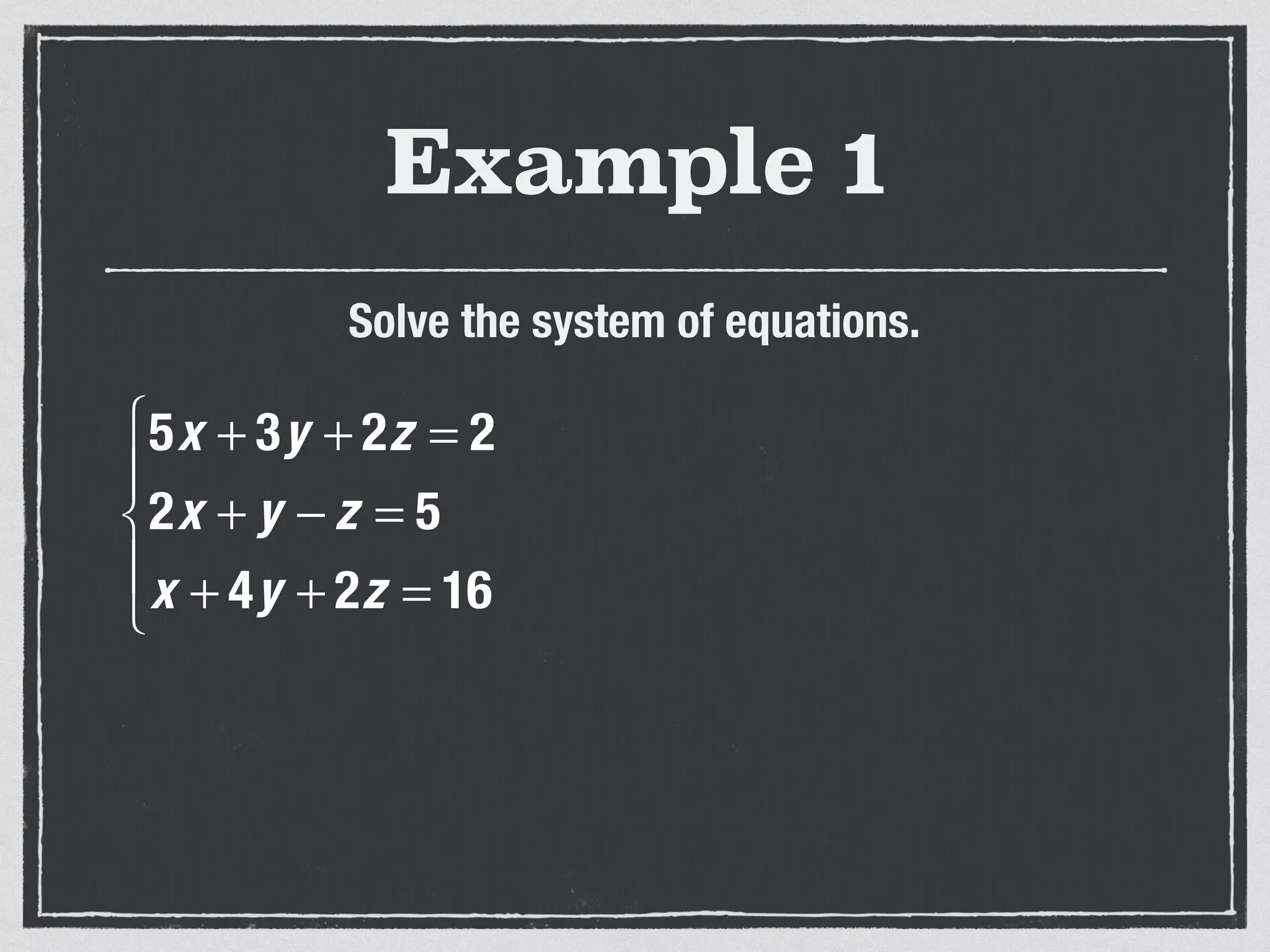
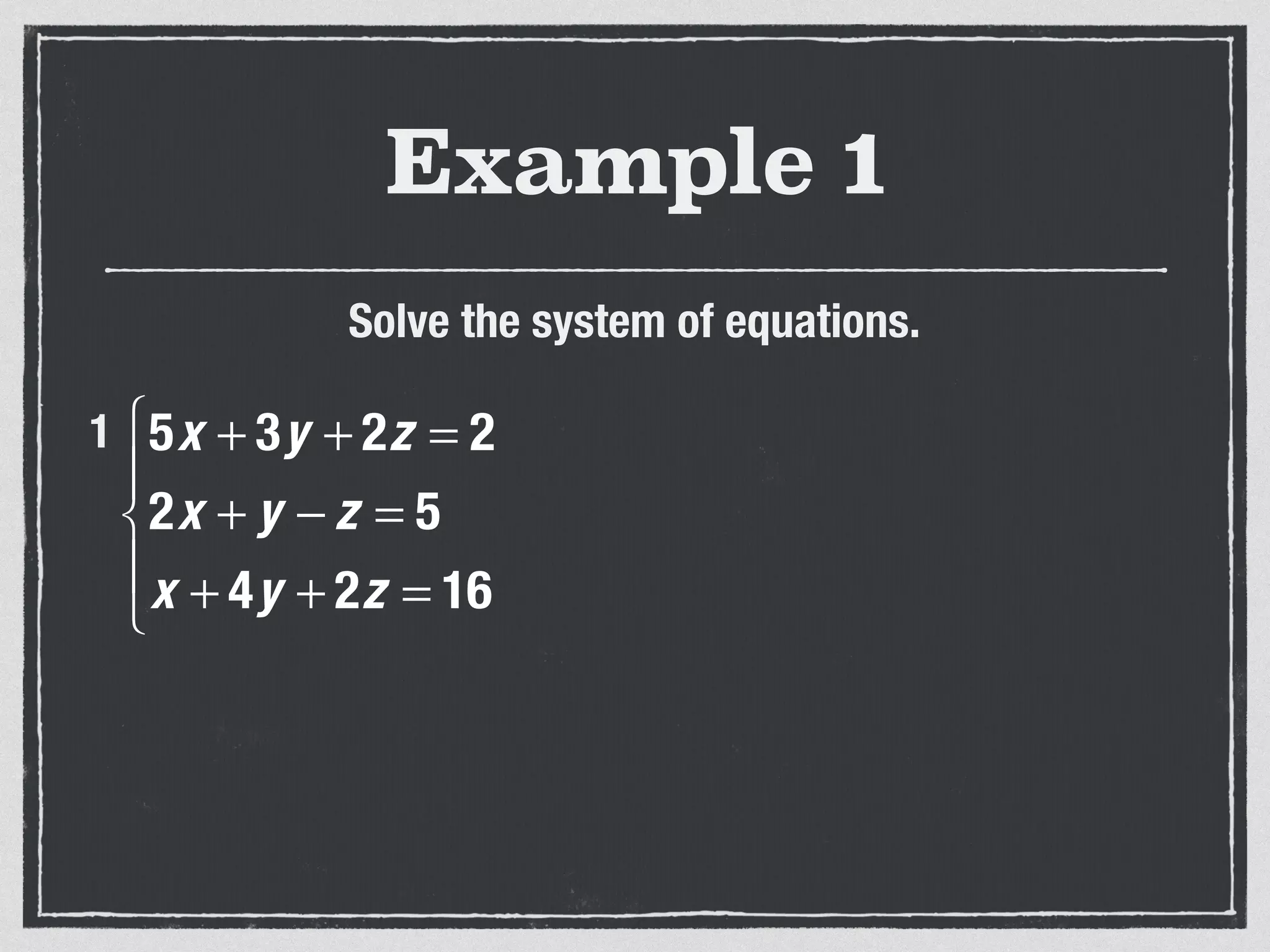
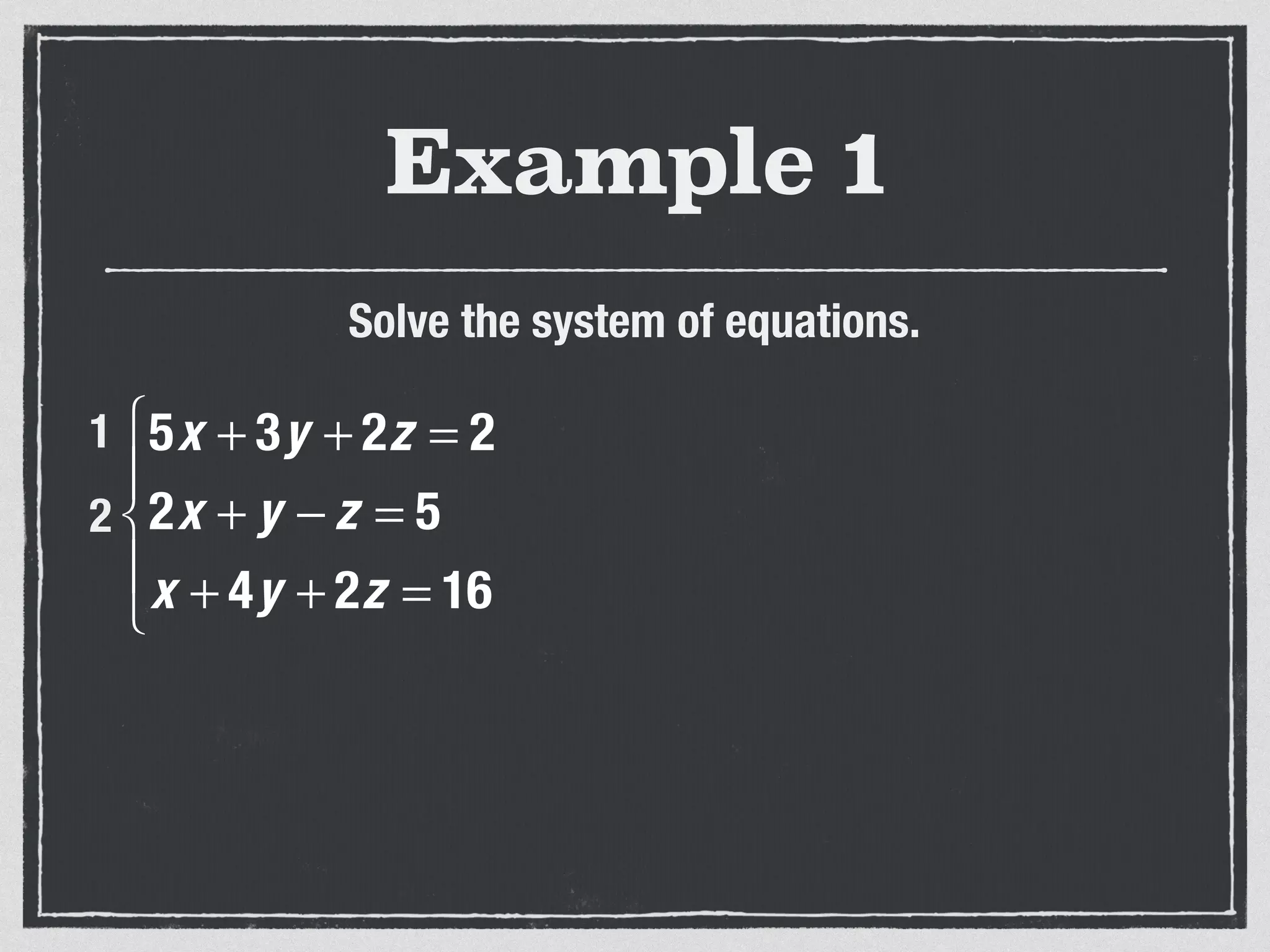
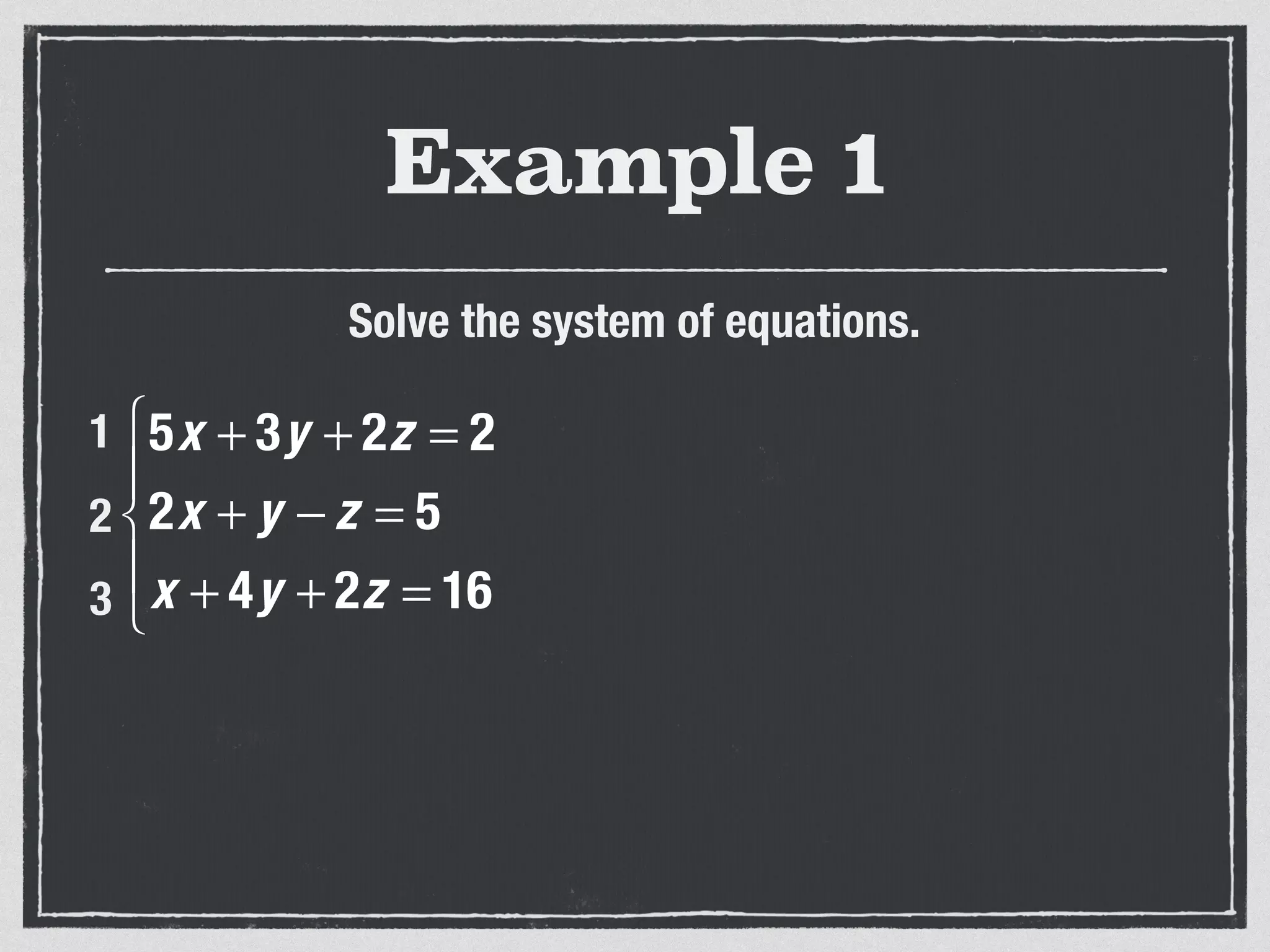
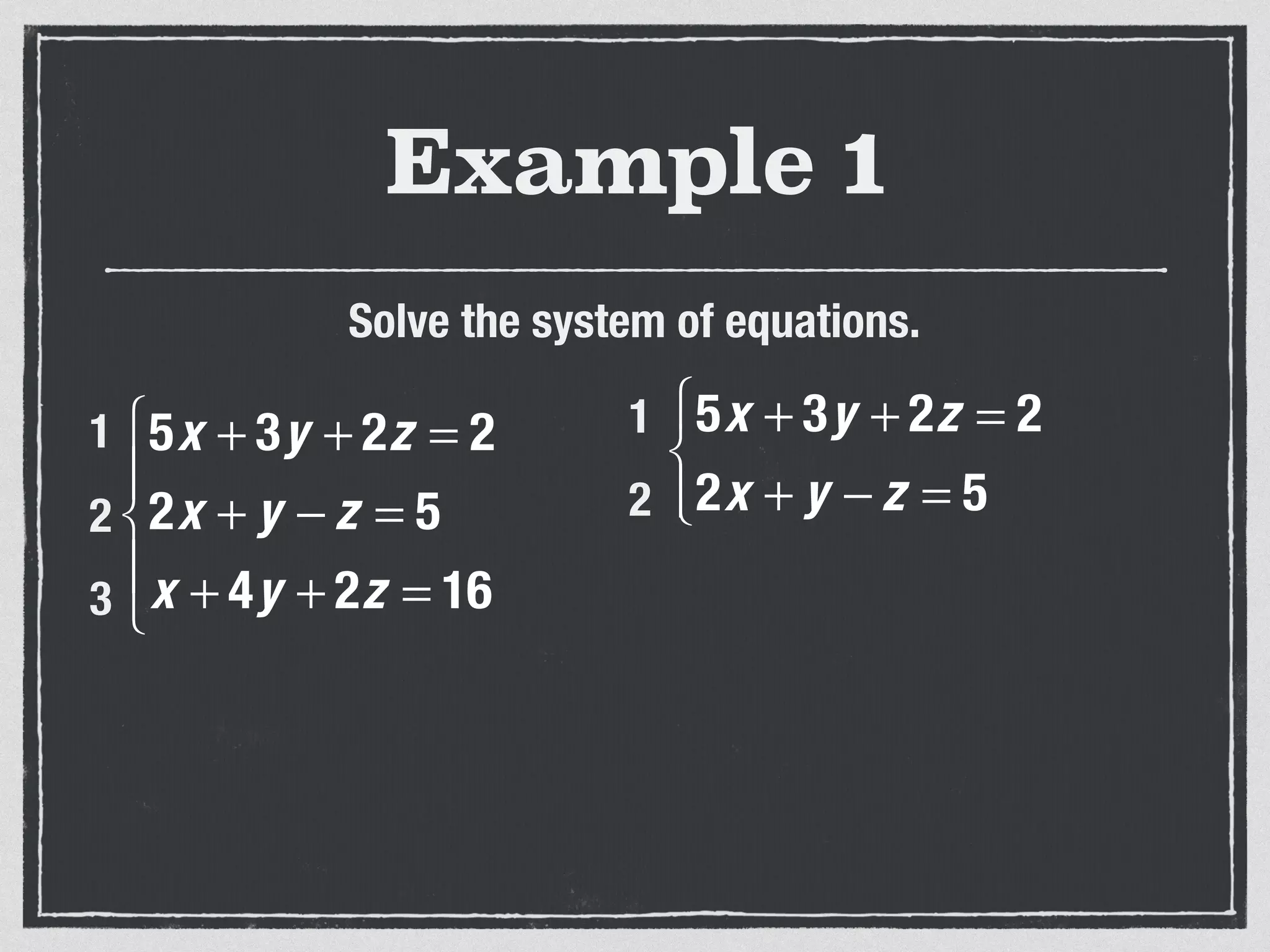
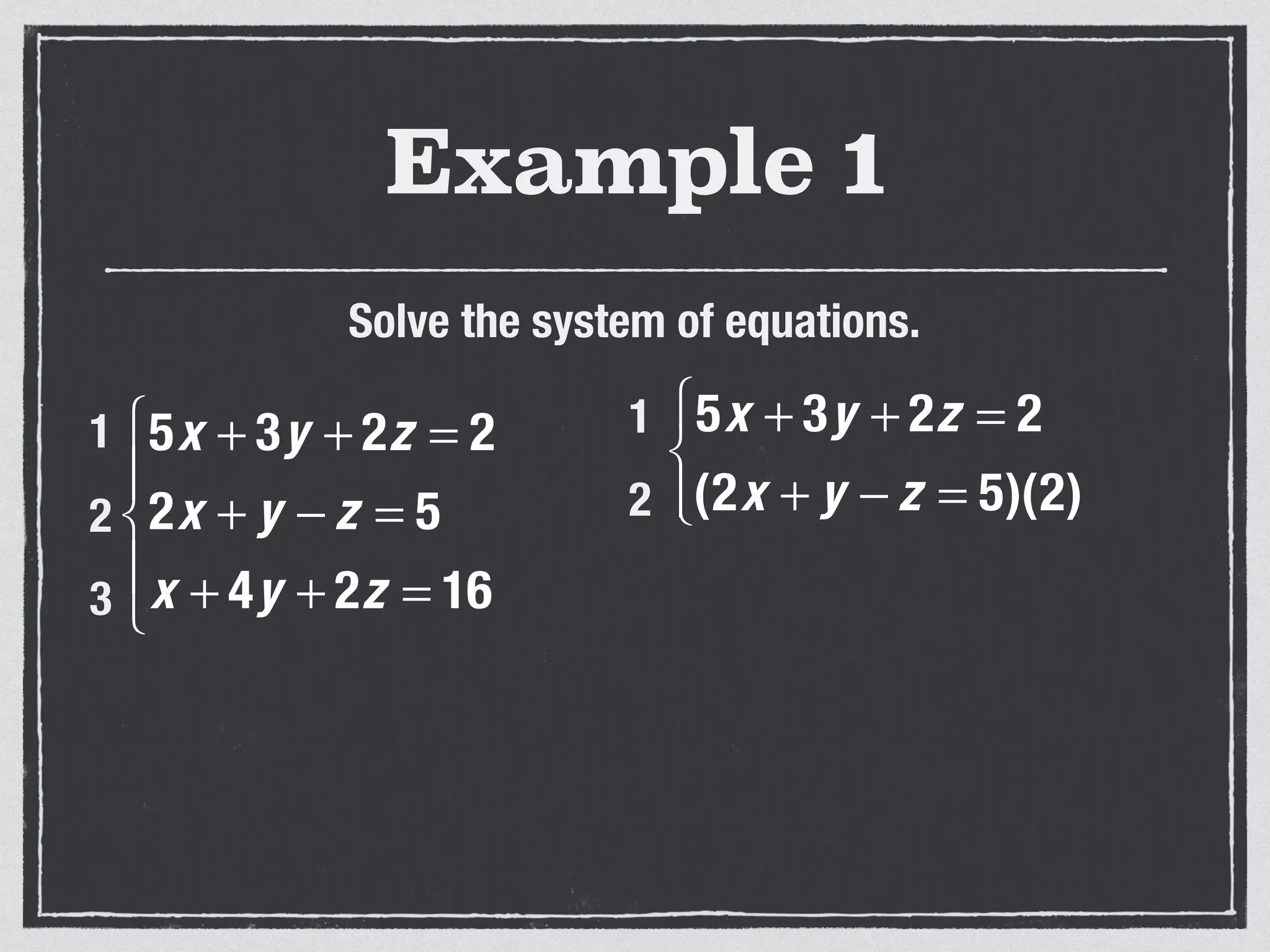
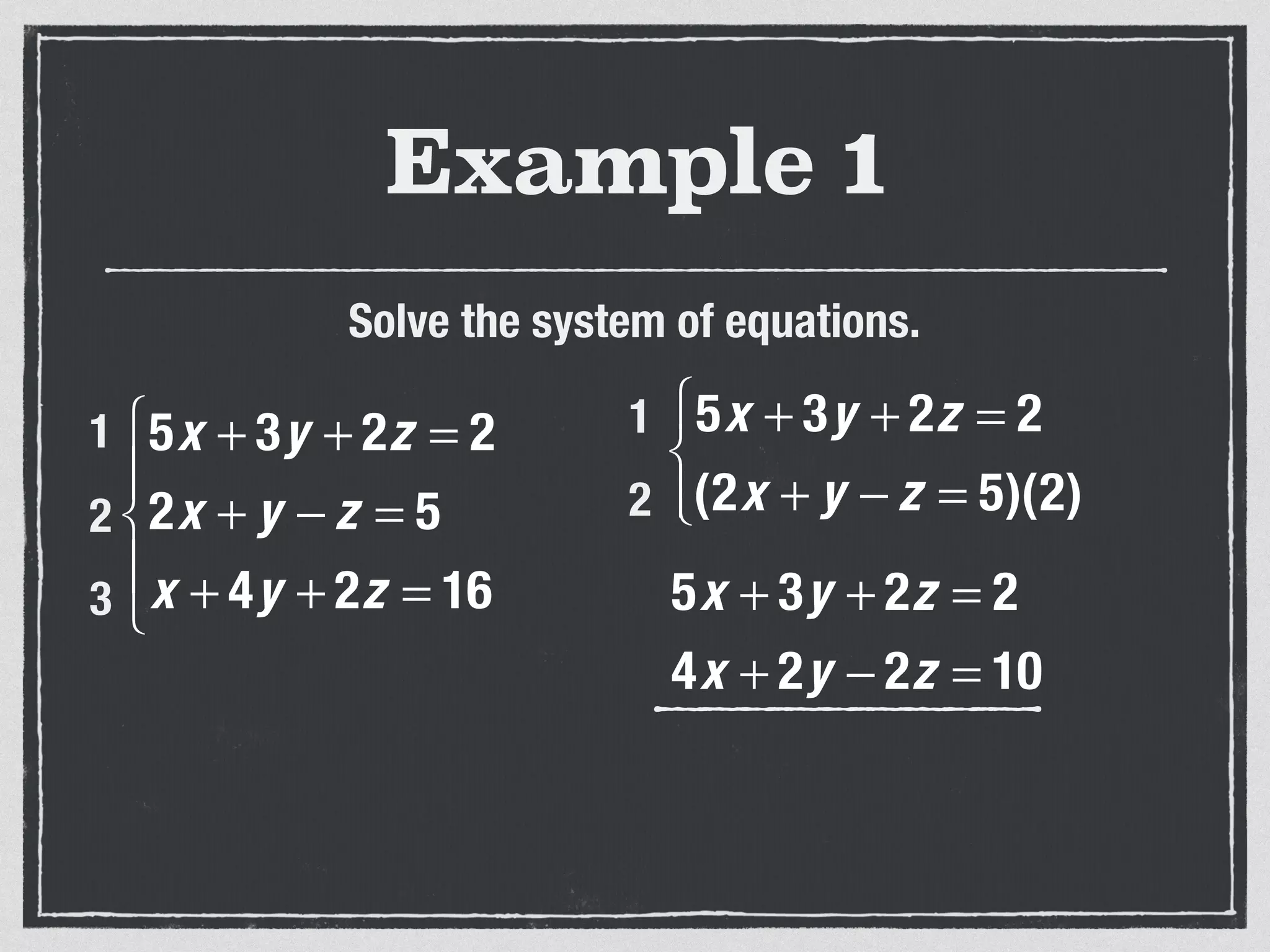
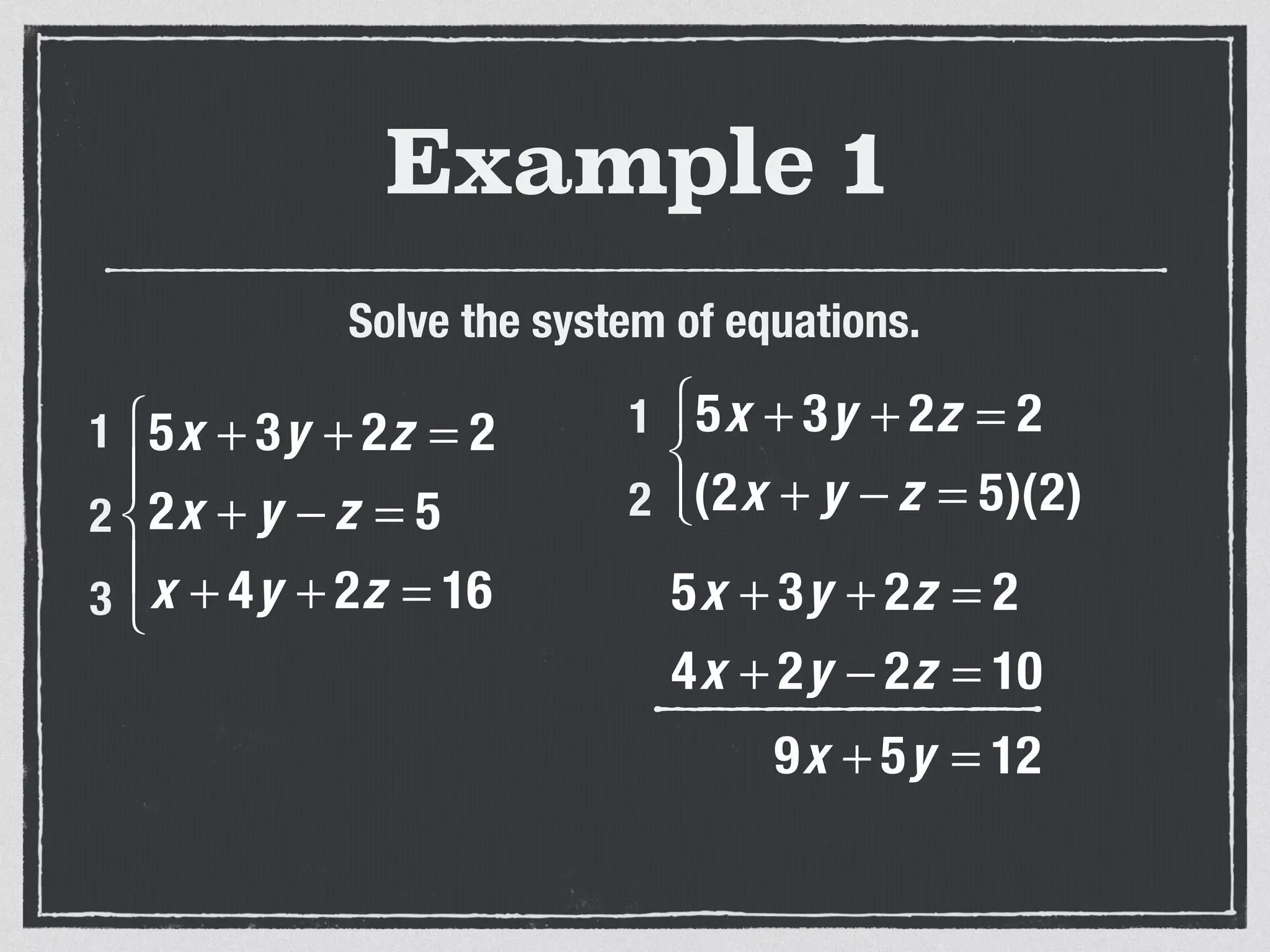
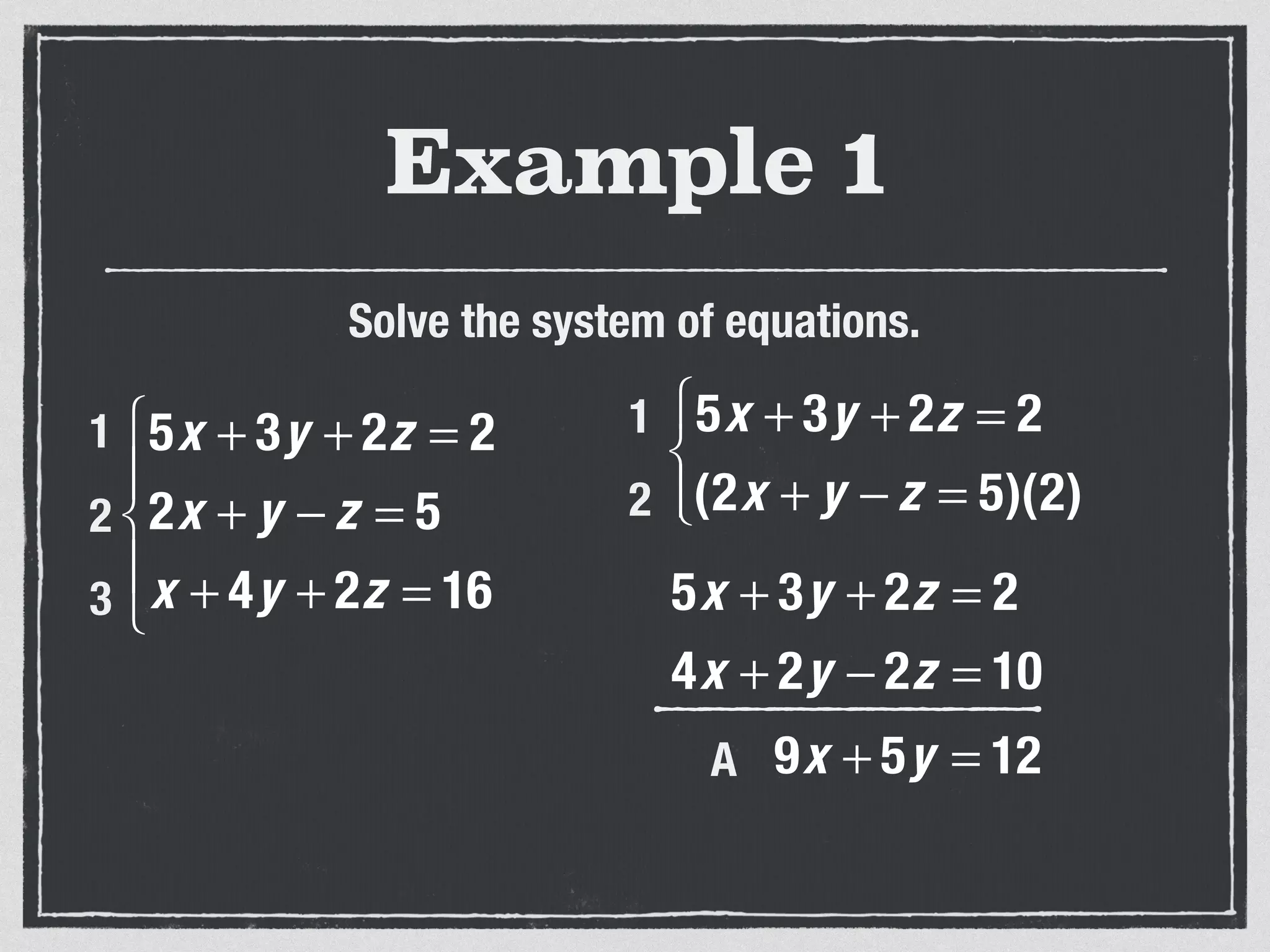
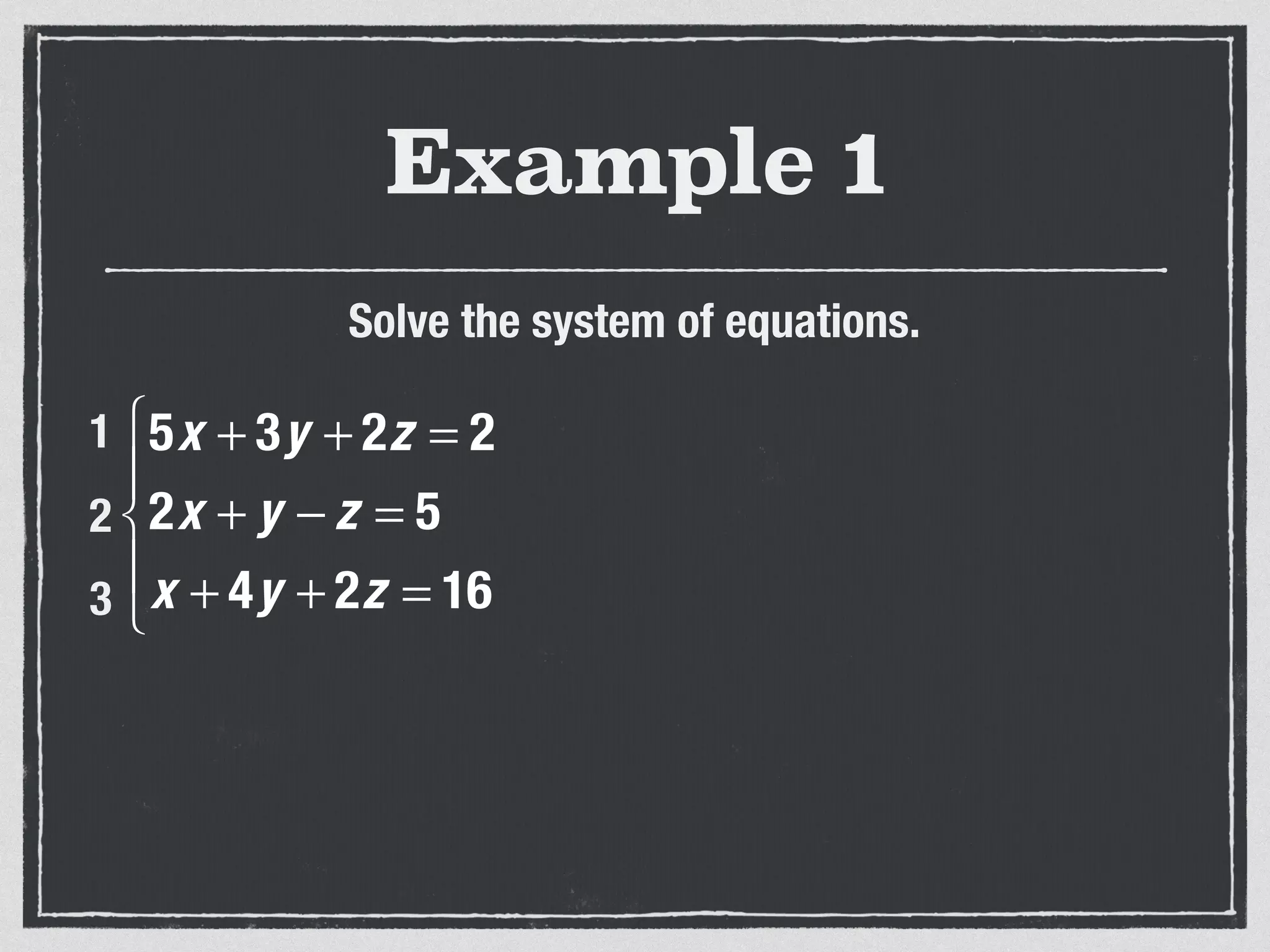
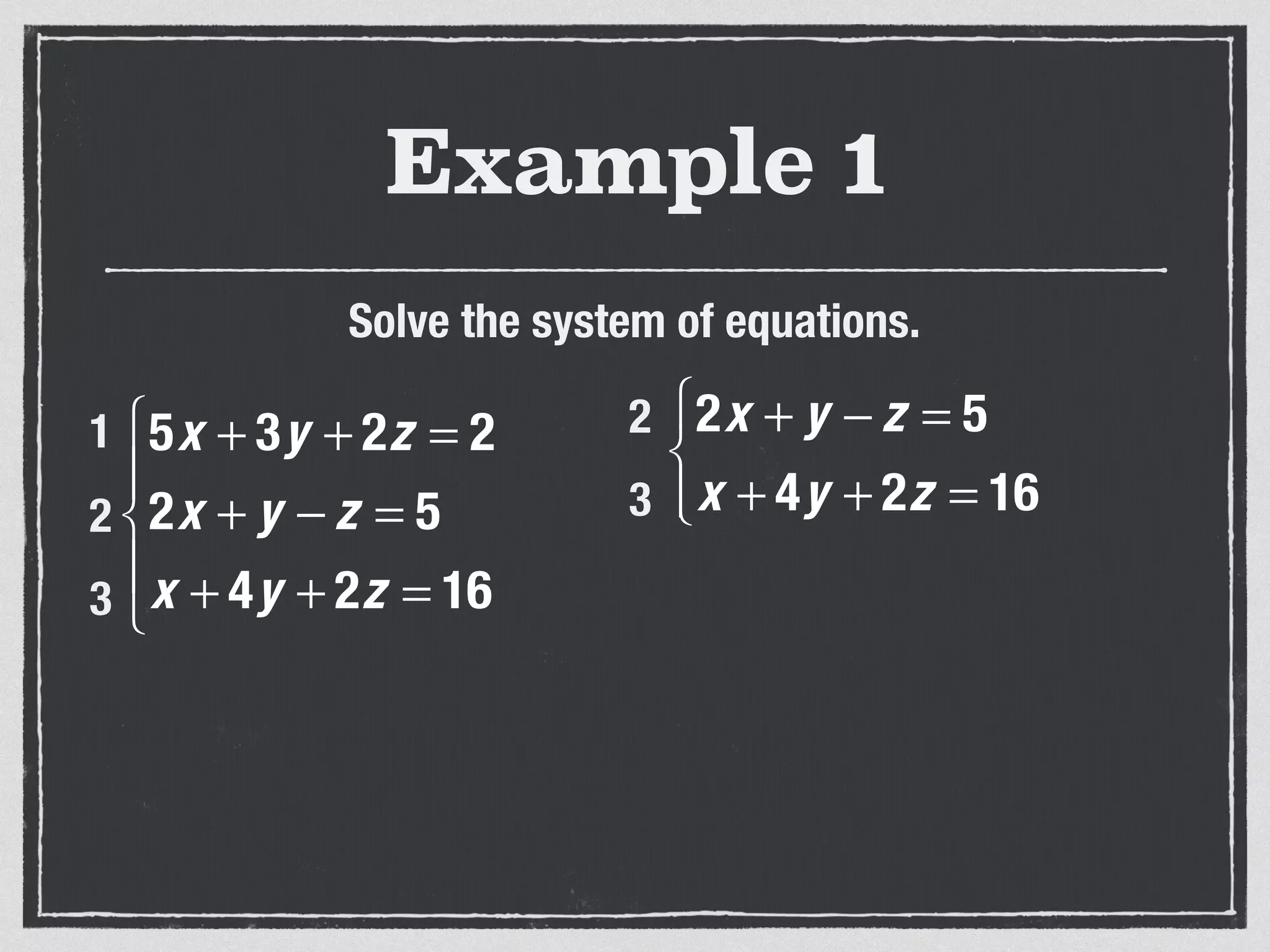
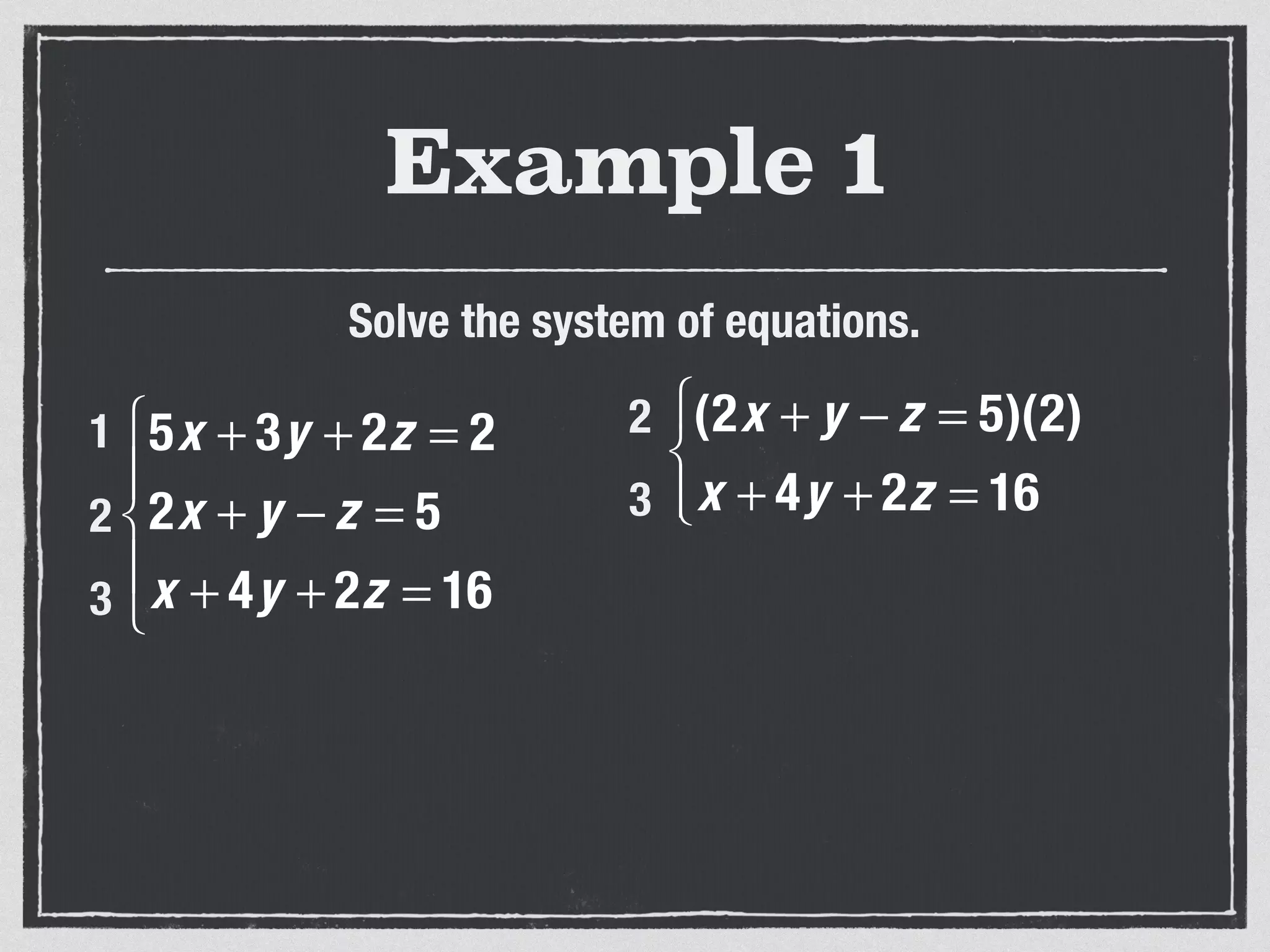
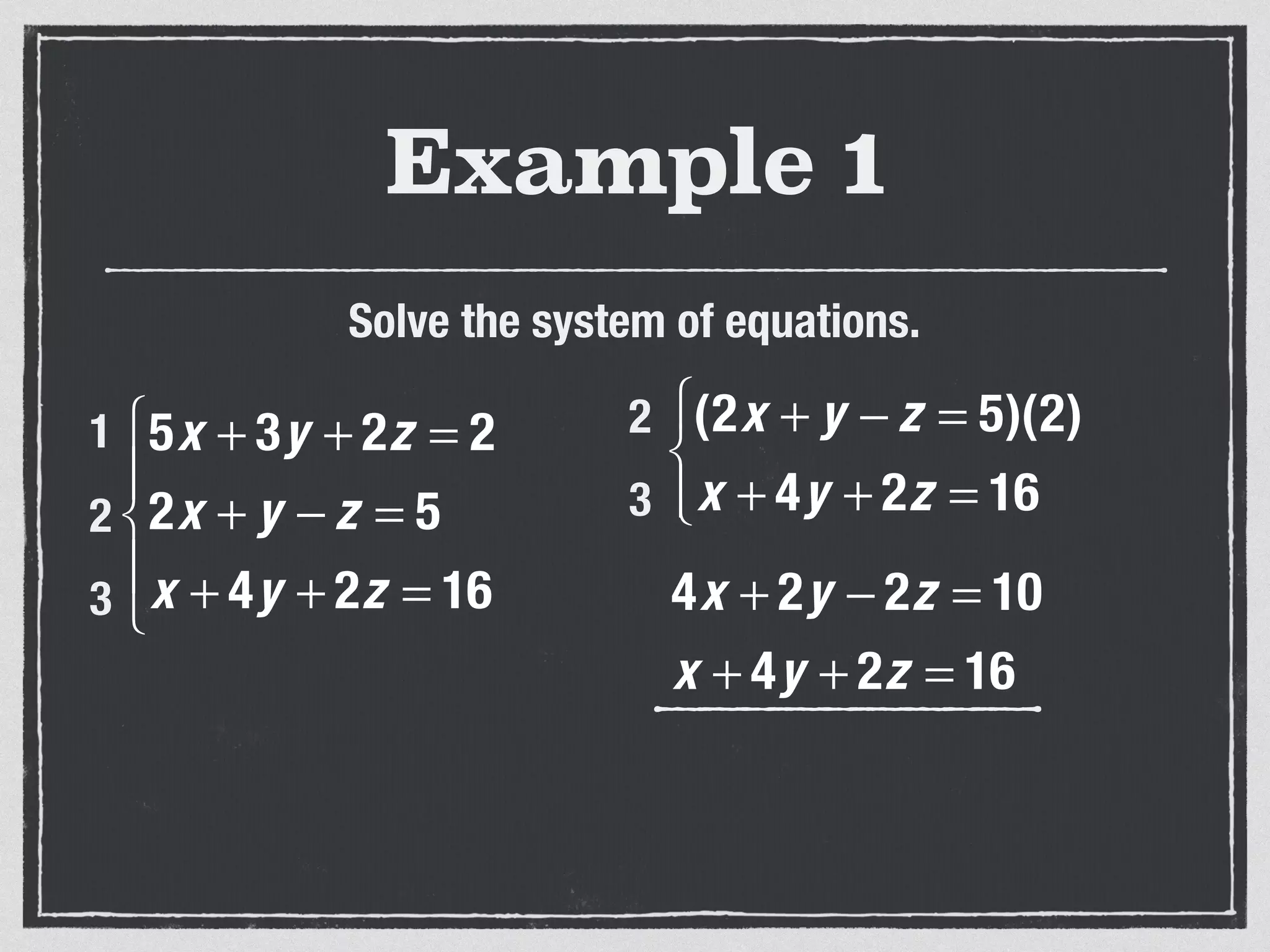
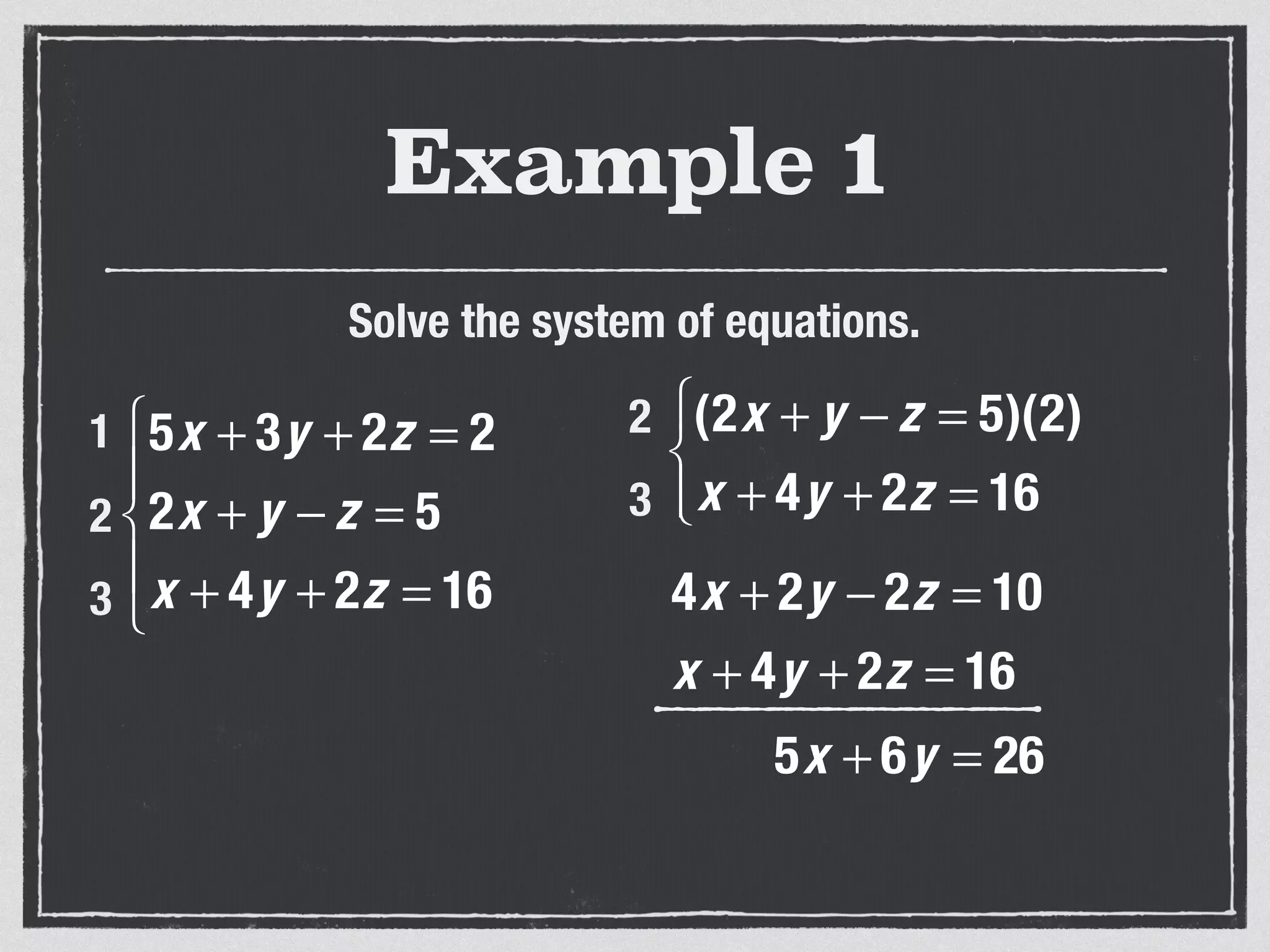
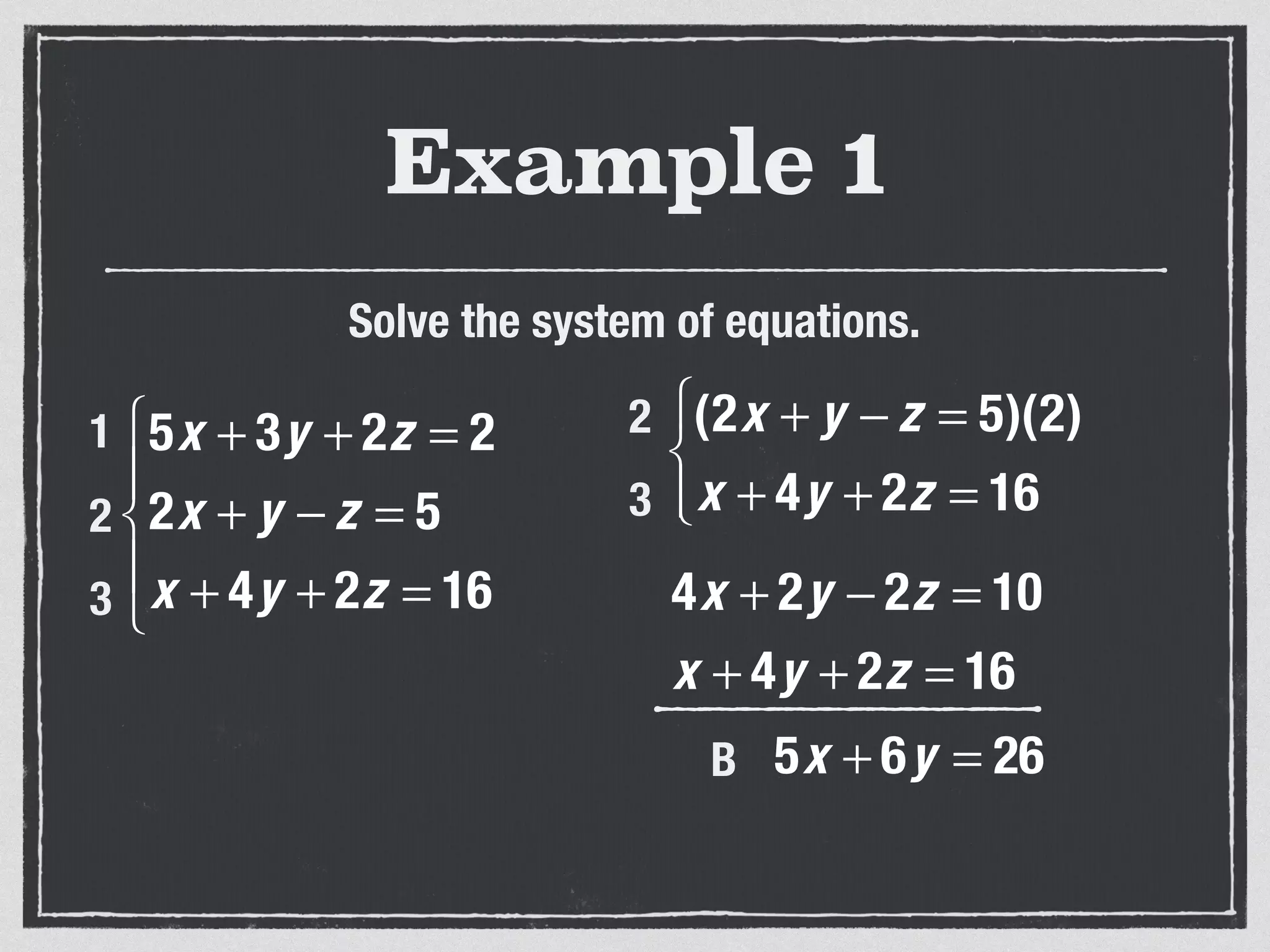
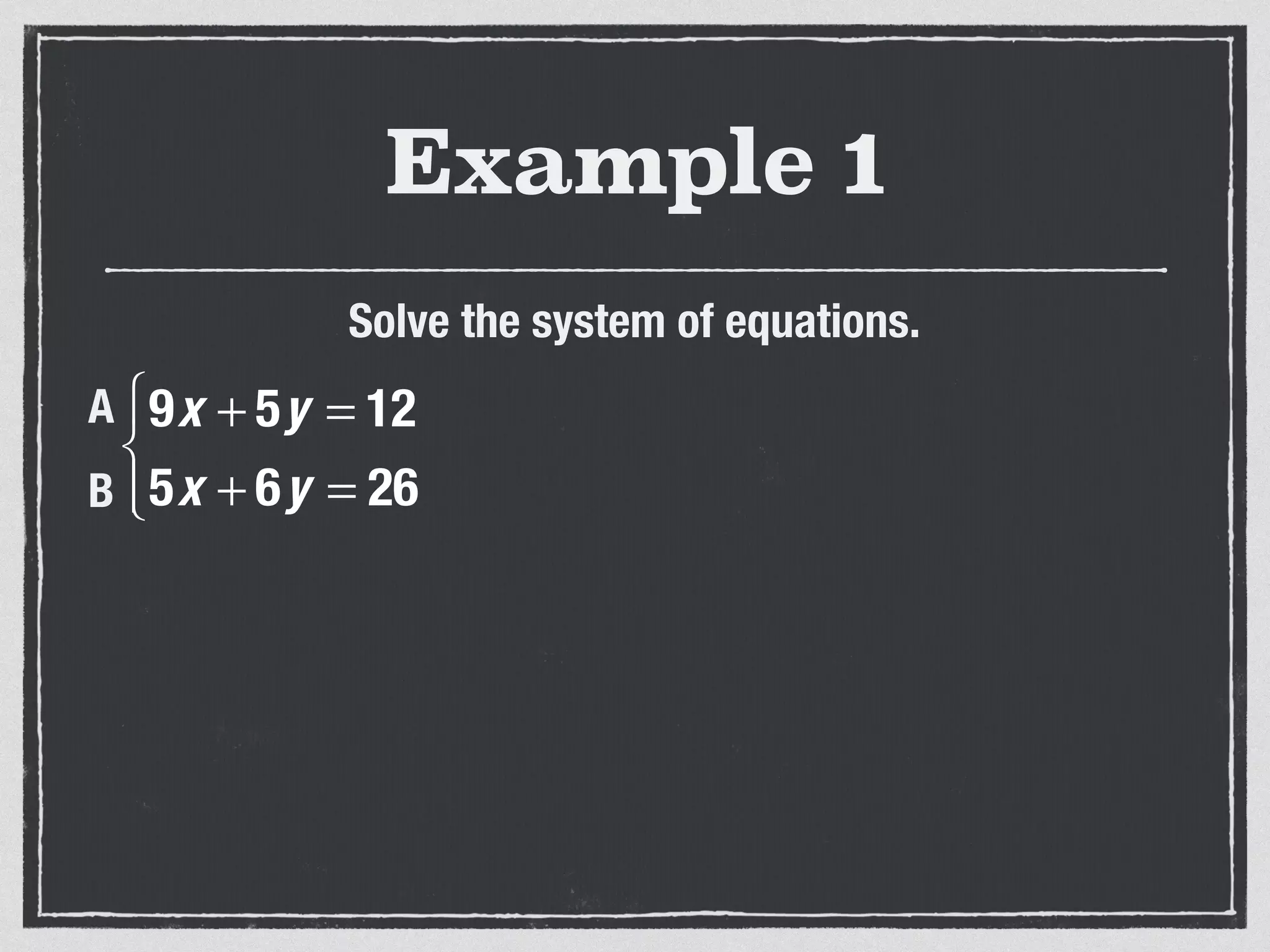
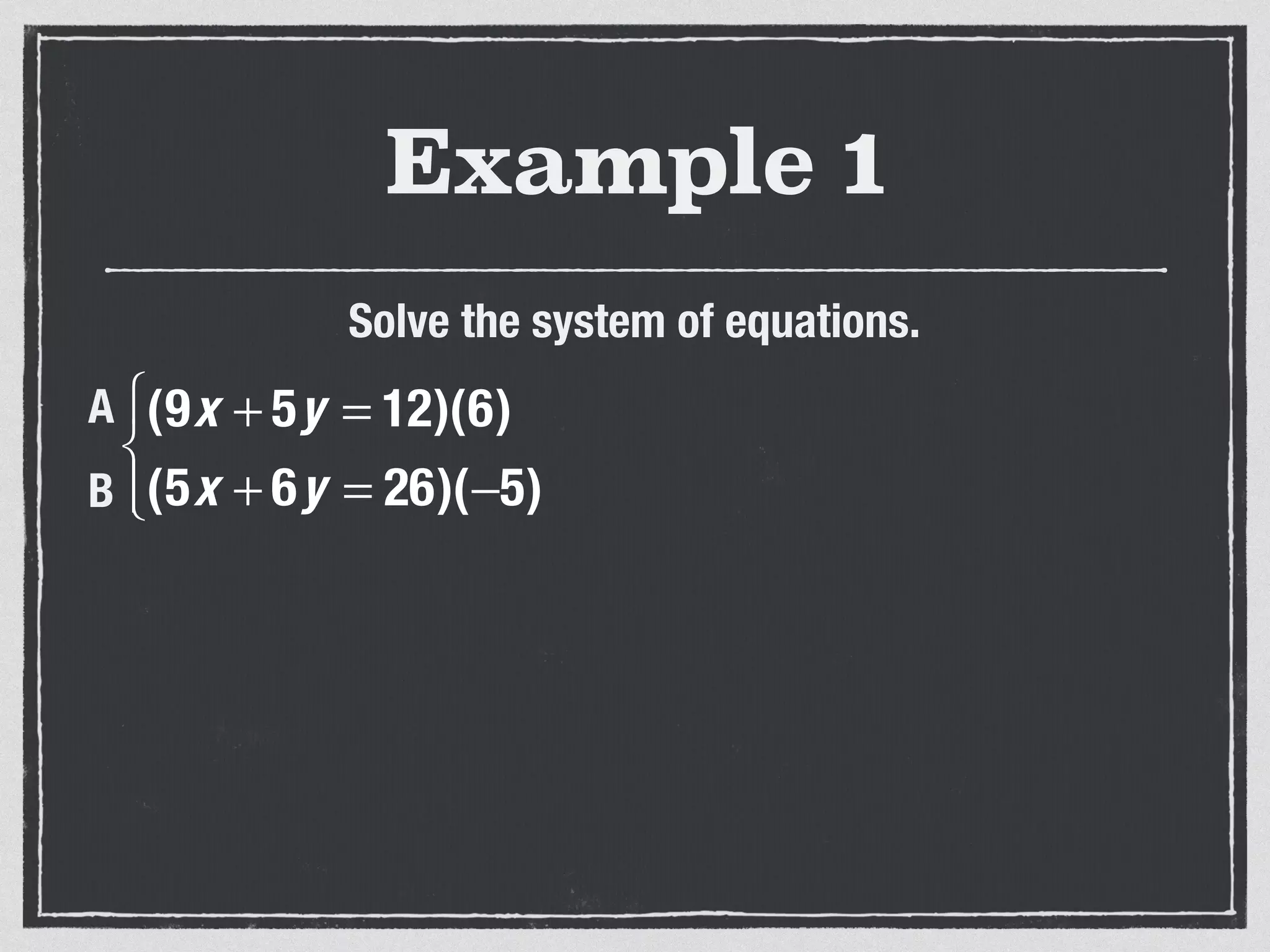
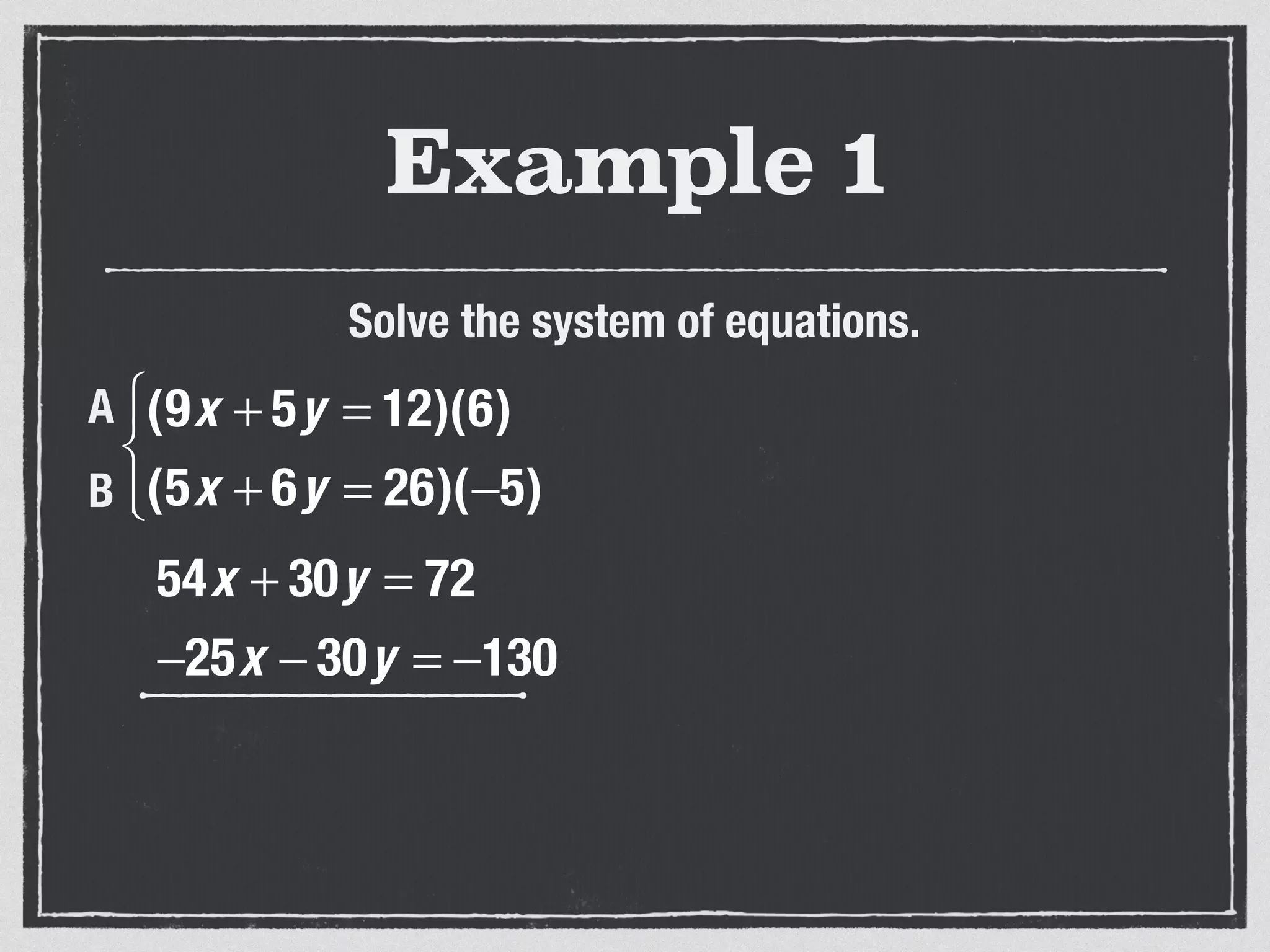
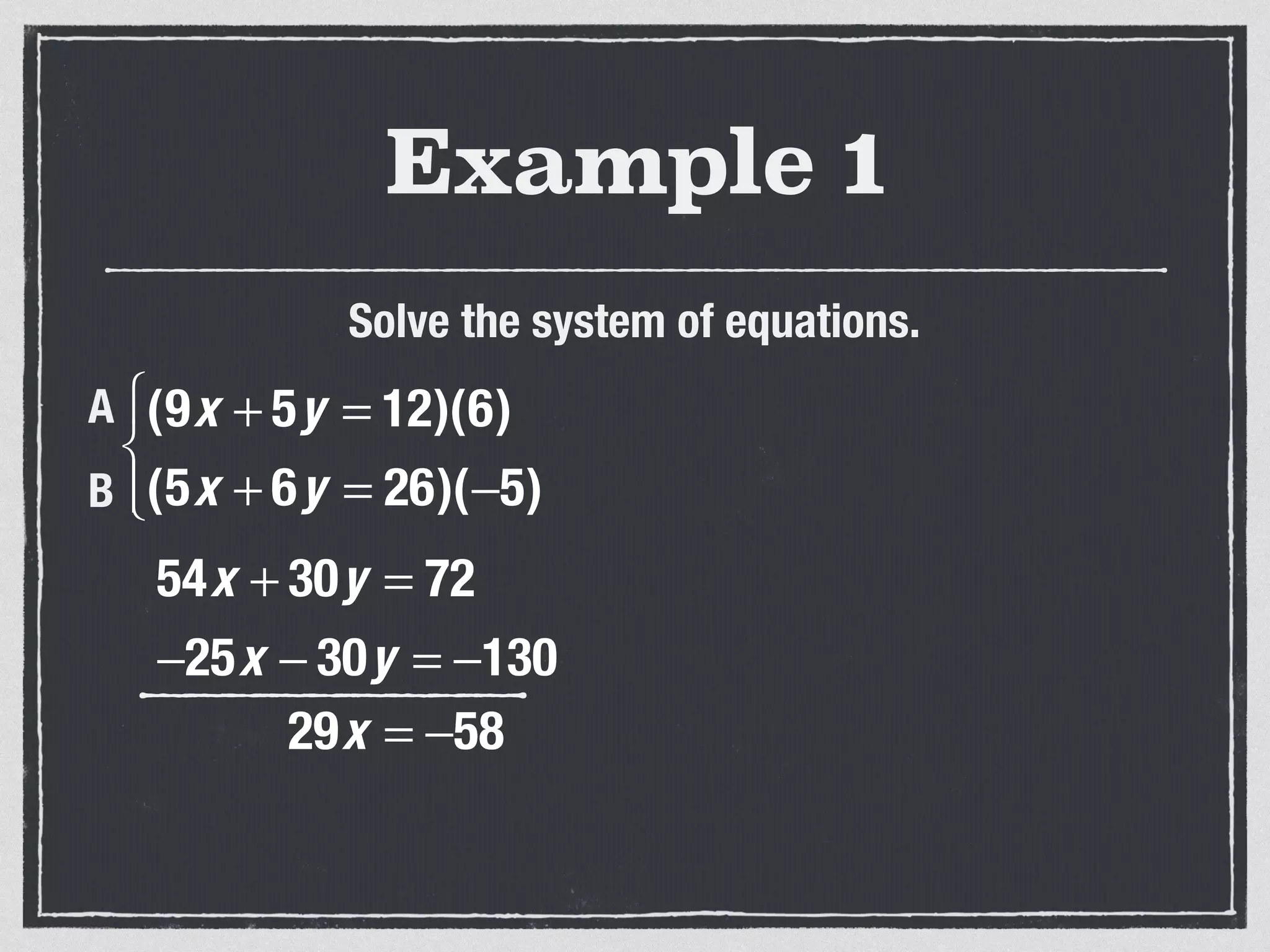
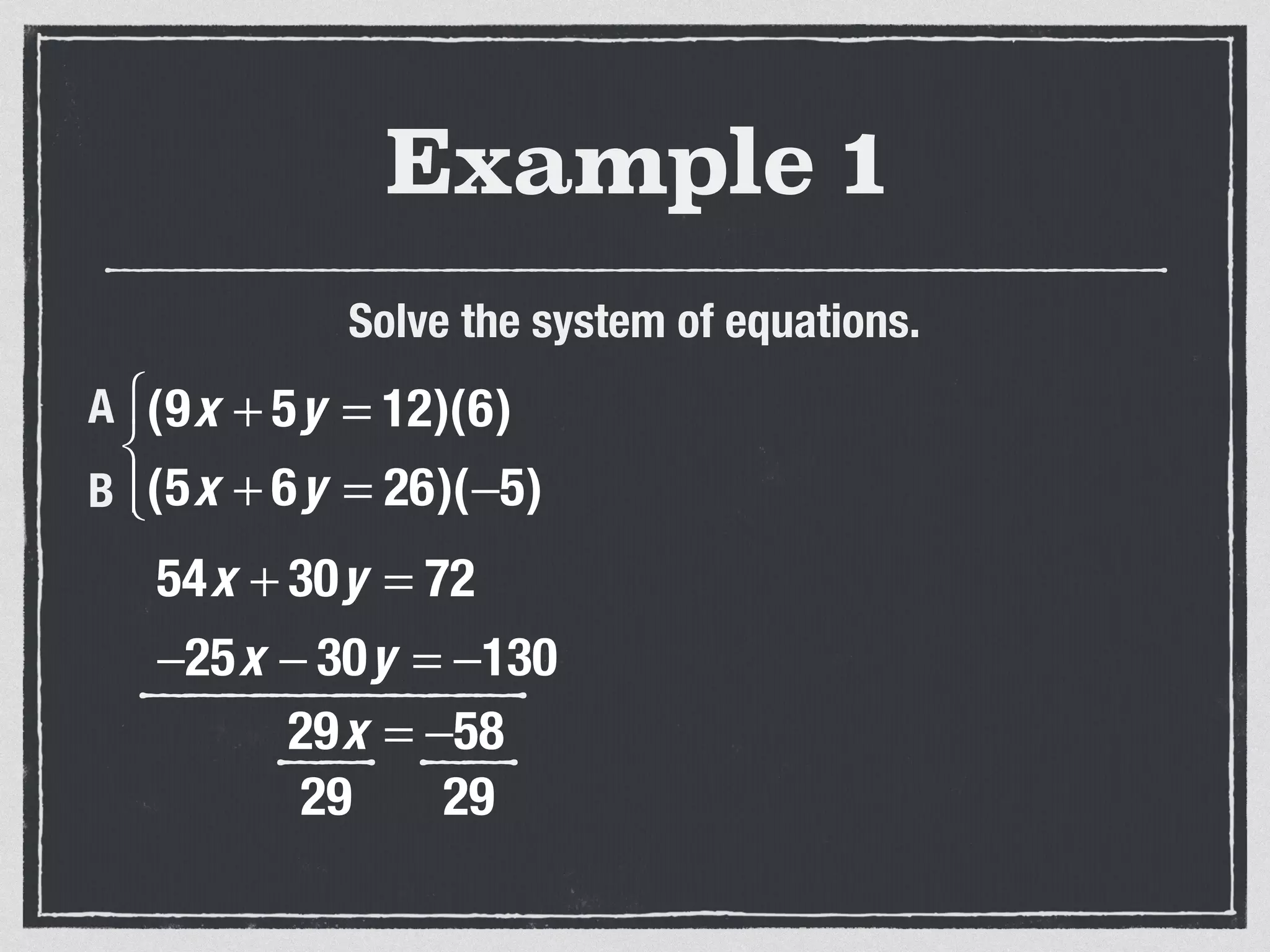
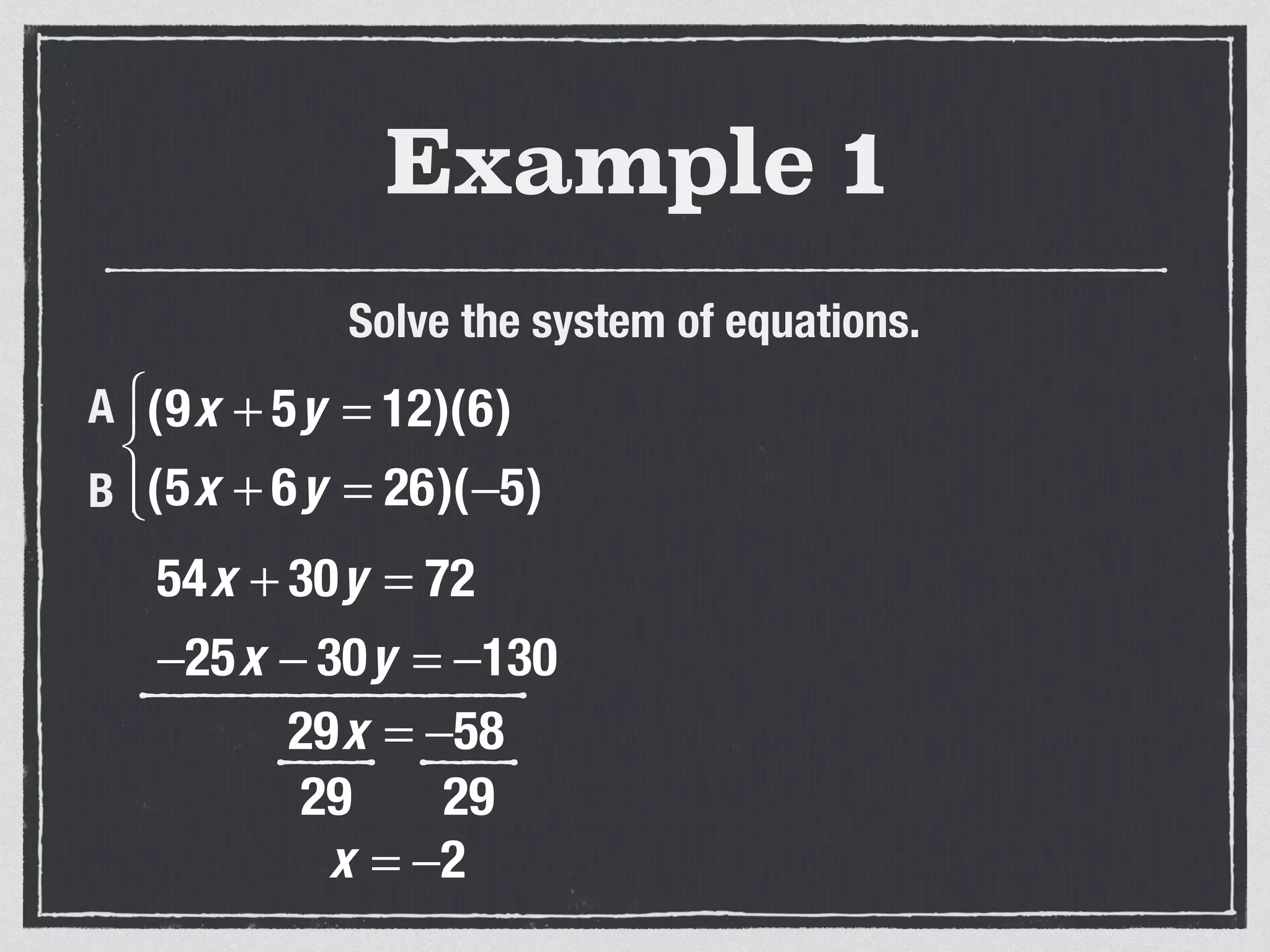
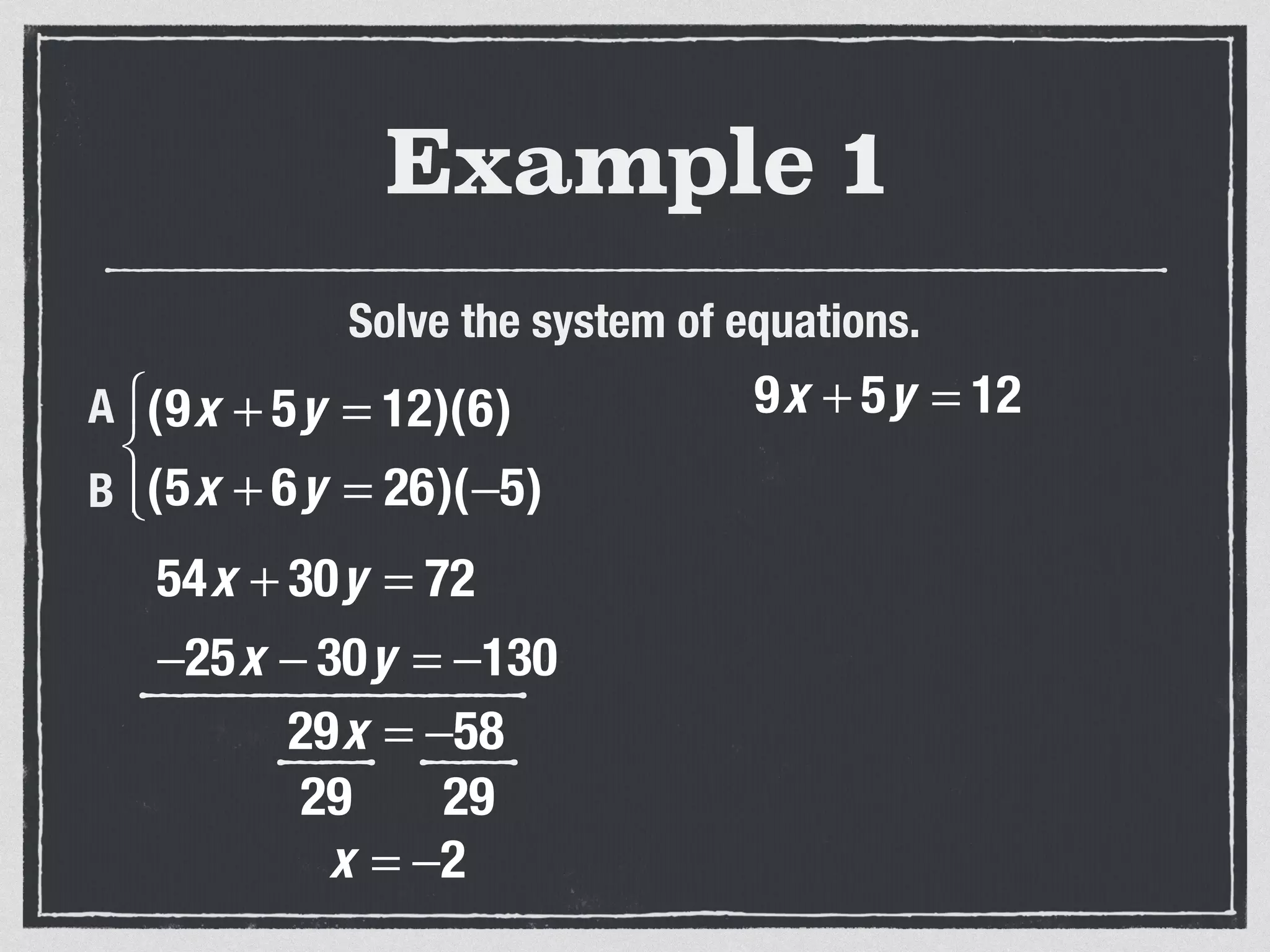
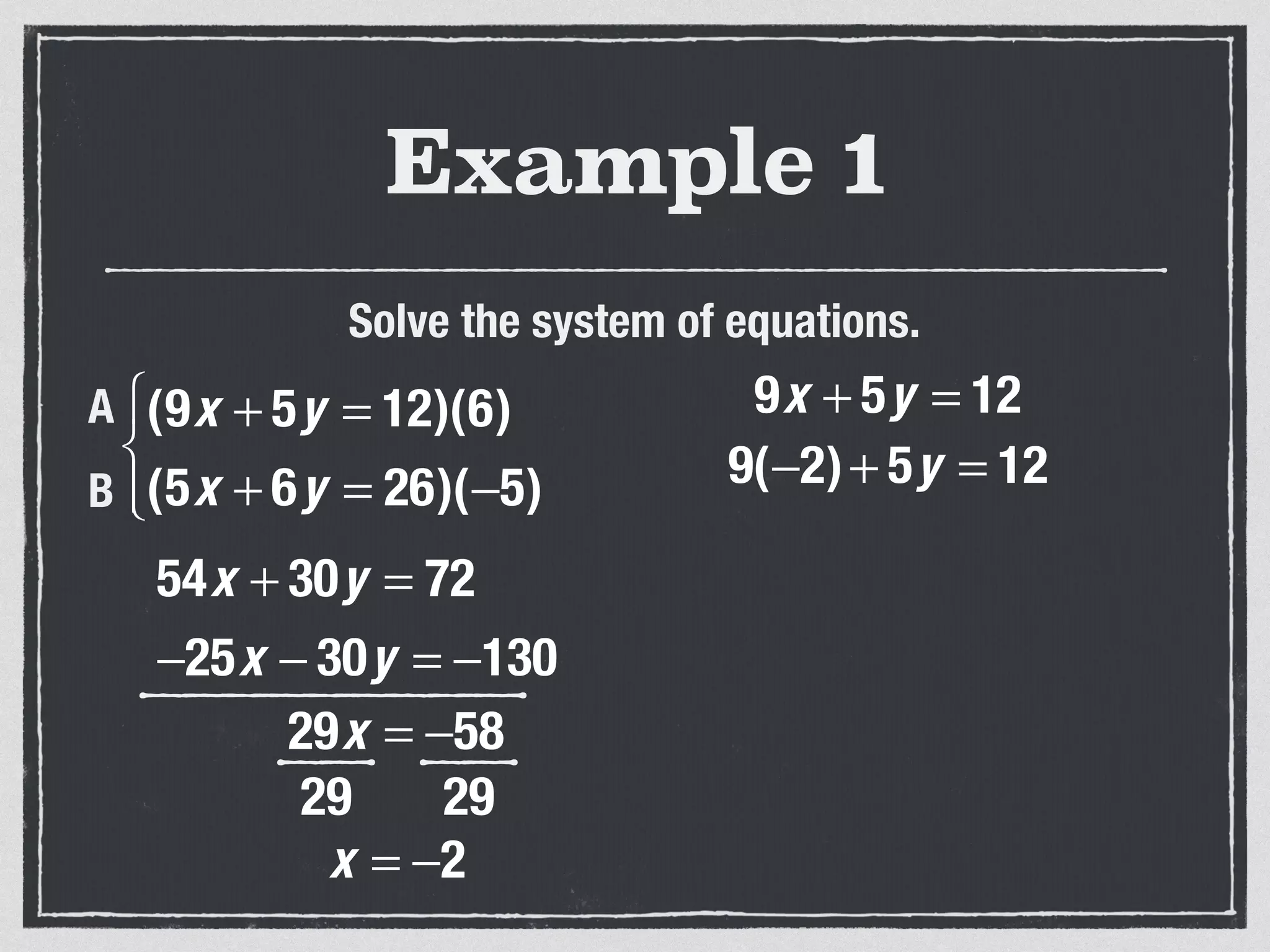
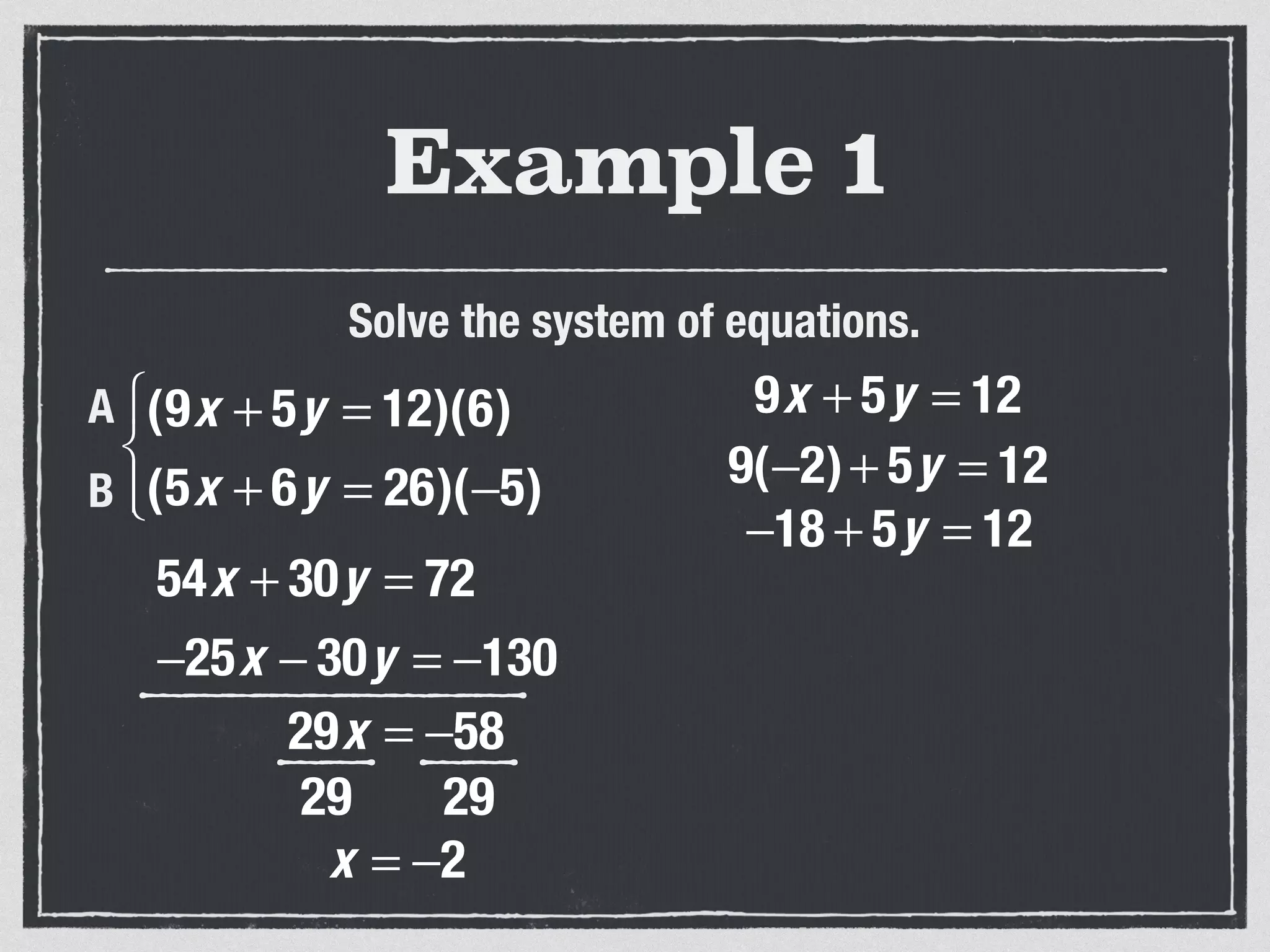
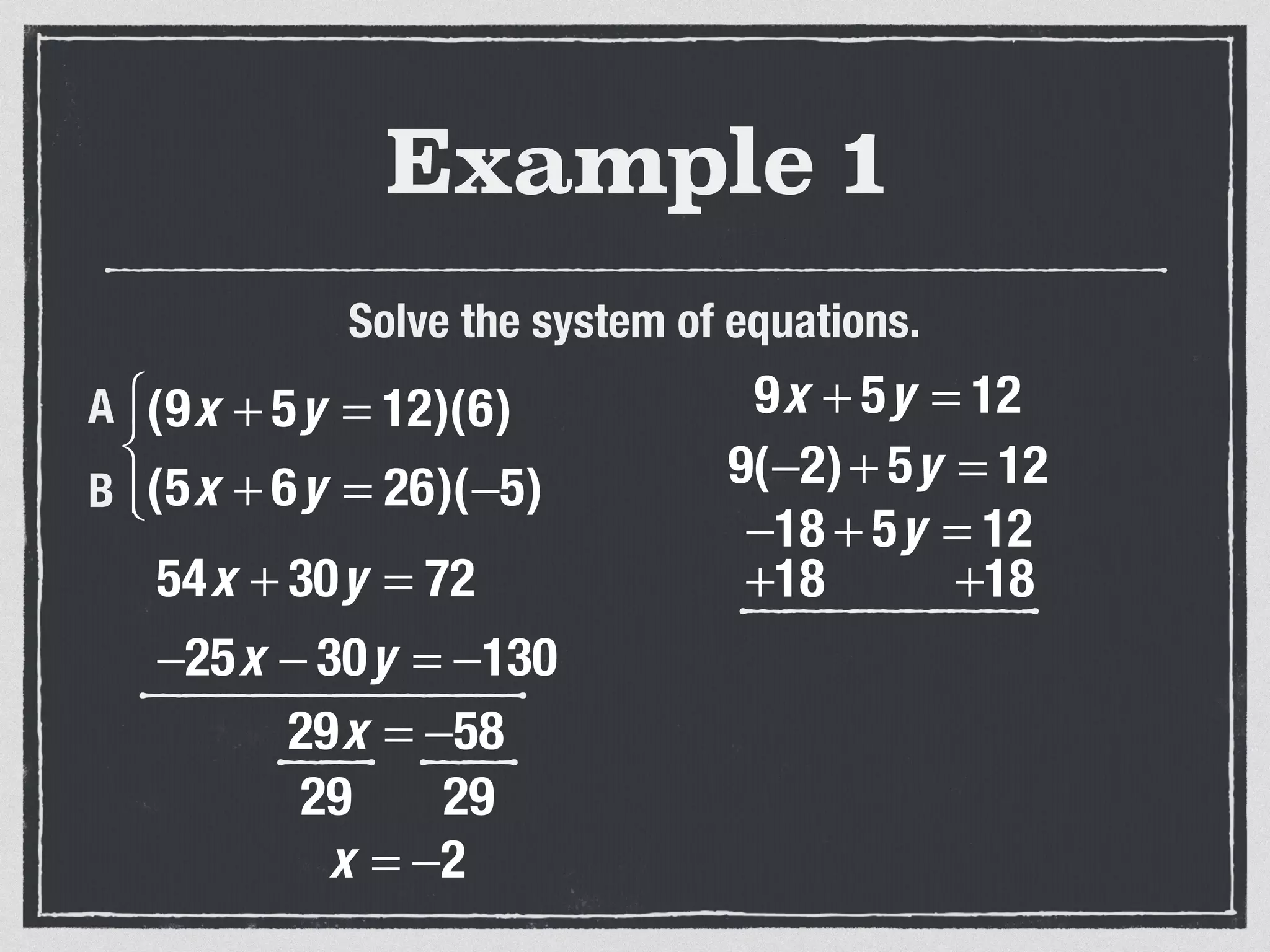
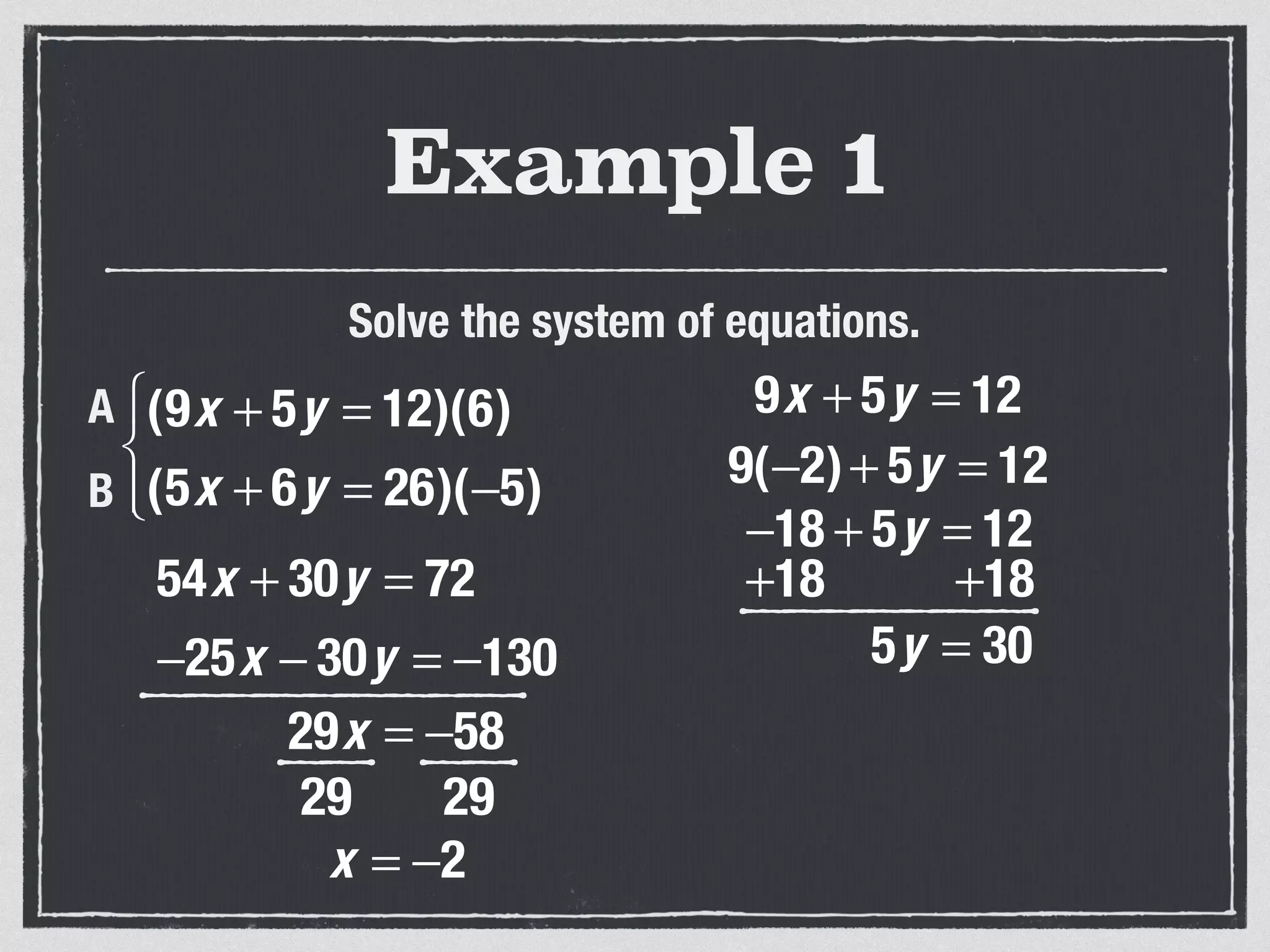
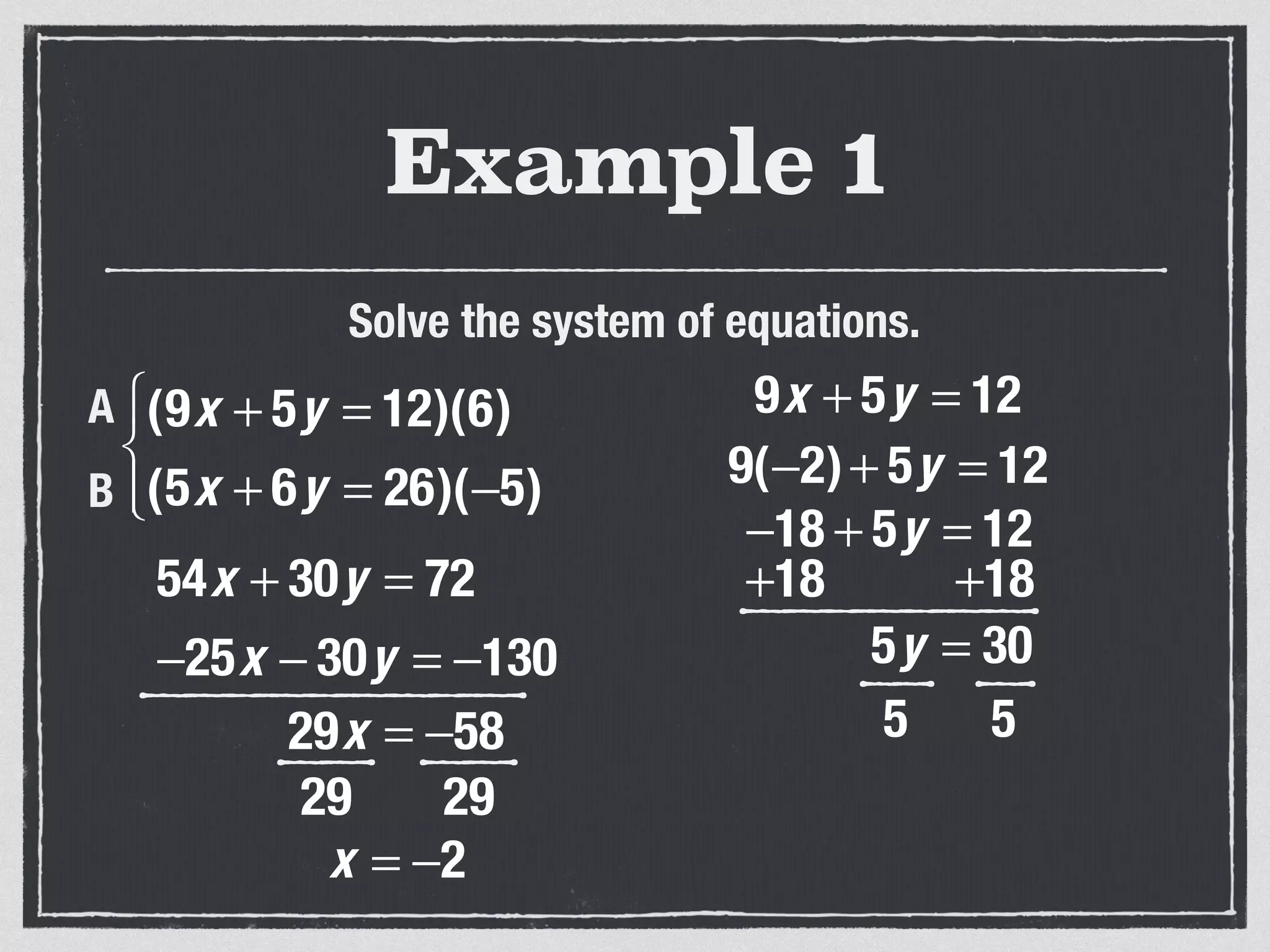
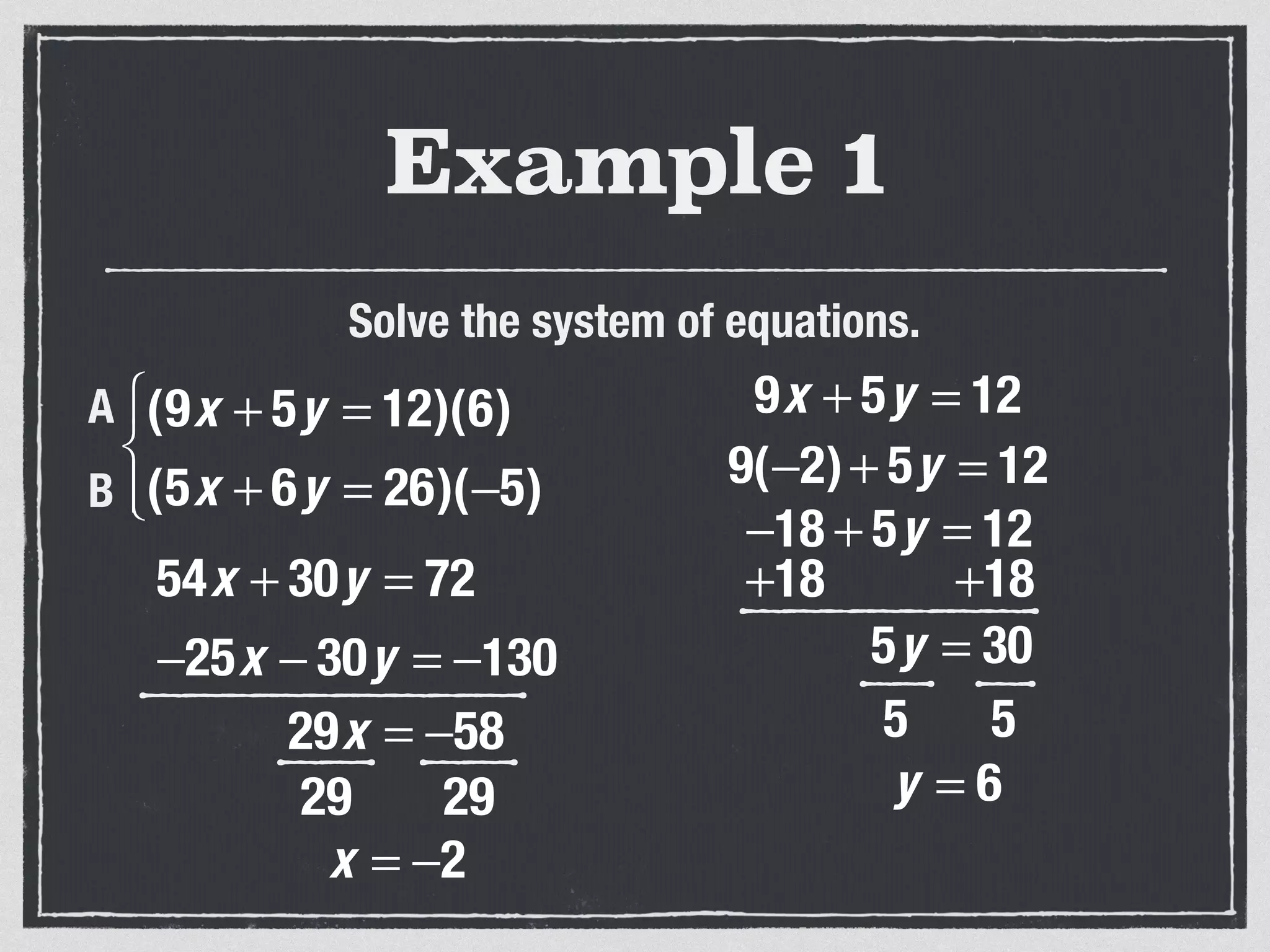
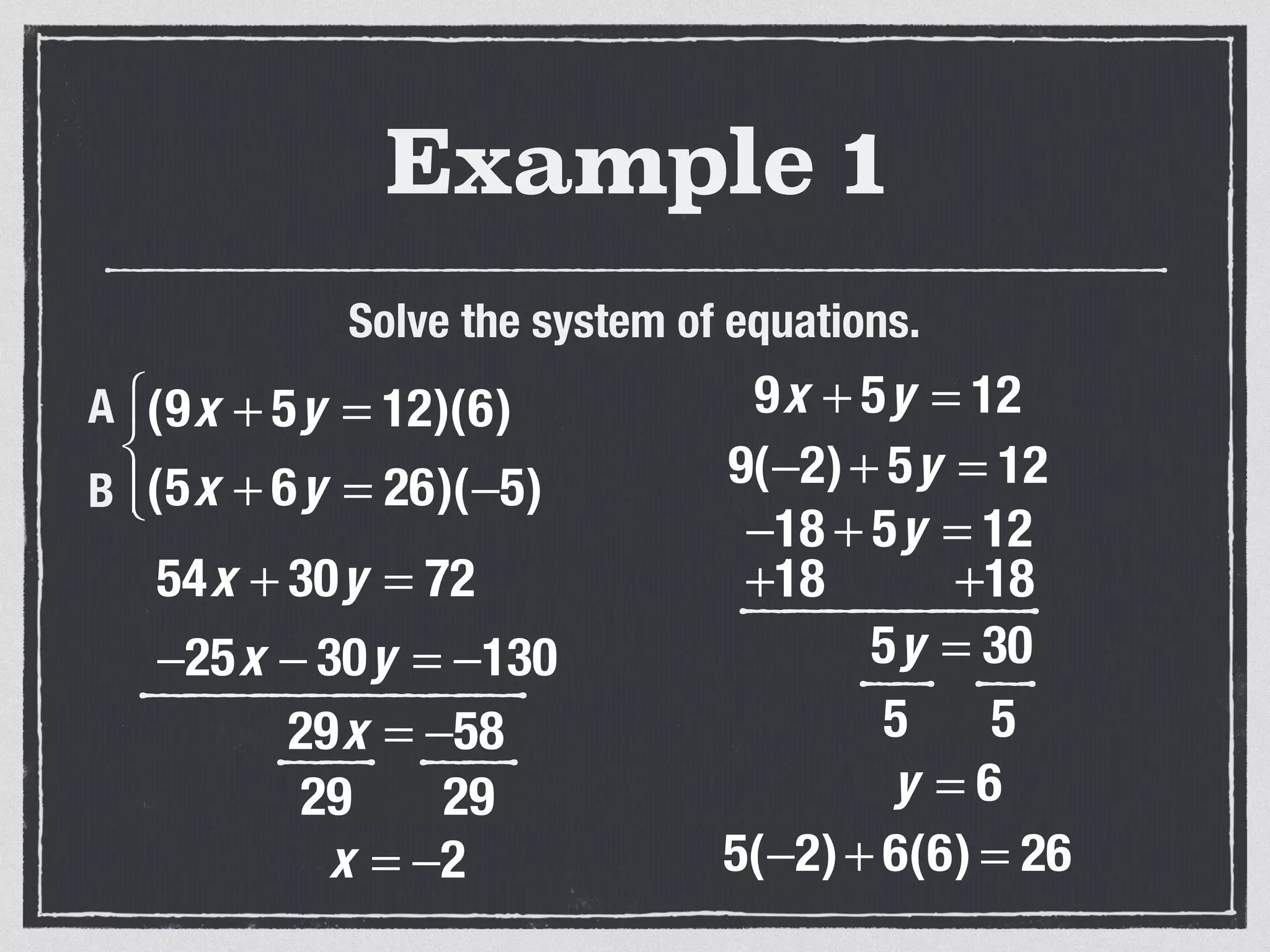
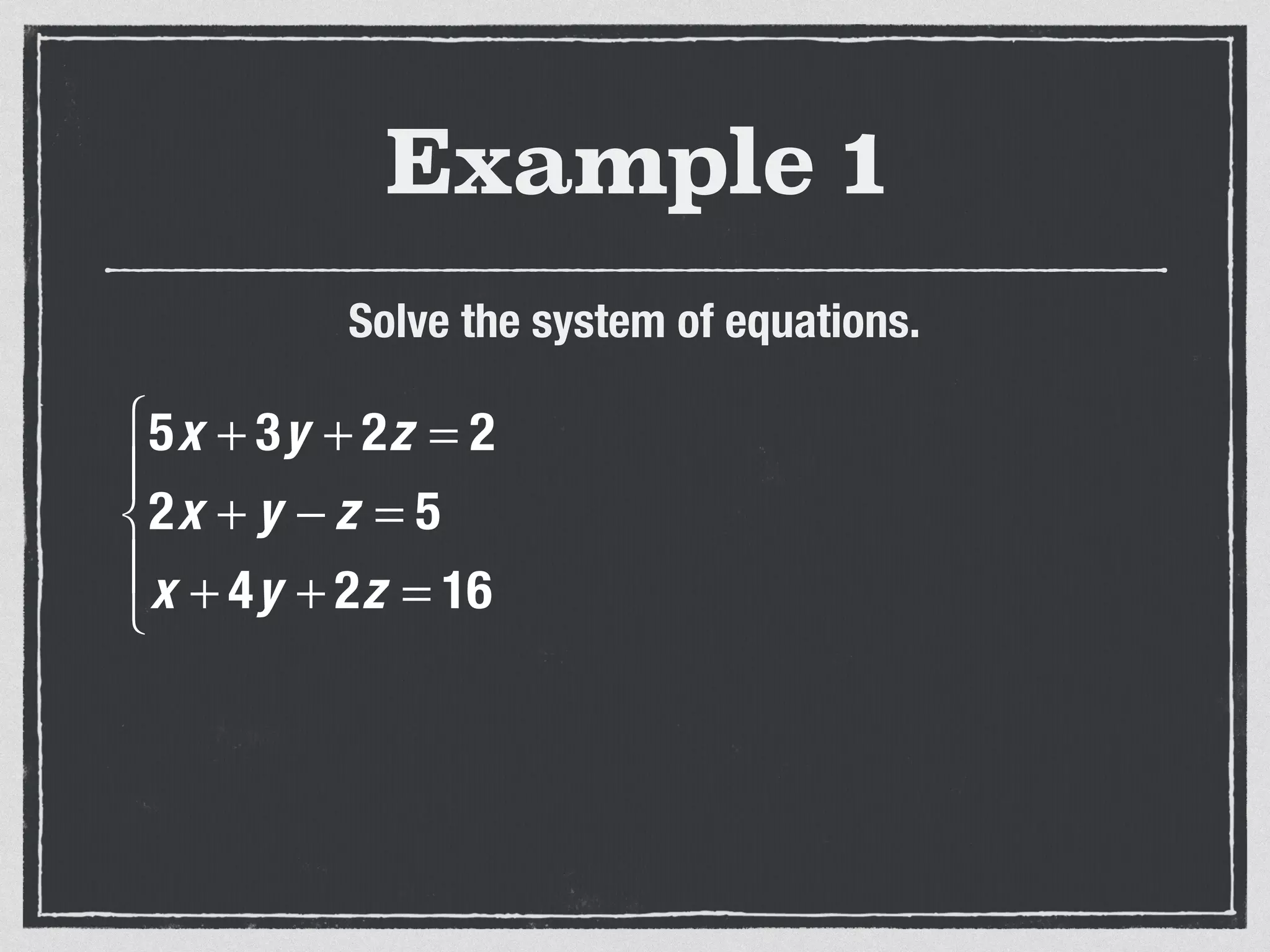
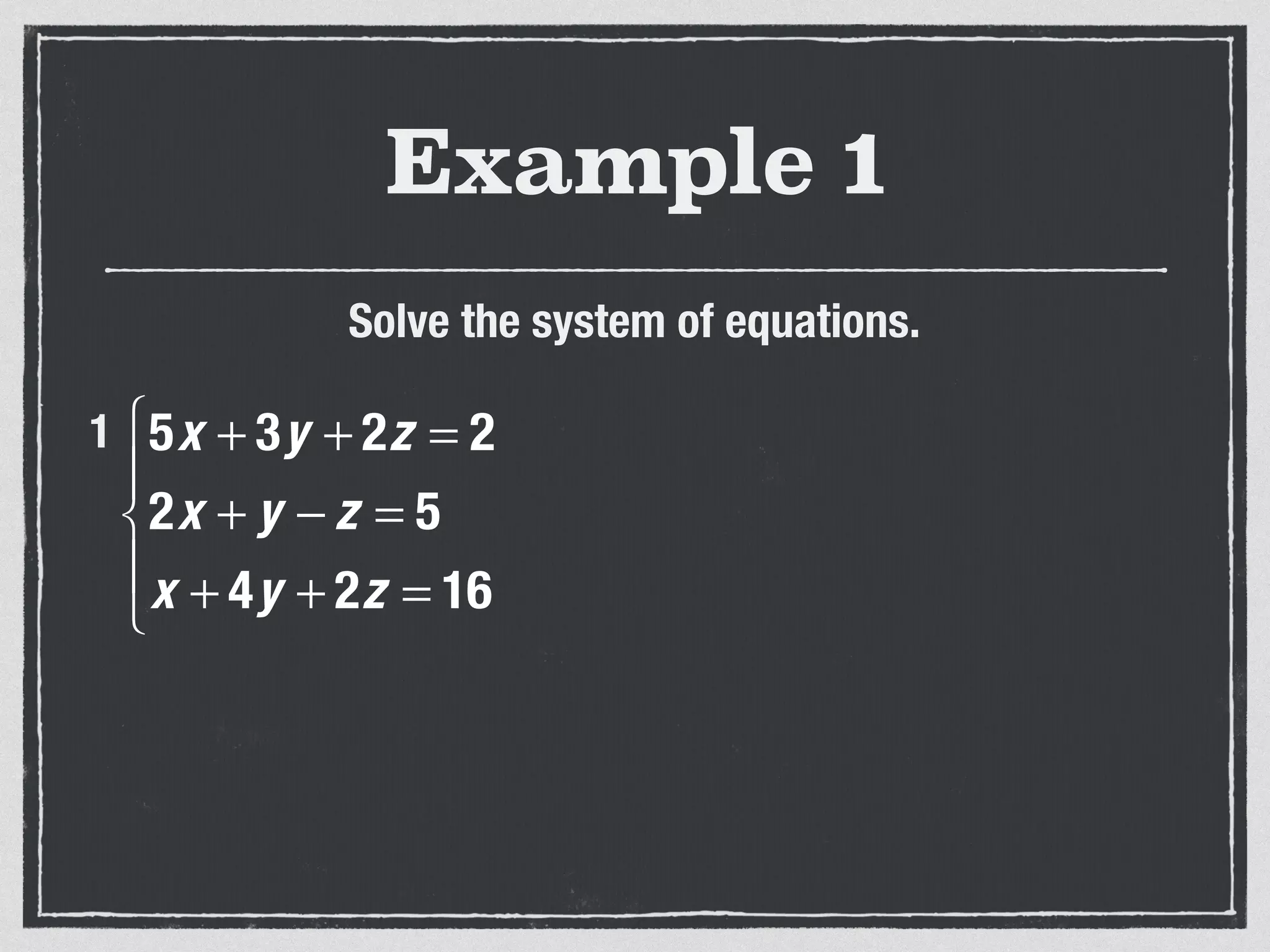
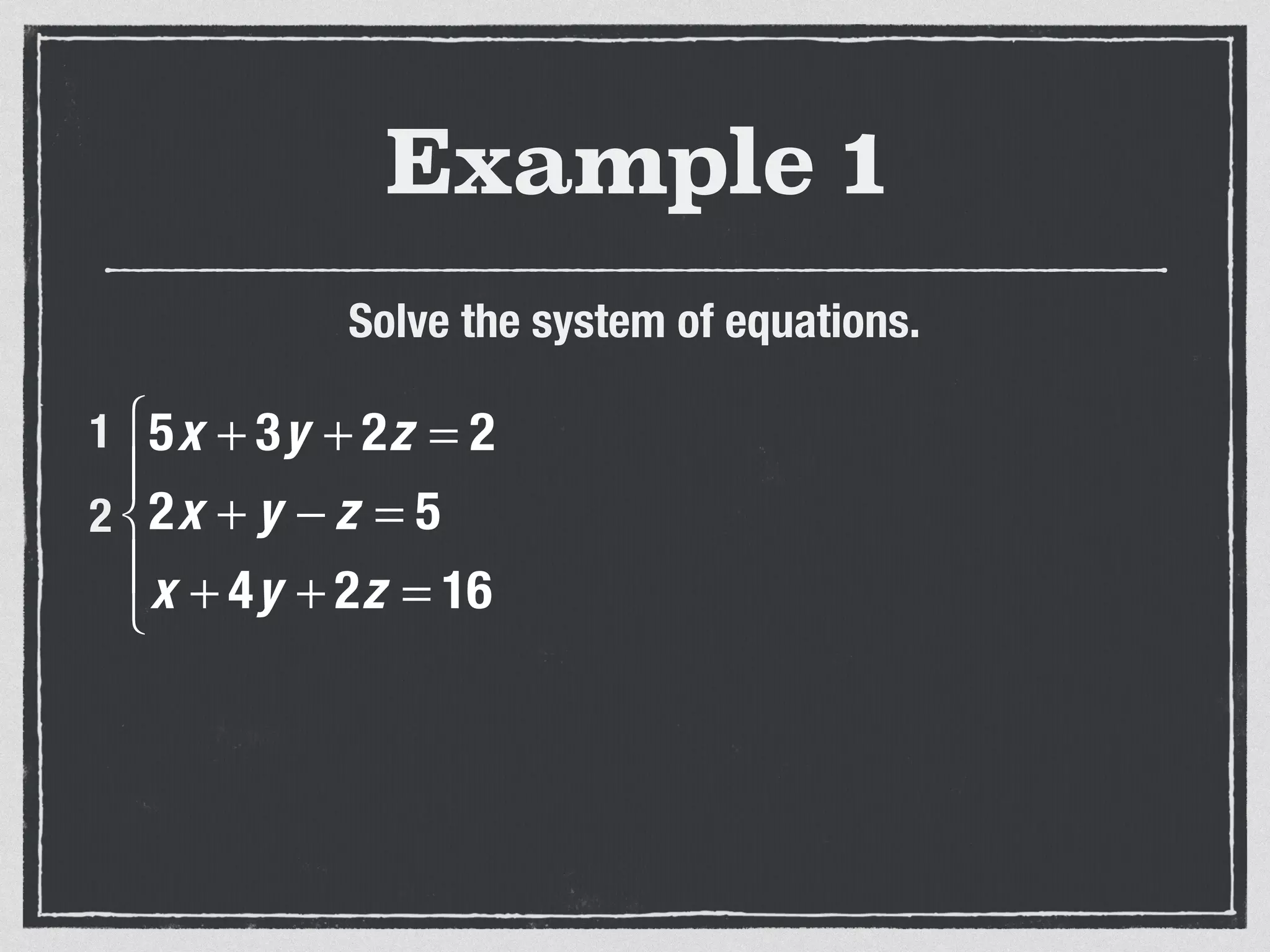
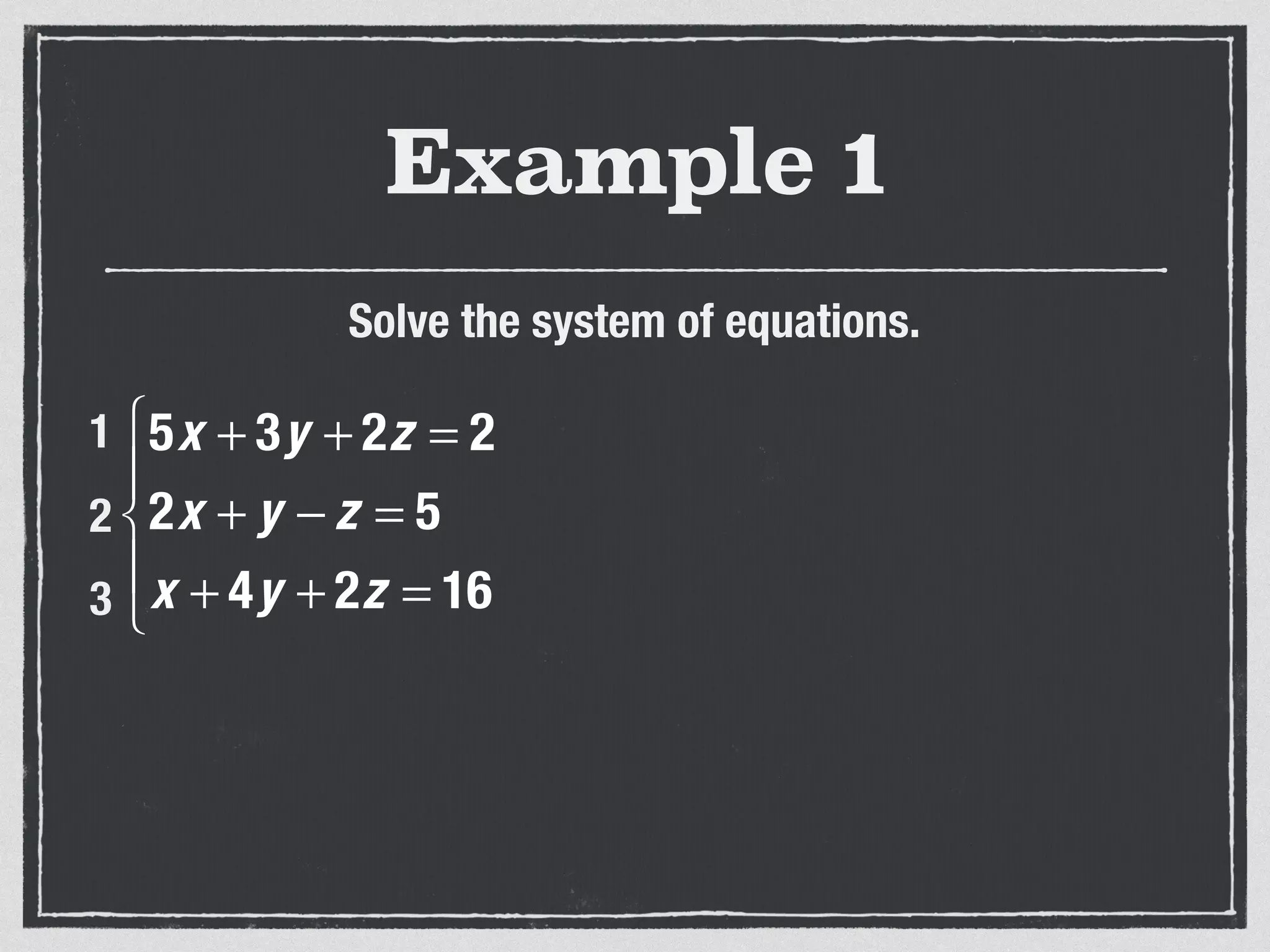
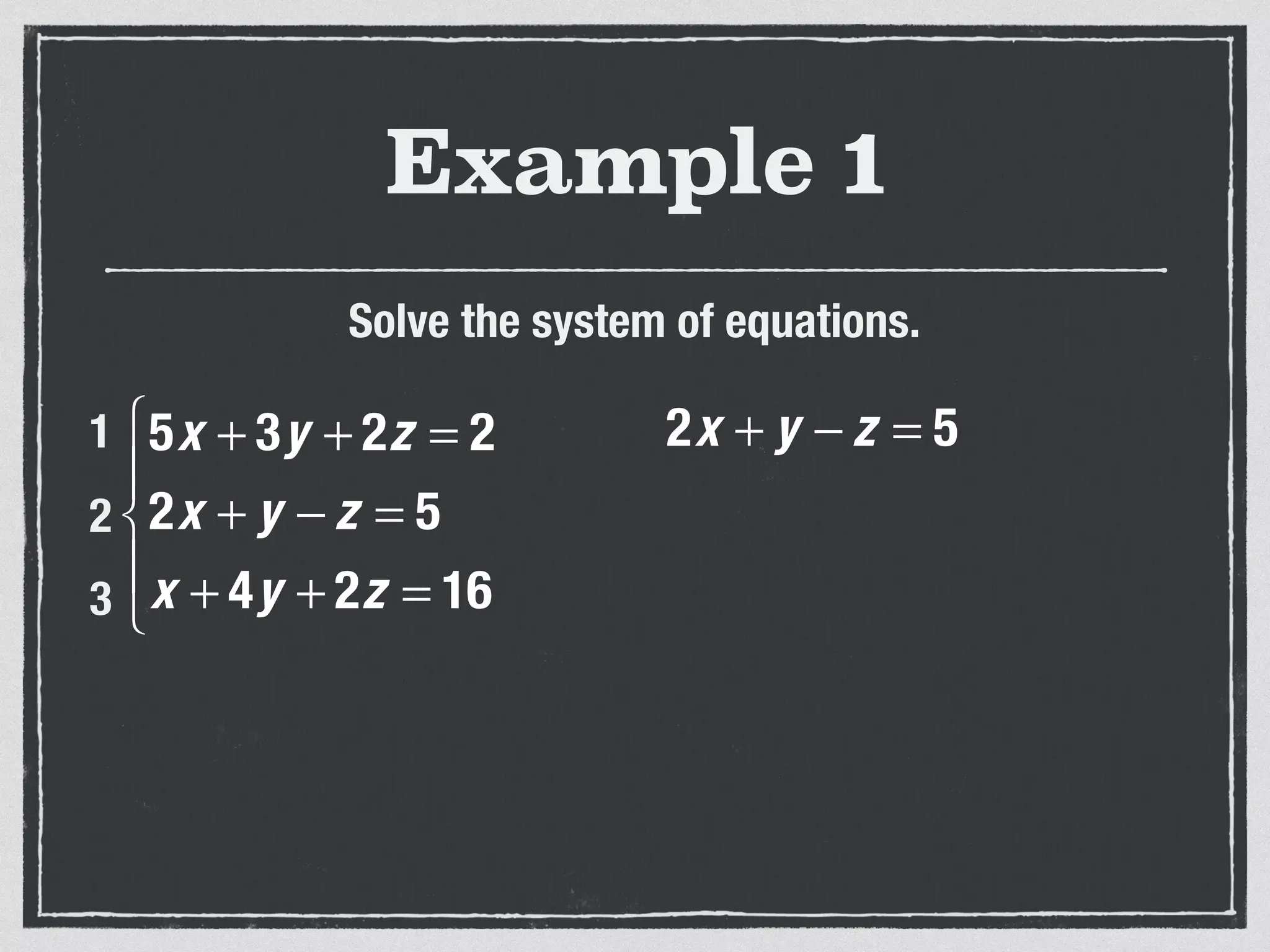
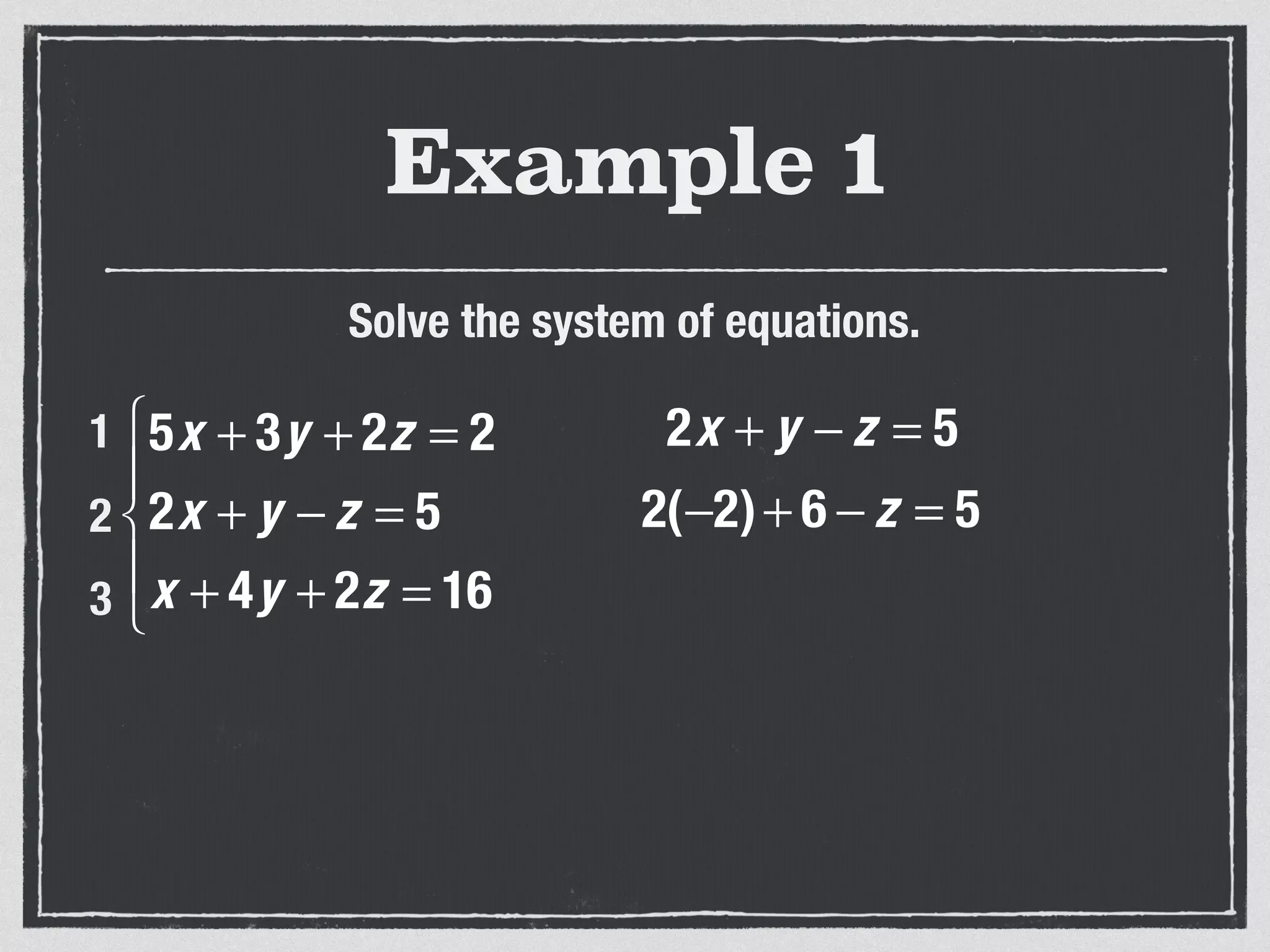
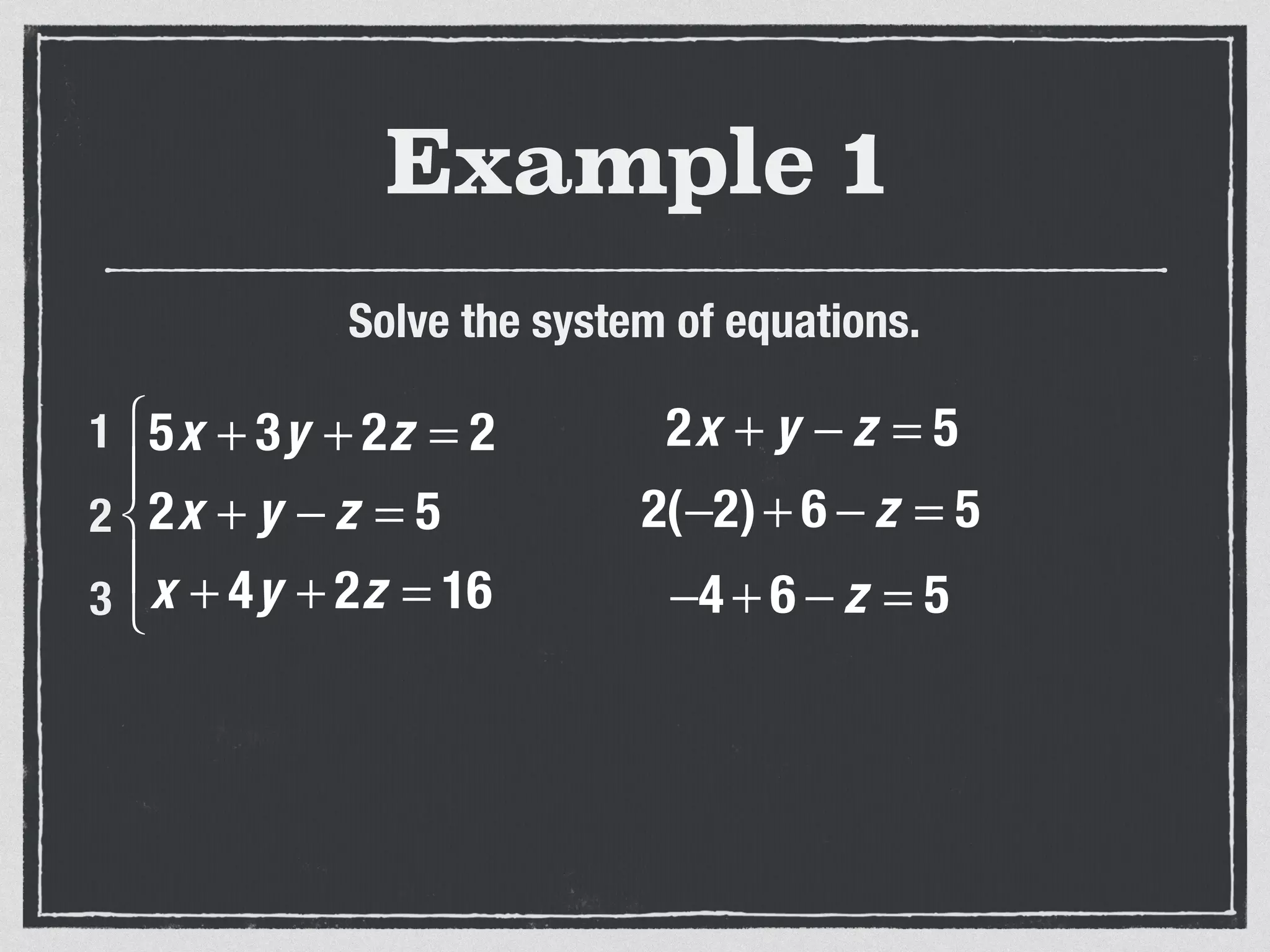
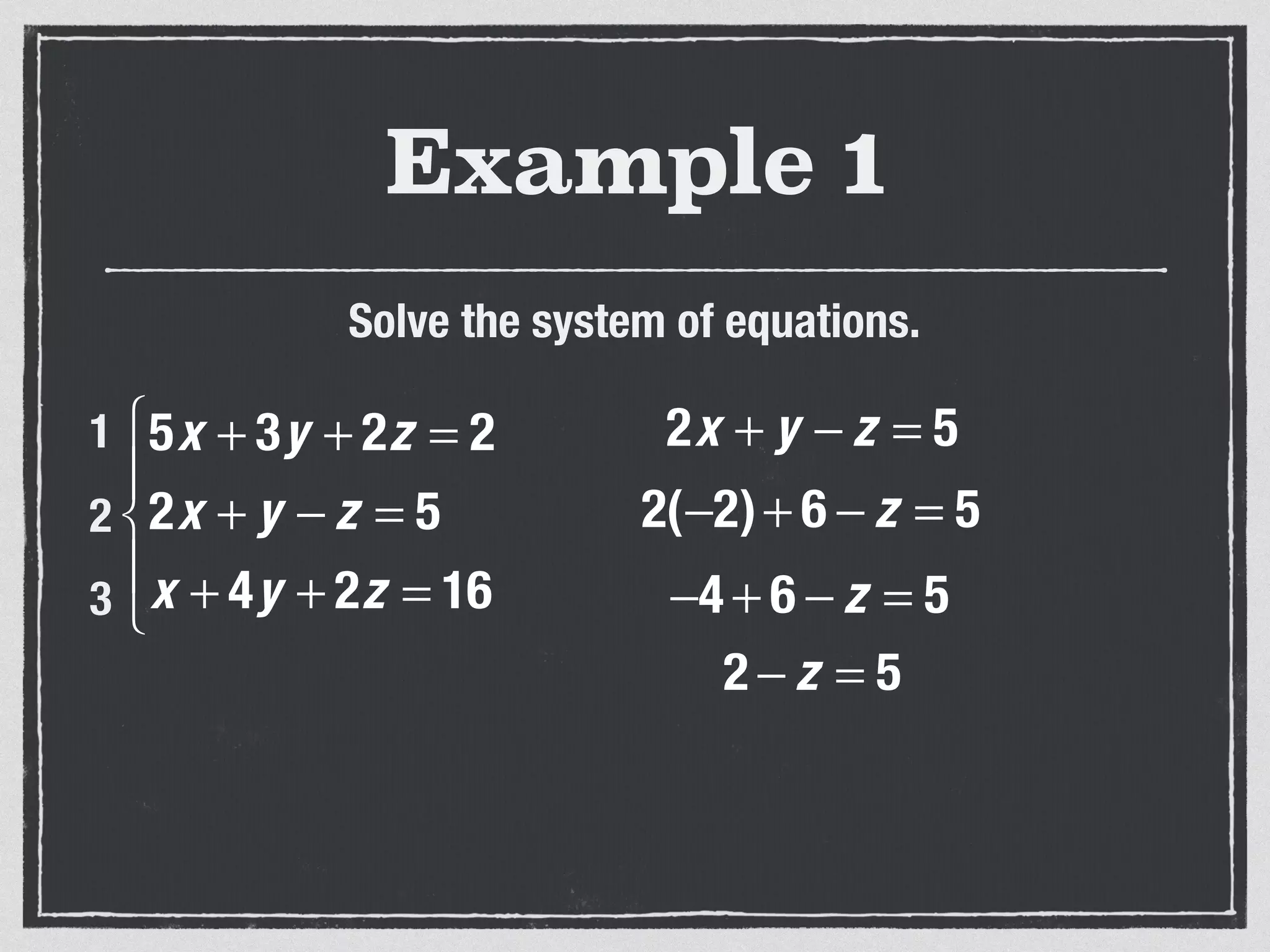
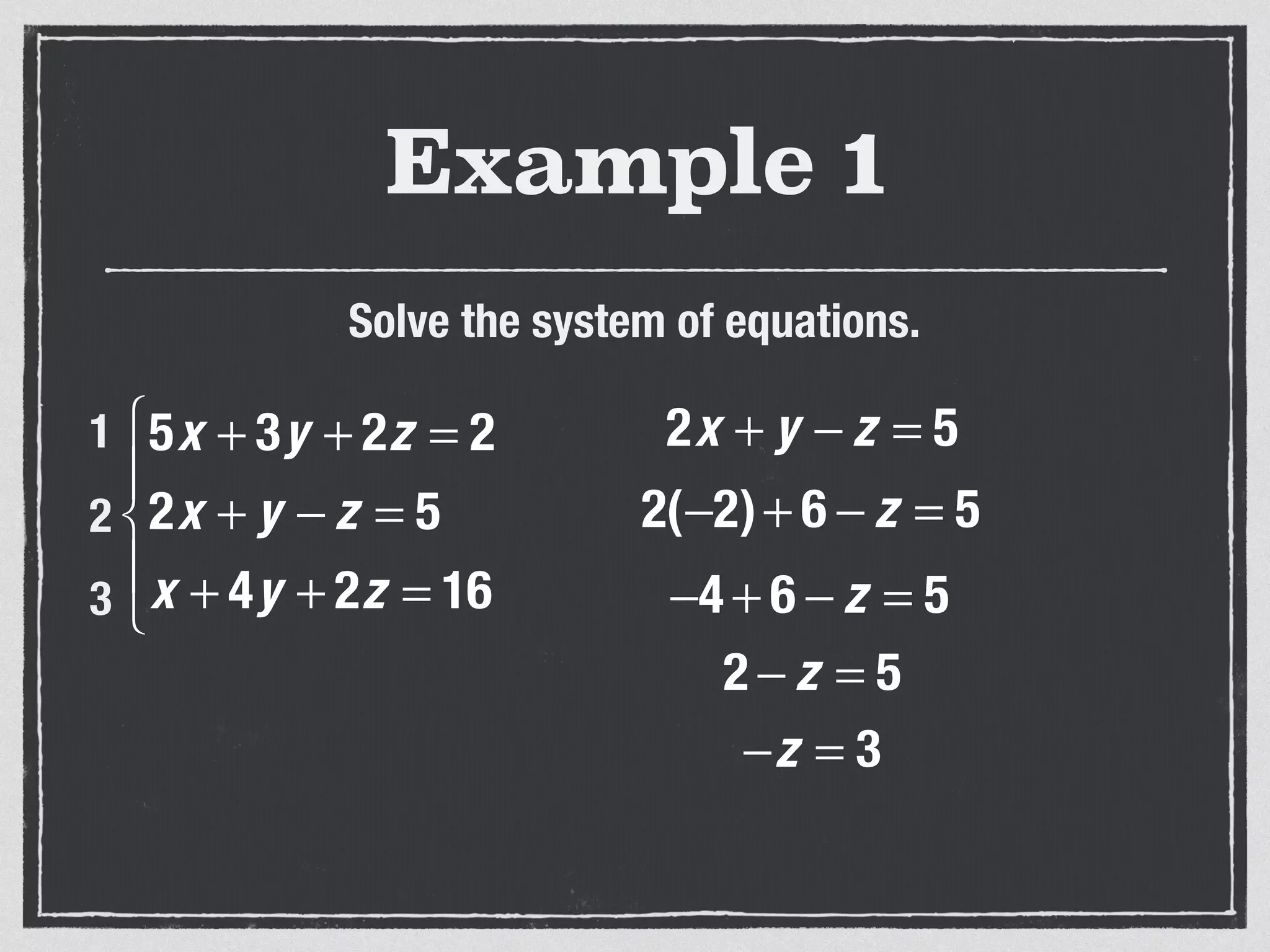
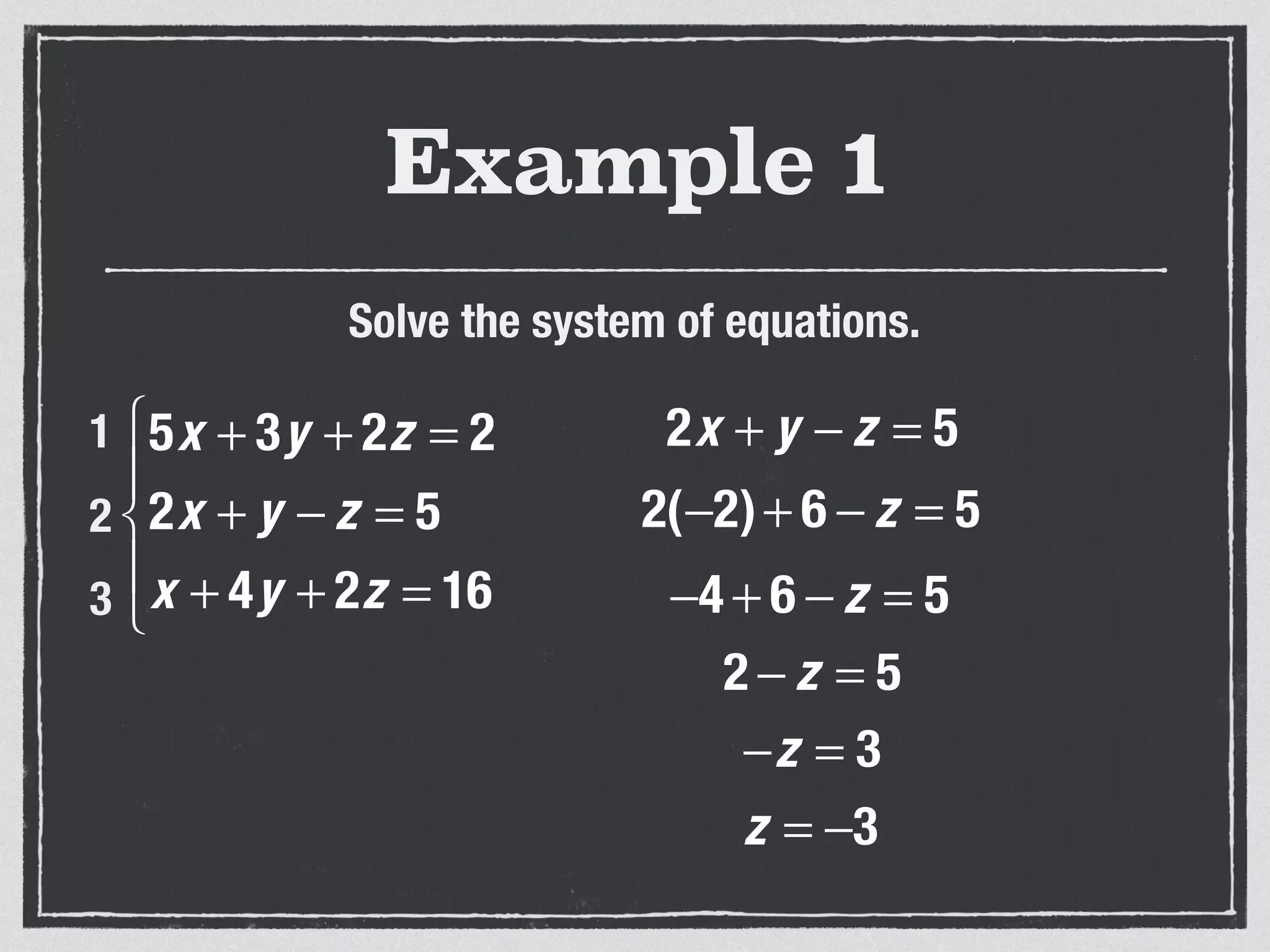
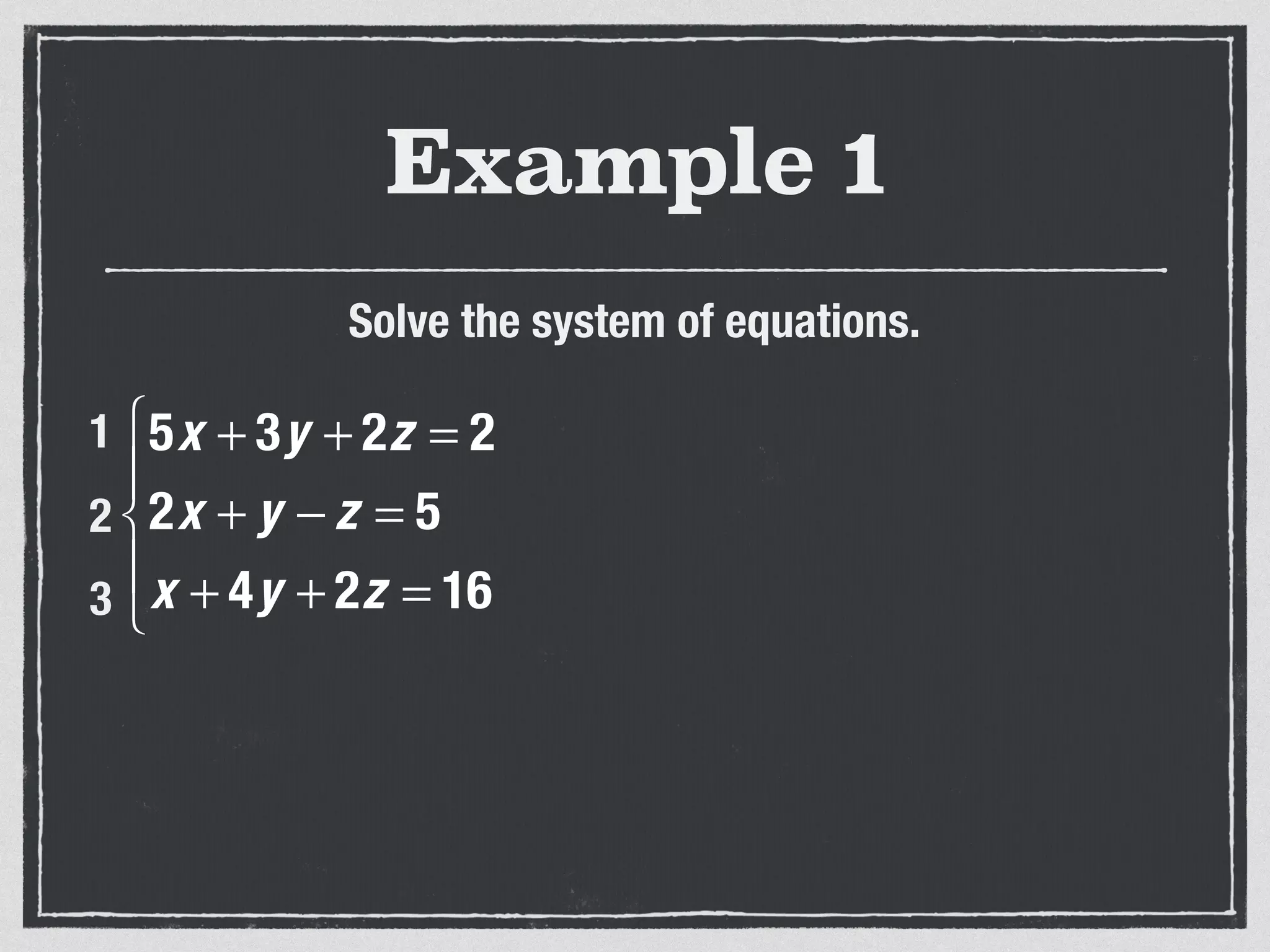
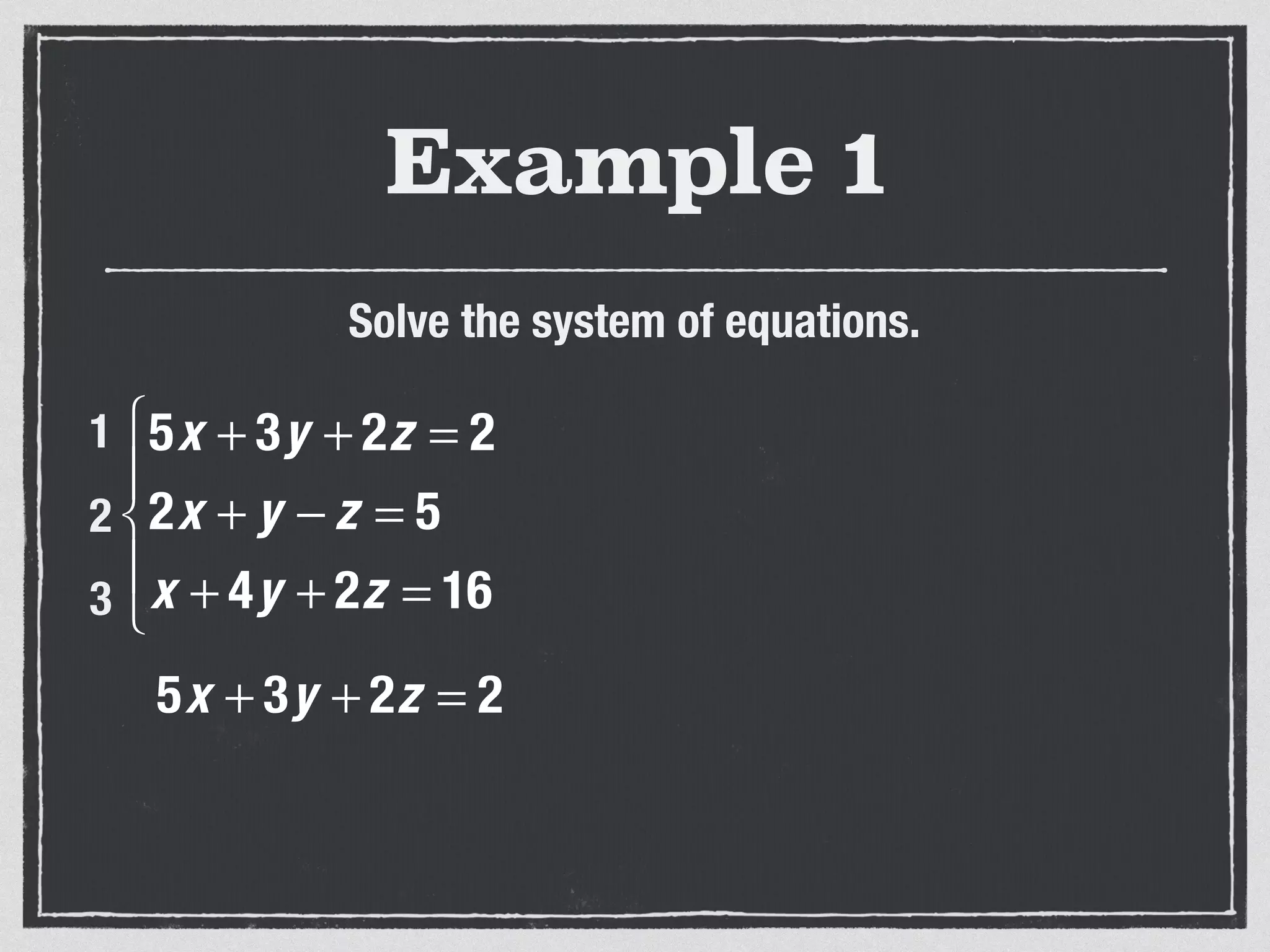
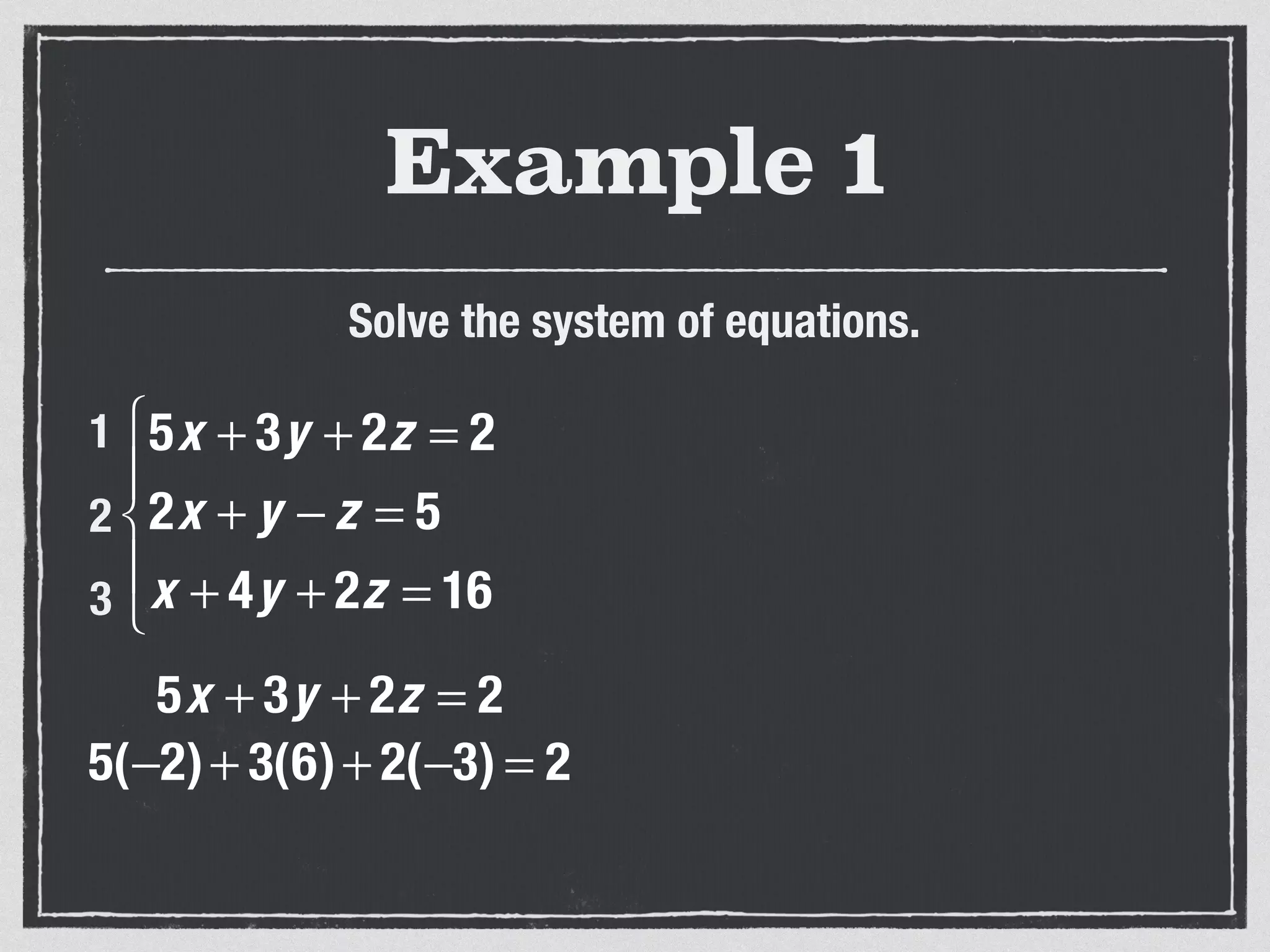
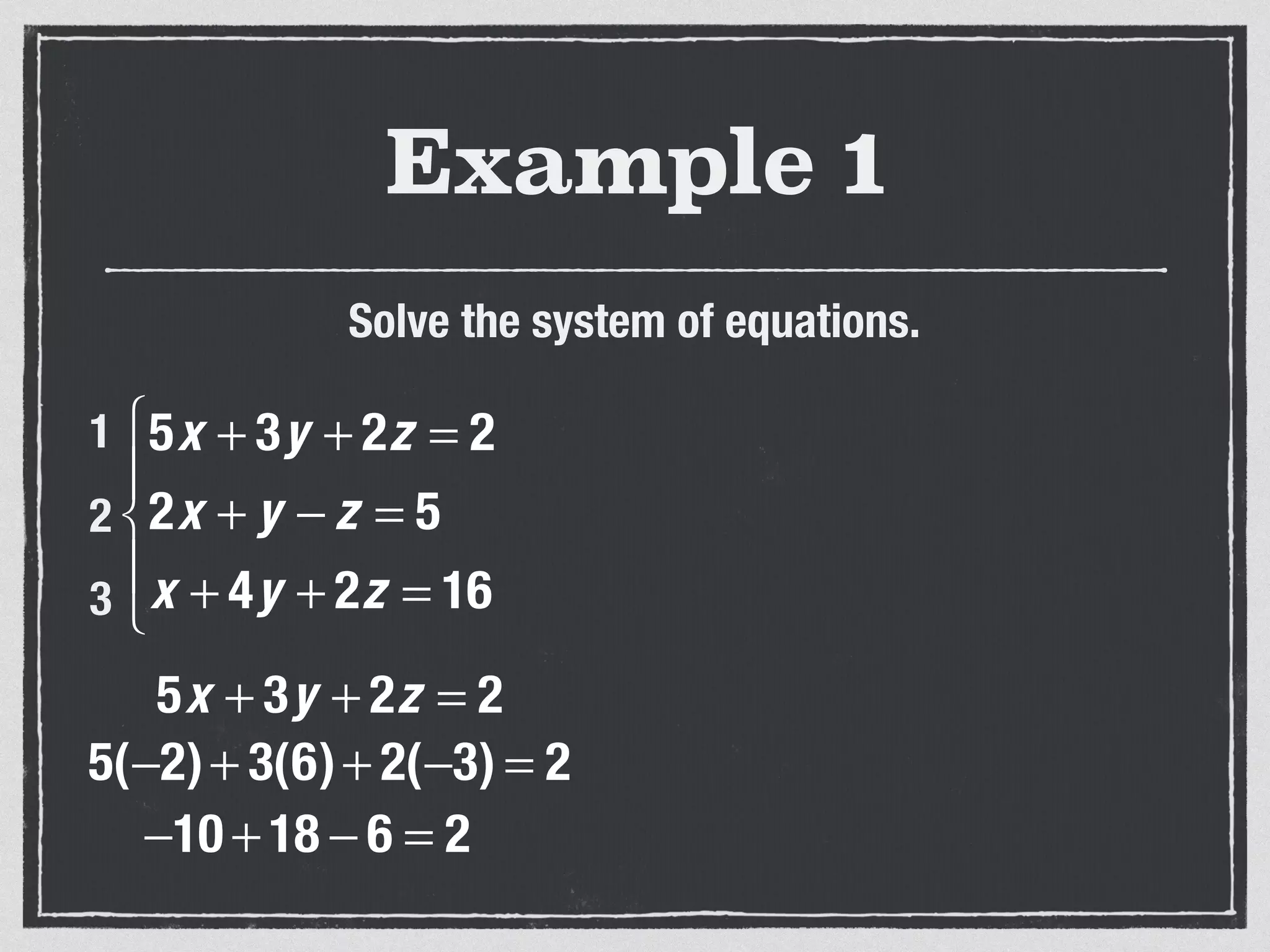
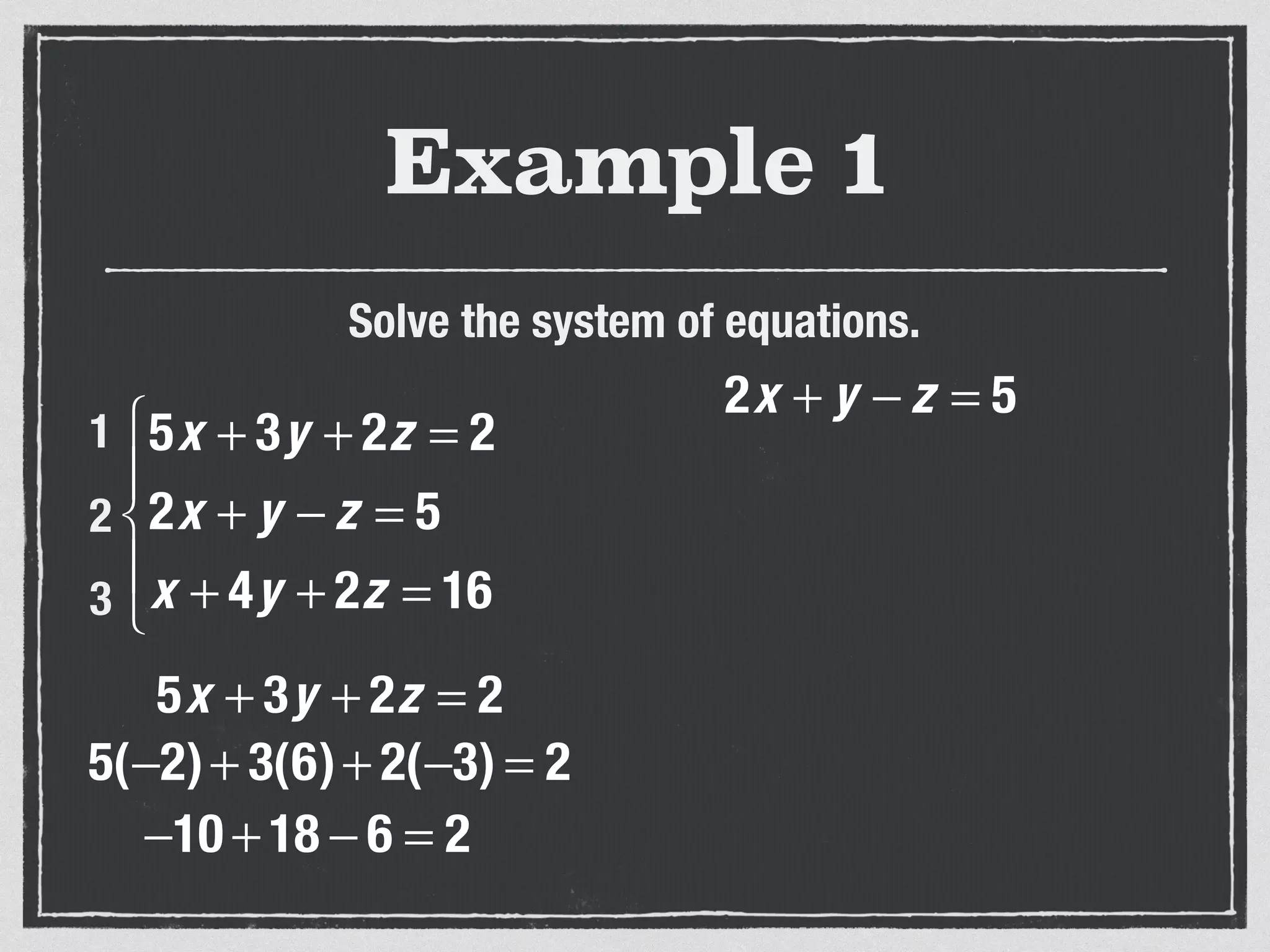
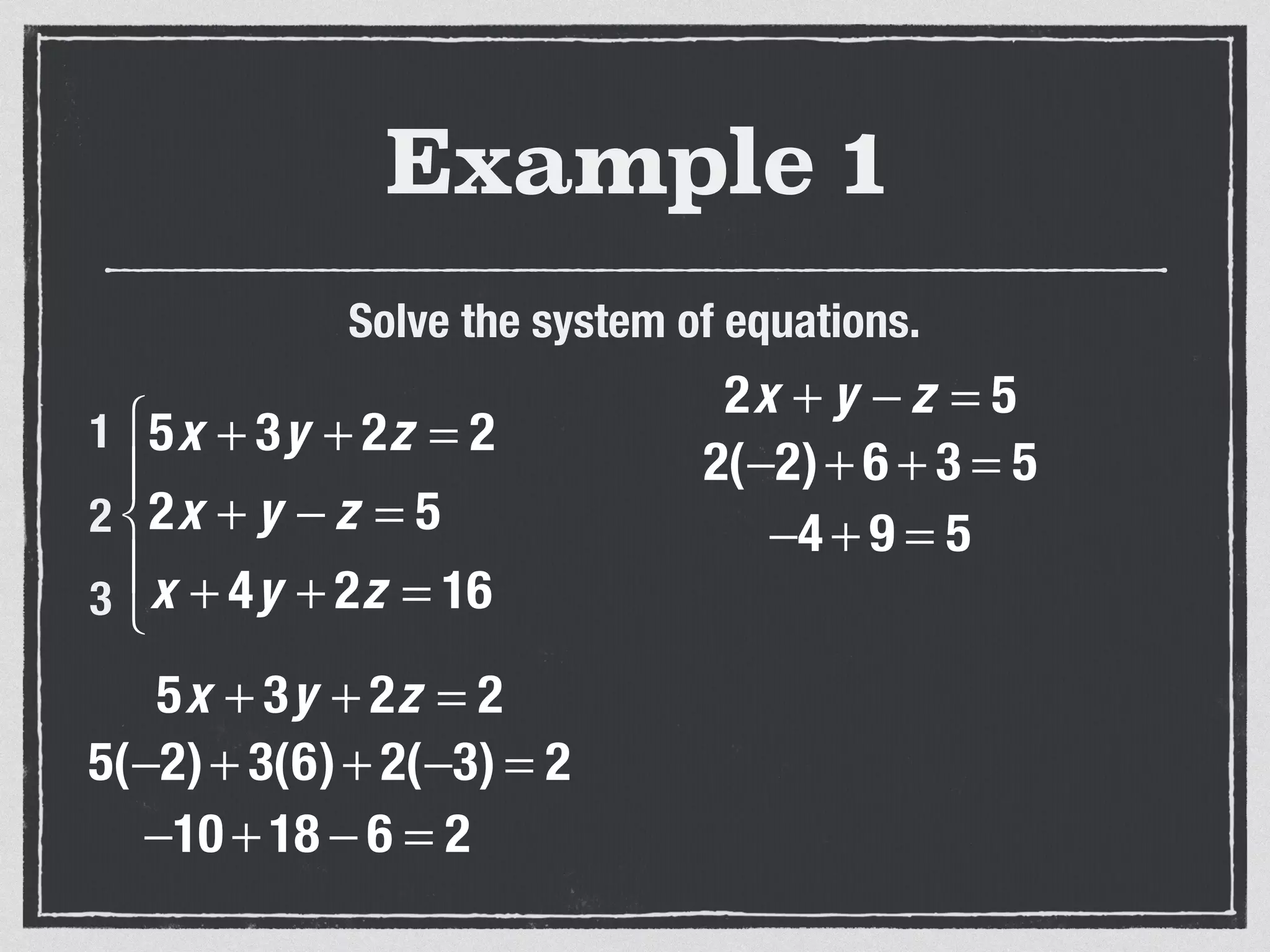
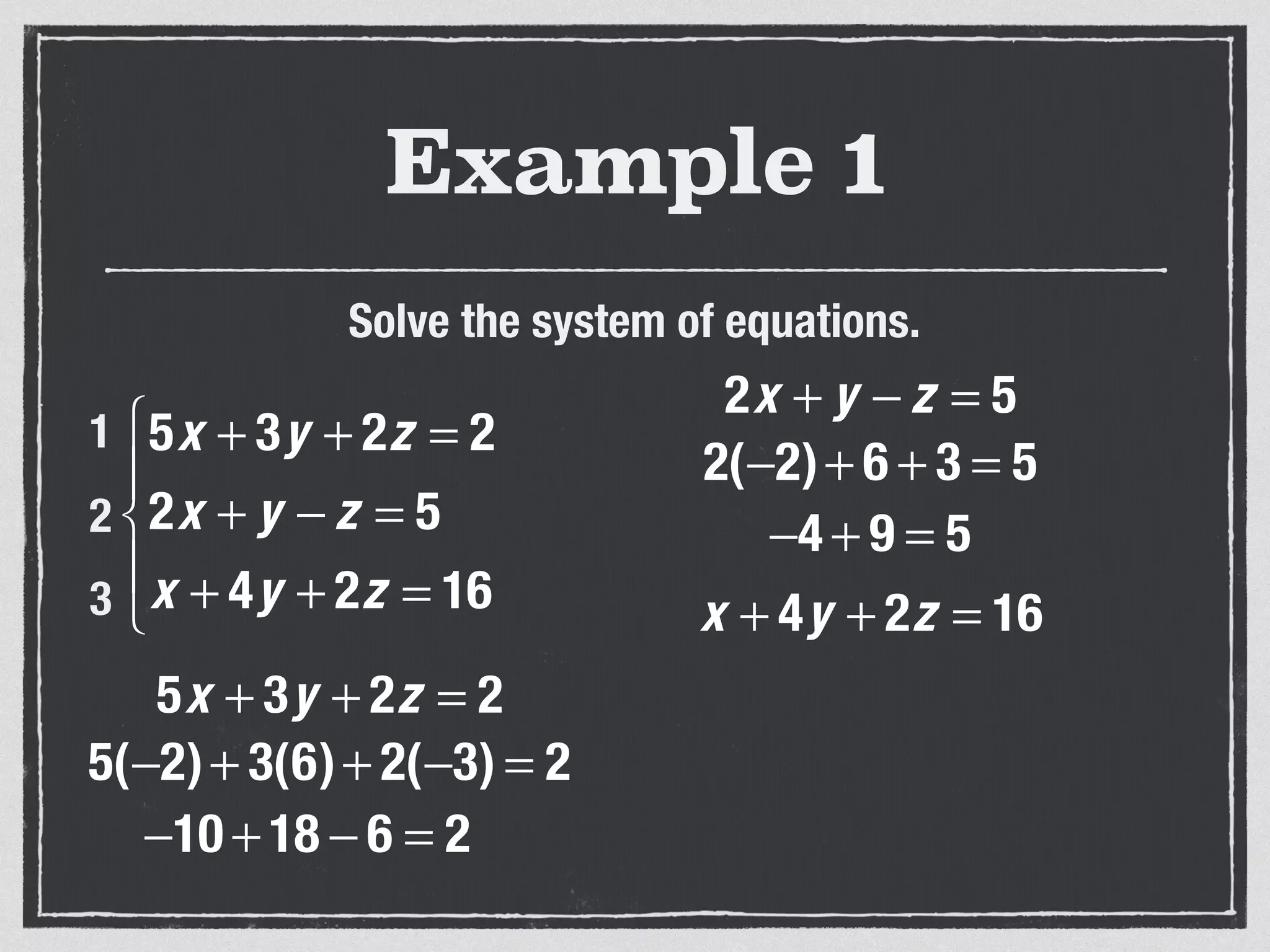
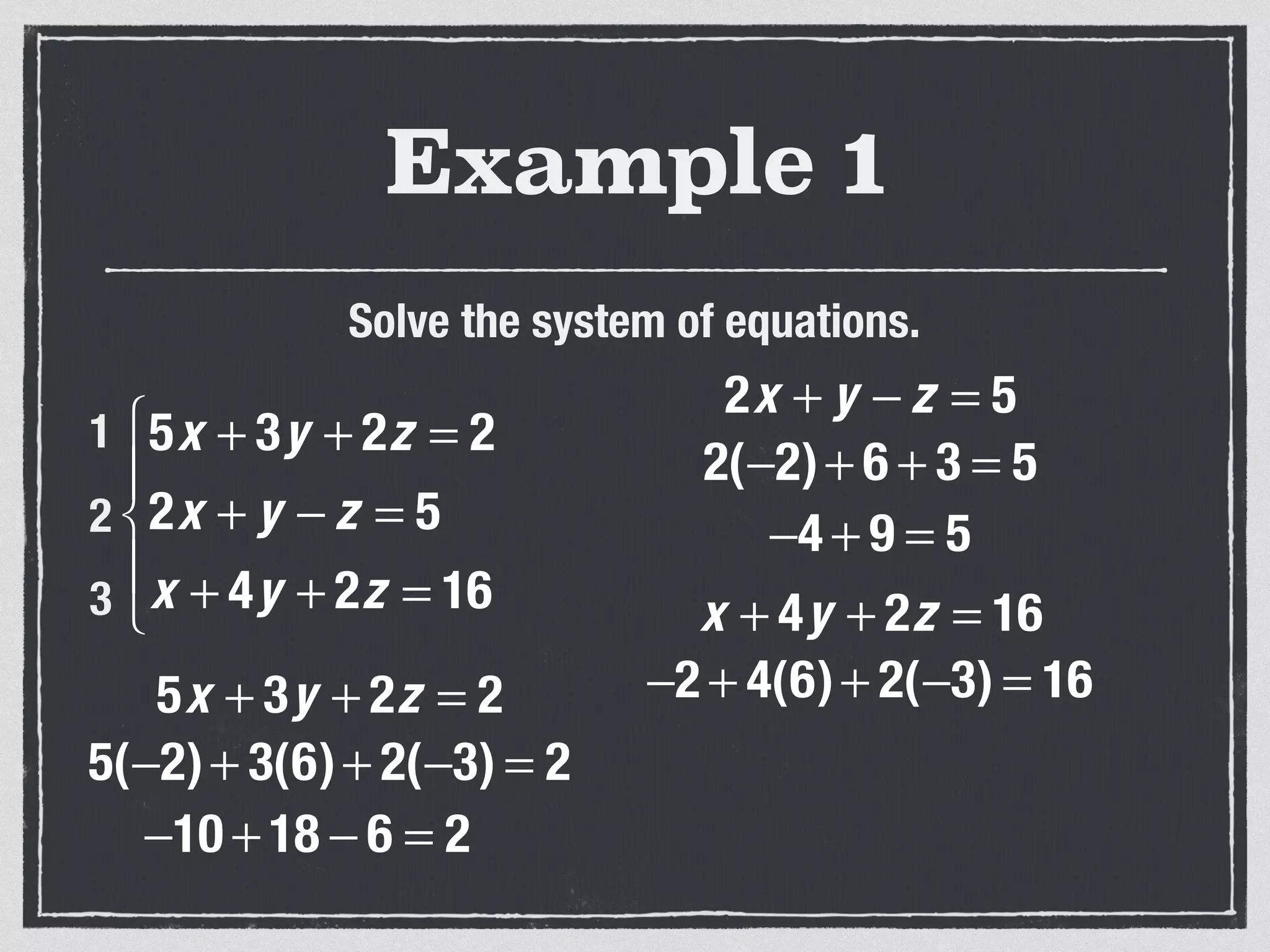
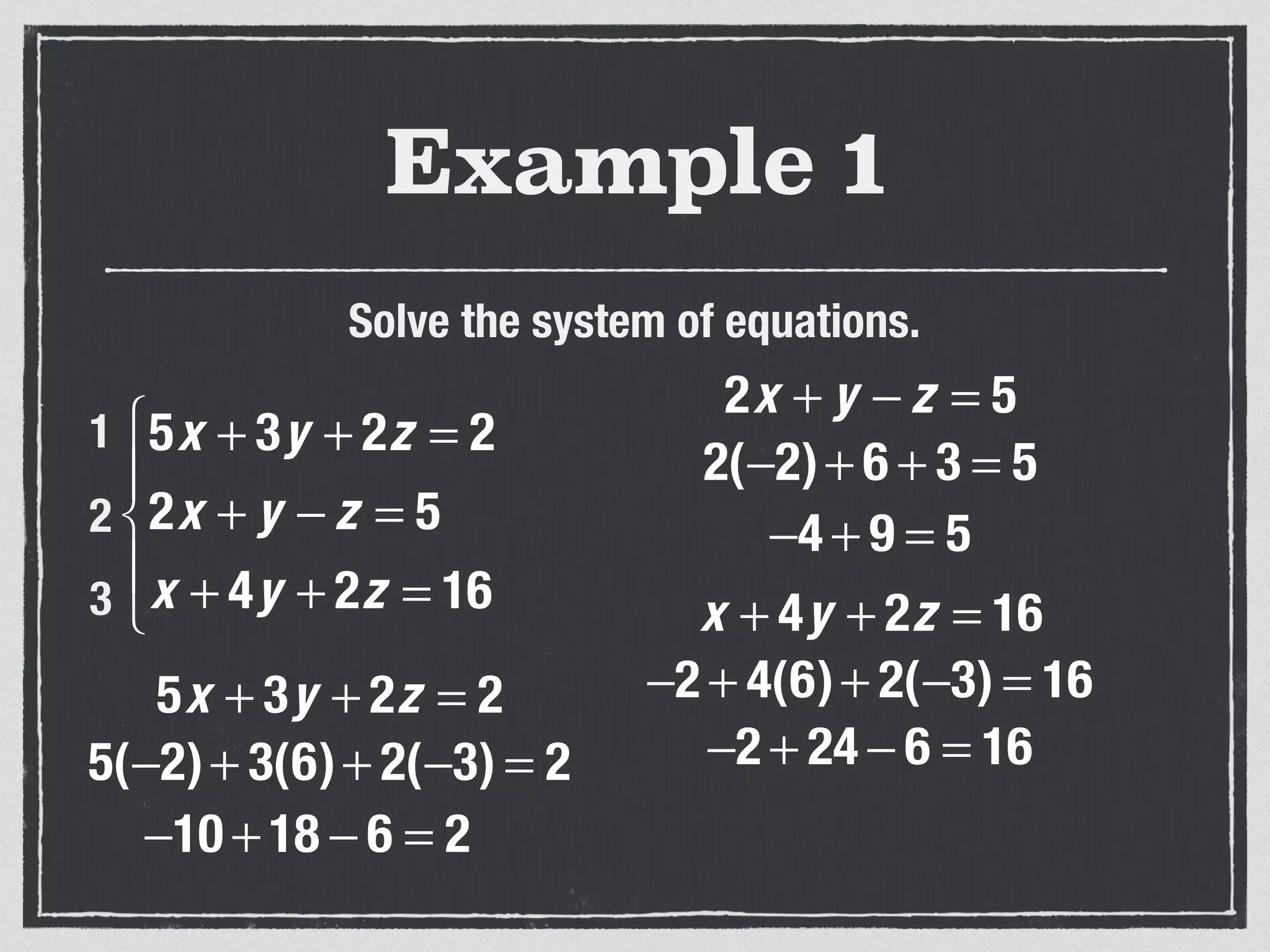
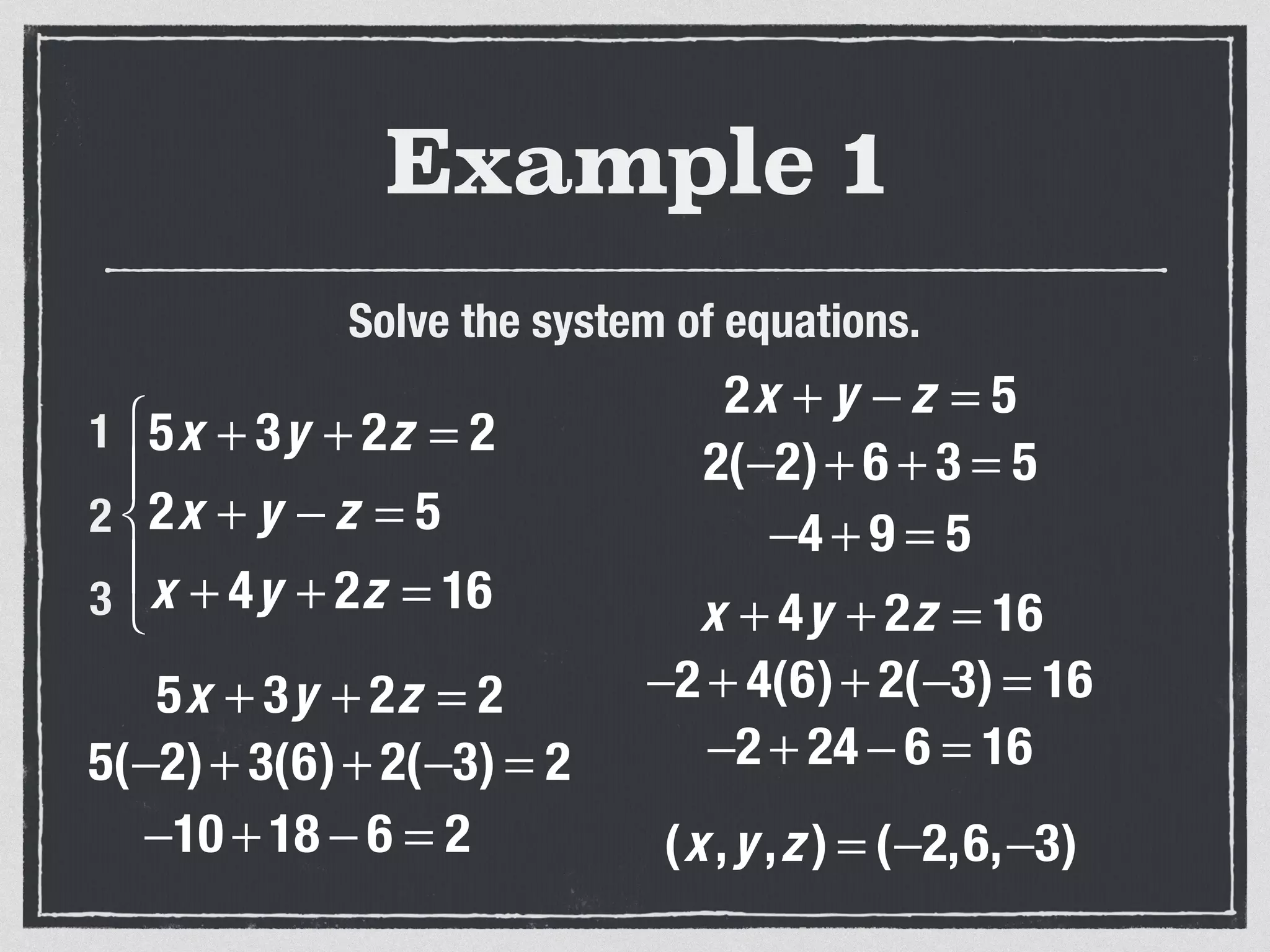
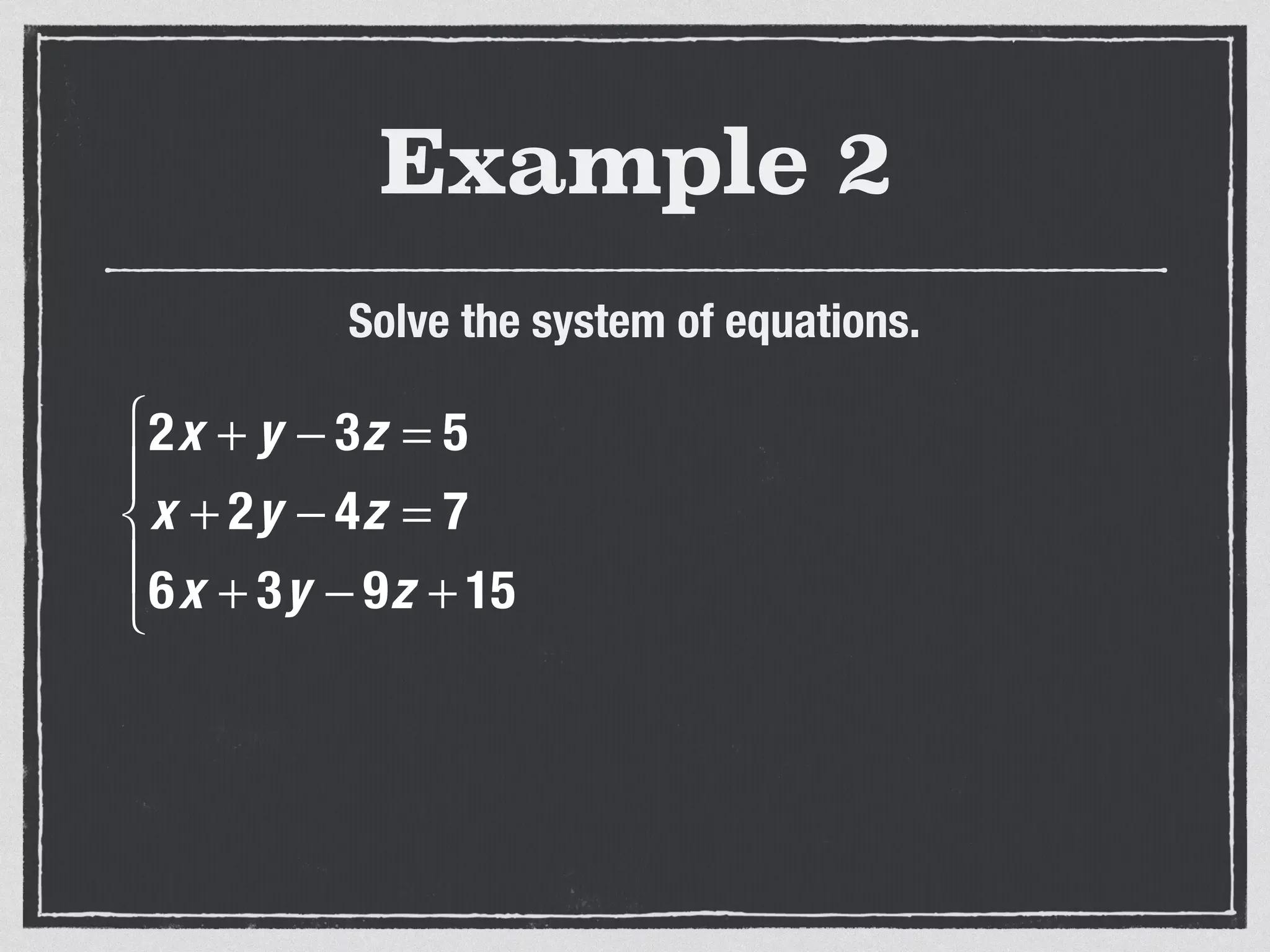
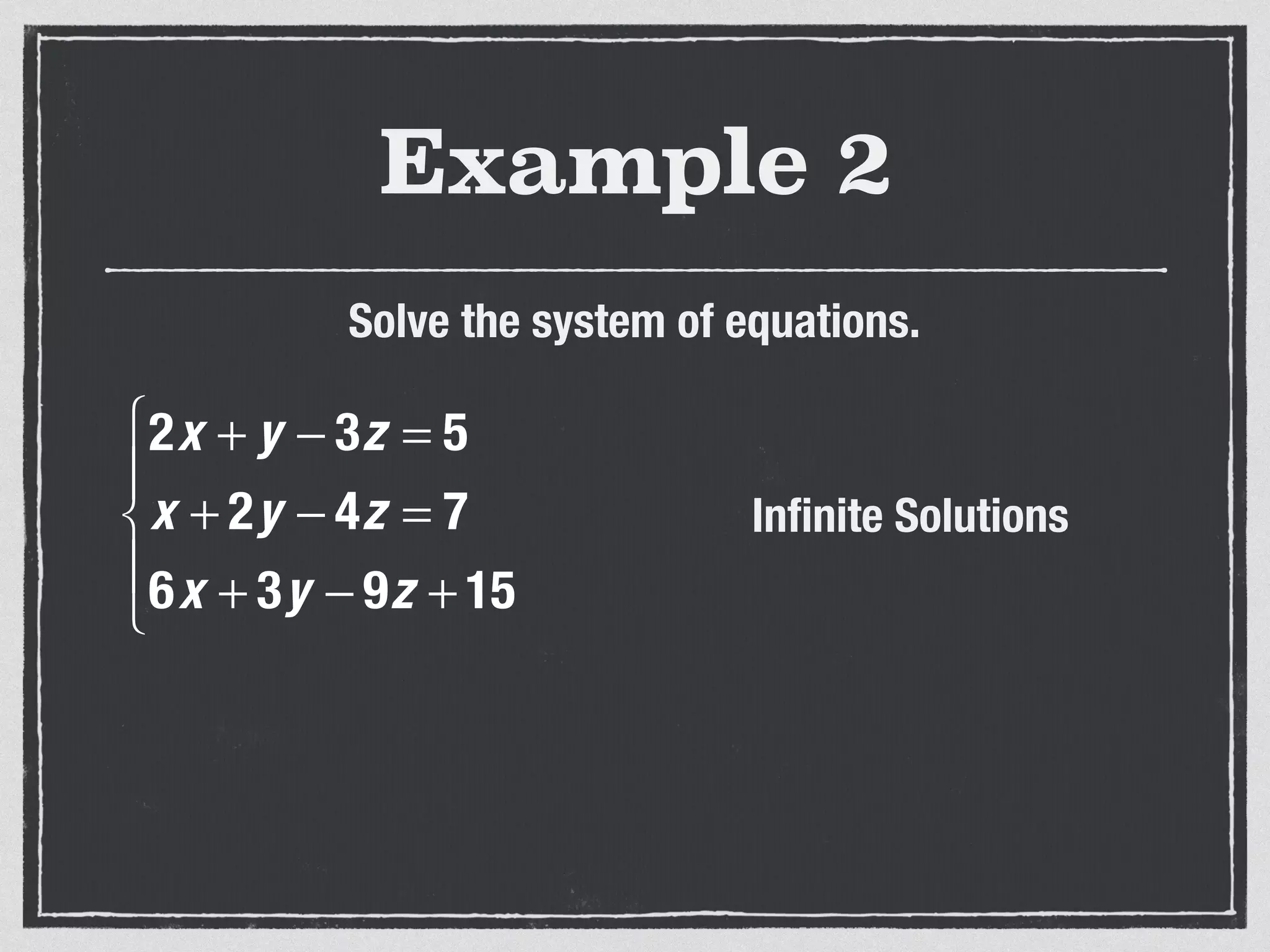
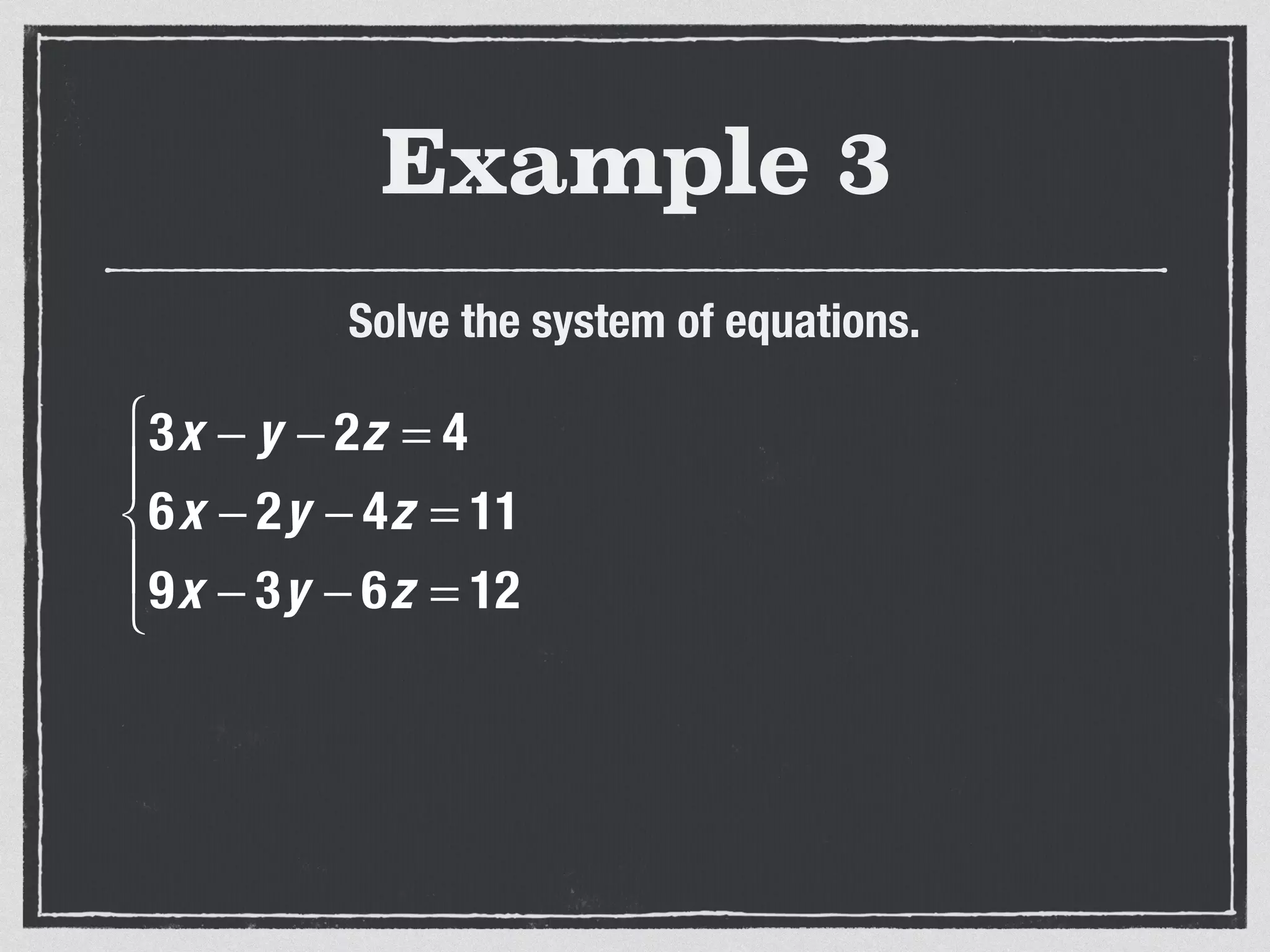
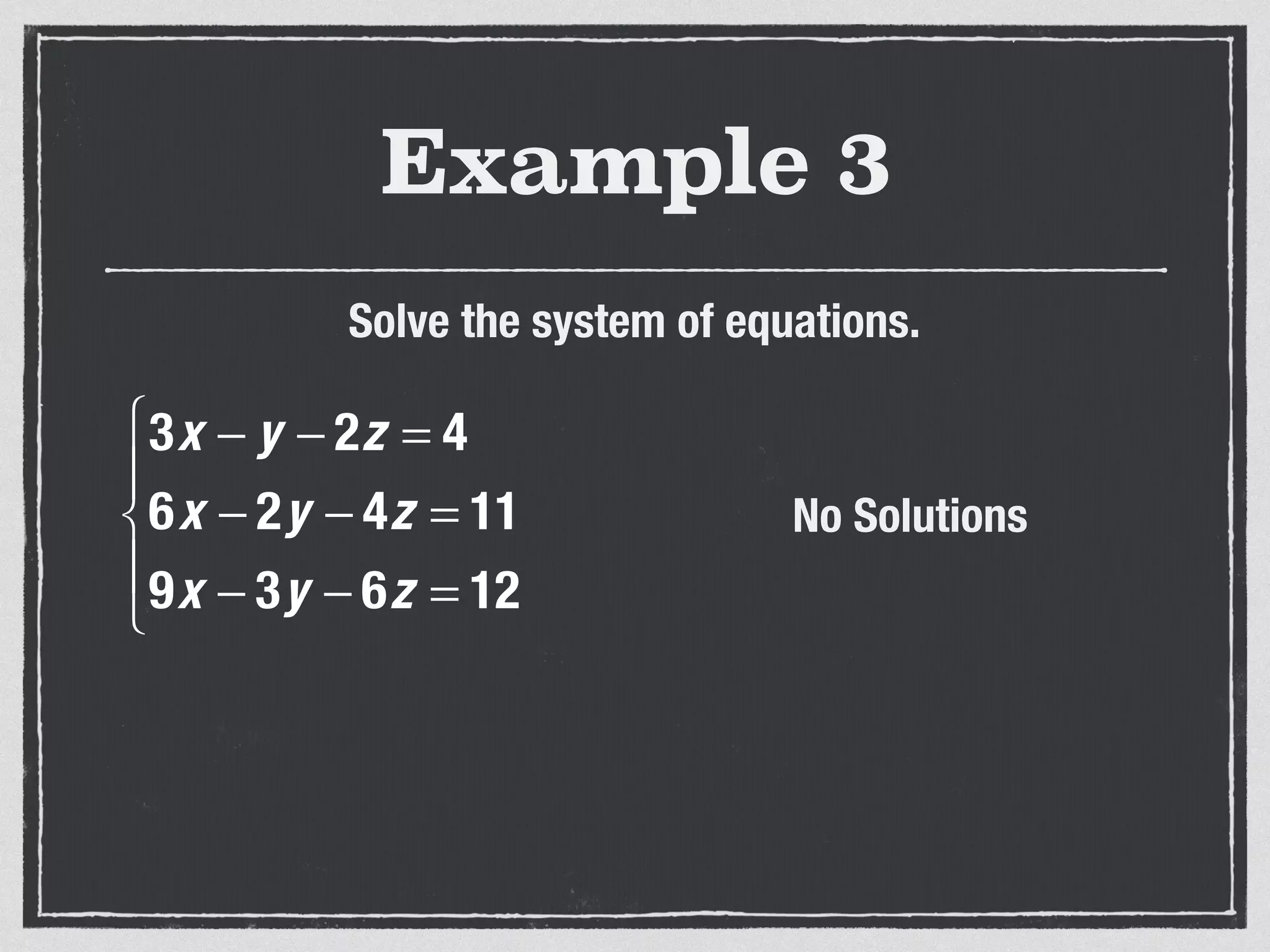
This document provides an example of solving a system of 3 linear equations in 3 variables. It shows setting the equations equal to each other to eliminate variables, resulting in a single variable that can be solved for. Plugging this solution back into the original equations finds the solutions for the other 2 variables, providing the ordered triple solution. The example solves for x = -2, y = 6, z = 4.