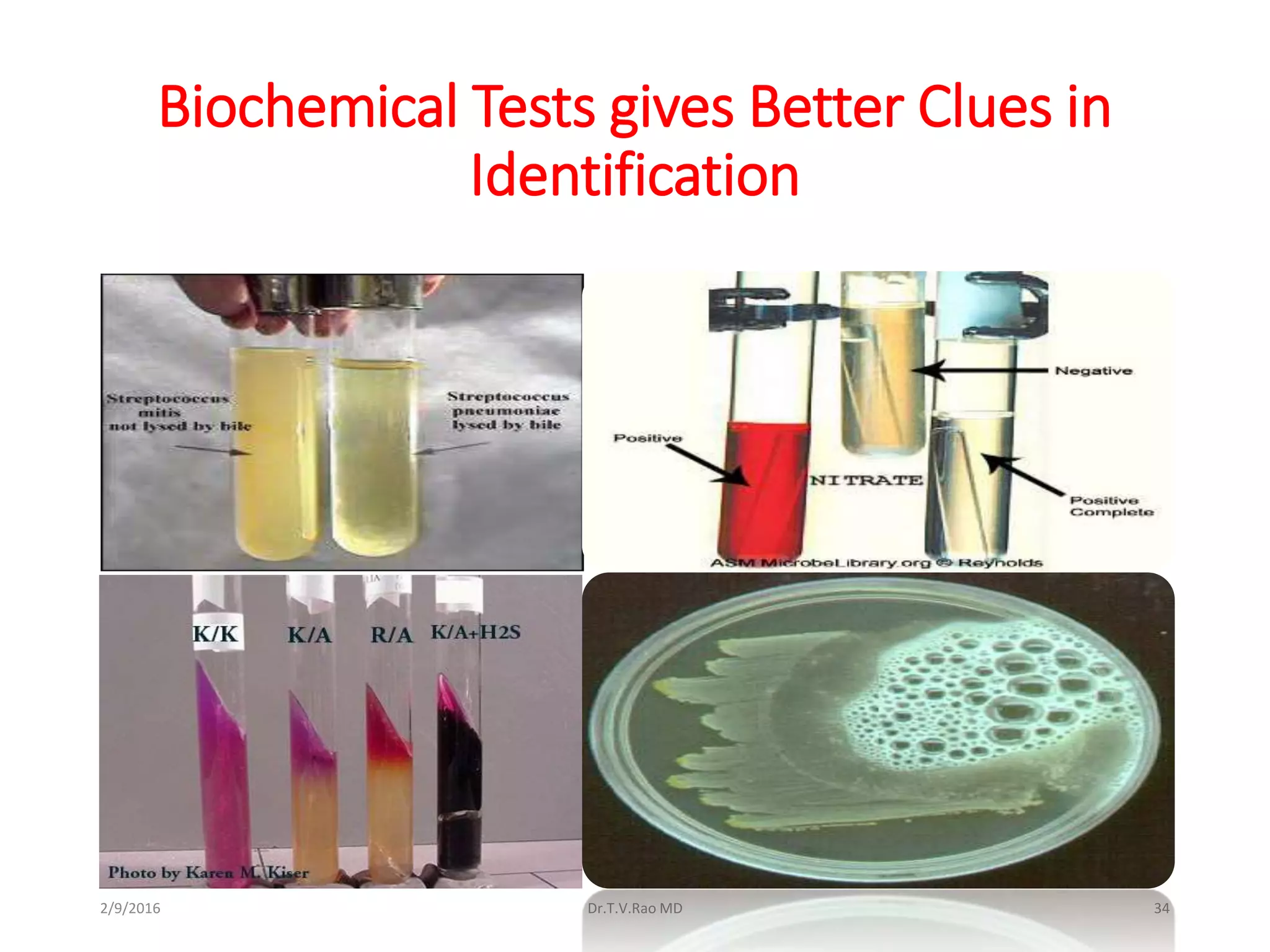
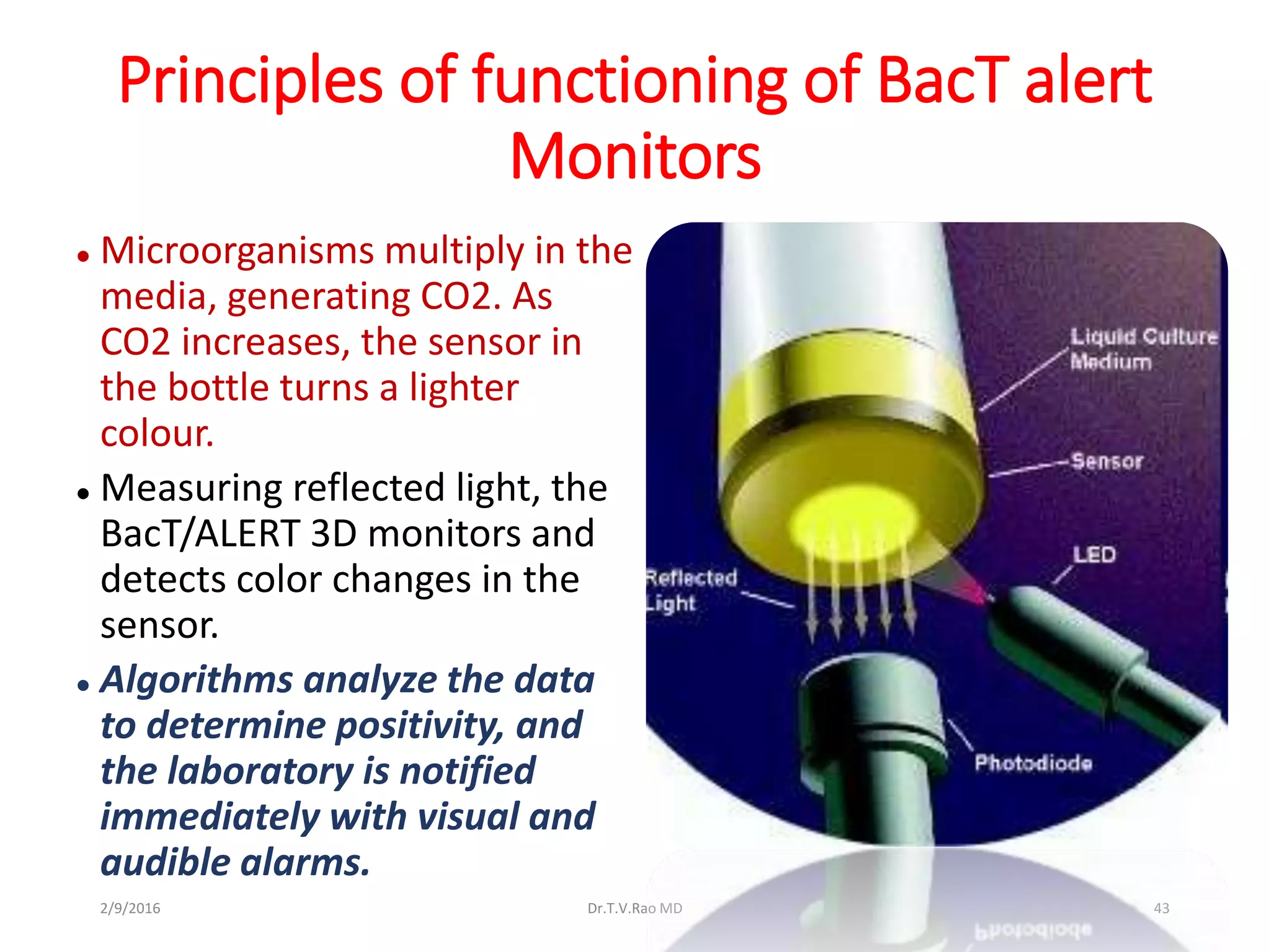
Blood culturing is the most important test for detecting pathogens in the bloodstream. It involves collecting blood in specialized bottles that contain growth media for aerobic and anaerobic organisms. It is critical that the collection procedure is done aseptically. Newer automated systems can continuously monitor blood cultures and detect microbial growth within 24-48 hours, providing faster results than conventional methods. Rapid identification of pathogens in positive blood cultures is important for guiding appropriate treatment.