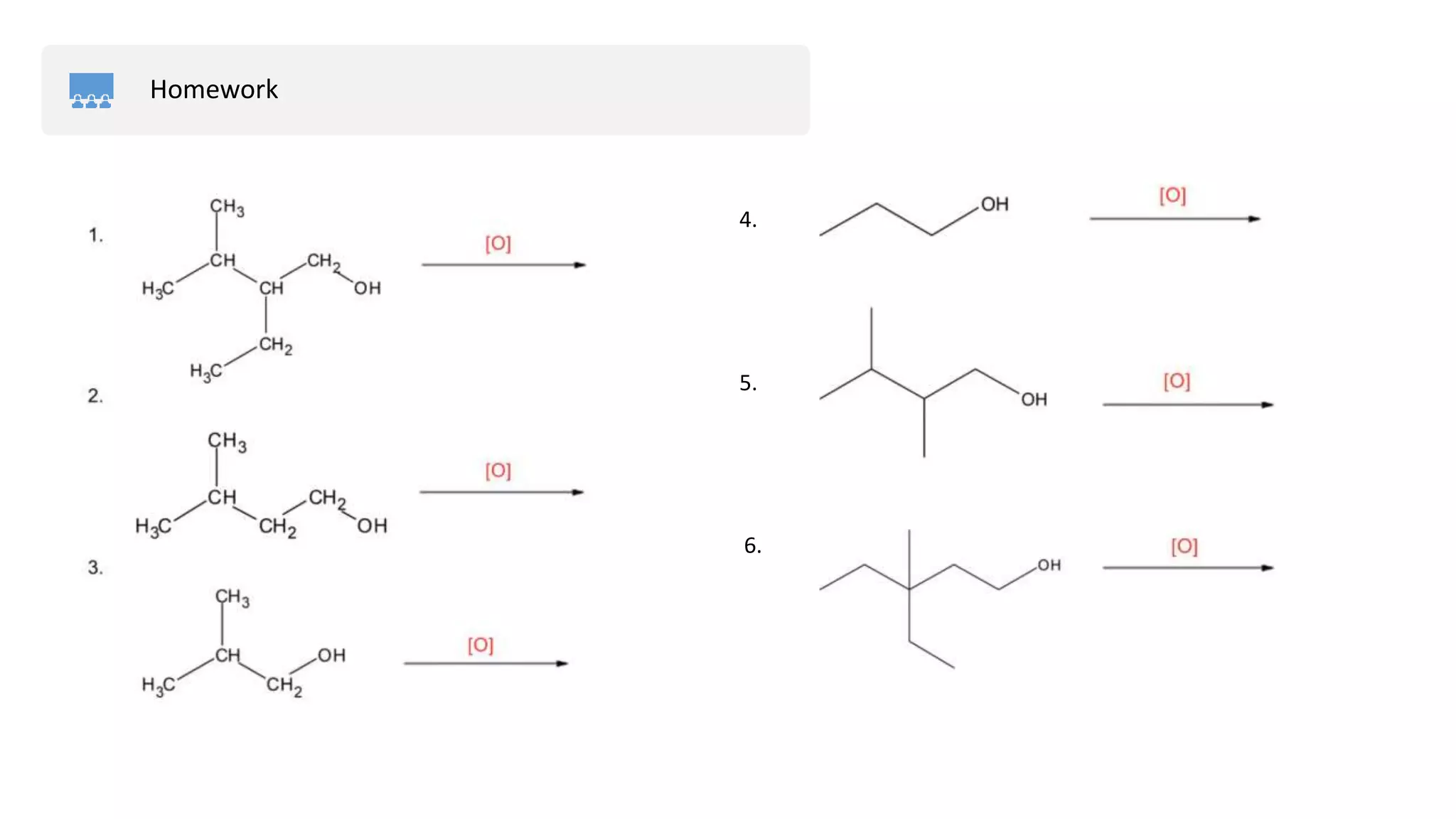
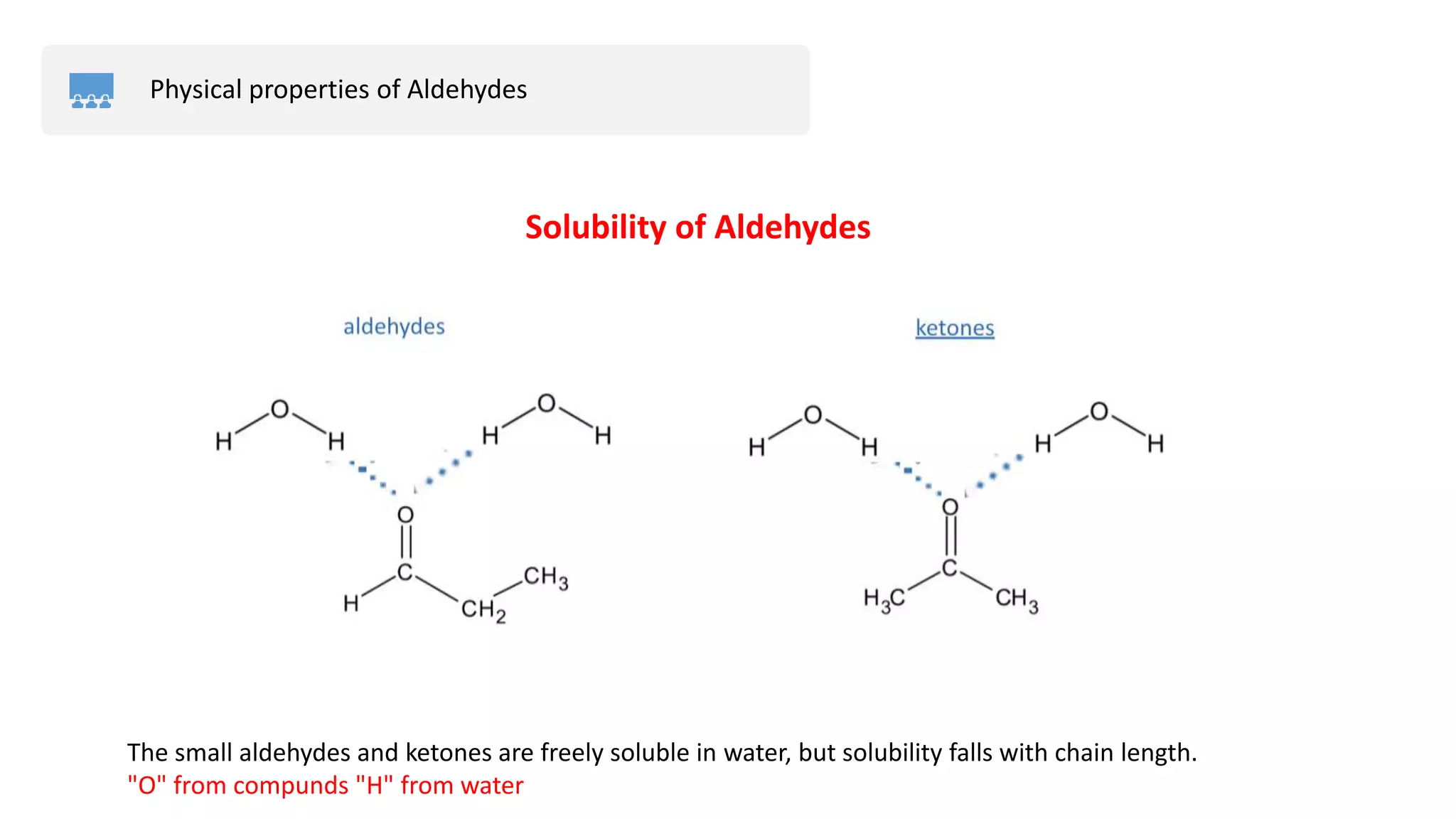
The document provides an overview of aldehydes, including their physical properties, applications, and preparation methods. It discusses specific examples like formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, detailing their characteristics and uses. The document also details the solubility of aldehydes and compares their boiling points with those of other compounds.









![Preparation of Aldehydes
Oxidizing Agents → [O]
KMnO4 / H+(potassium permanganate)K2Cr2O7 / H+
(potassium dichromate) CuO or H2O2(copper oxide or hydrogen
peroxide)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aldehydes-physicalpropertiesandpreparation-211124051503/75/Aldehydes-physical-properties-and-preparation-12-2048.jpg)