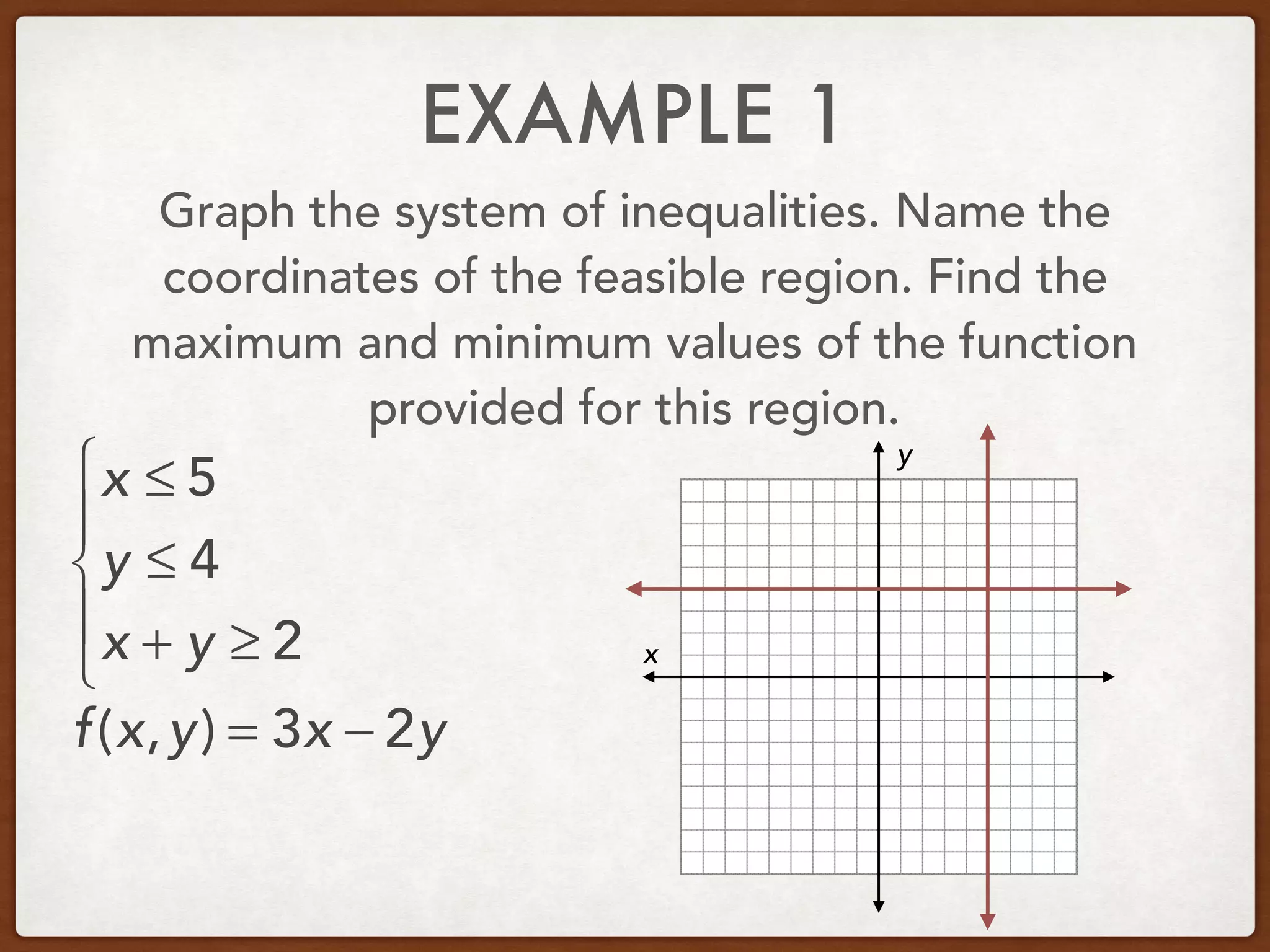
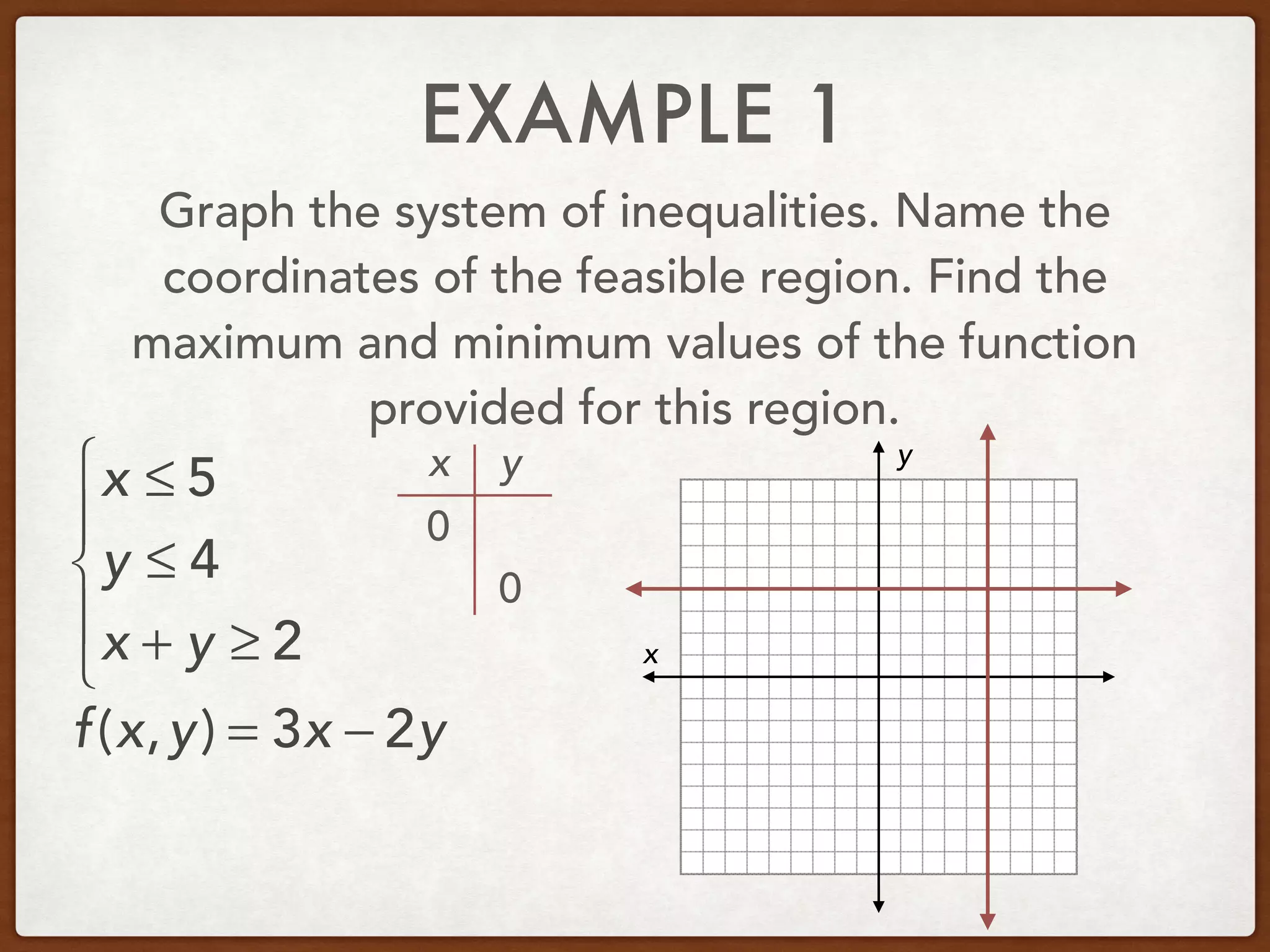
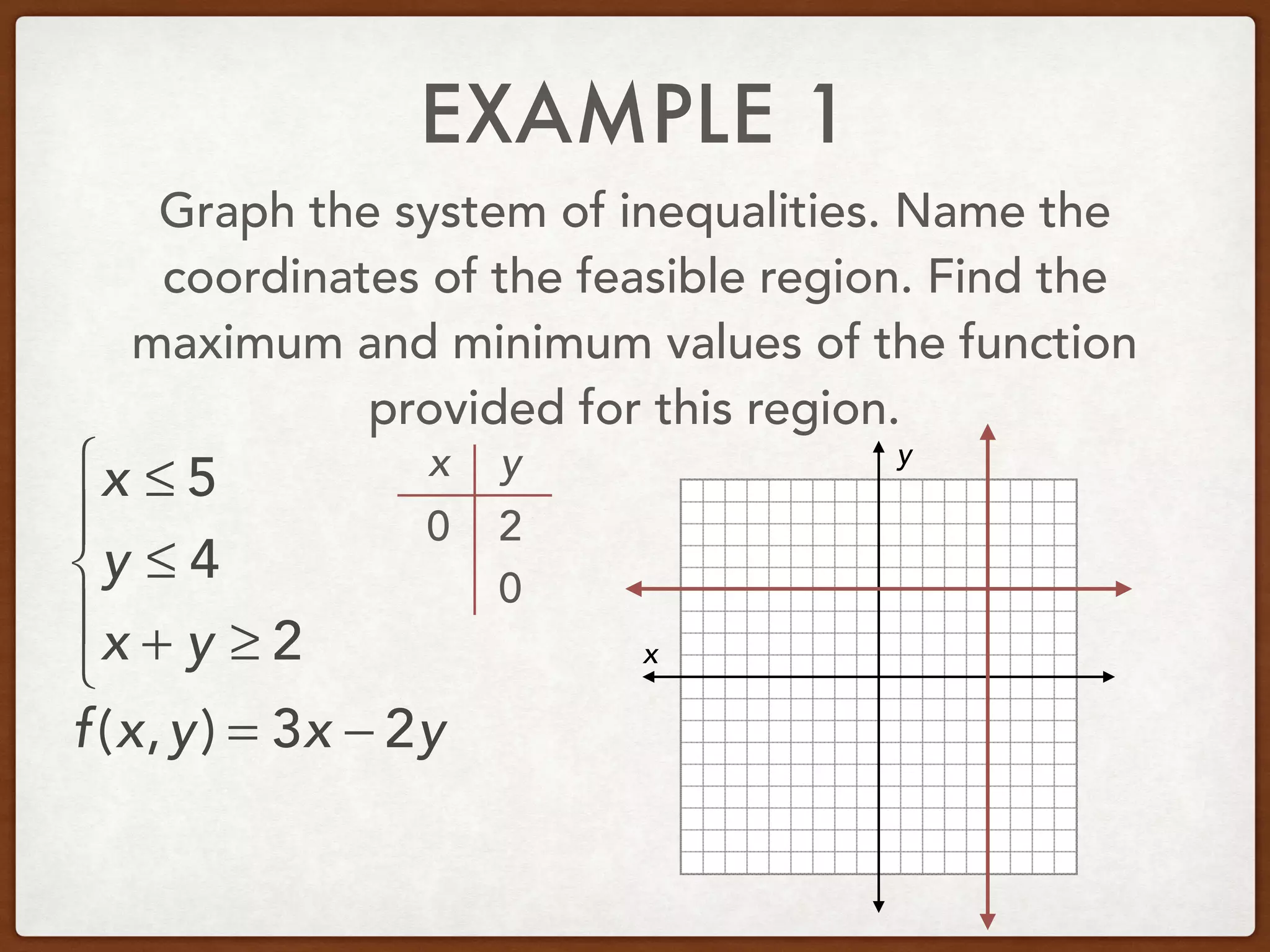
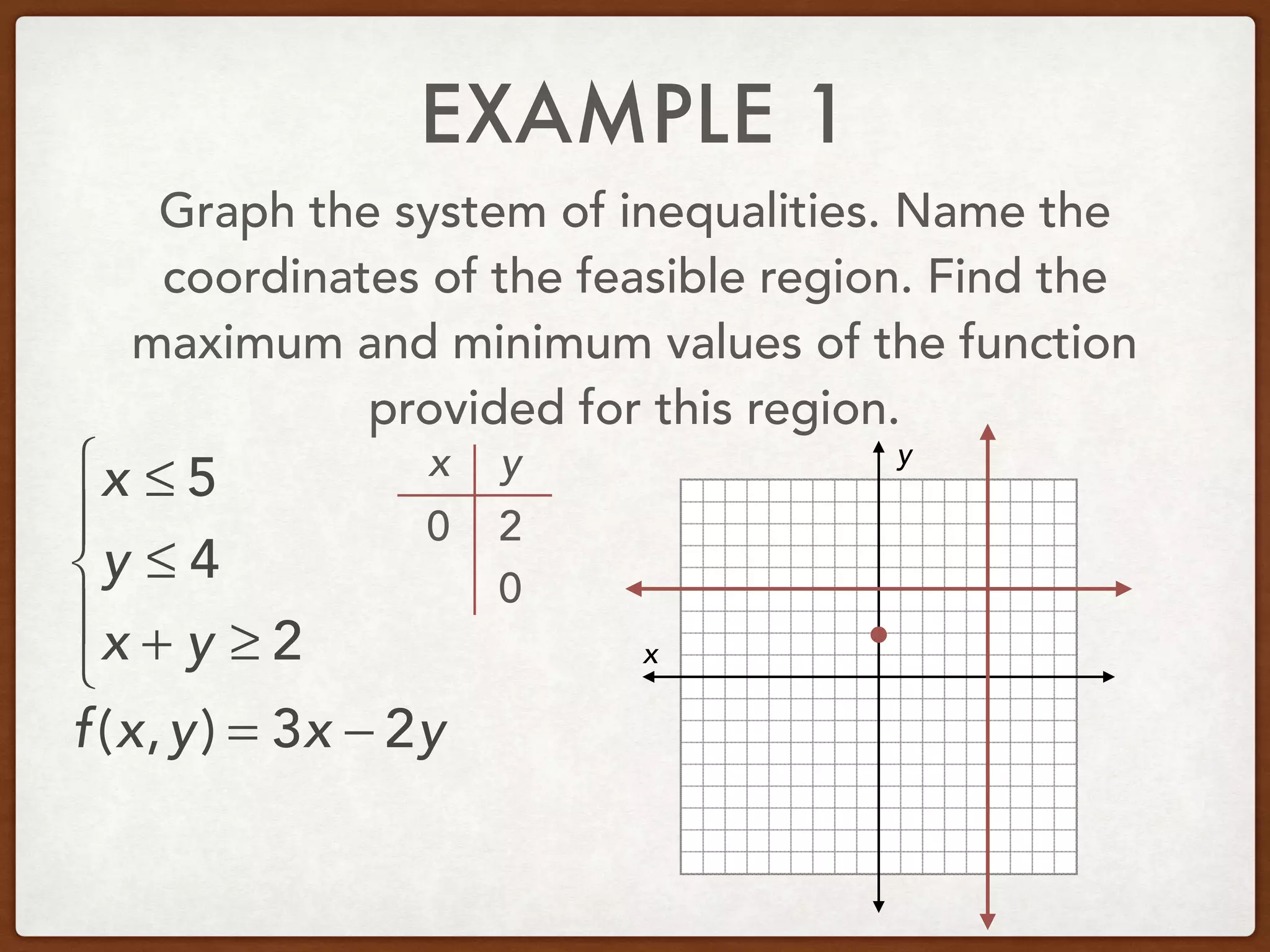
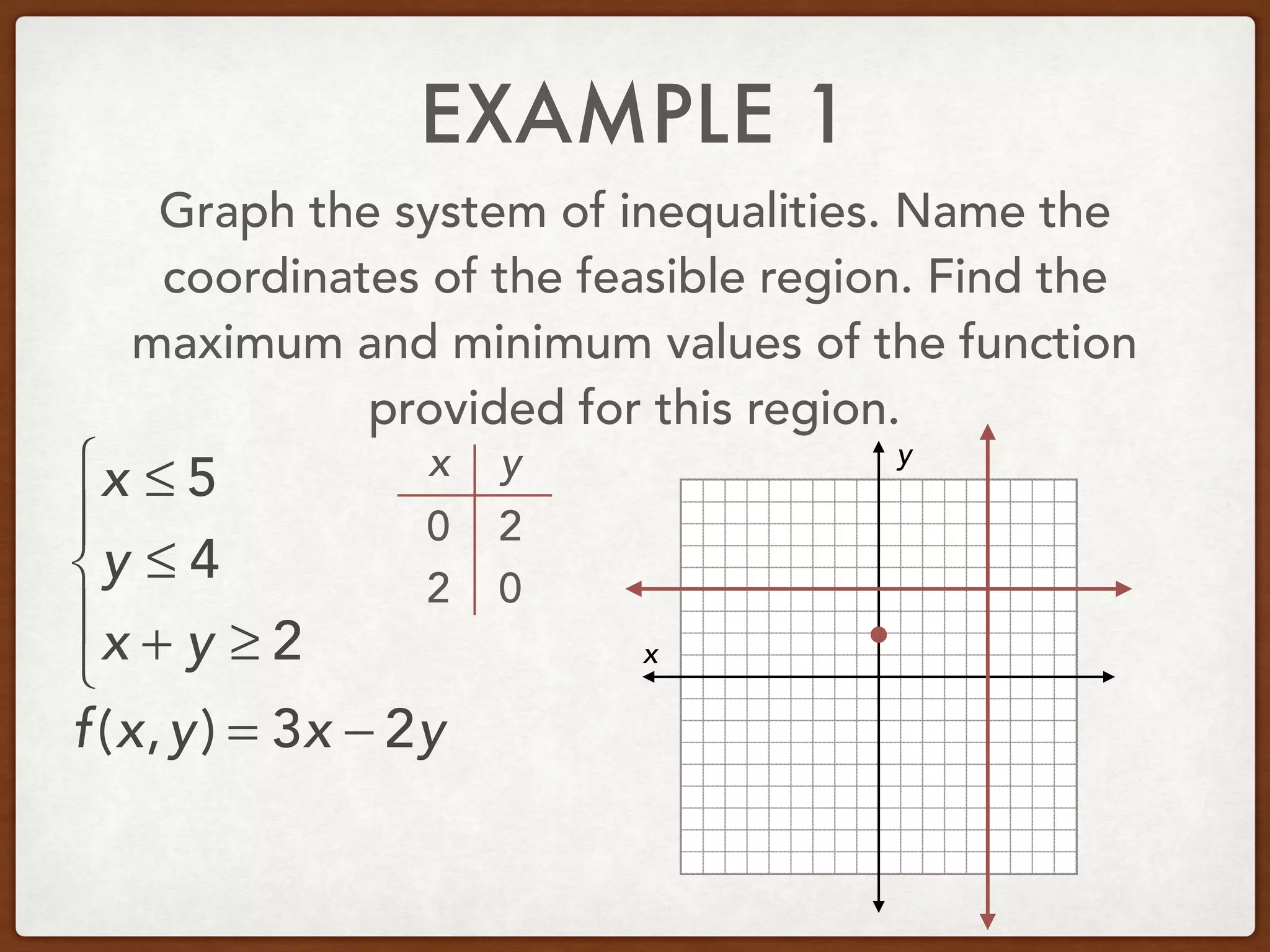
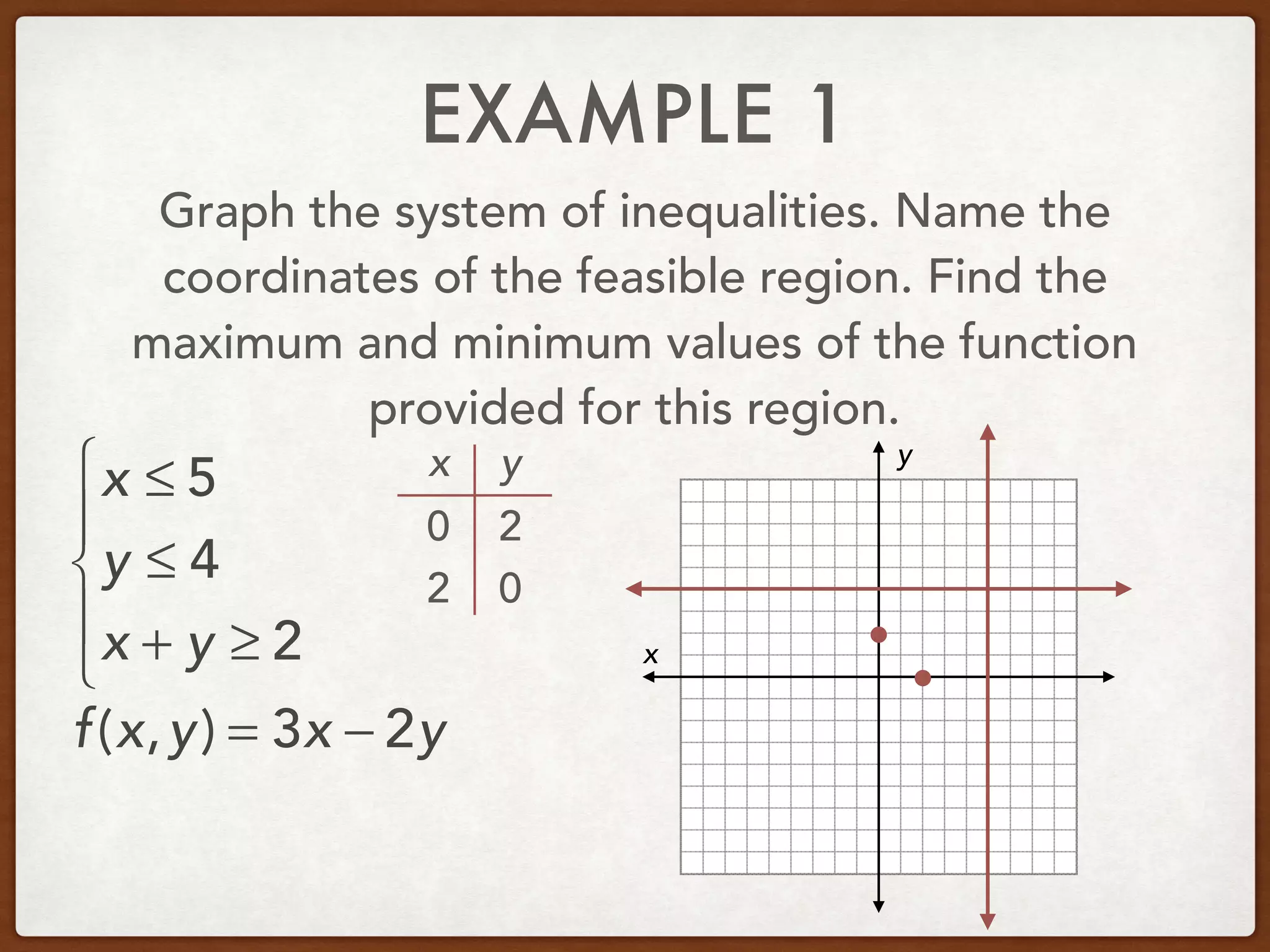
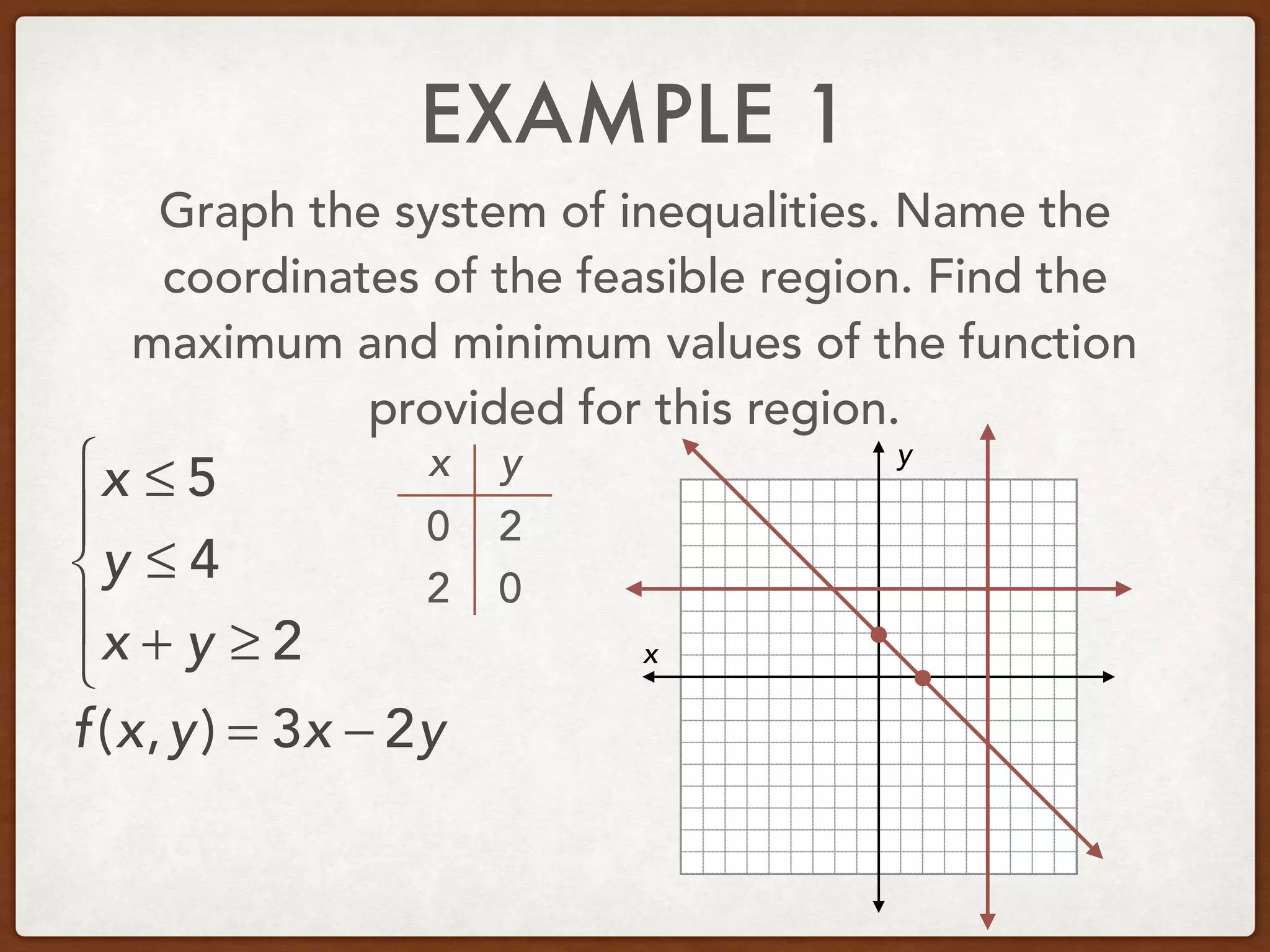
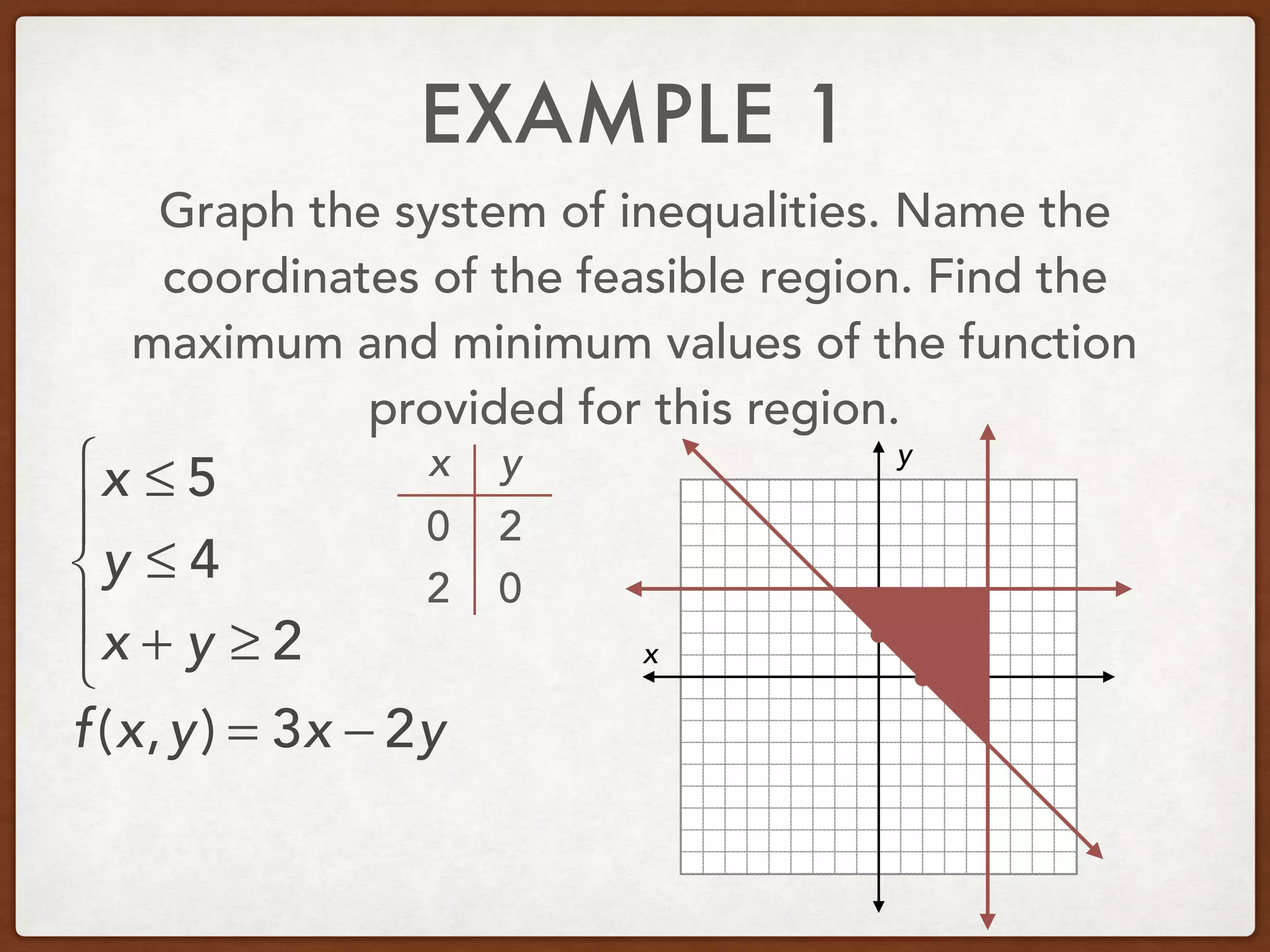
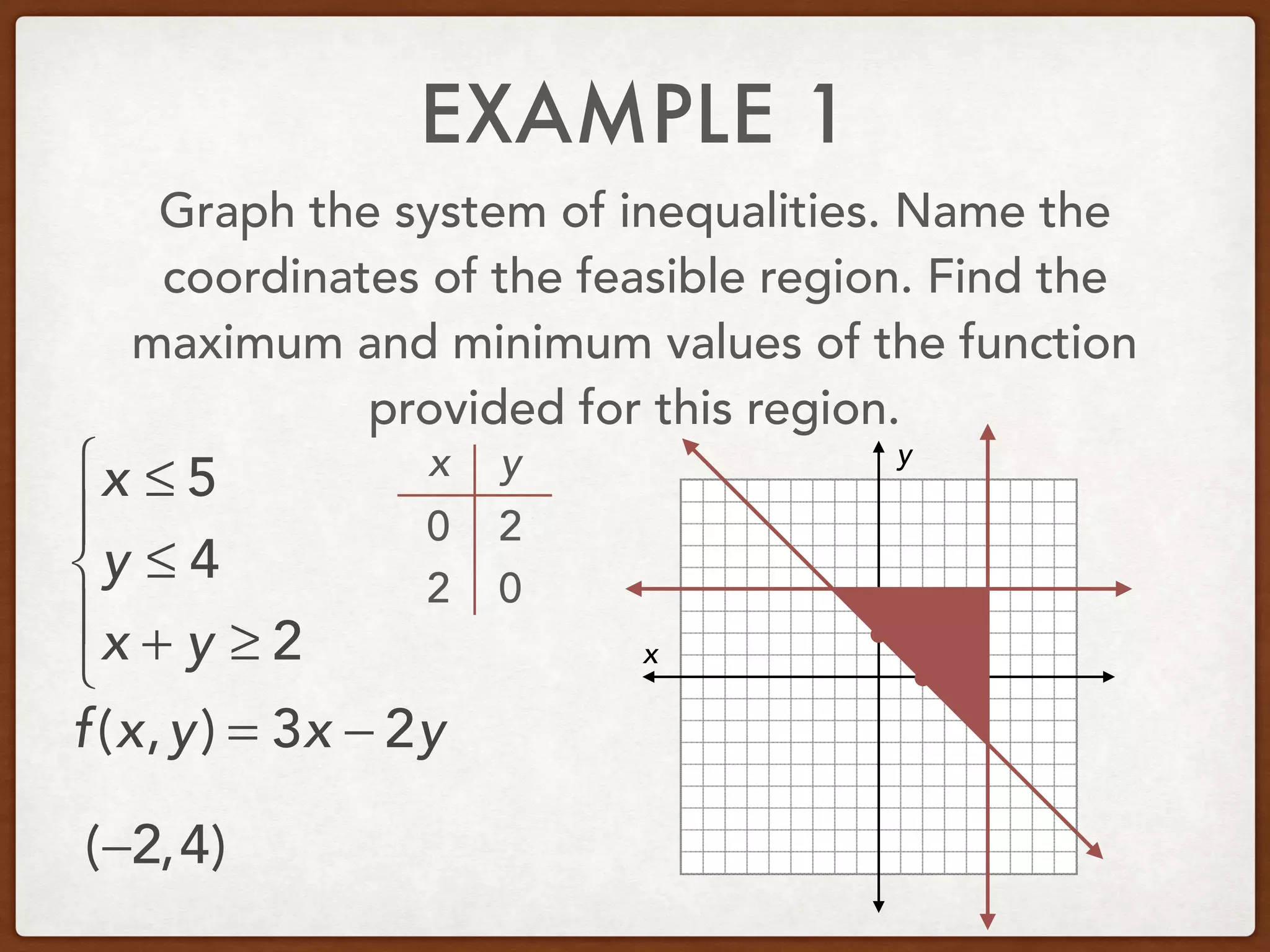
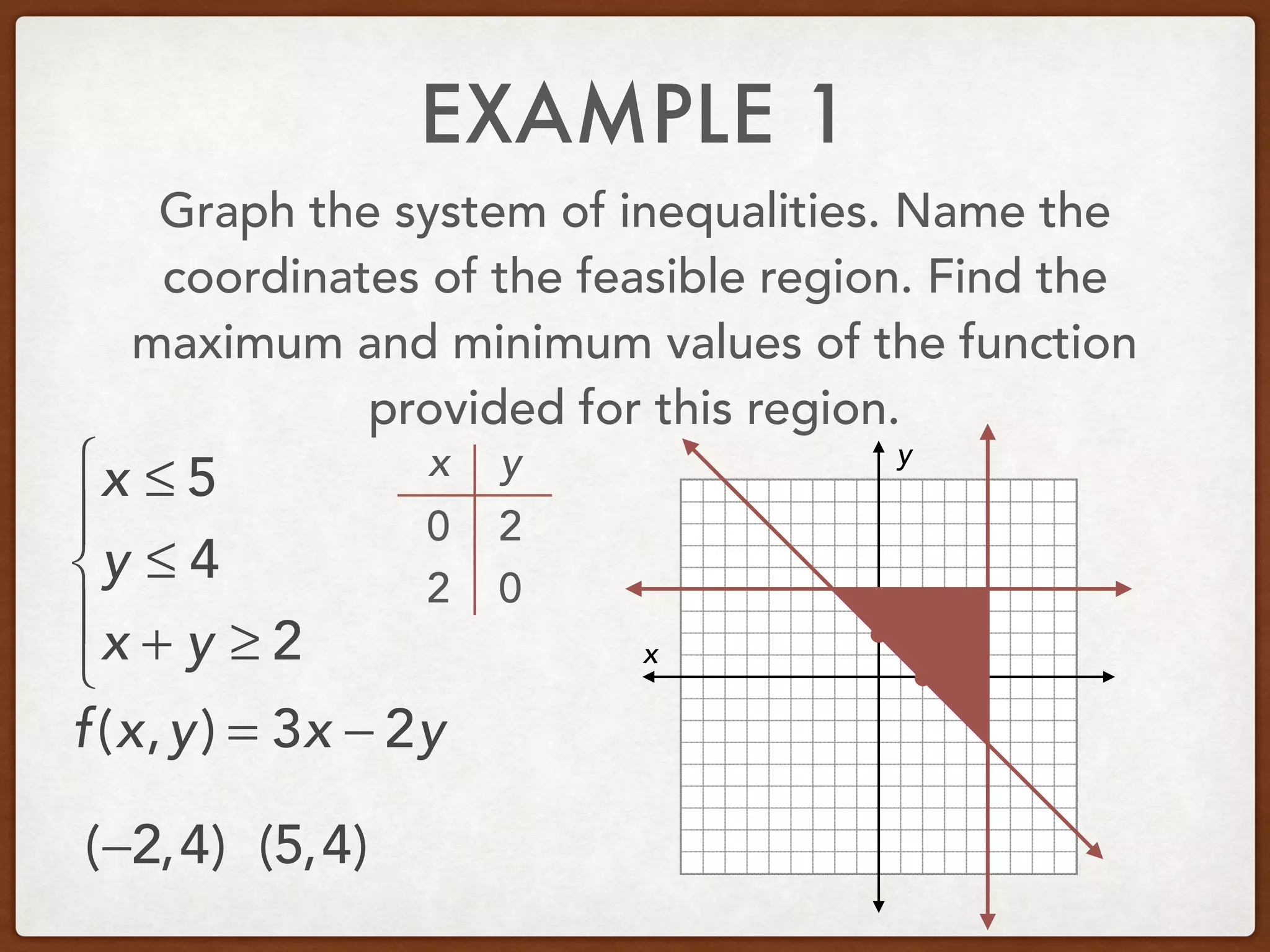
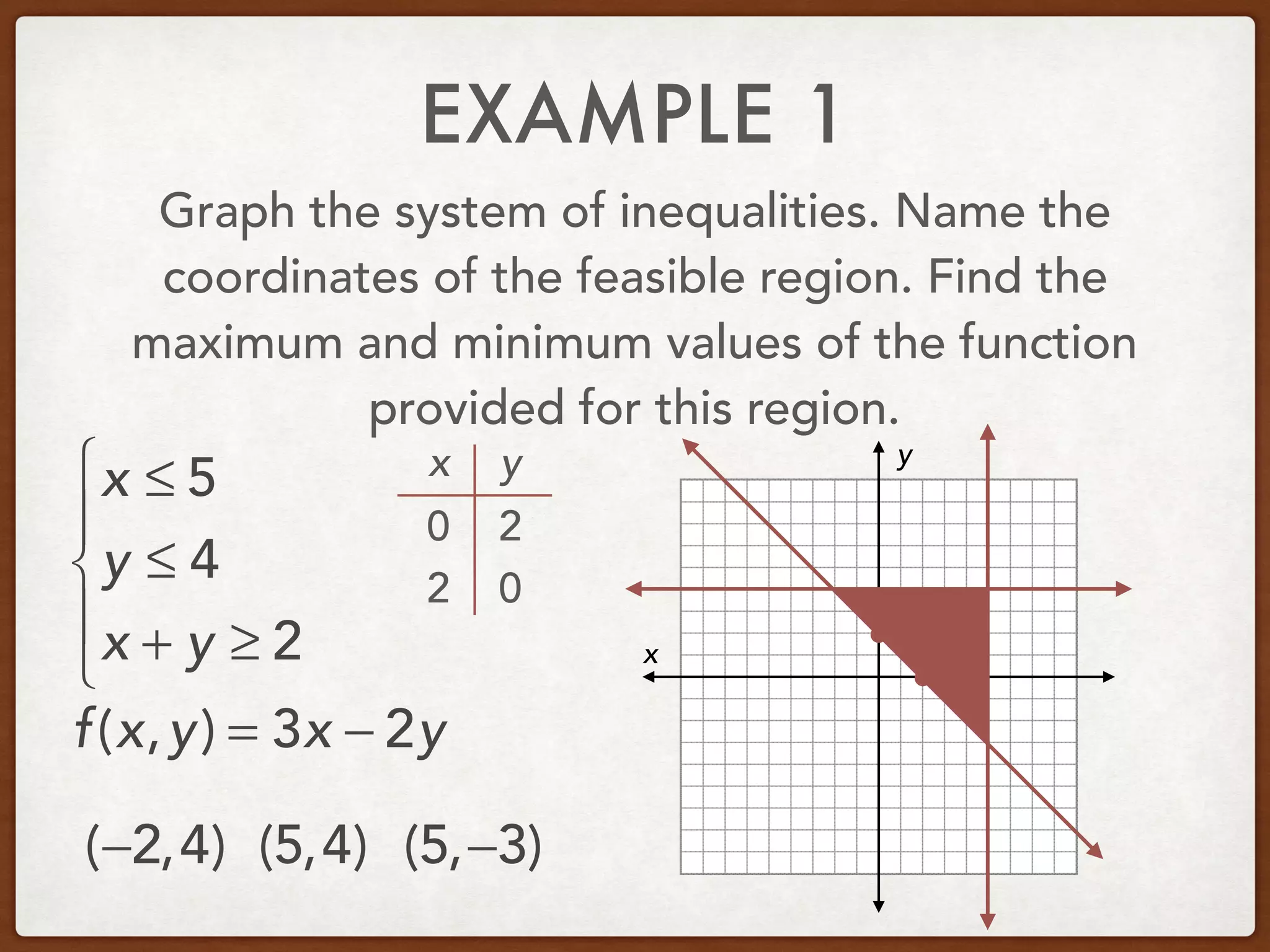
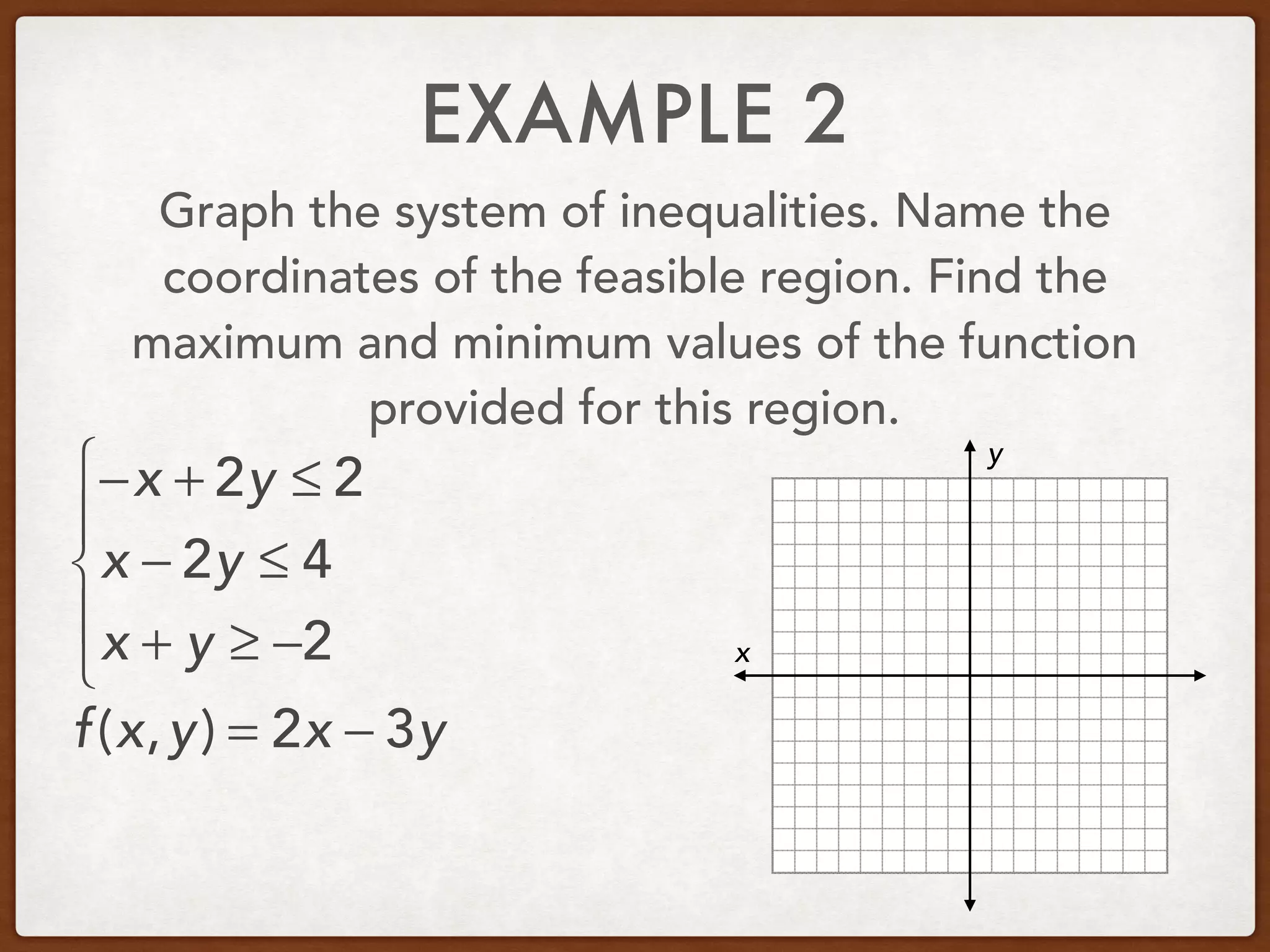
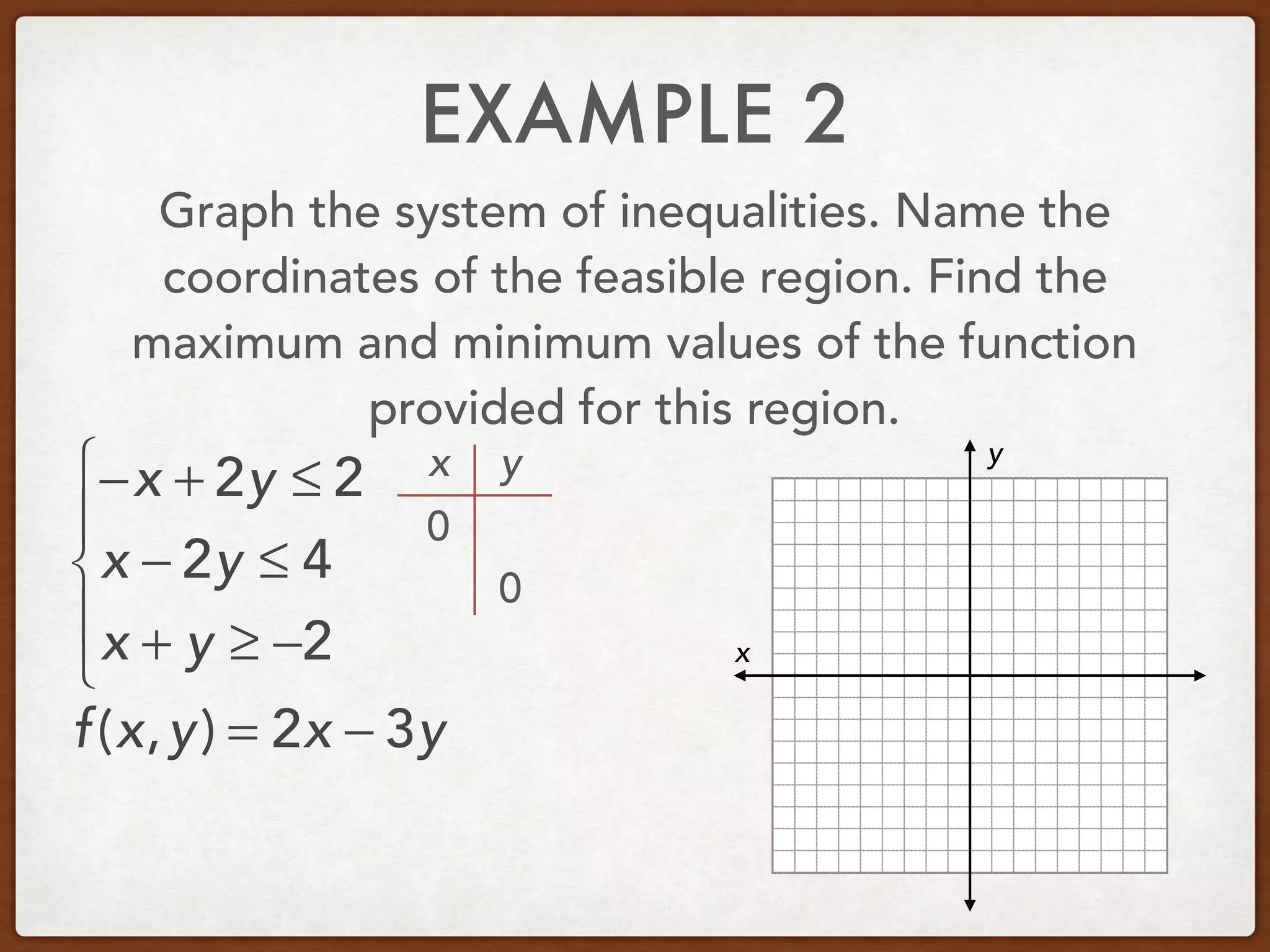
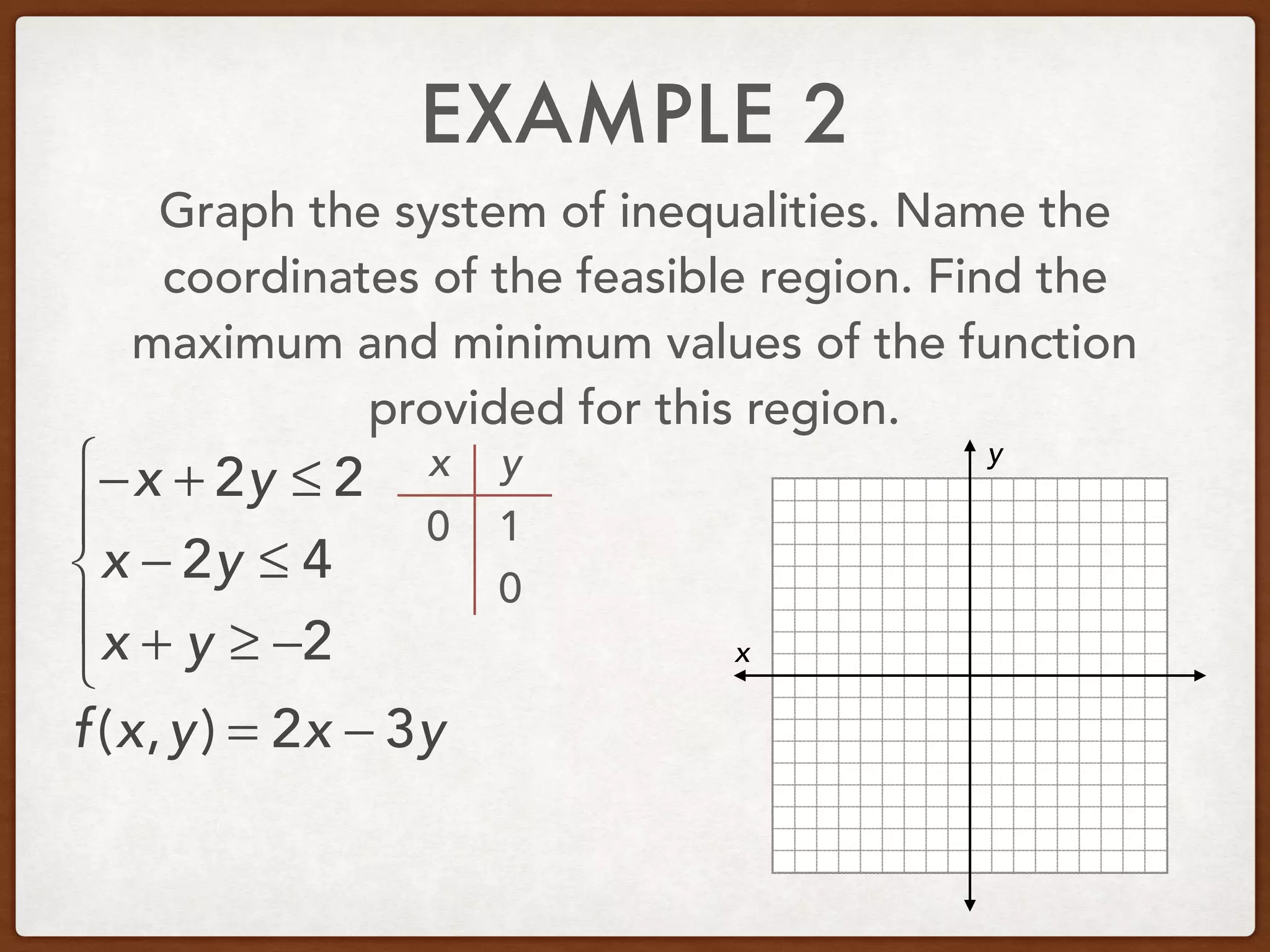
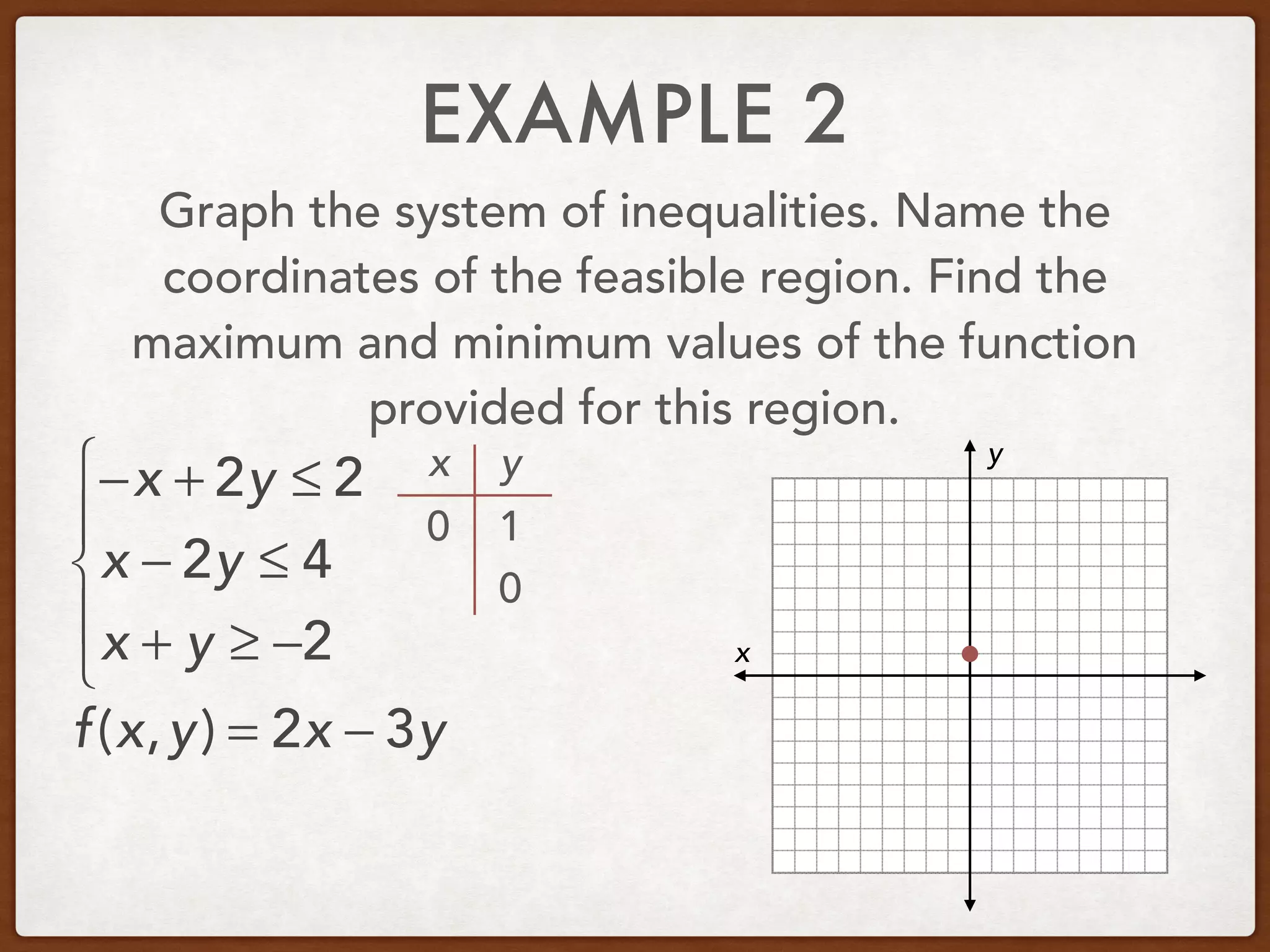
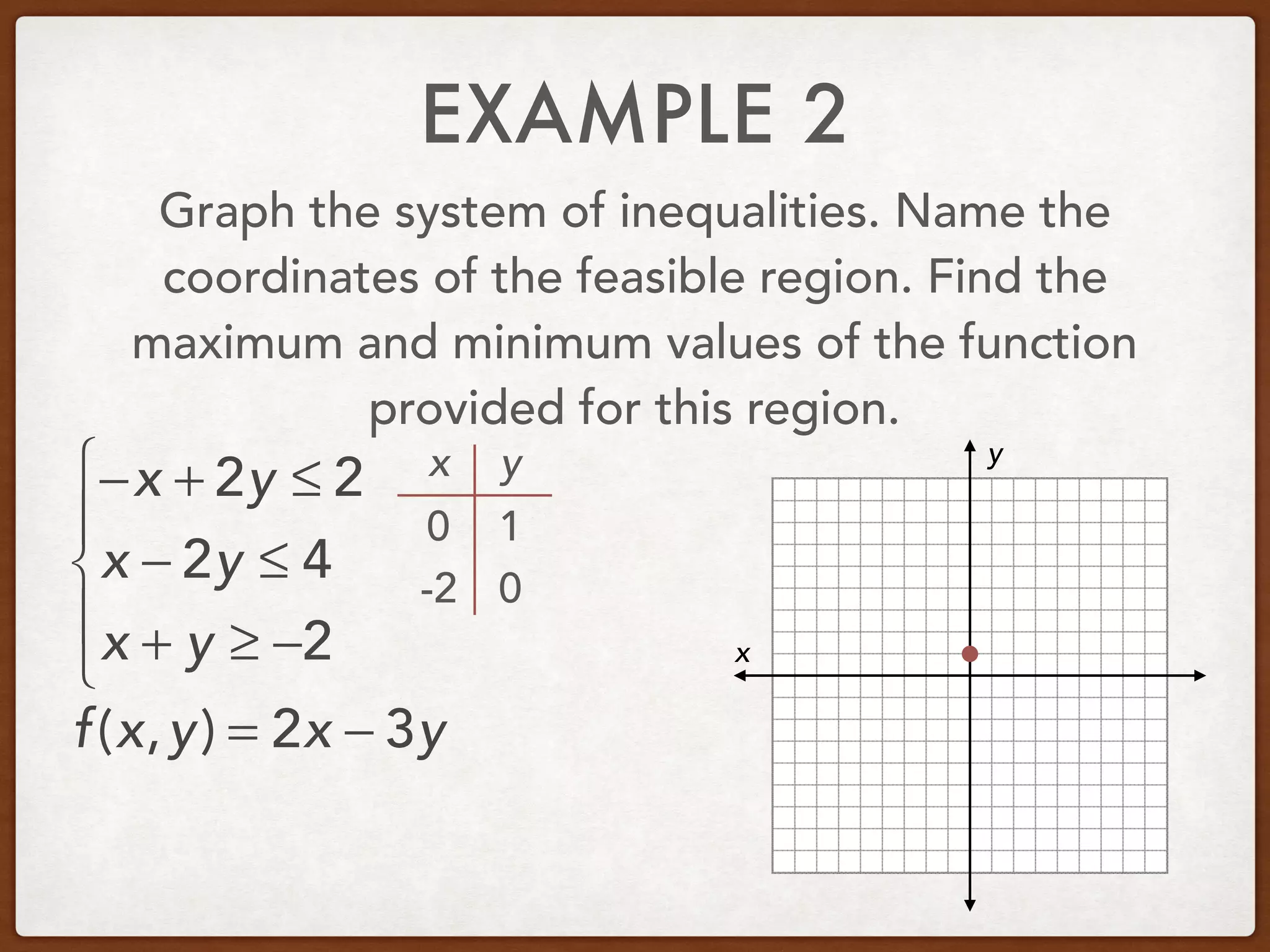
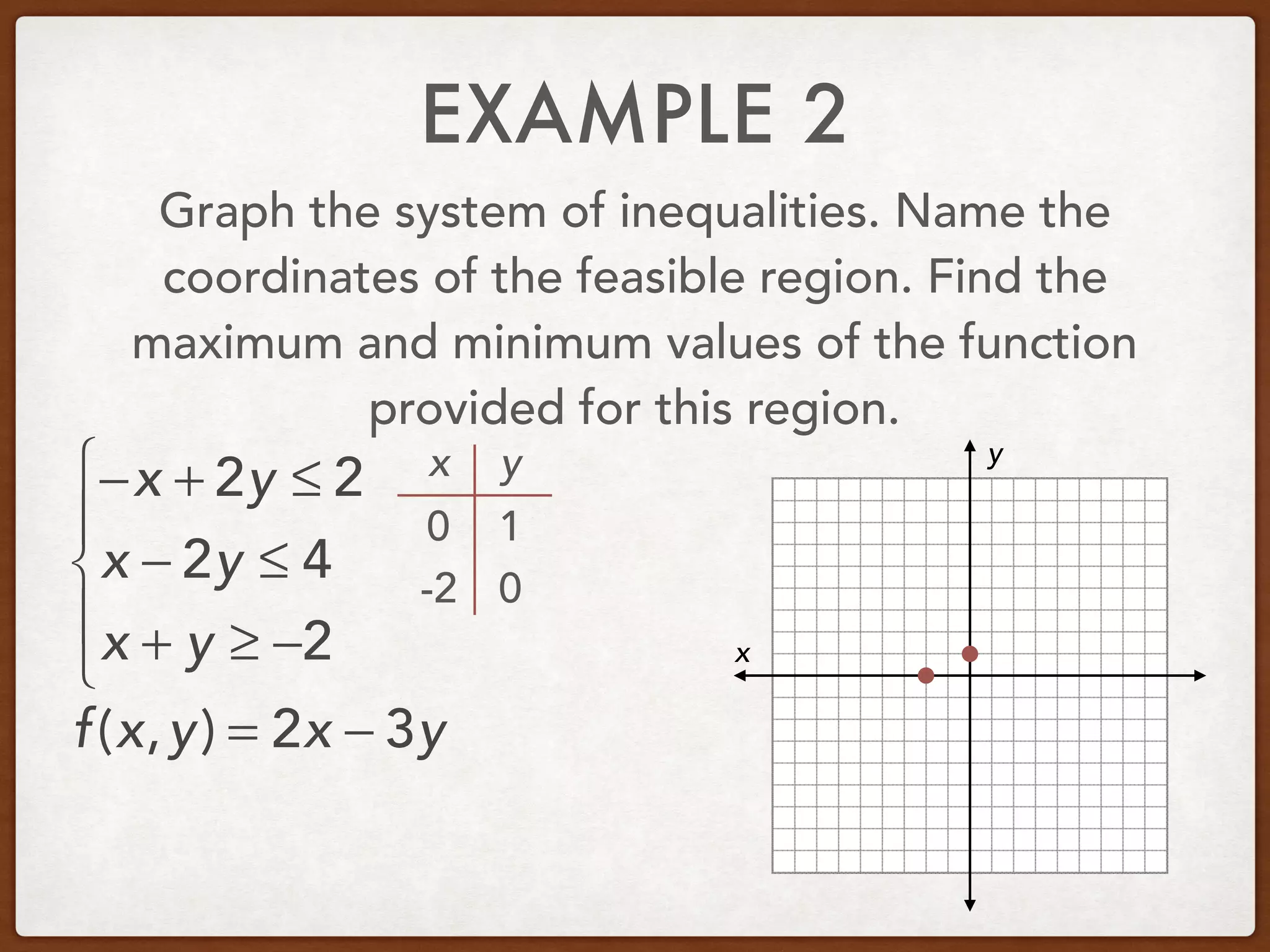
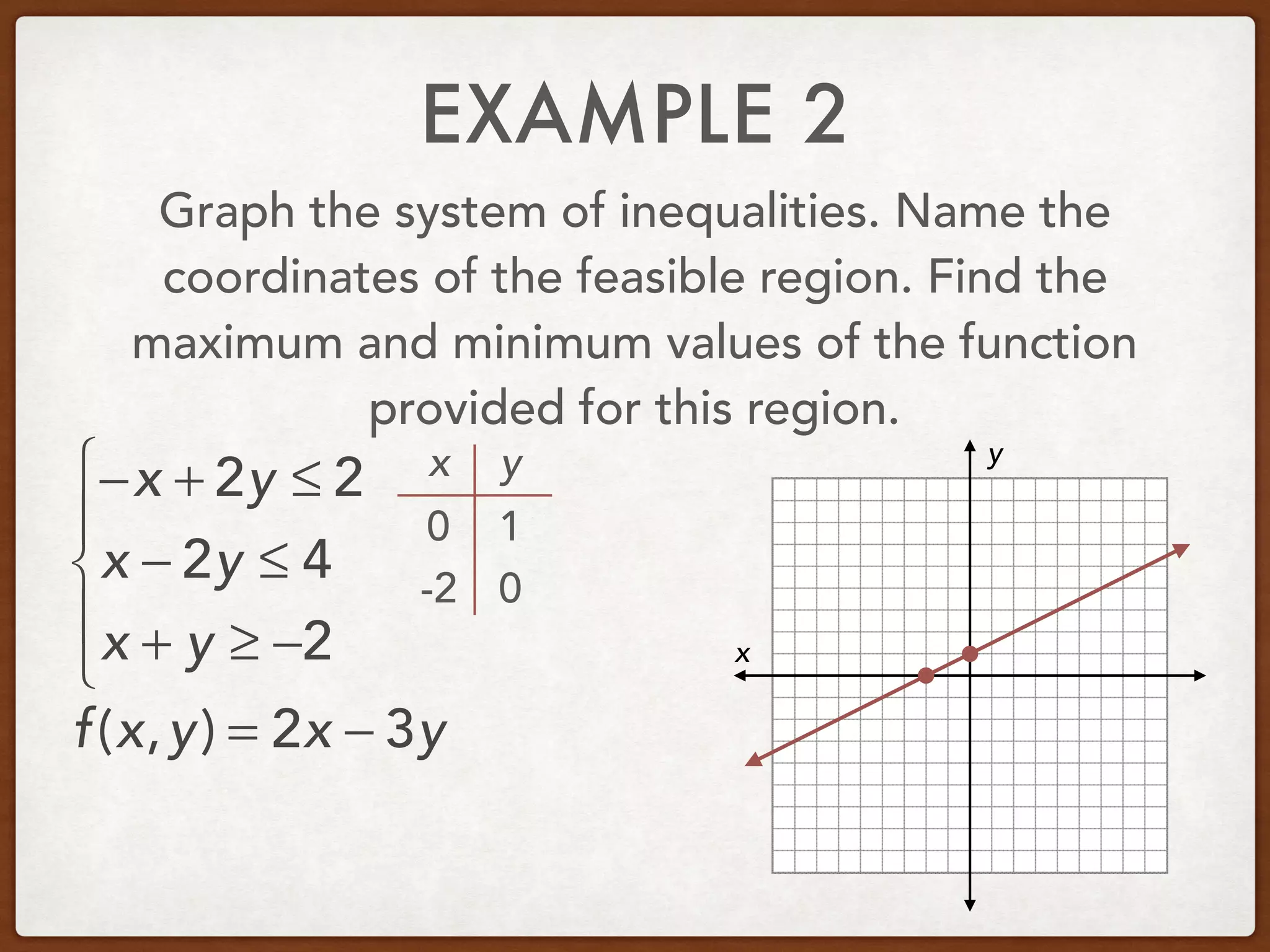
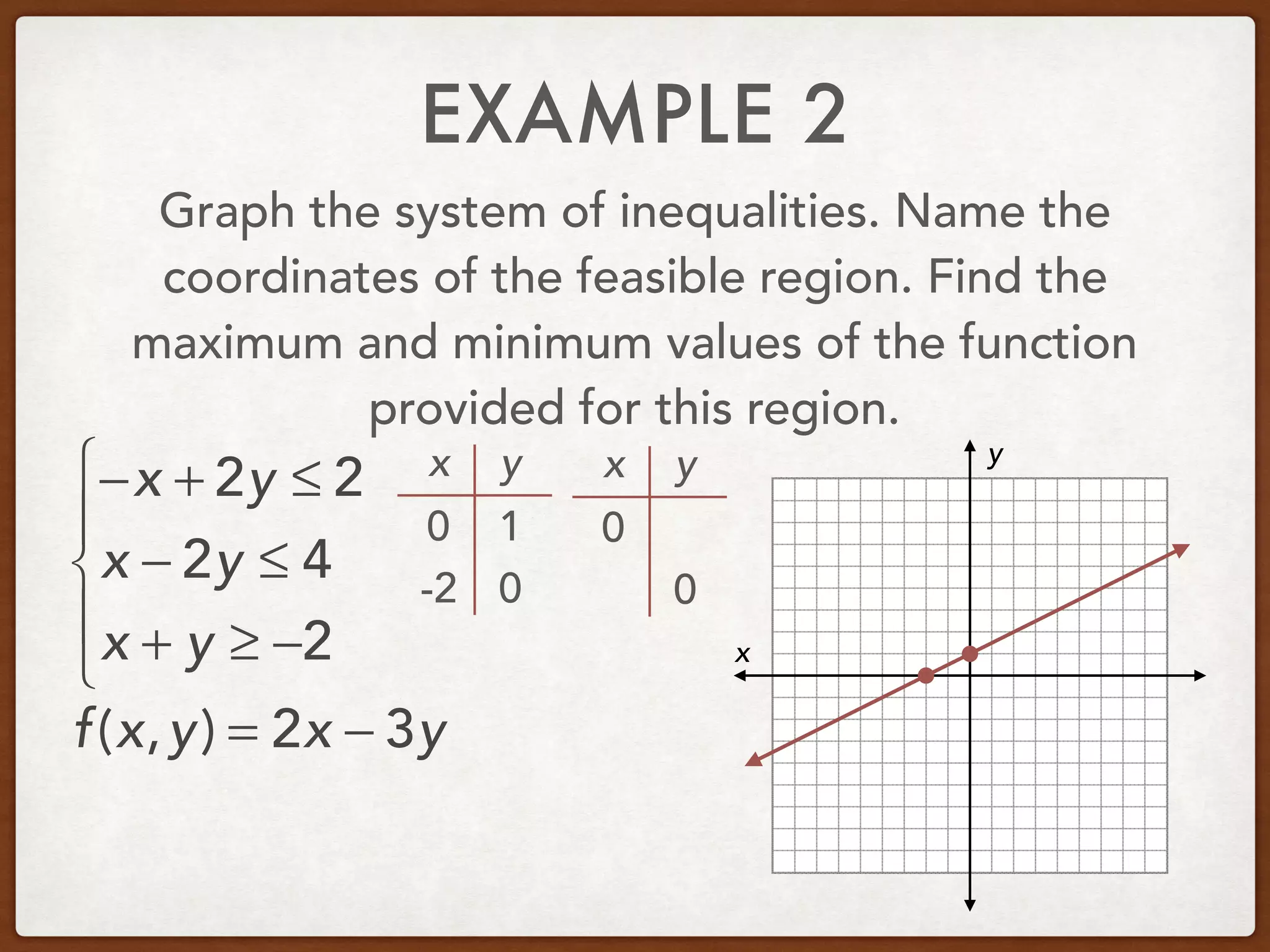
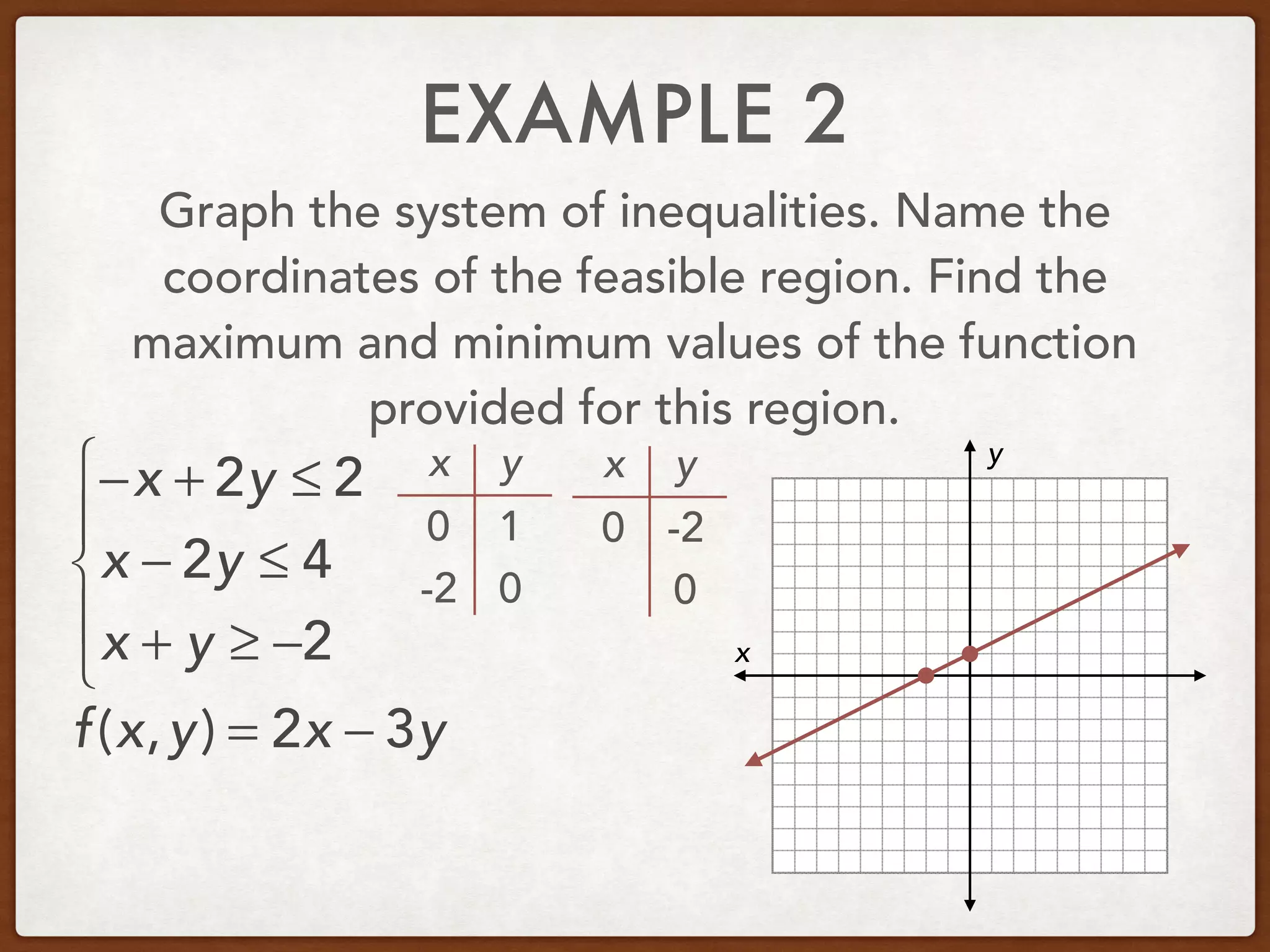
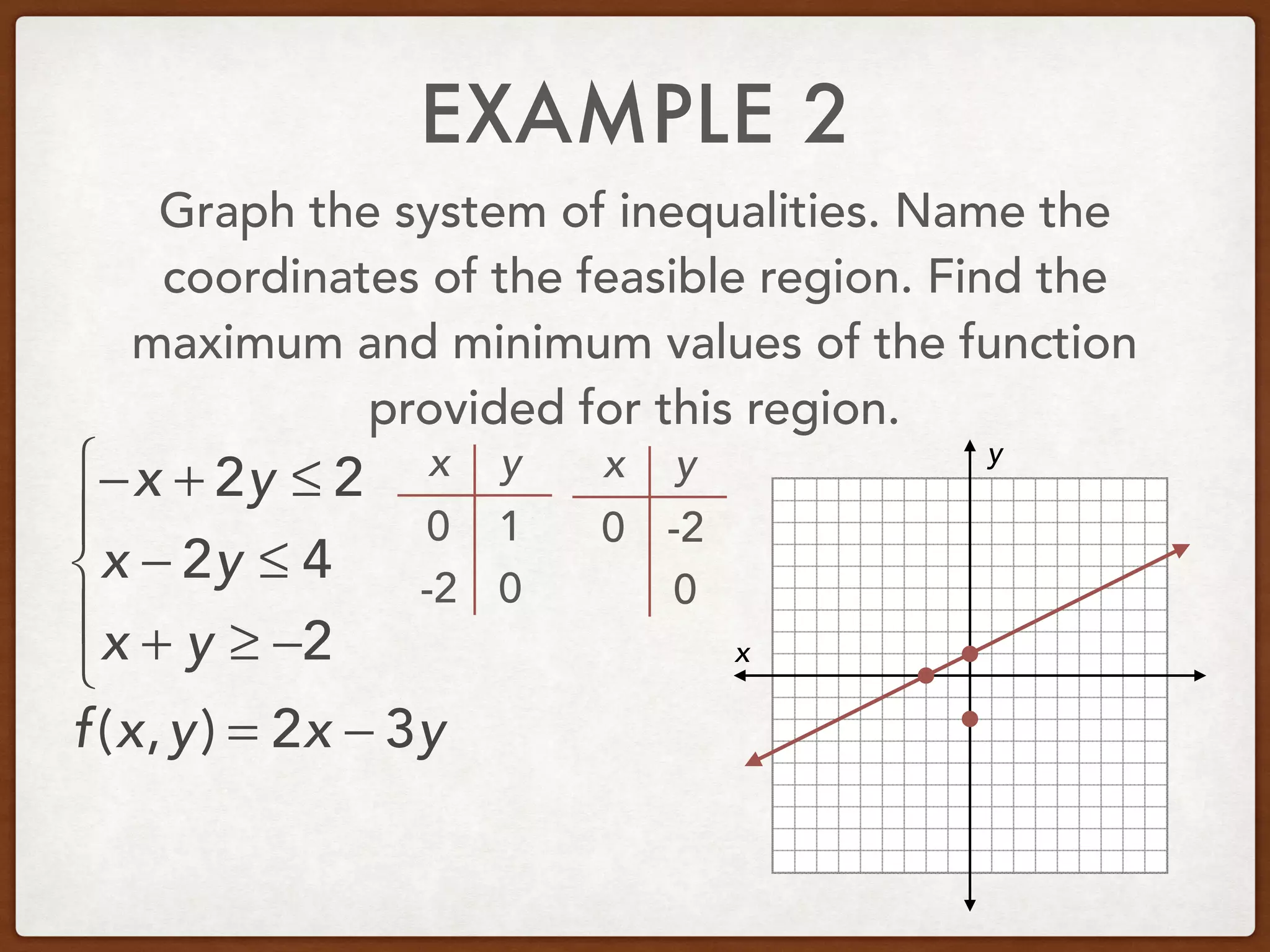
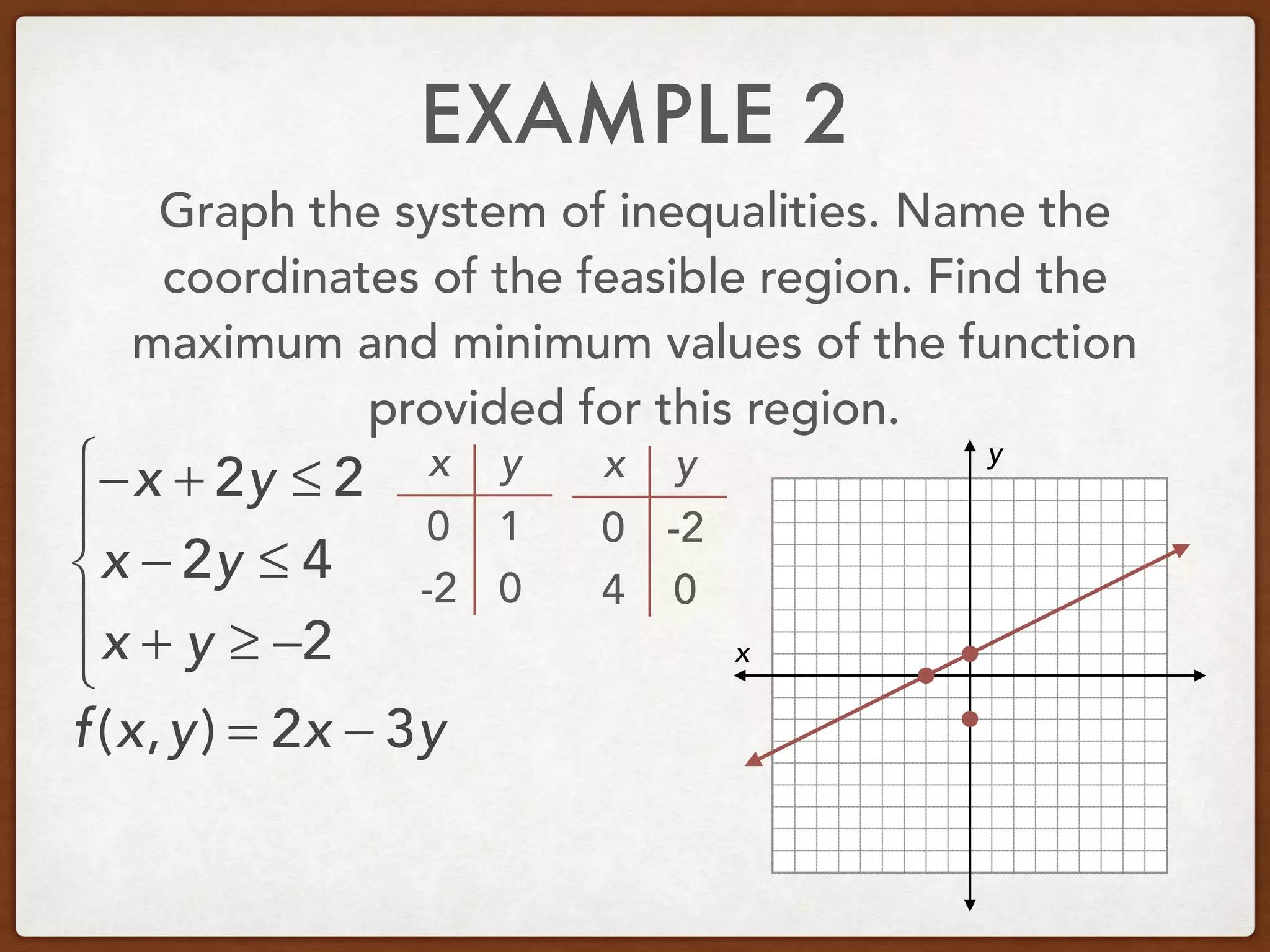
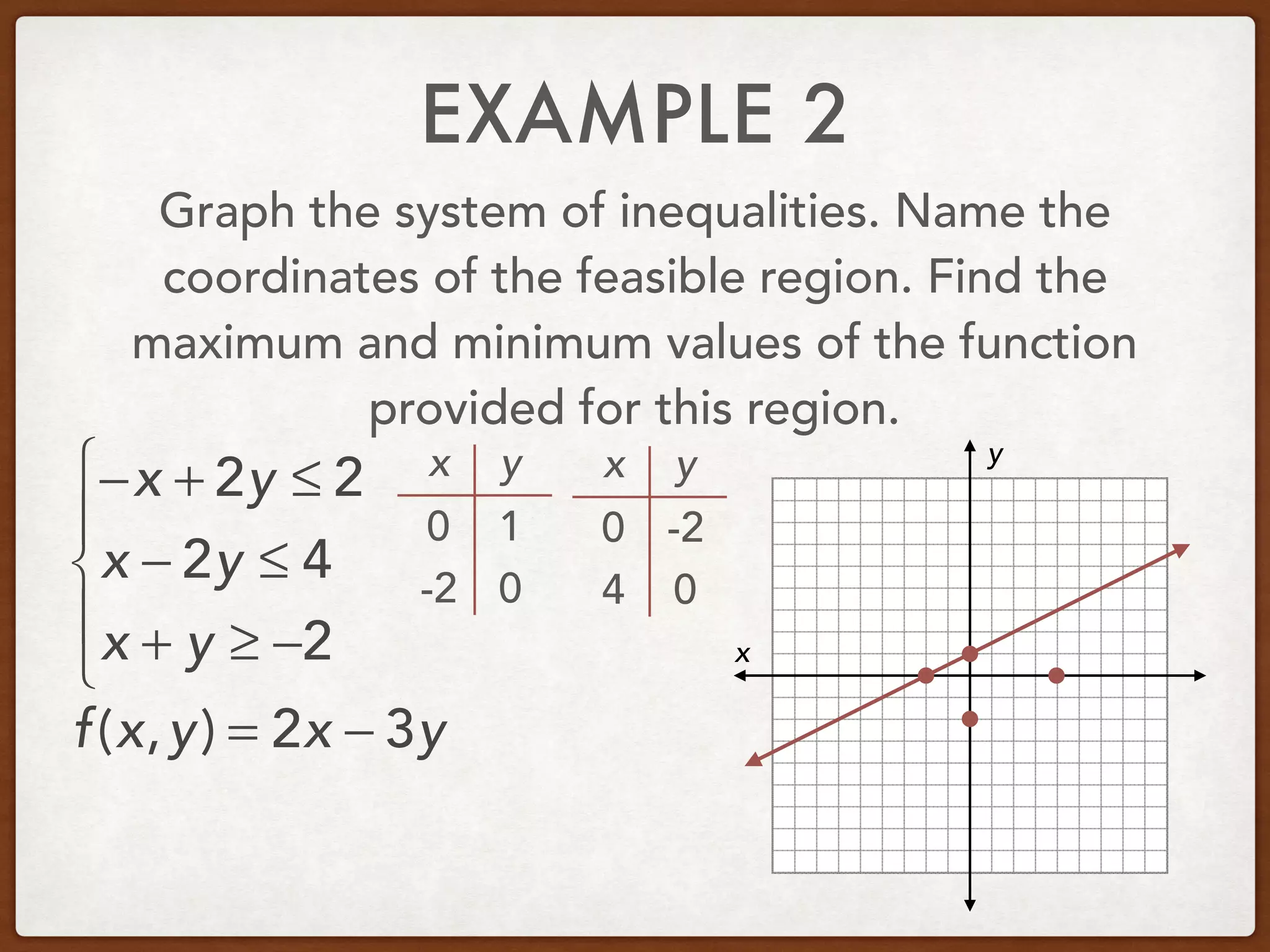
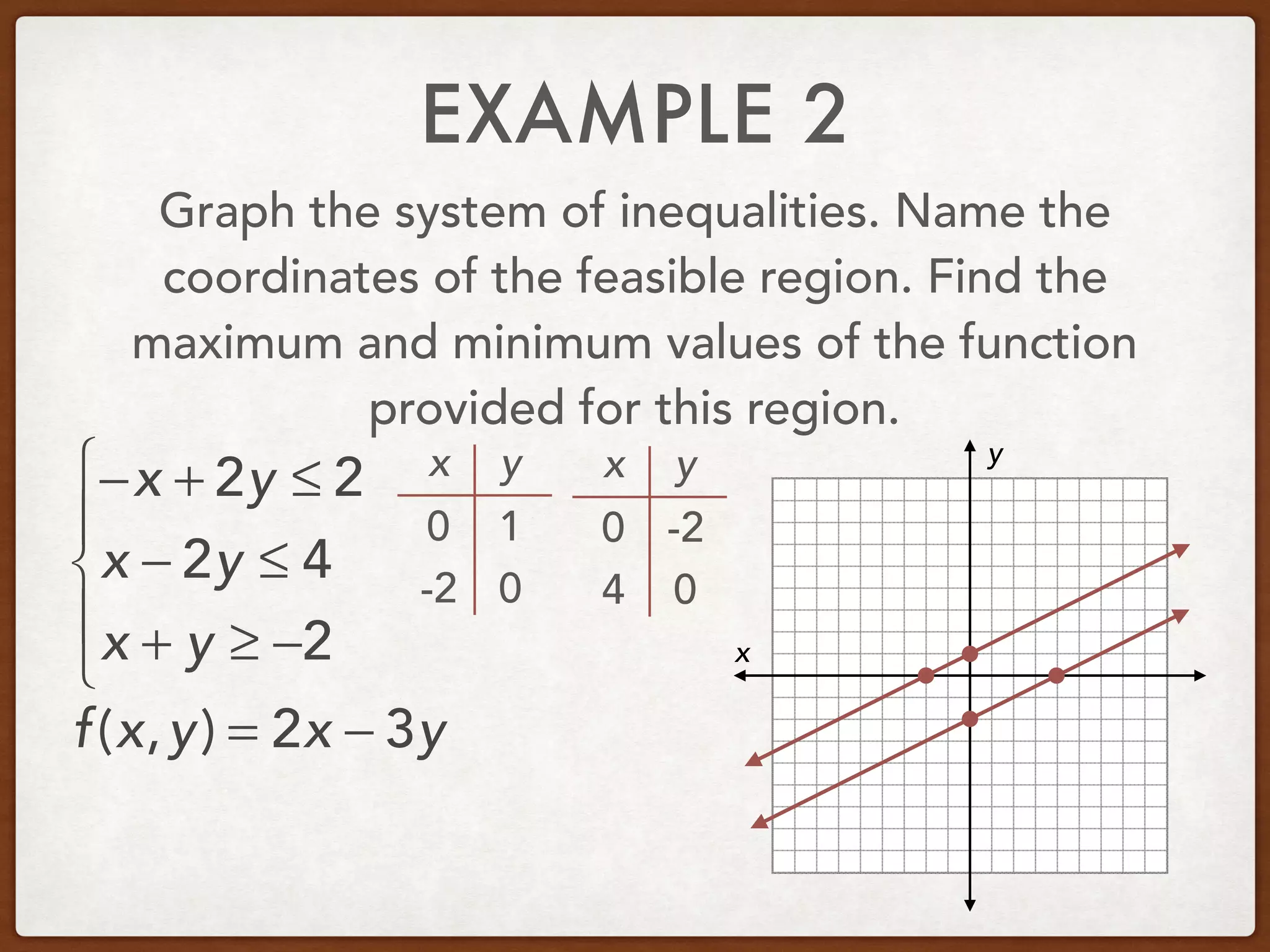
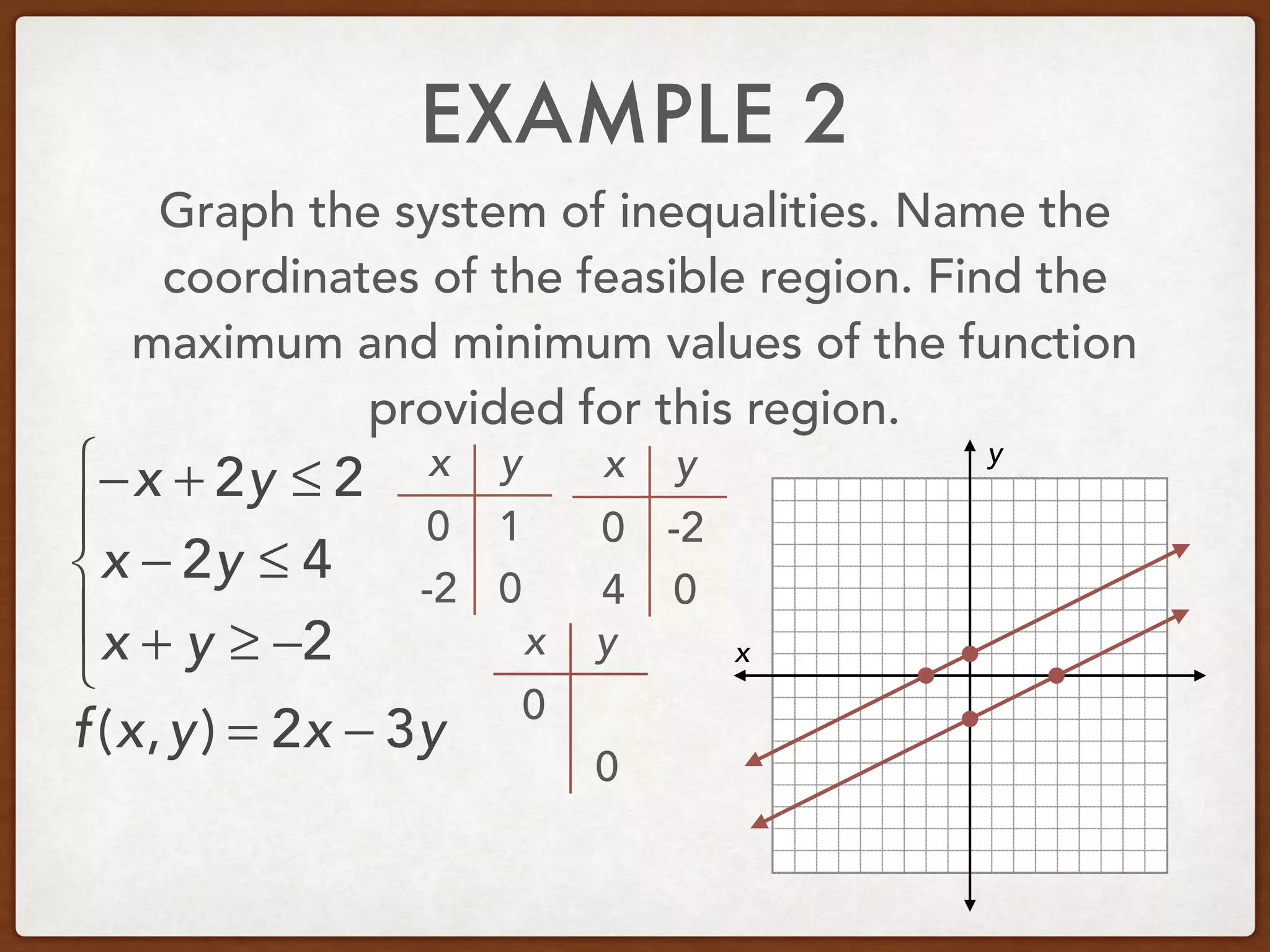
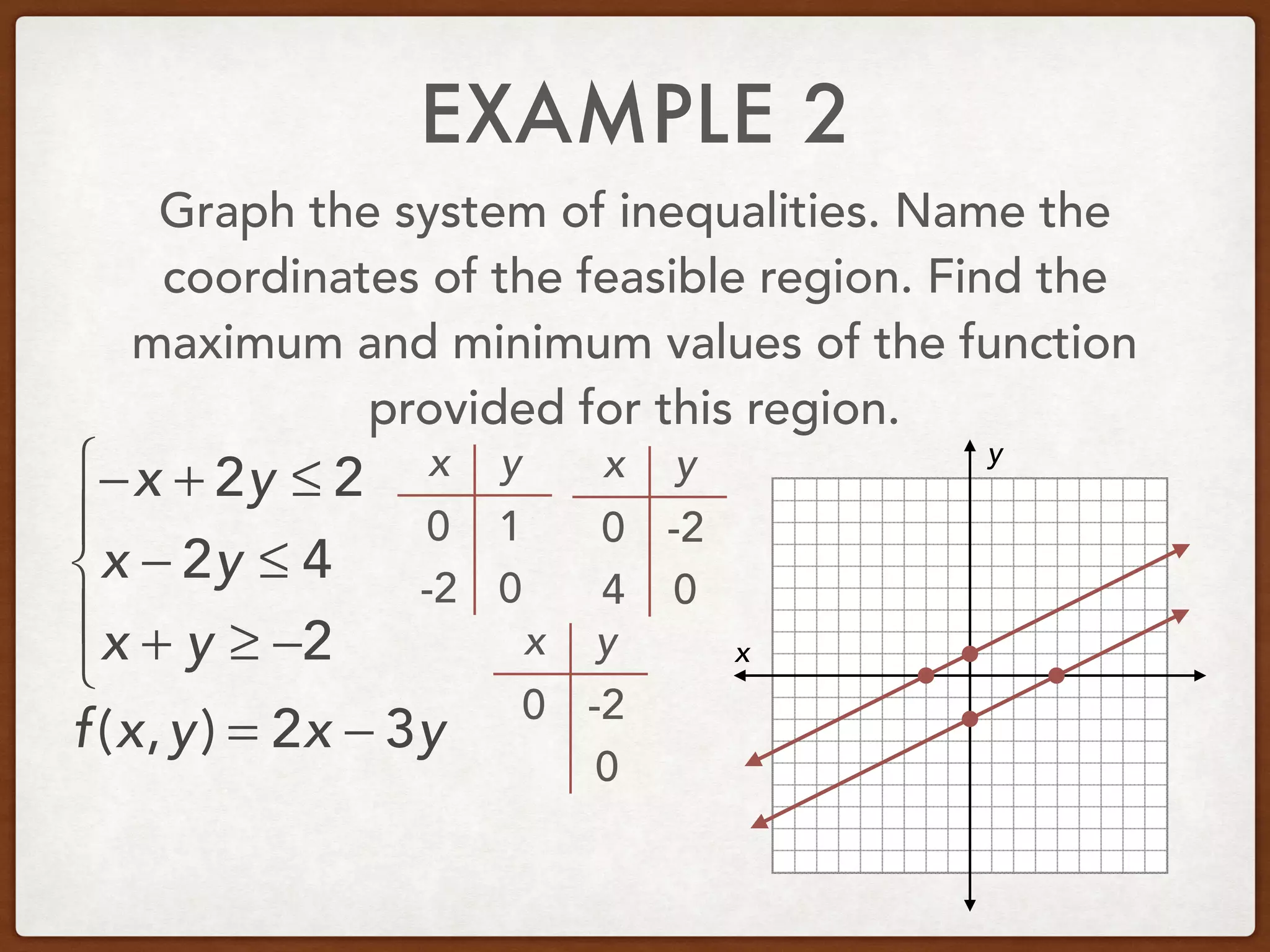
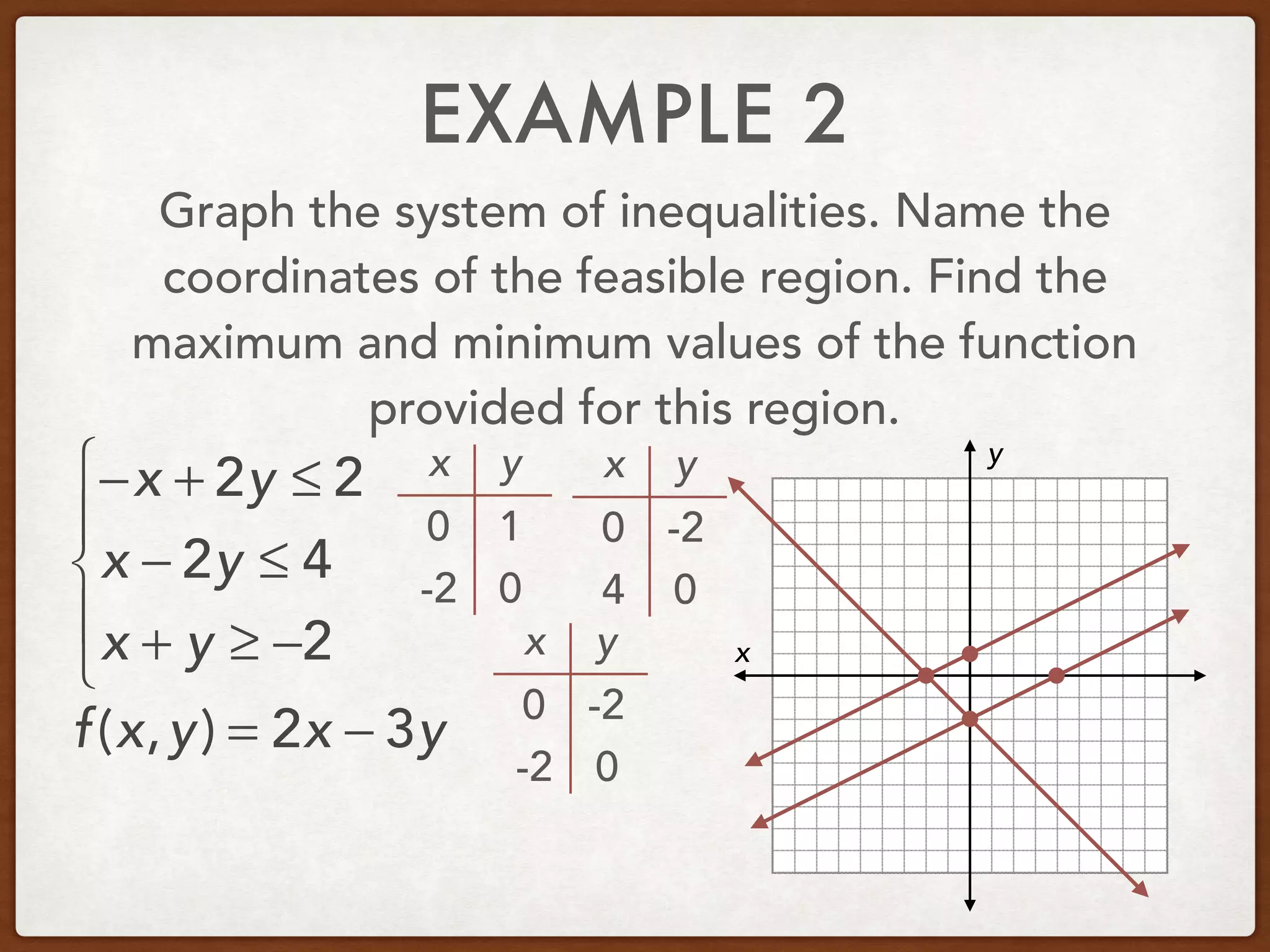
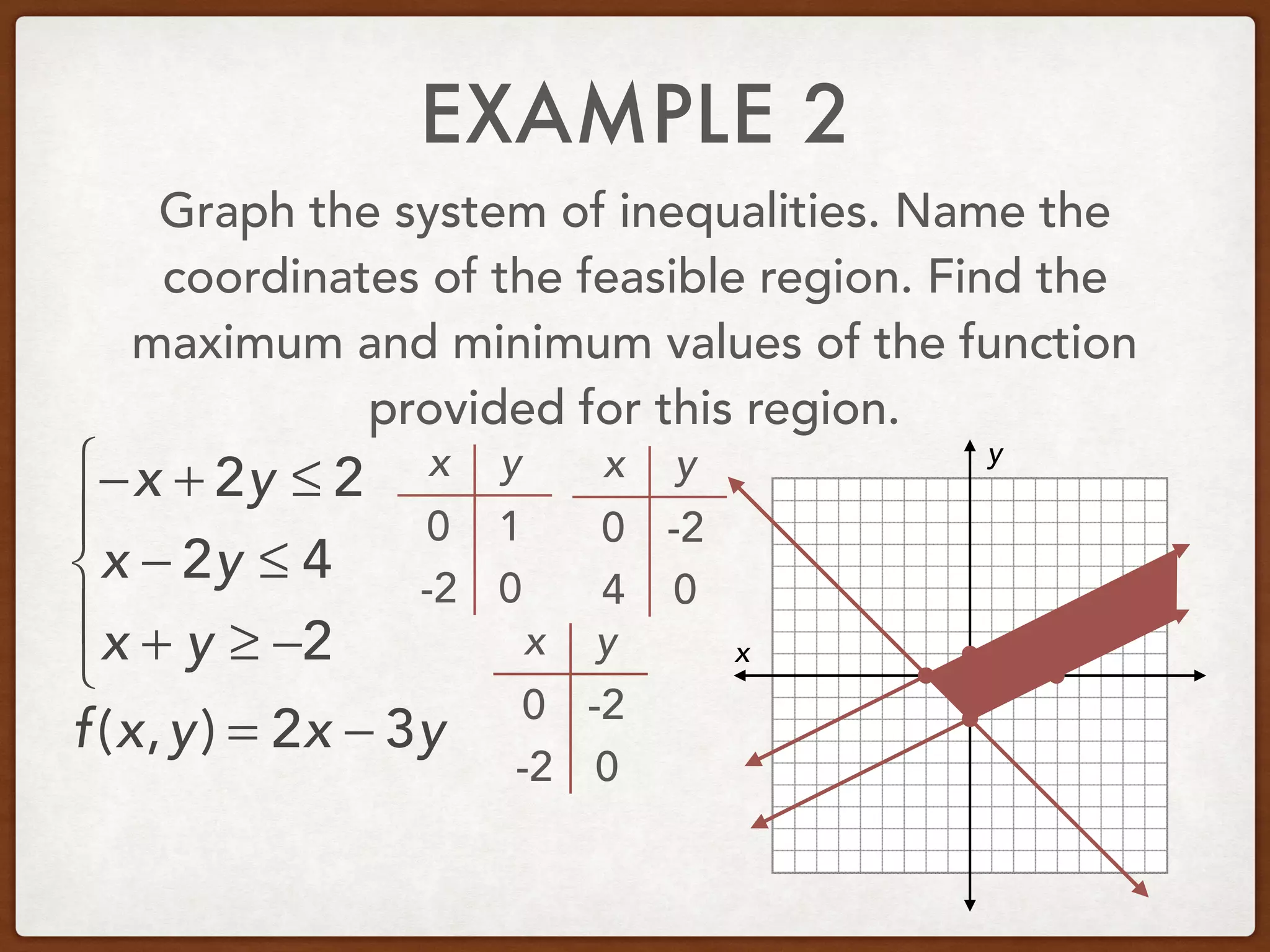
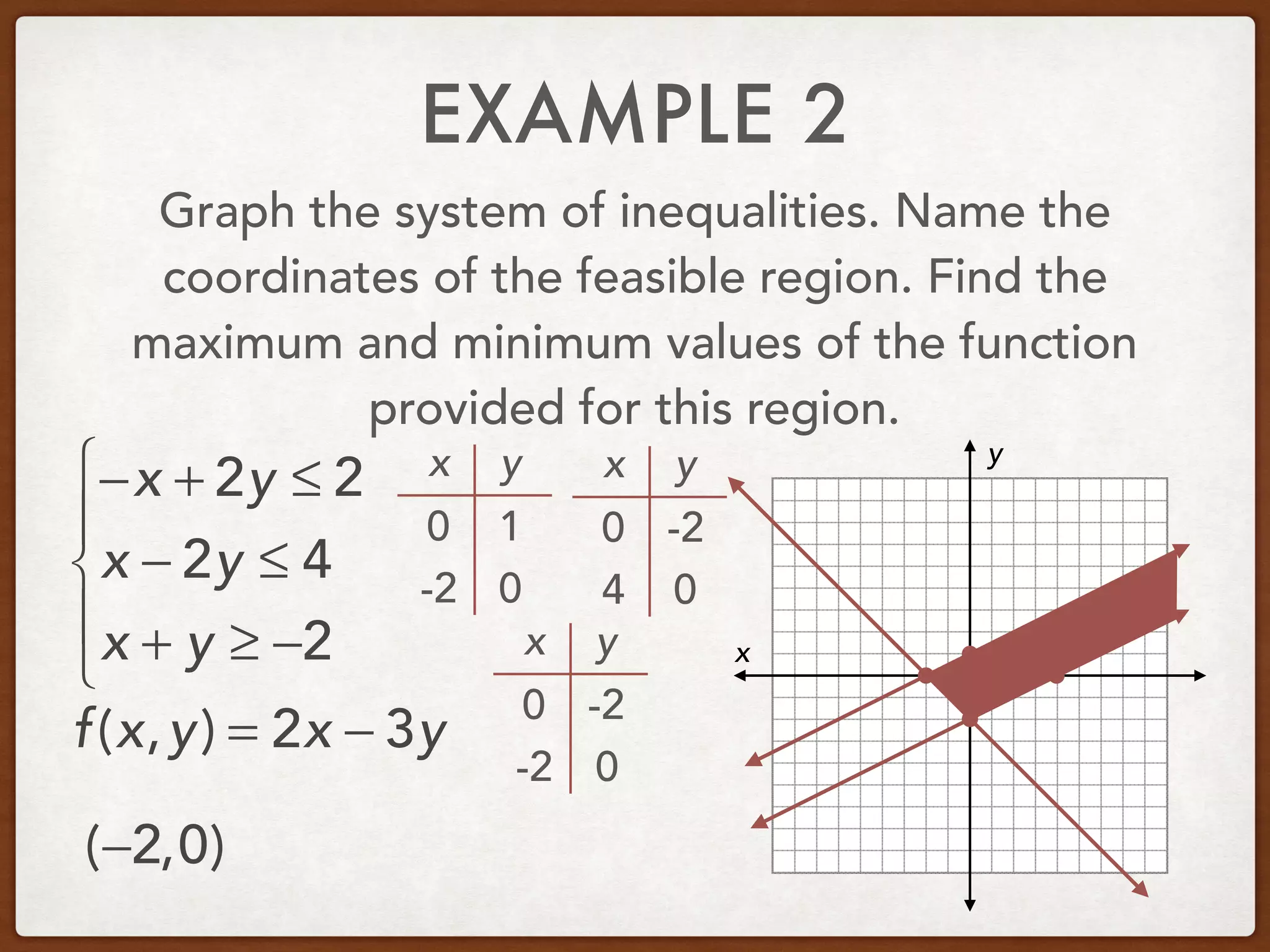
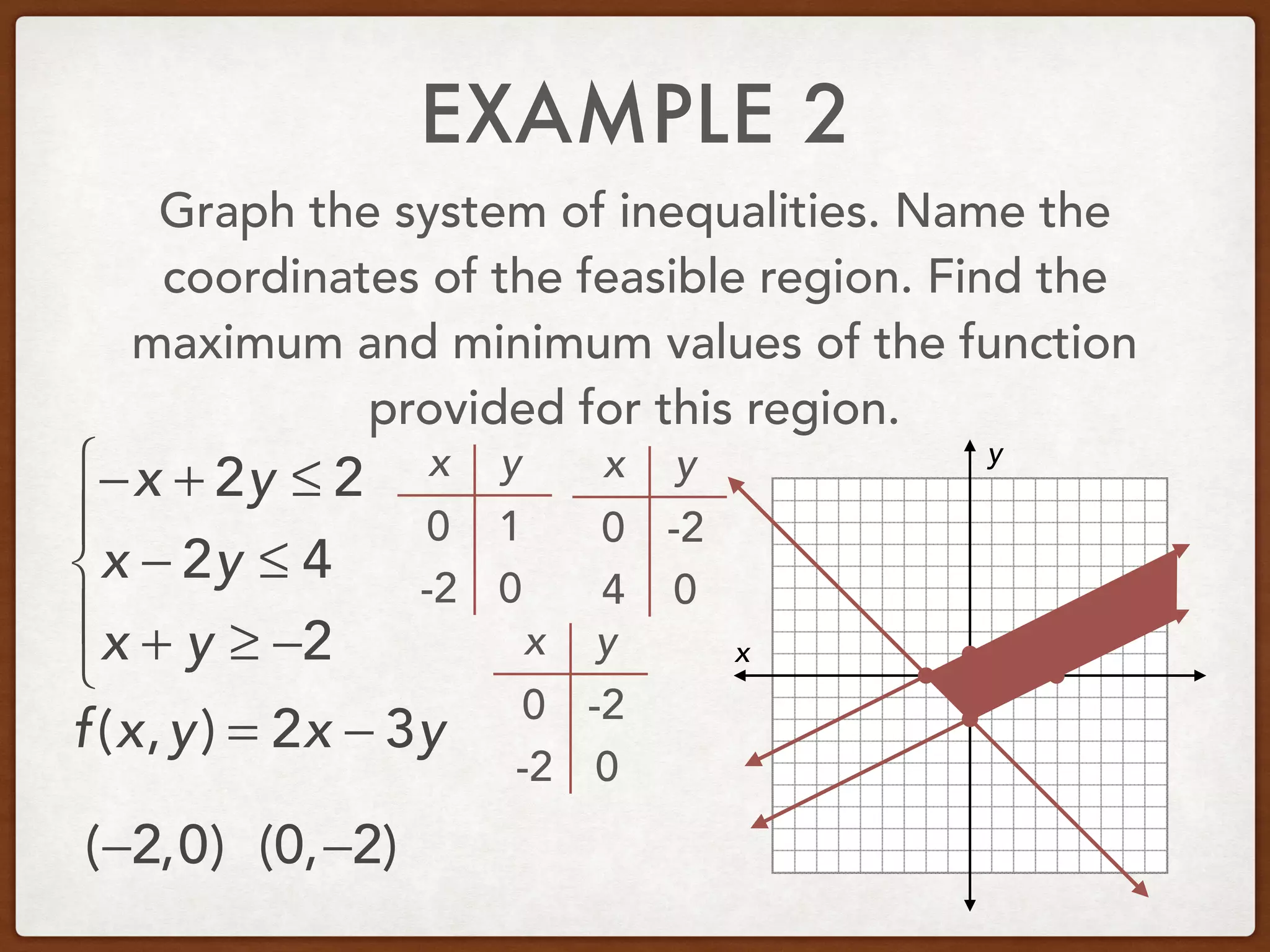
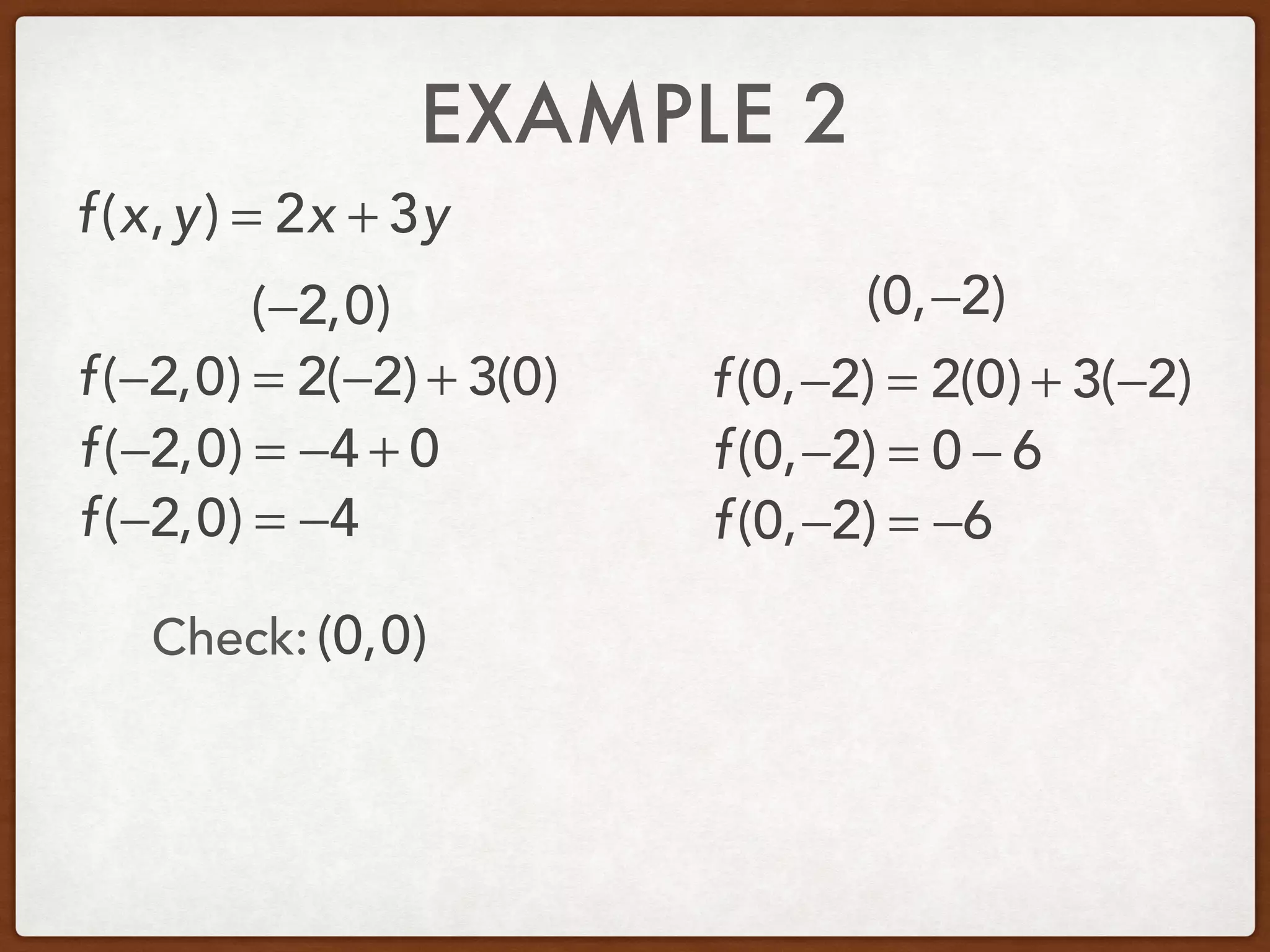
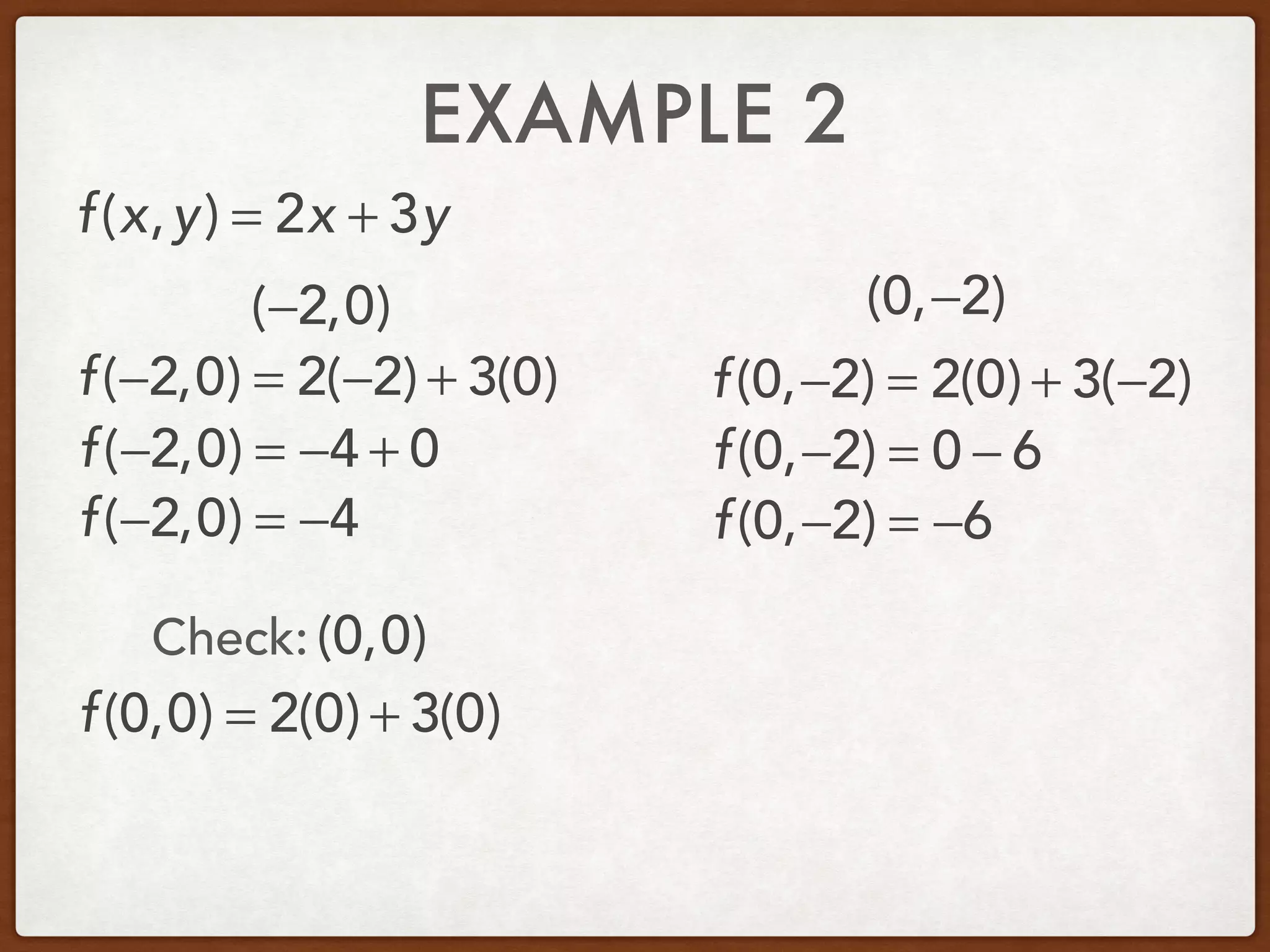
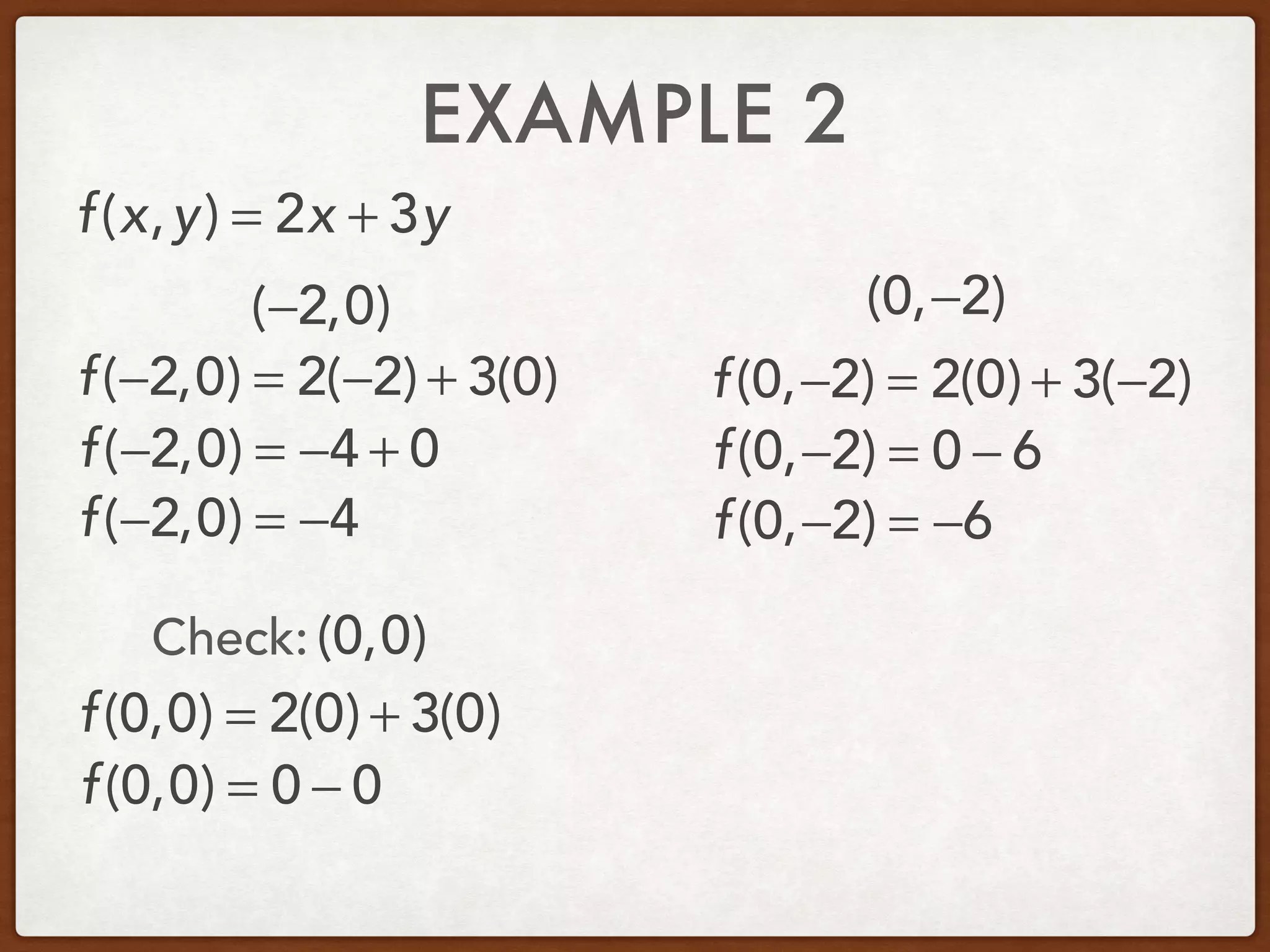
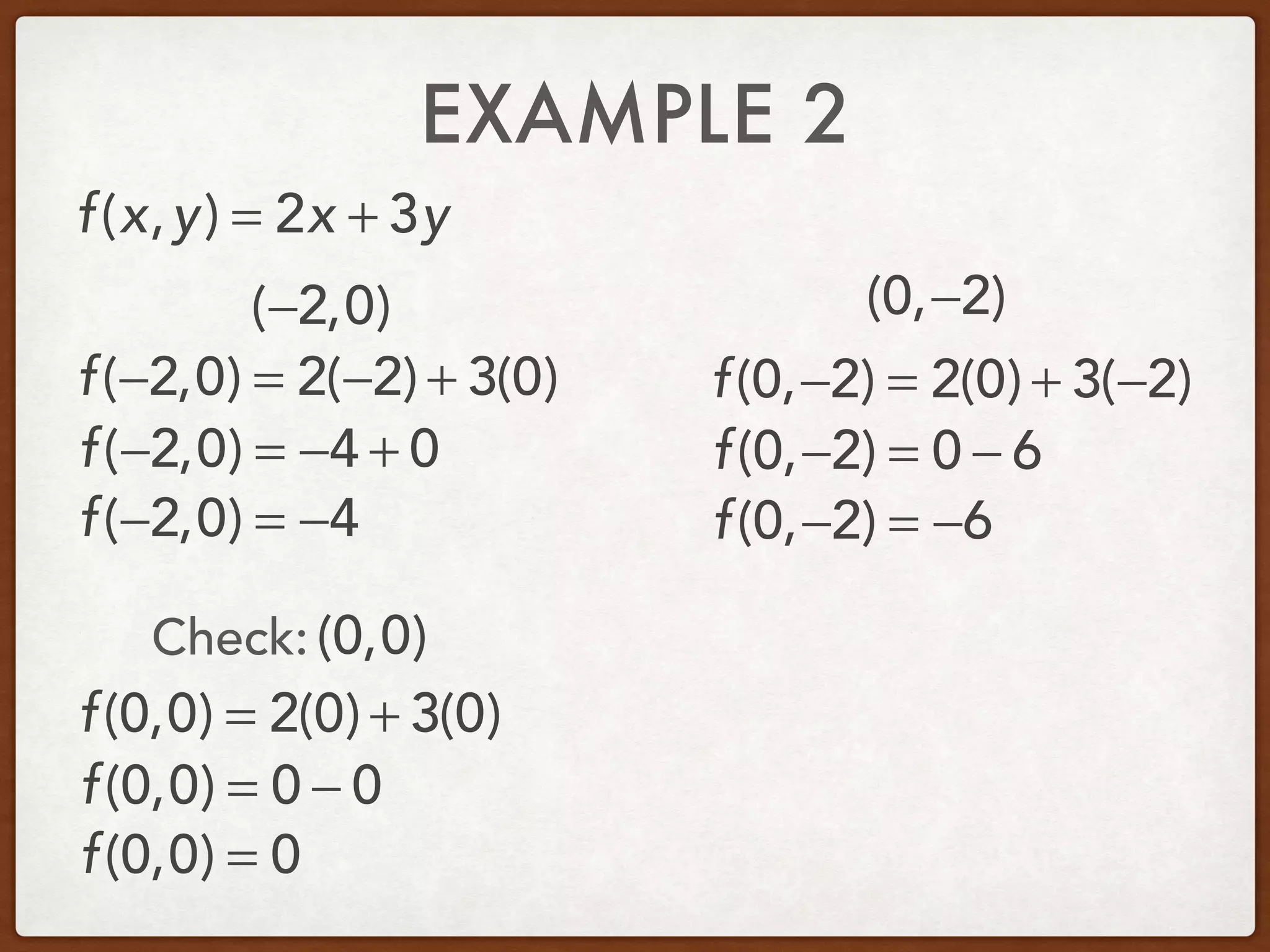
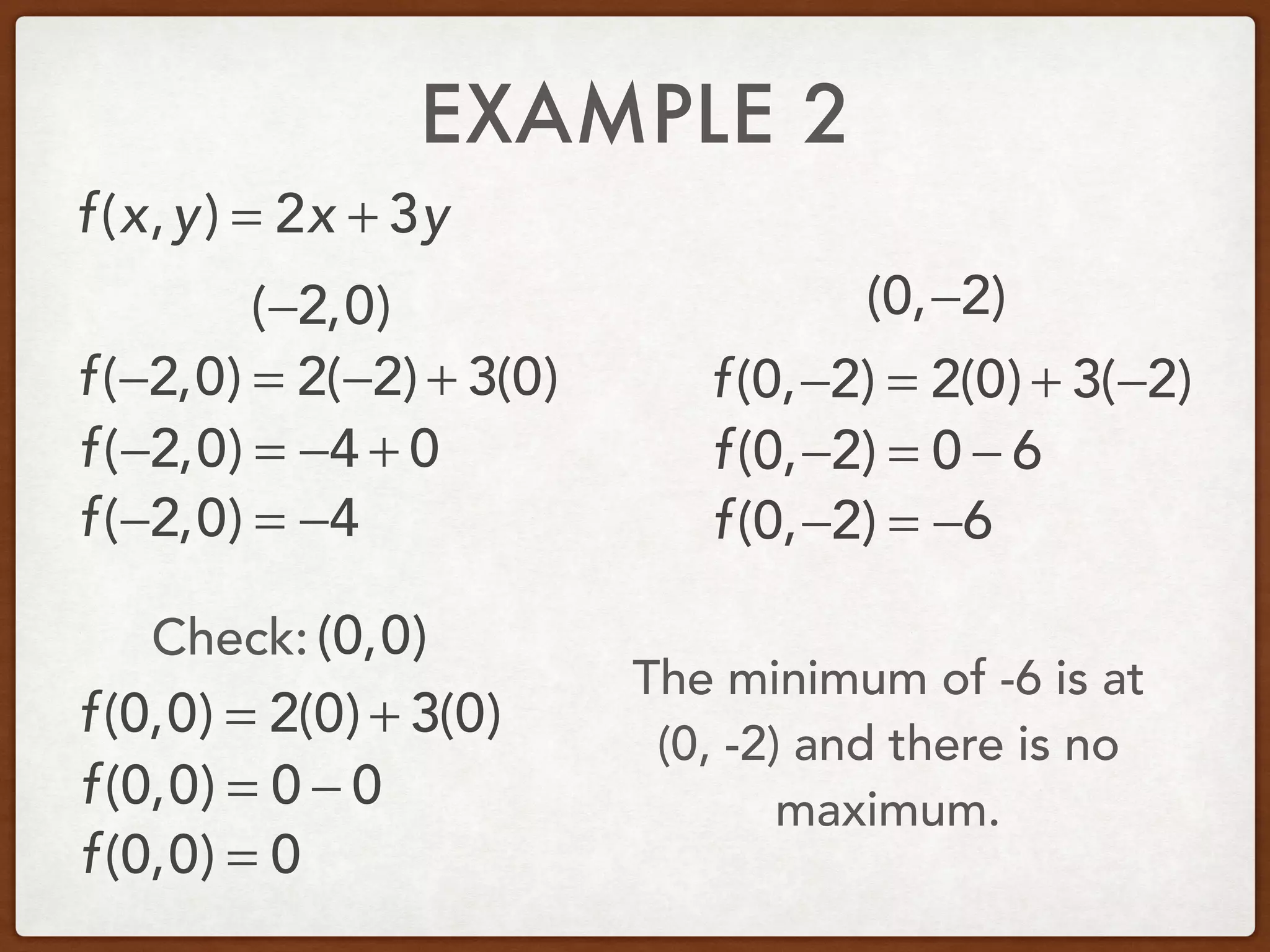
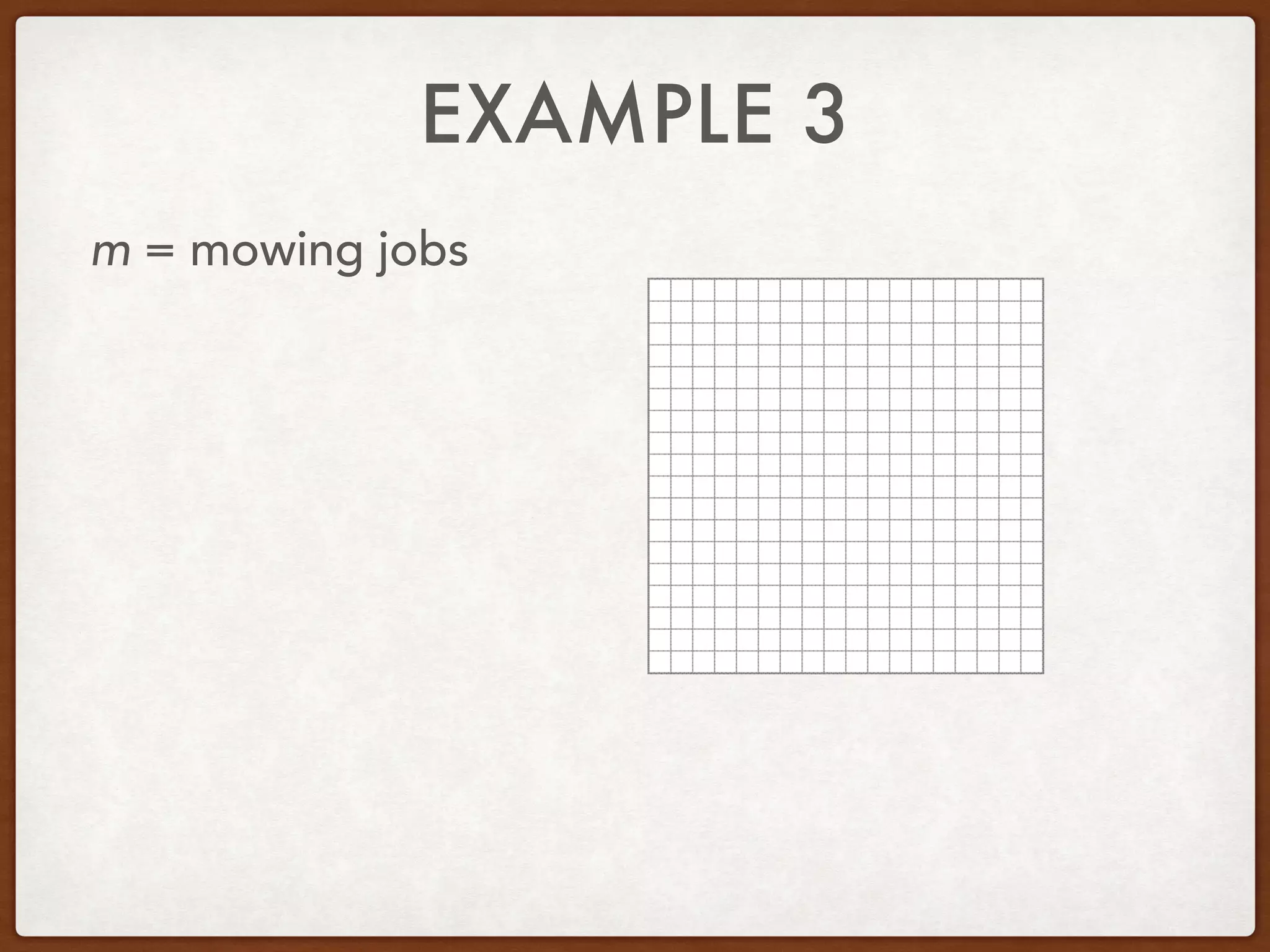
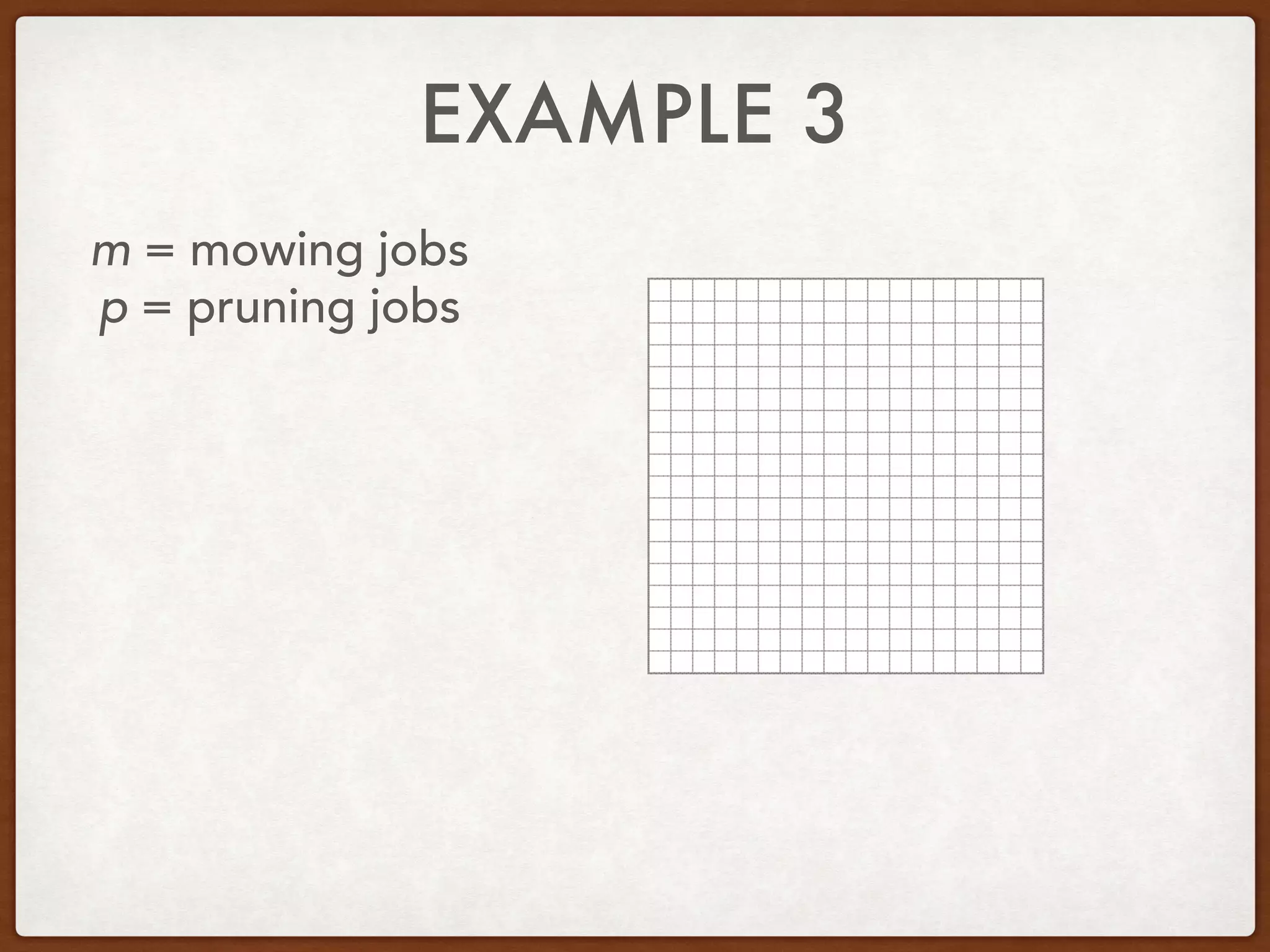
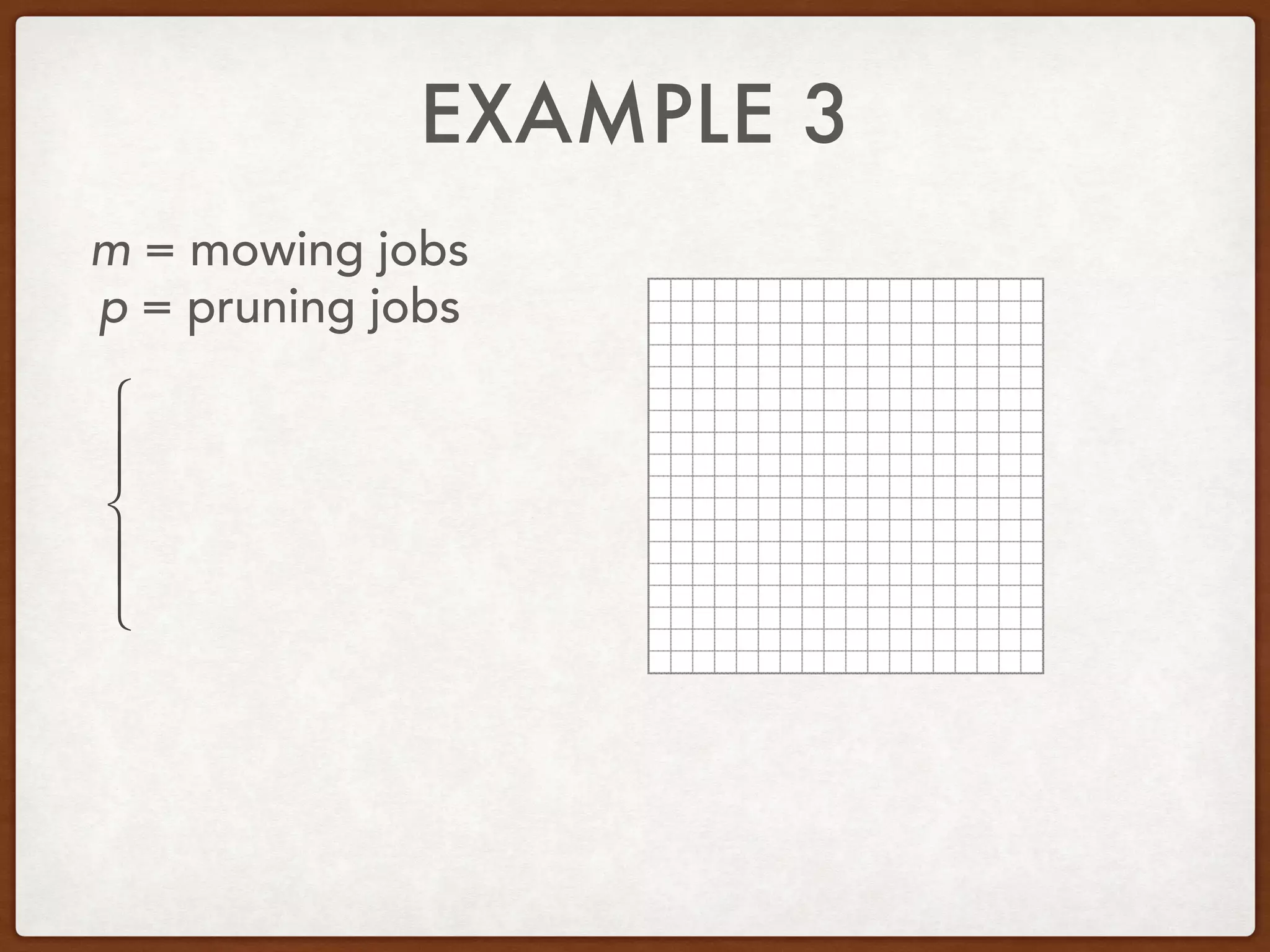
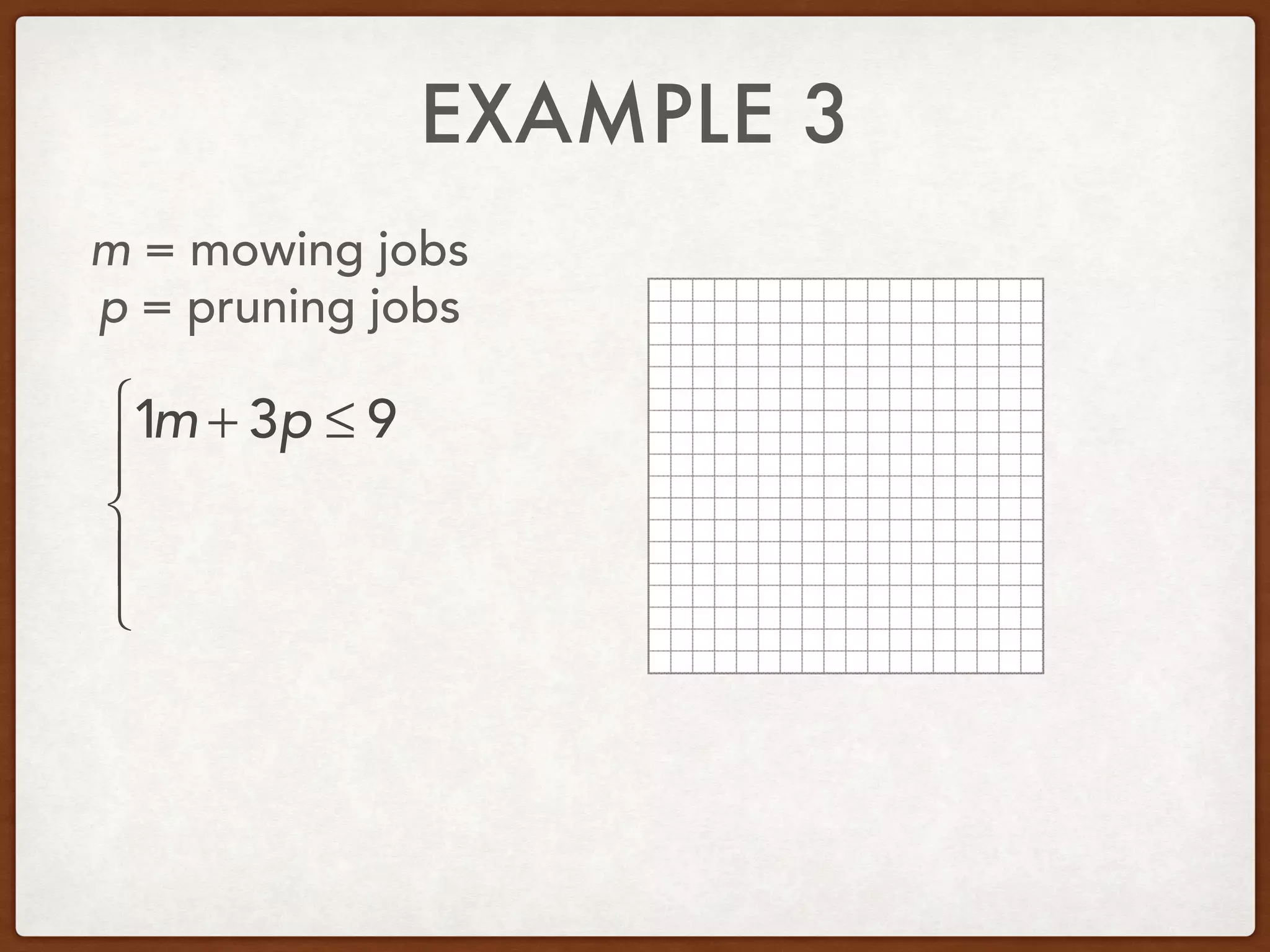
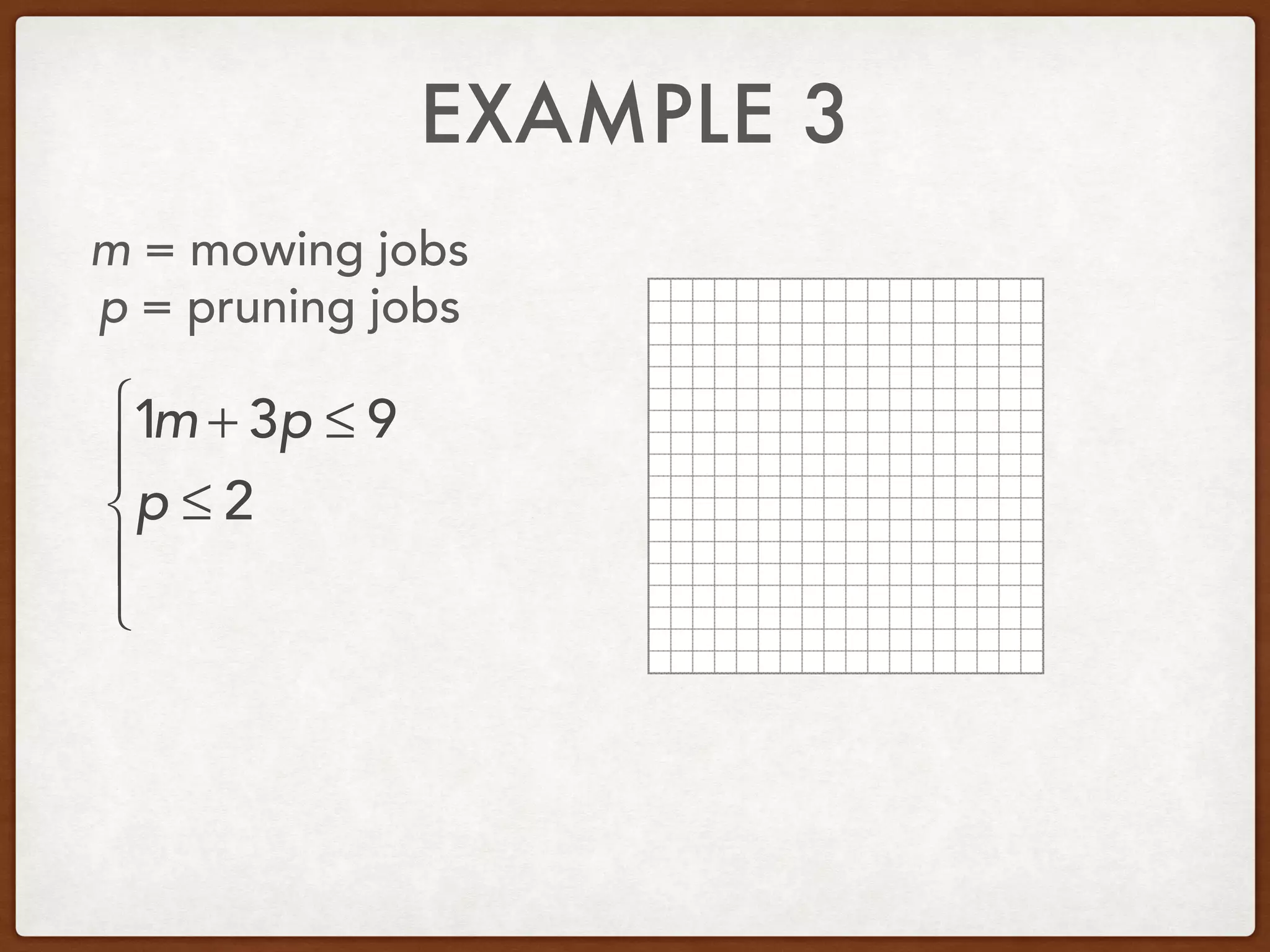
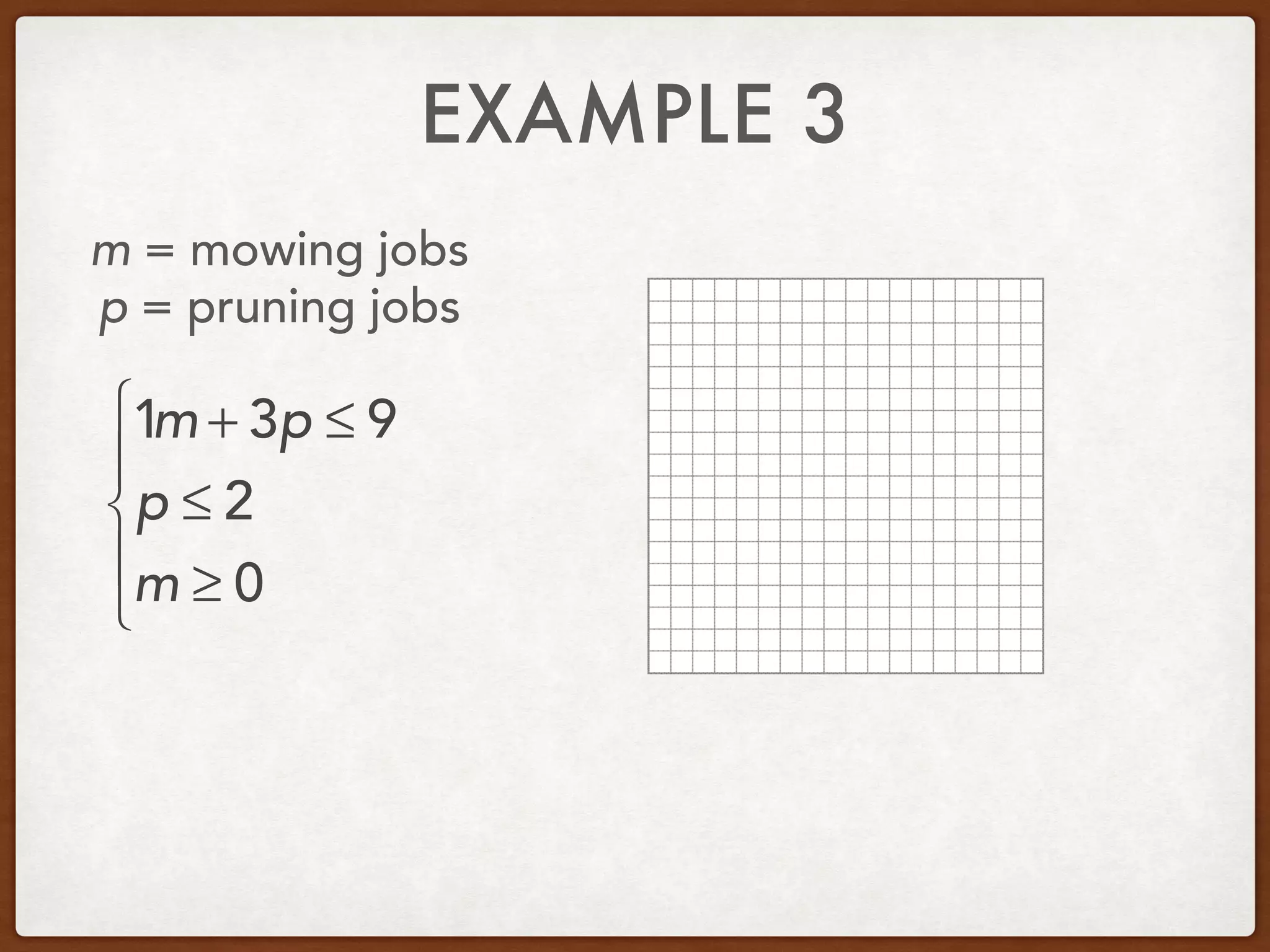
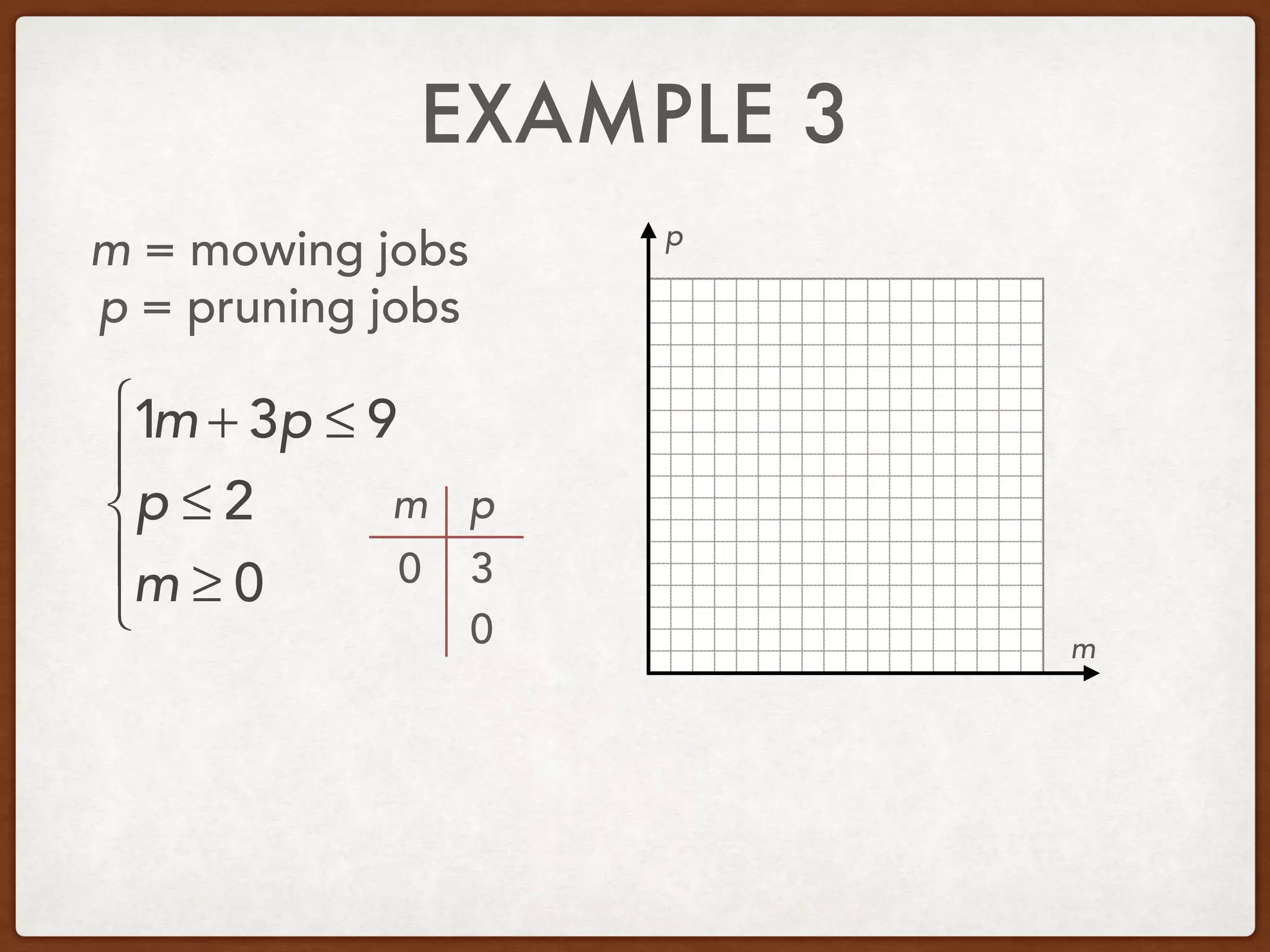
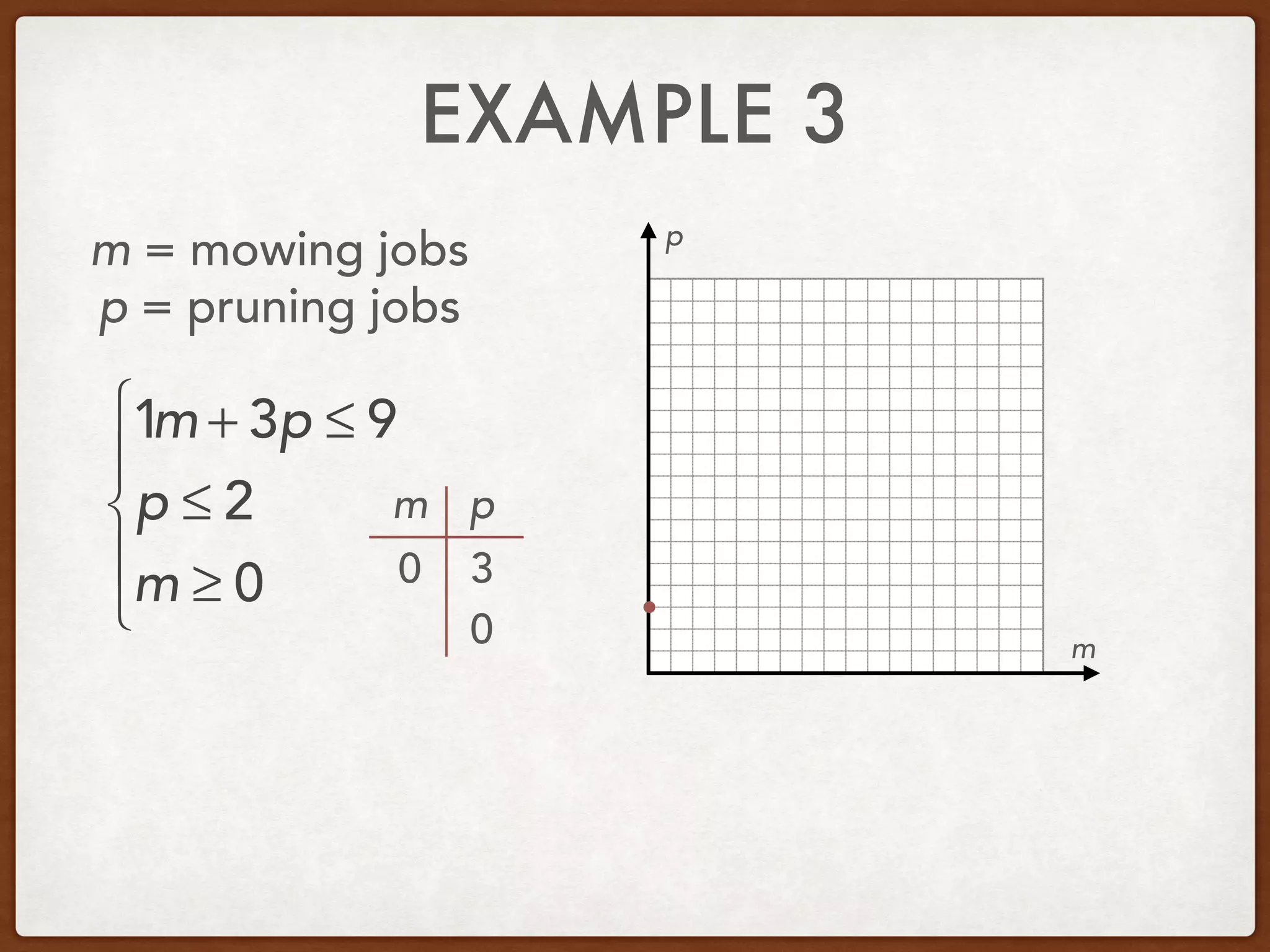
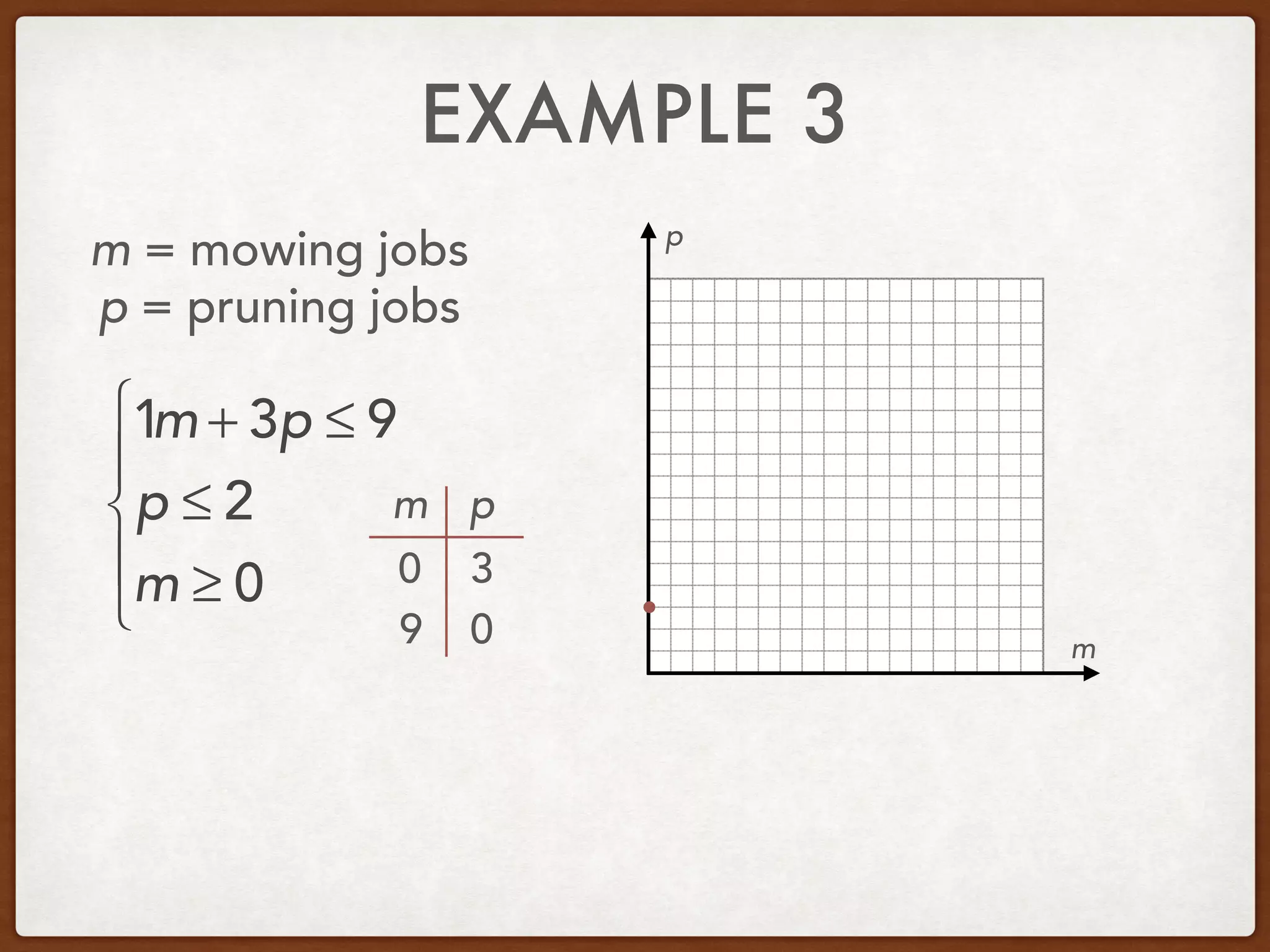
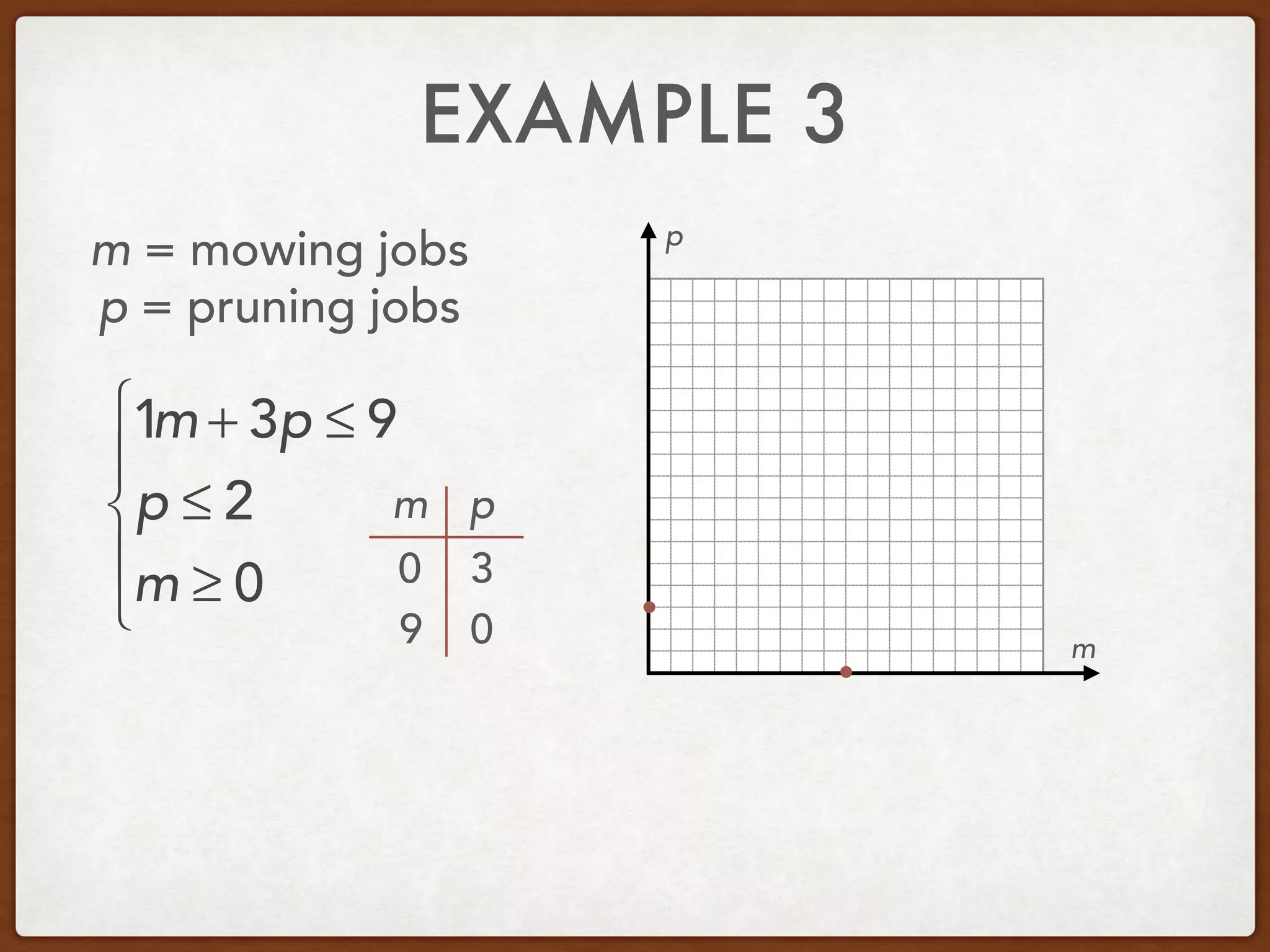
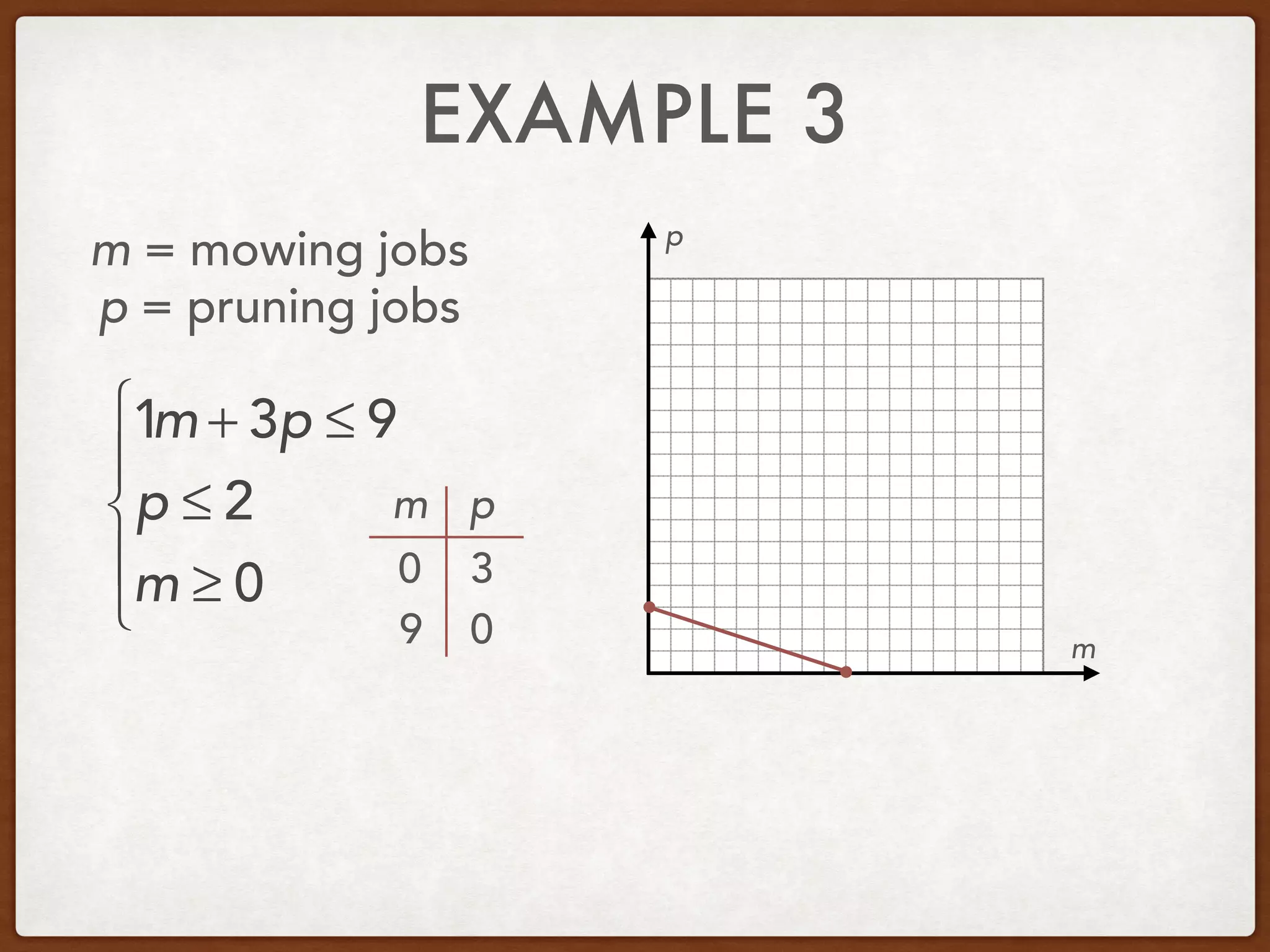
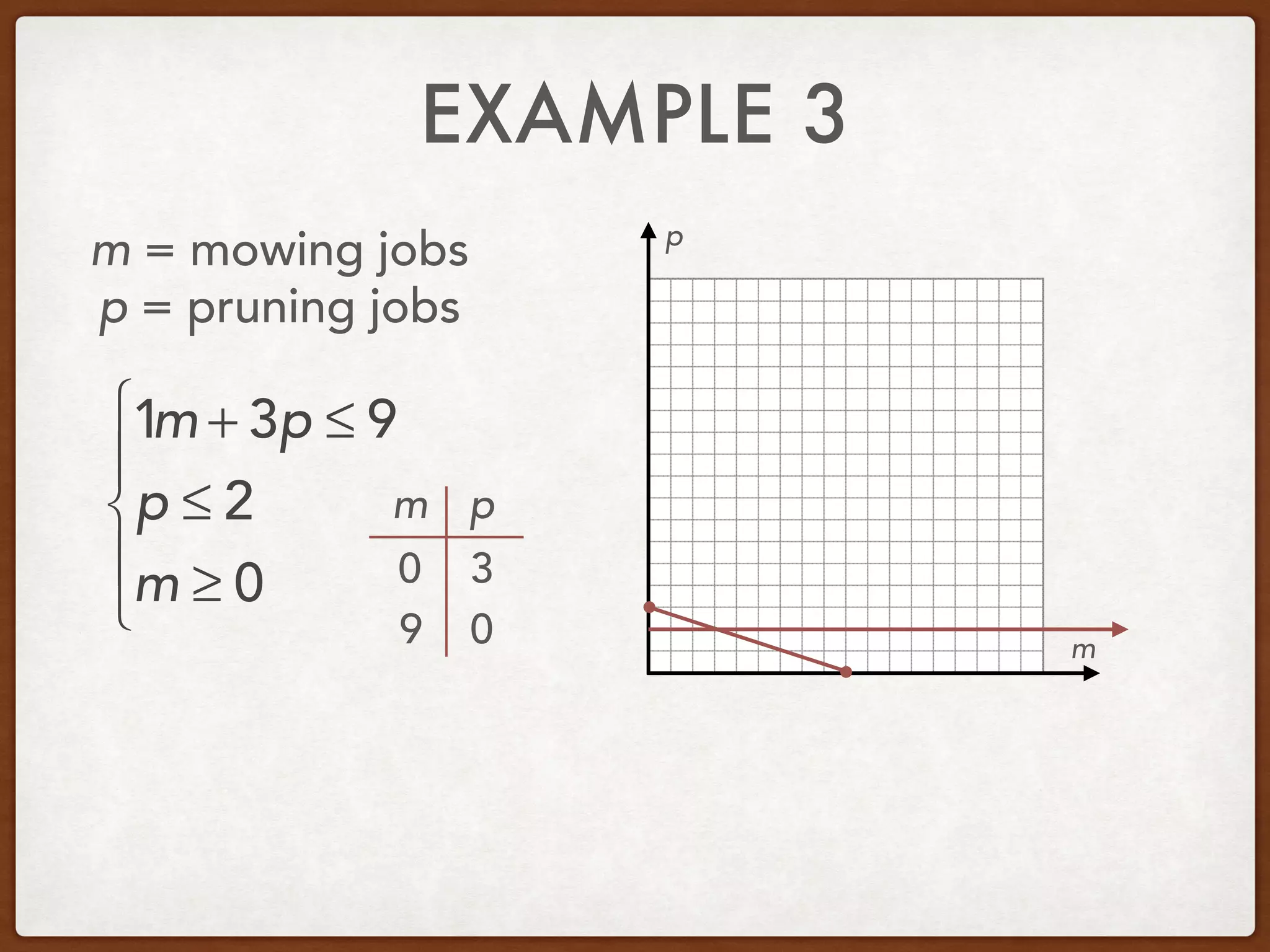
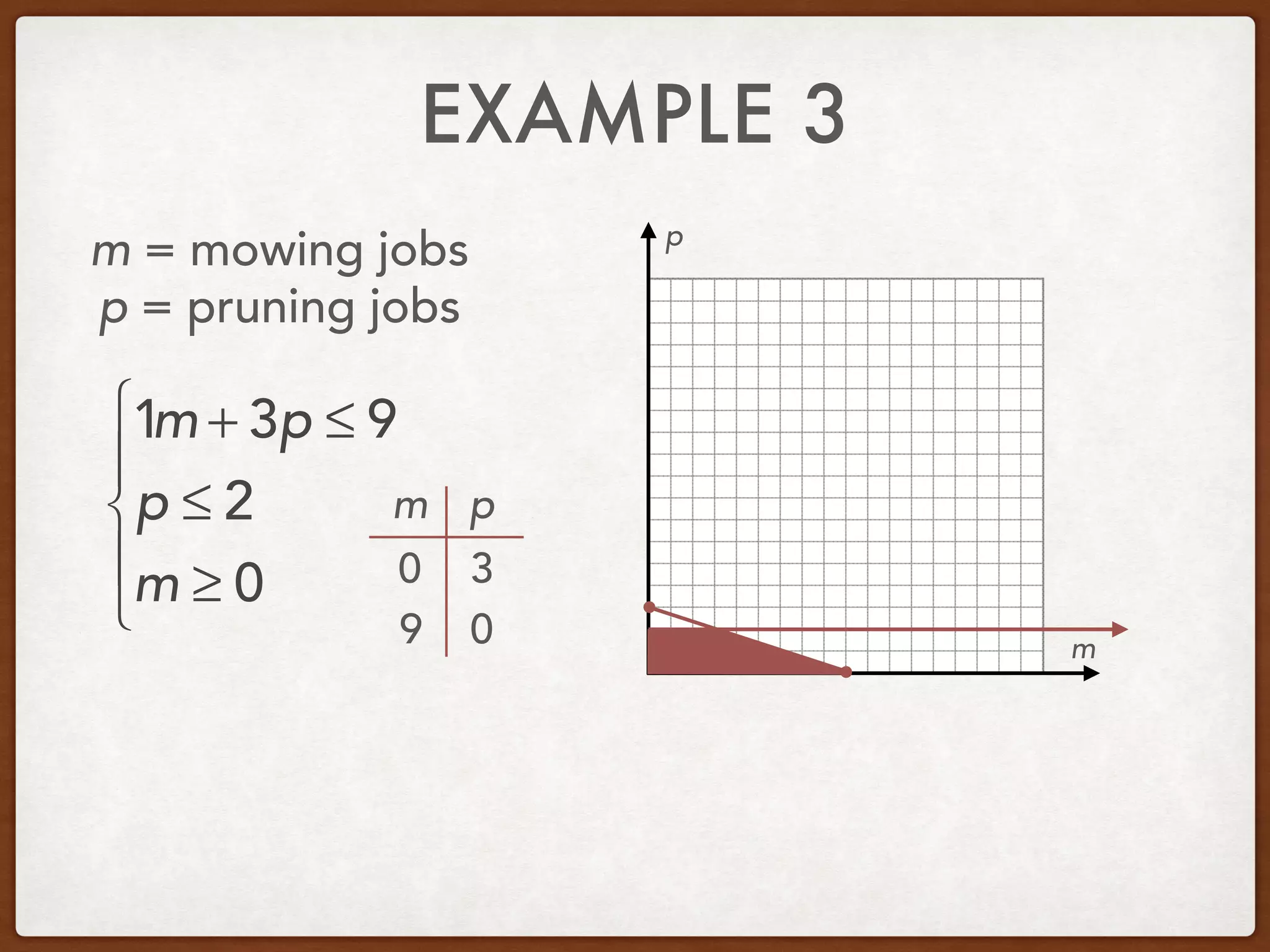
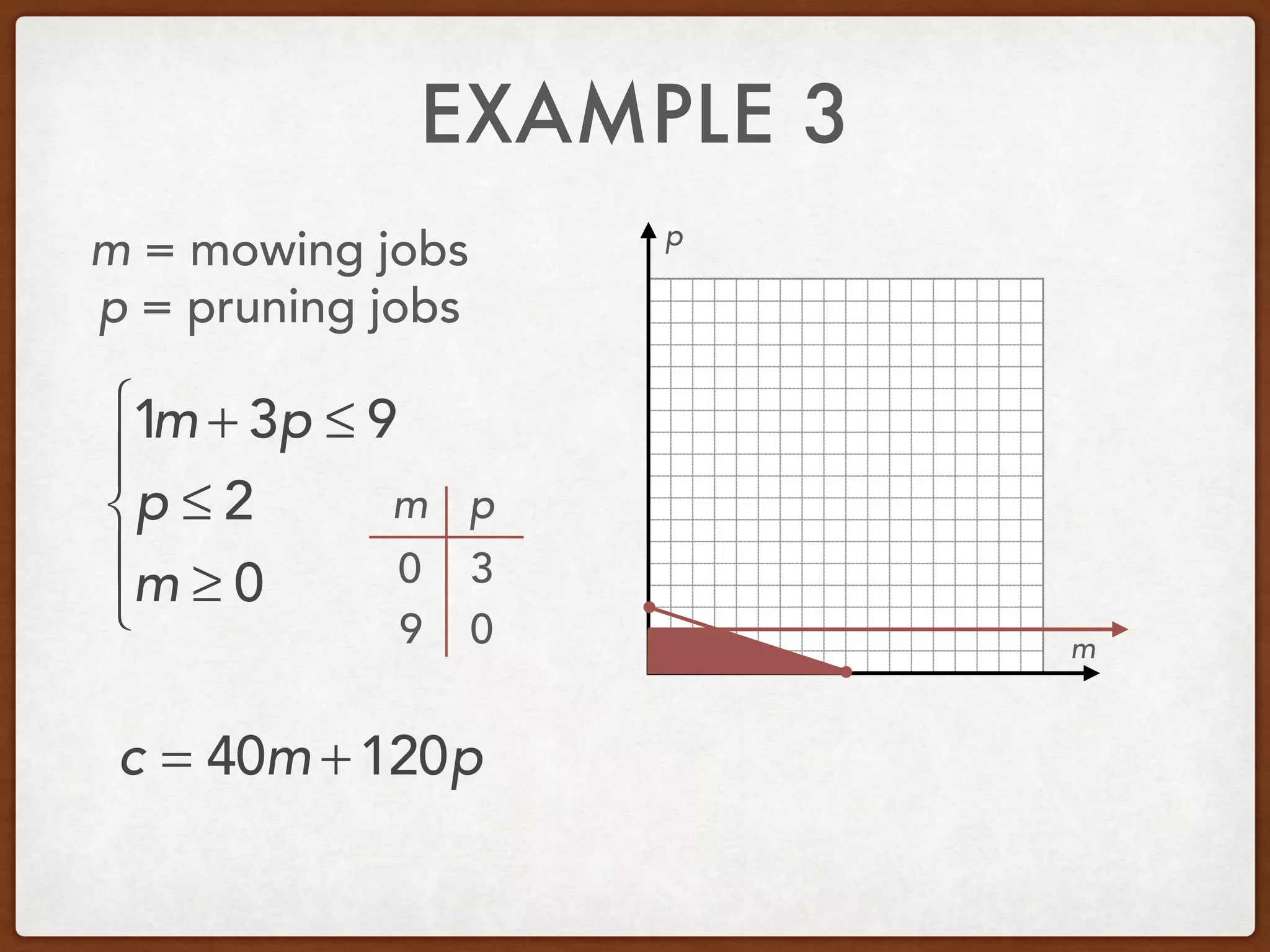
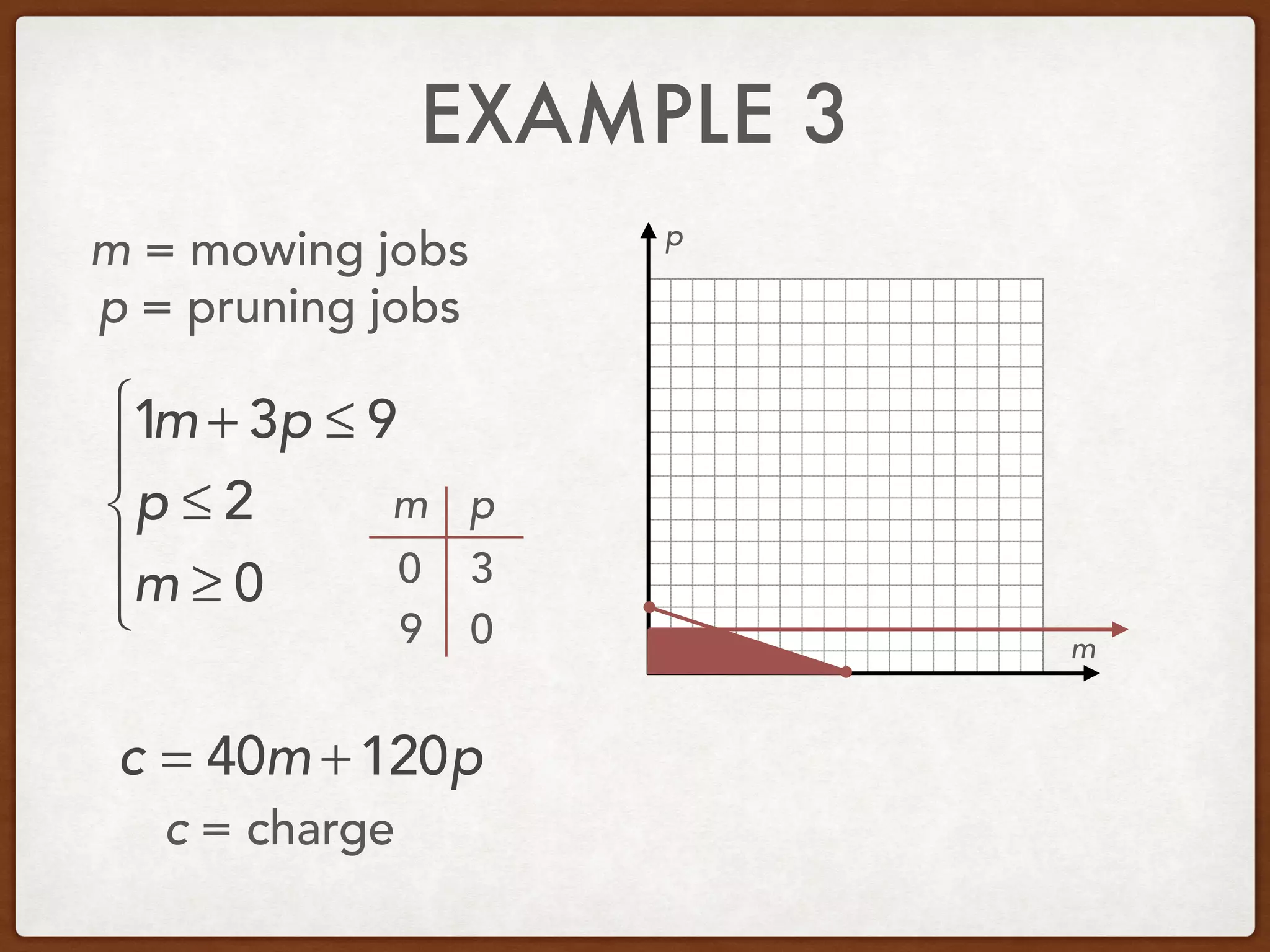
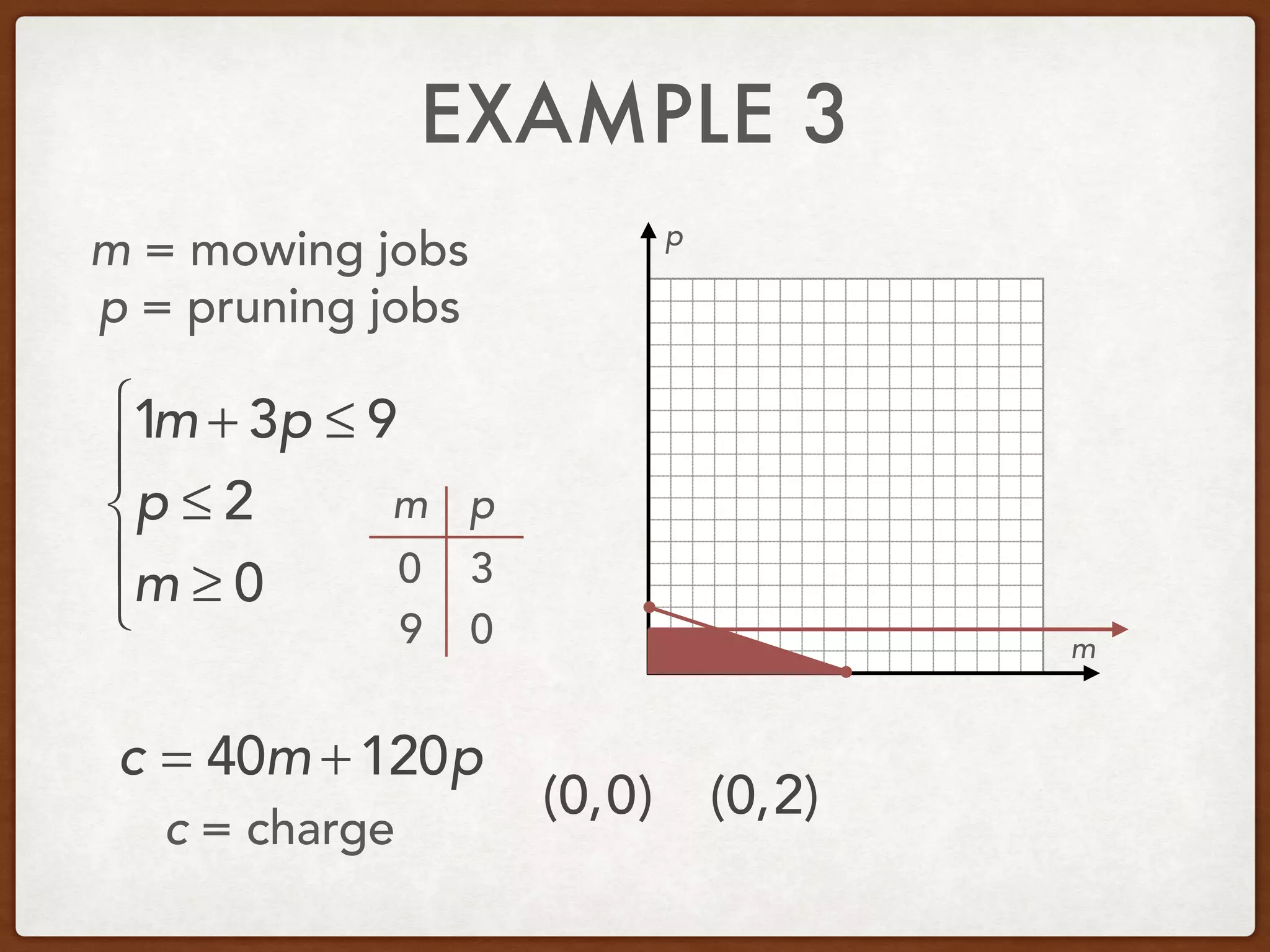
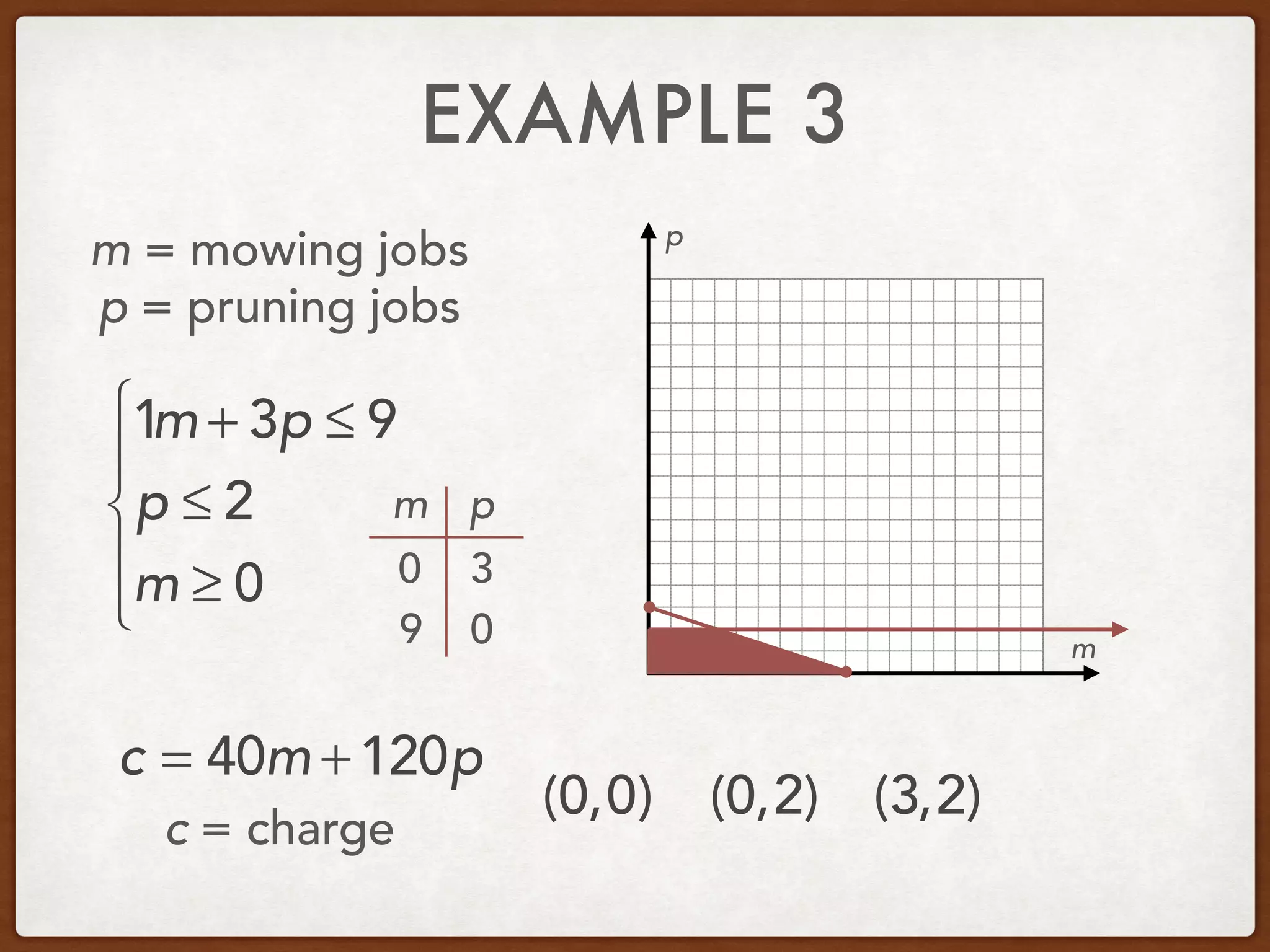
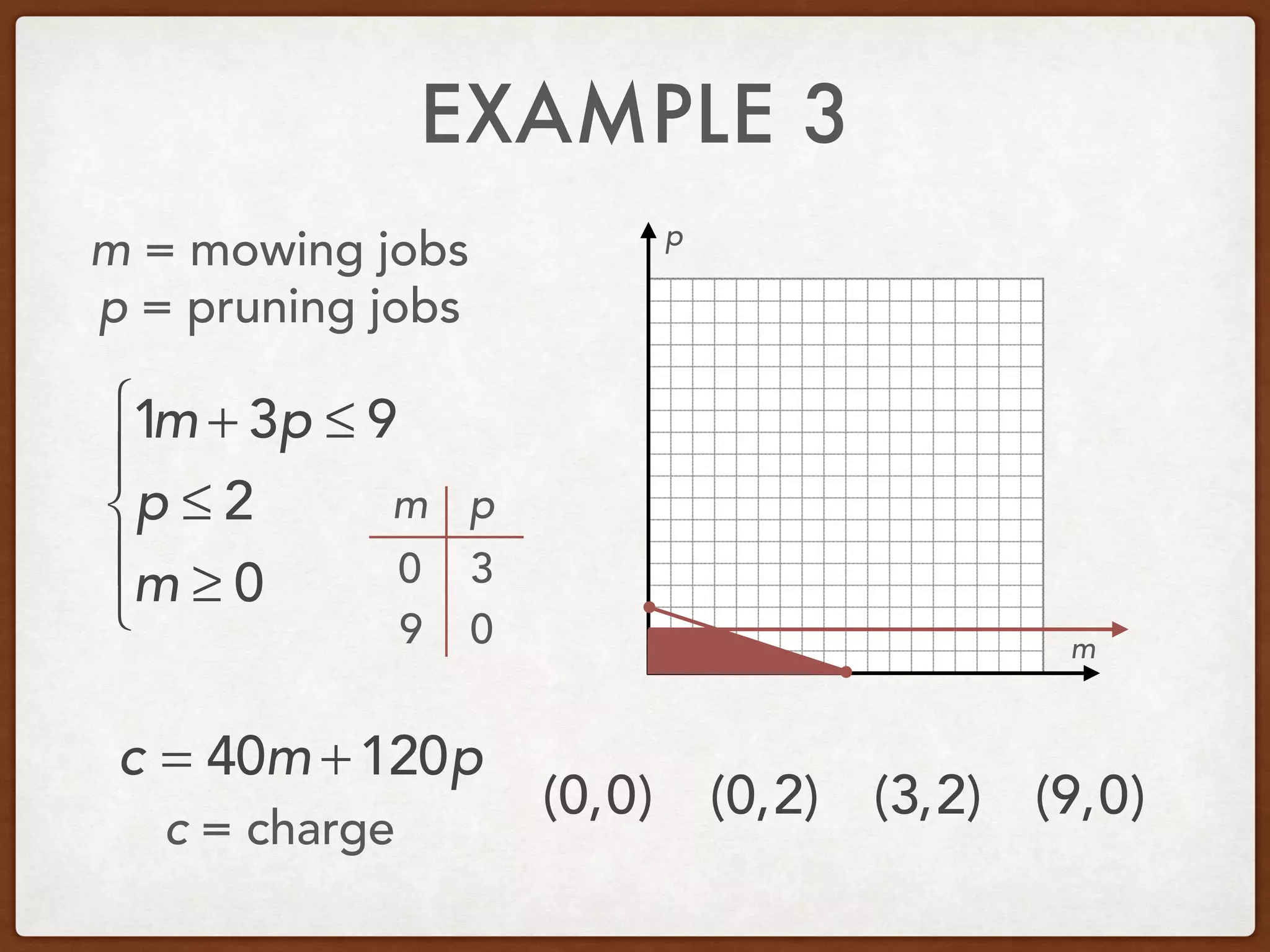
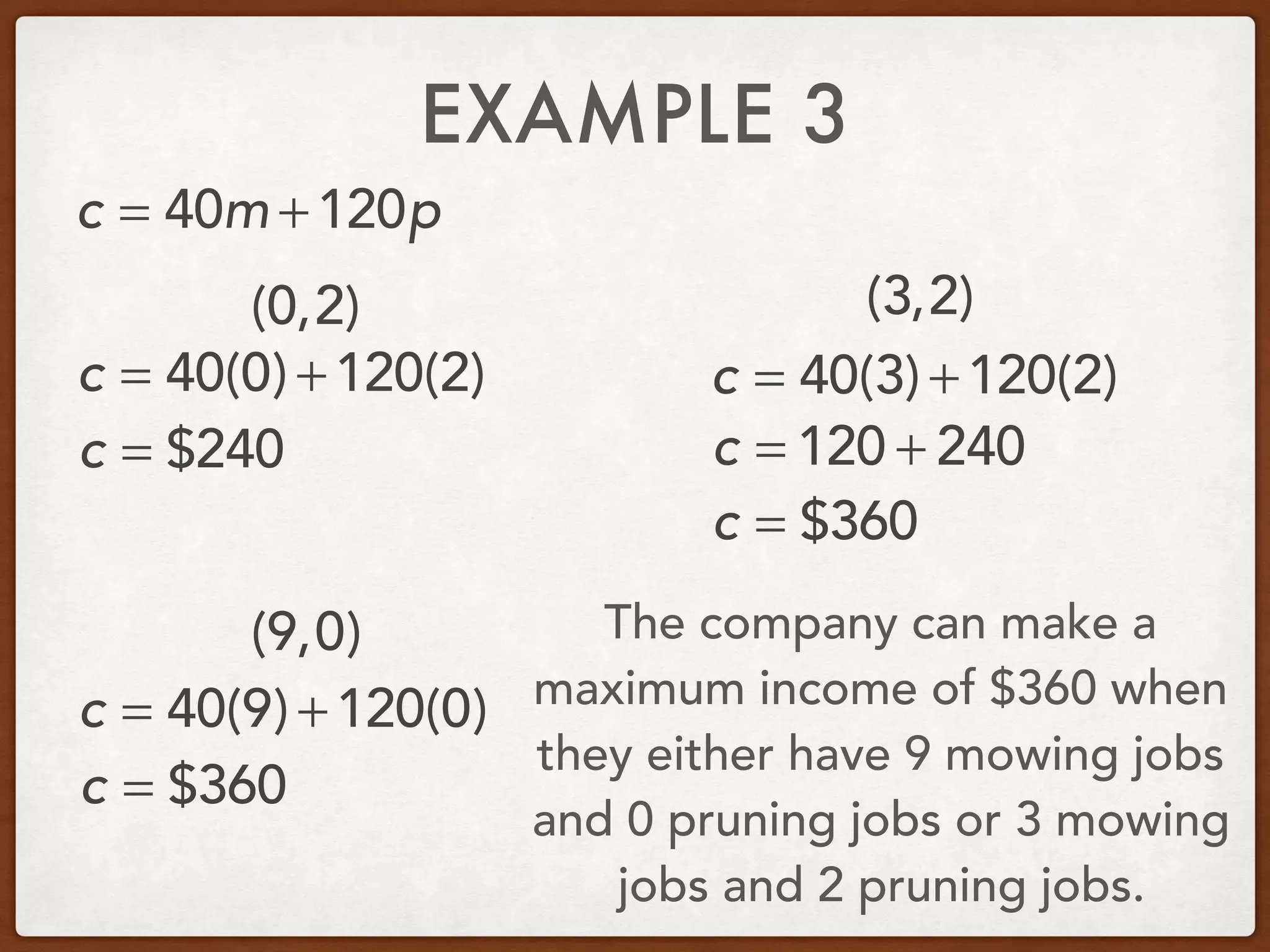
This document discusses linear programming and optimization. It begins with essential questions about finding maximum and minimum values of functions over regions. Key vocabulary is defined, including linear programming, feasible region, bounded, unbounded, and optimize. Two examples are provided to demonstrate how to graph inequality systems, identify feasible regions, and find the maximum and minimum values of an objective function over those regions using linear programming techniques.