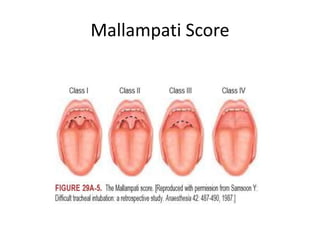
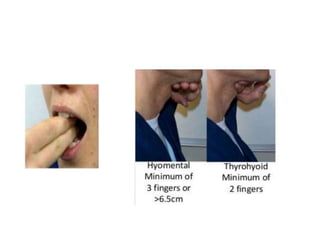
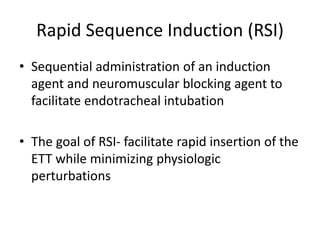
This document discusses airway management in a case of massive hemoptysis. It outlines the patient's history and examination findings, initial emergency management including fluid resuscitation and blood products, and subsequent deterioration requiring intubation. The document reviews airway assessment tools like the Mallampati score and LEMON criteria. Rapid sequence induction is described as the method of intubation, though initial attempts failed before successful intubation on the second try. Brief cardiac arrest occurred post-intubation but return of spontaneous circulation was achieved with flushing of the endotracheal tube. Key learning points include thorough pre-intubation airway assessment and being prepared to troubleshoot potential post-intubation issues.