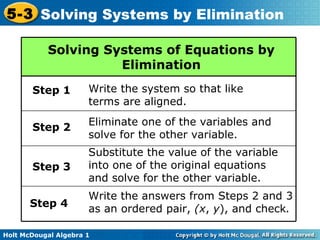
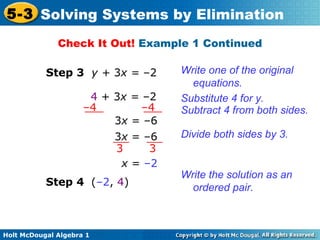
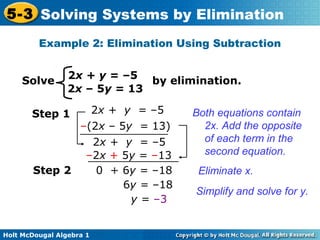
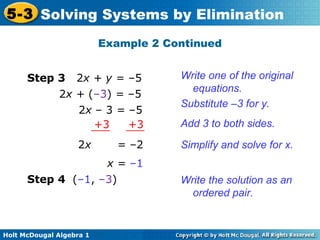
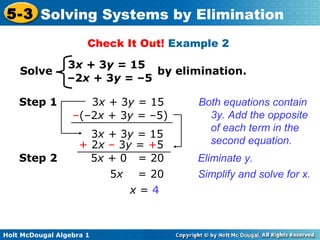
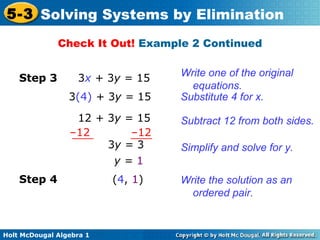
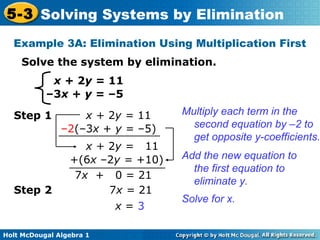
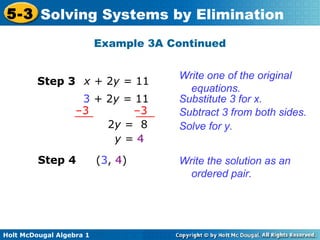
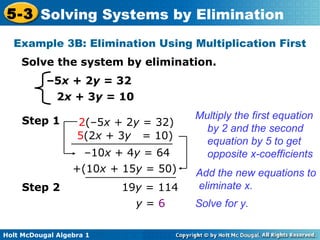
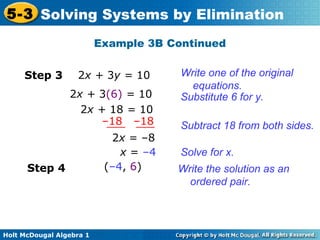
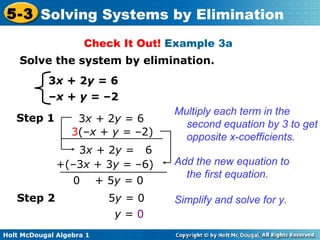
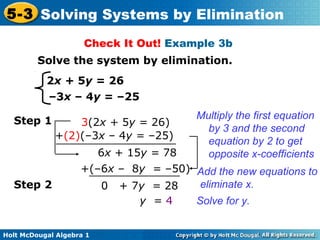
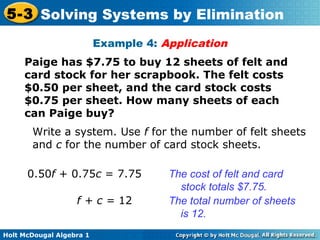
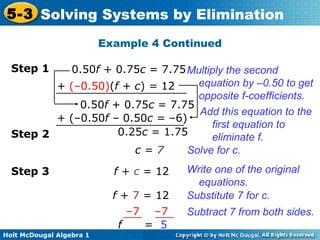
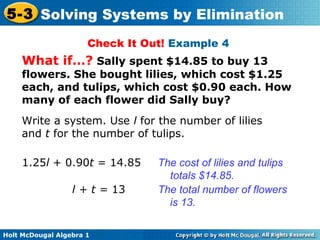
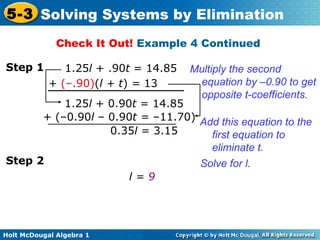
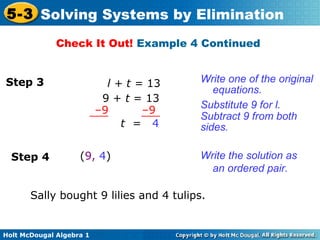
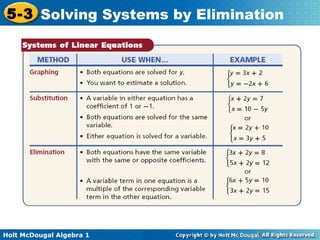
The document teaches how to solve systems of linear equations in two variables using the elimination method. It provides step-by-step examples, including aligning like terms, eliminating a variable, solving for the other variable, and checking the solution. The document also discusses methods for achieving opposite coefficients to facilitate elimination.