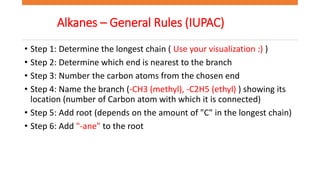
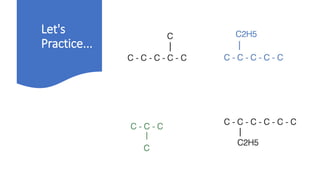
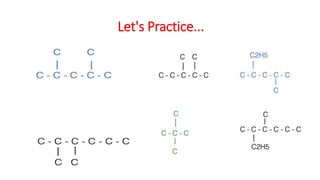
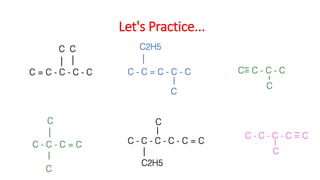
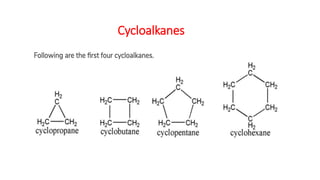
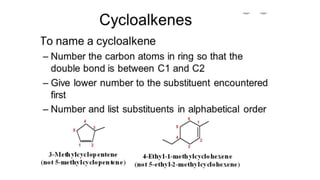
The document discusses IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming hydrocarbons including alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and cycloalkanes. For alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes, the rules specify how to determine the parent chain, number the carbons, name any branches, and add the appropriate suffix to indicate an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. For cycloalkanes, the rules specify how to number the carbons in the ring to minimize the sum of the numbers and name any branches alphabetically. The document encourages practicing examples and visualizing line structures.