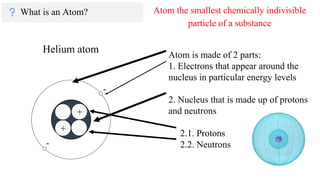
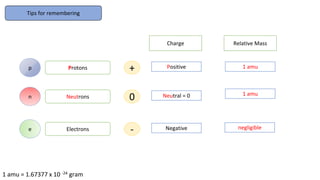
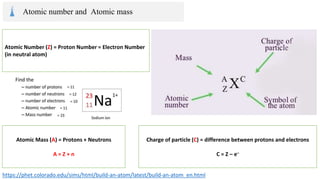
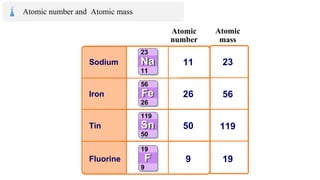
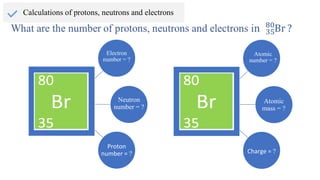
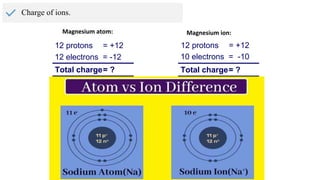
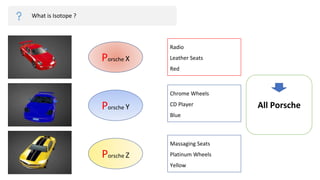
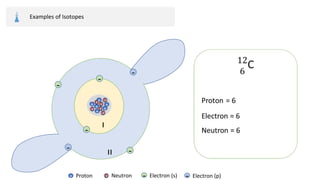
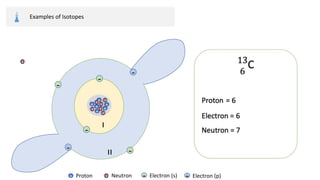
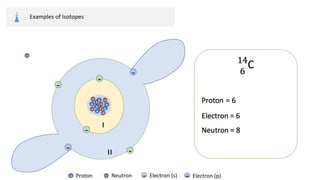
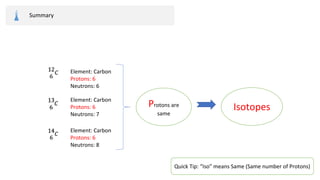
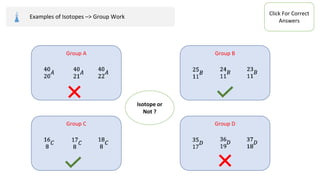
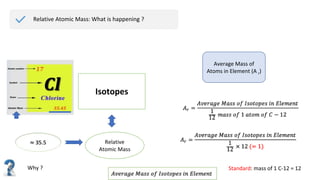
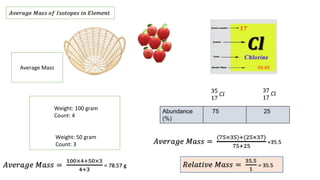
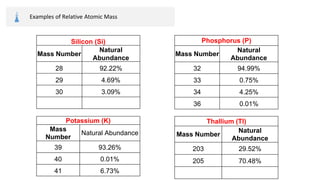
The document provides an overview of atomic structure, detailing the components of an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. It explains concepts like atomic number, atomic mass, and the calculation of charges in ions, along with examples of isotopes and relative atomic mass. Additionally, it offers learning objectives and resources for further exploration of the material.