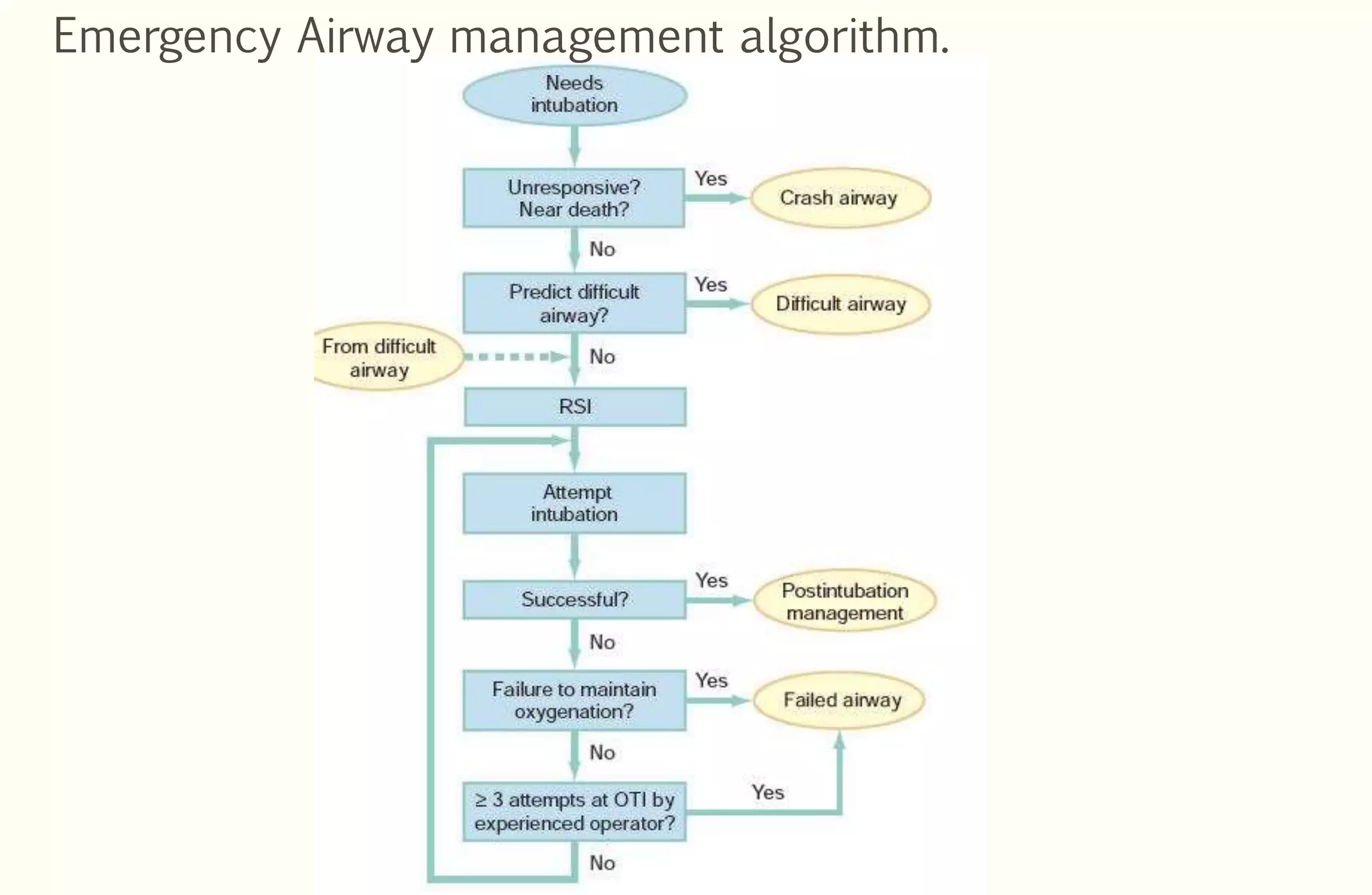
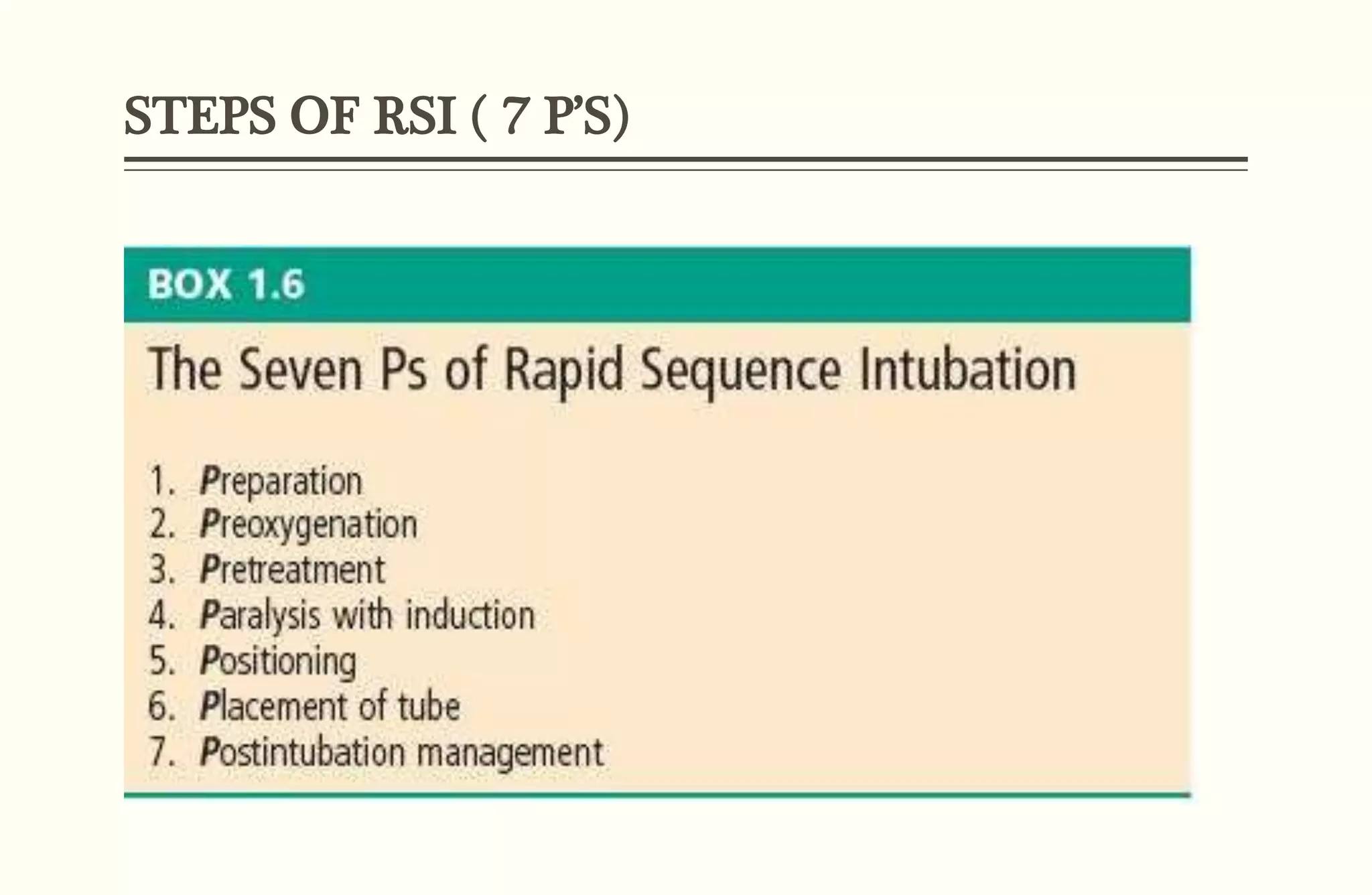
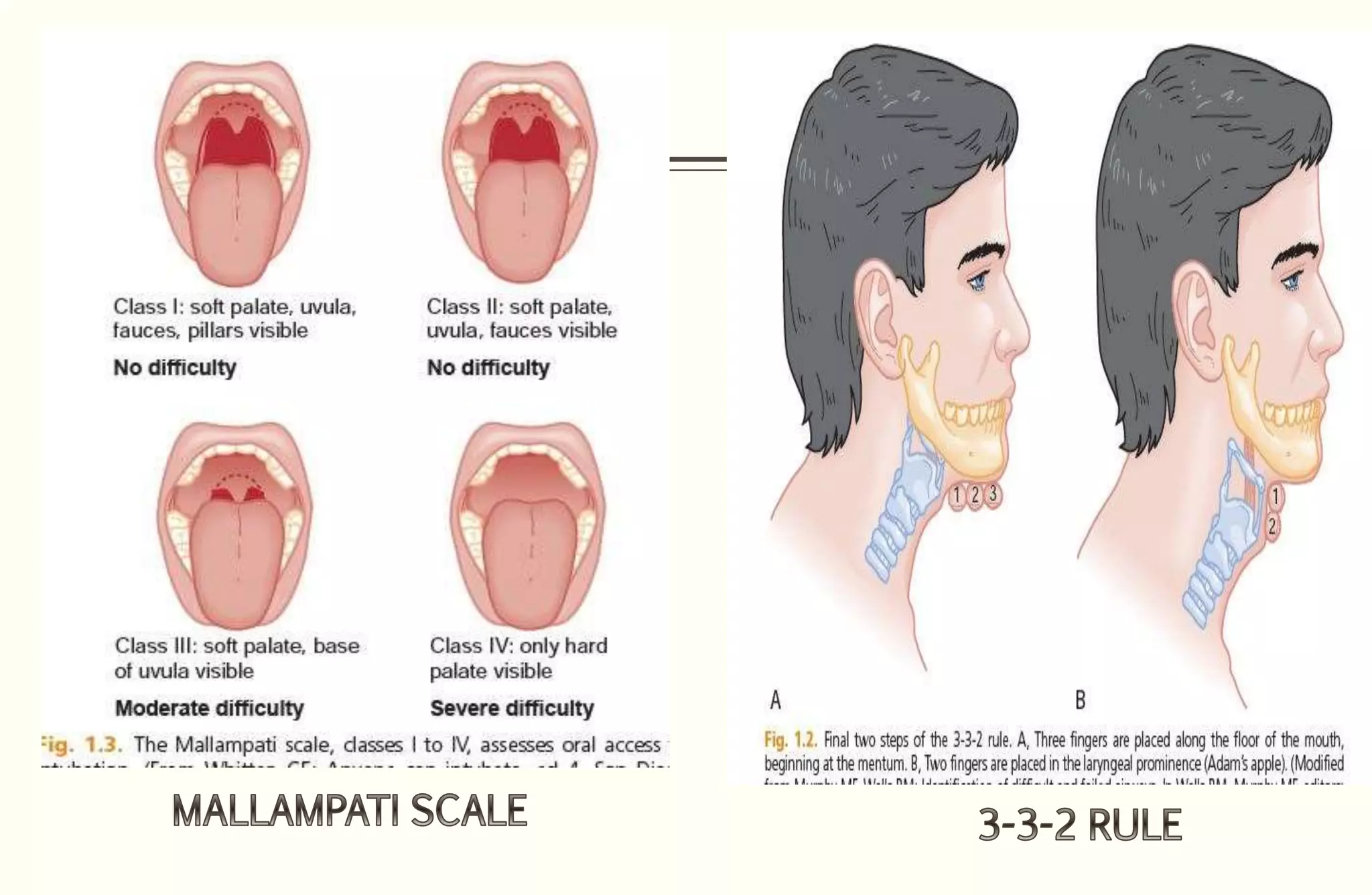
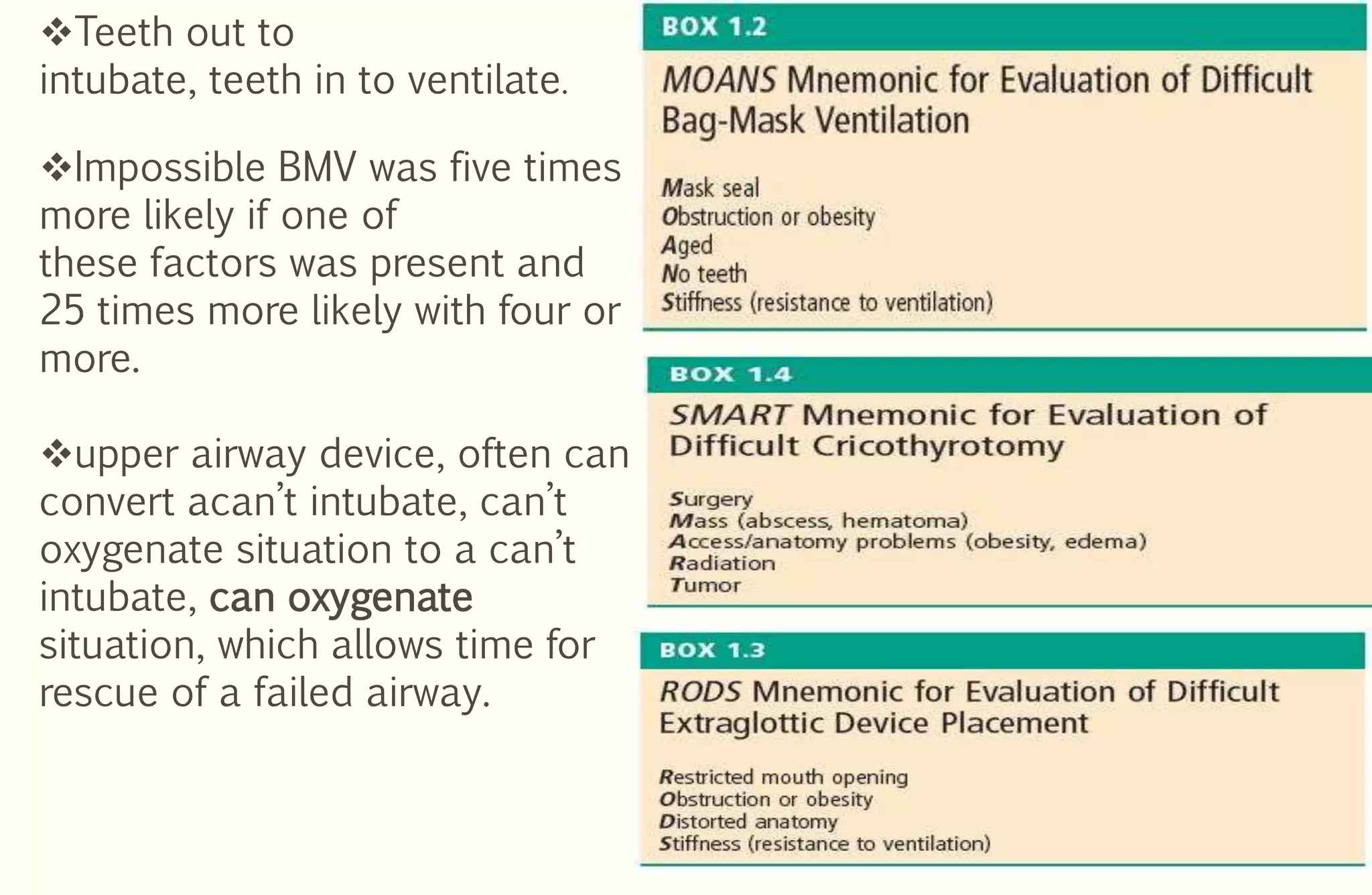
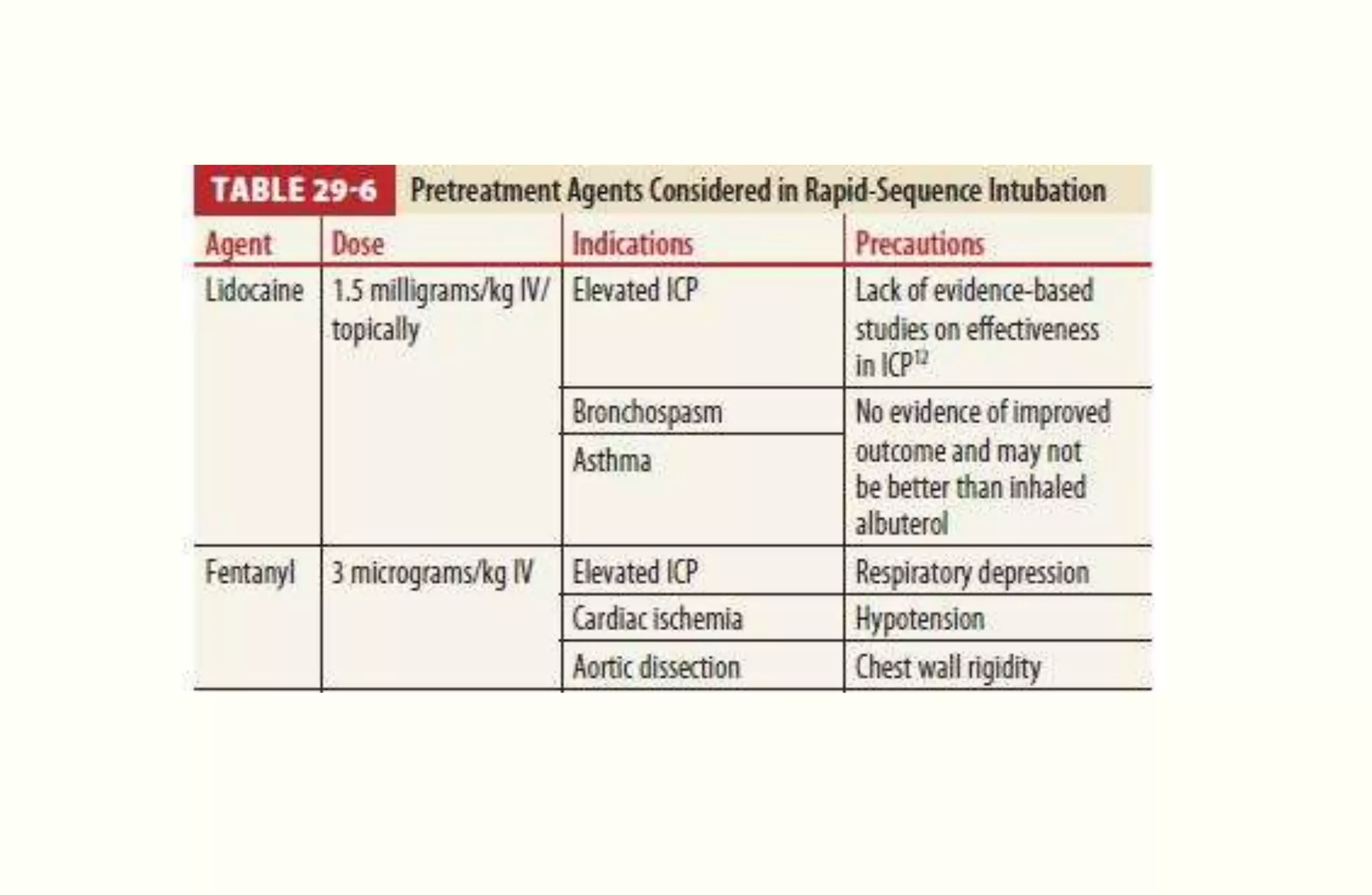
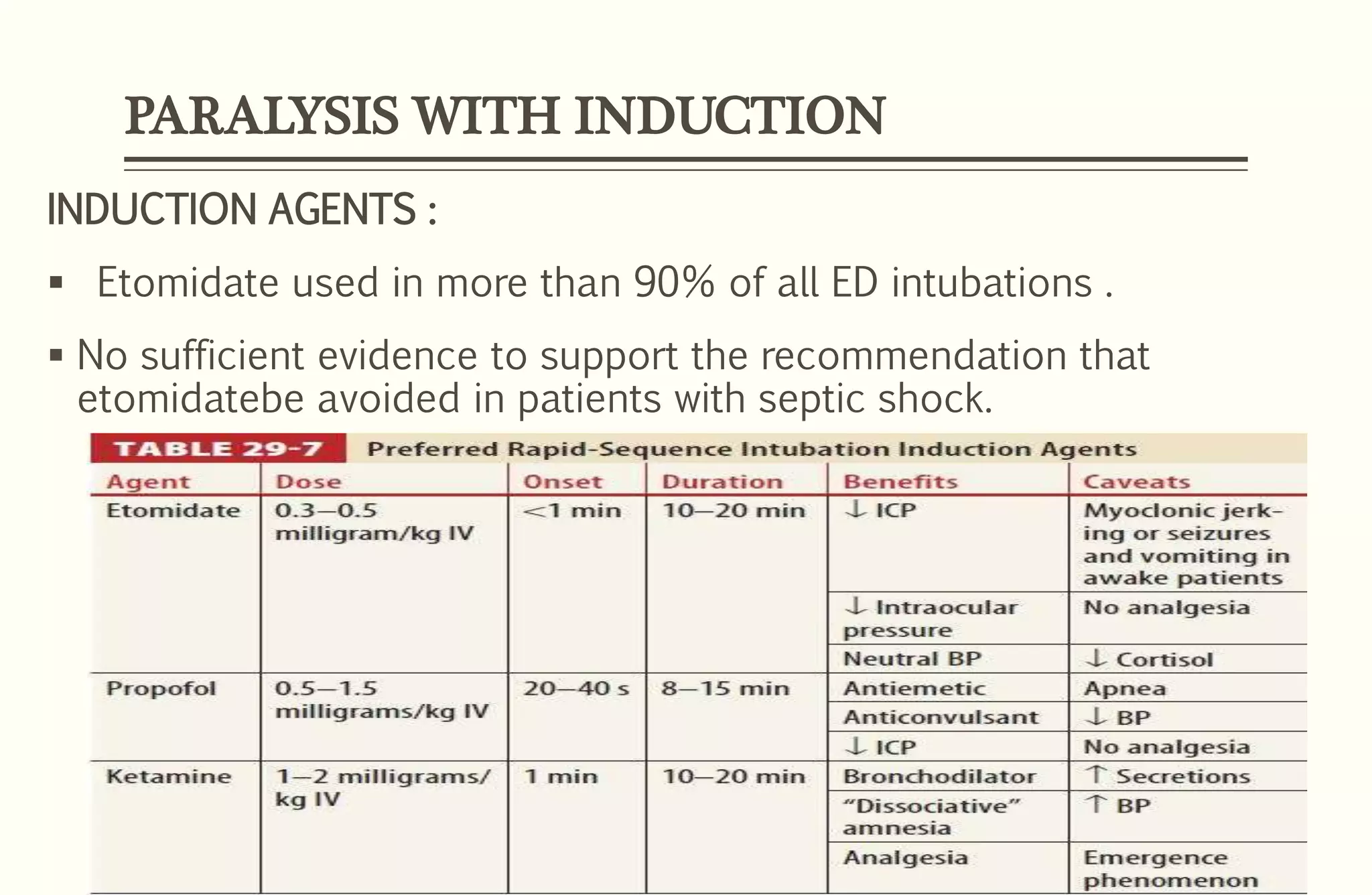
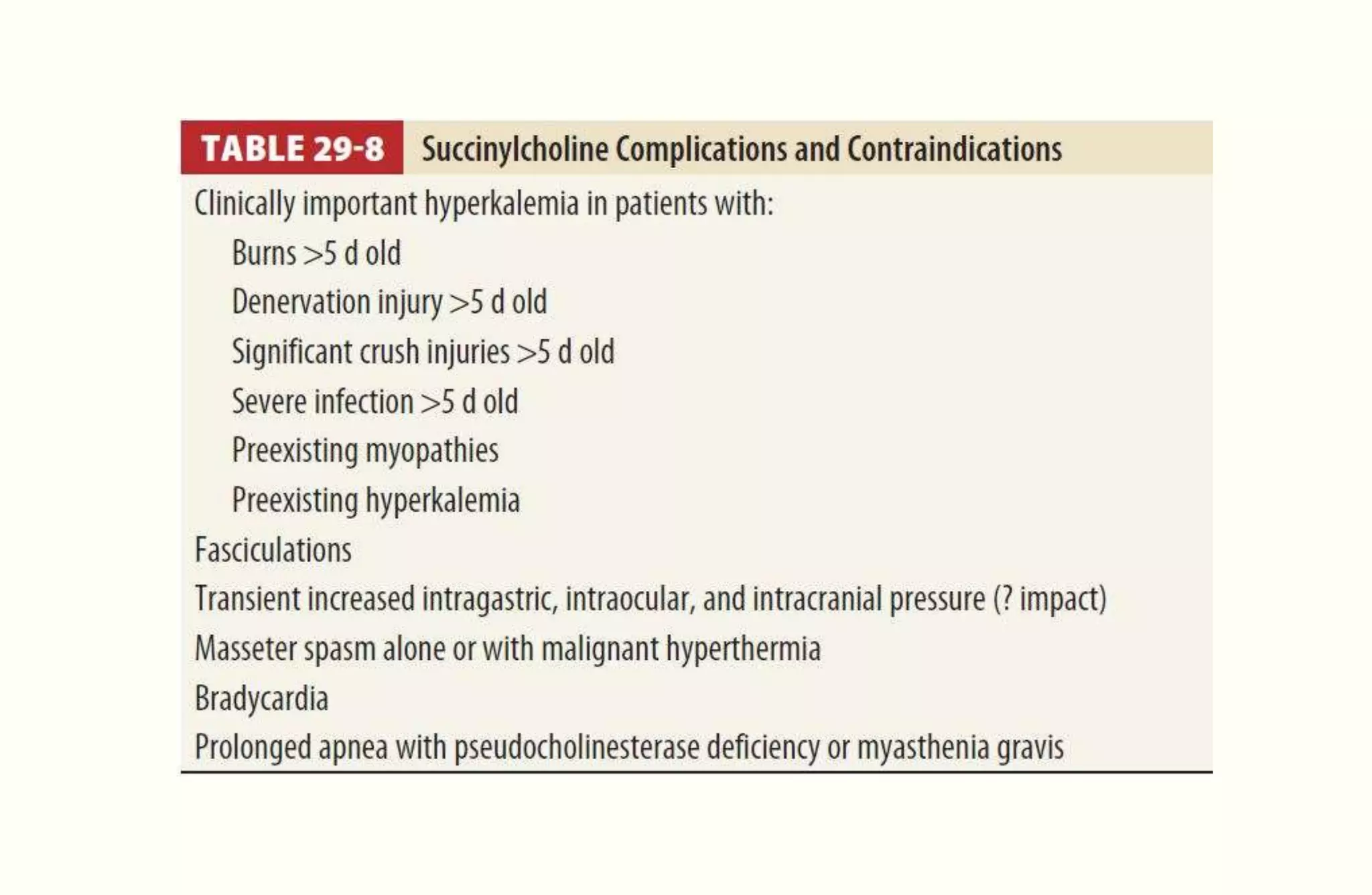
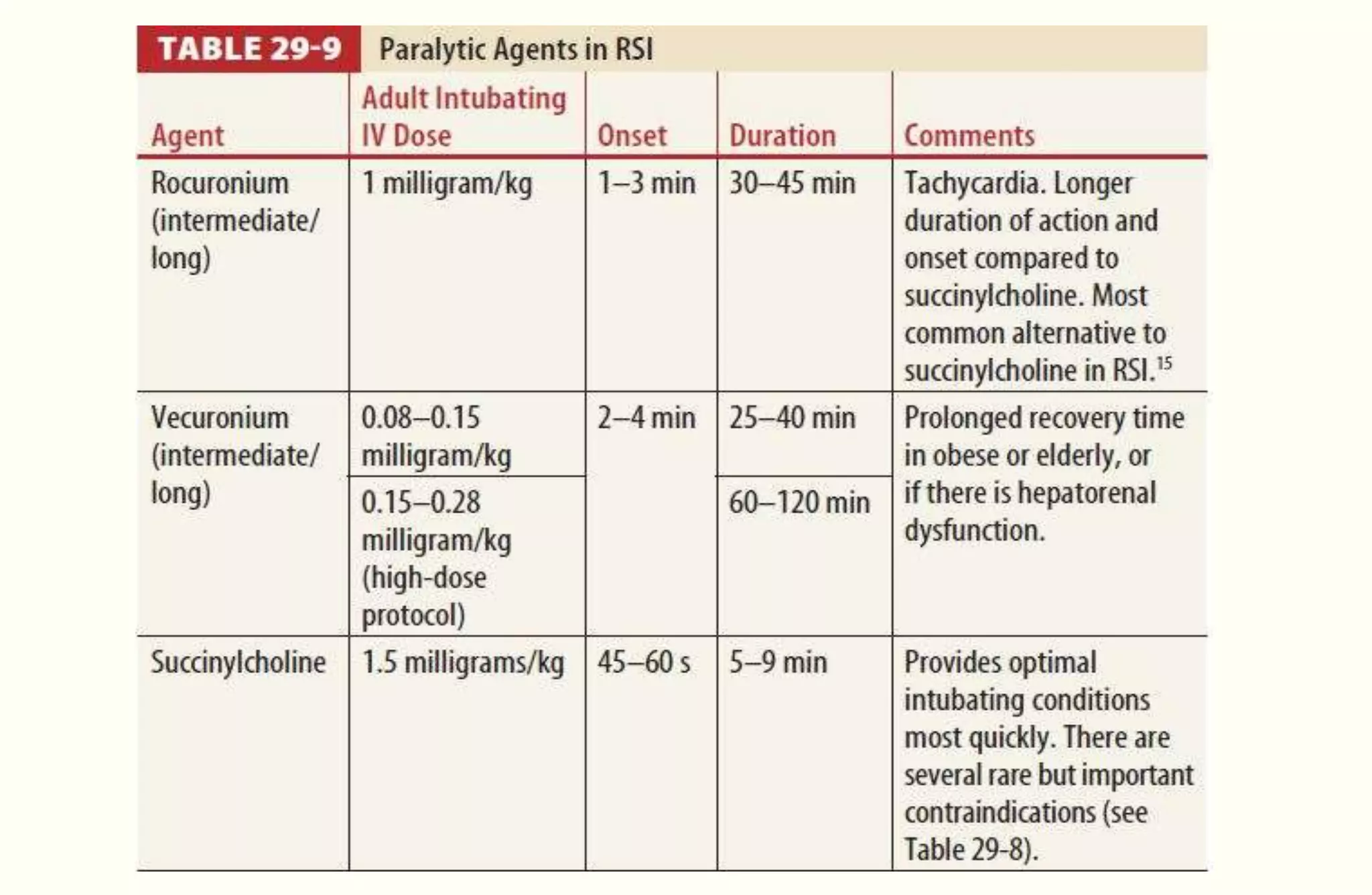
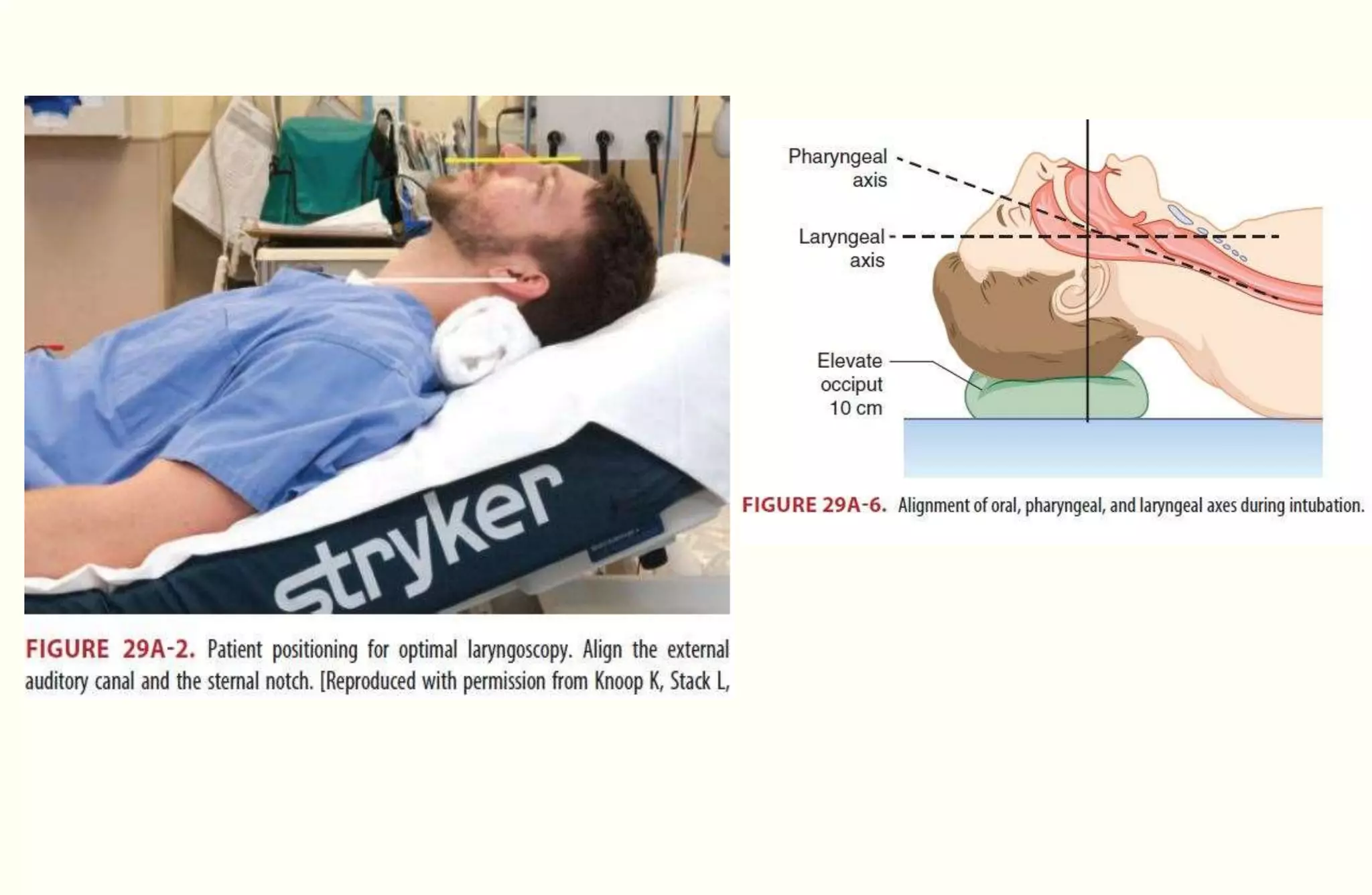
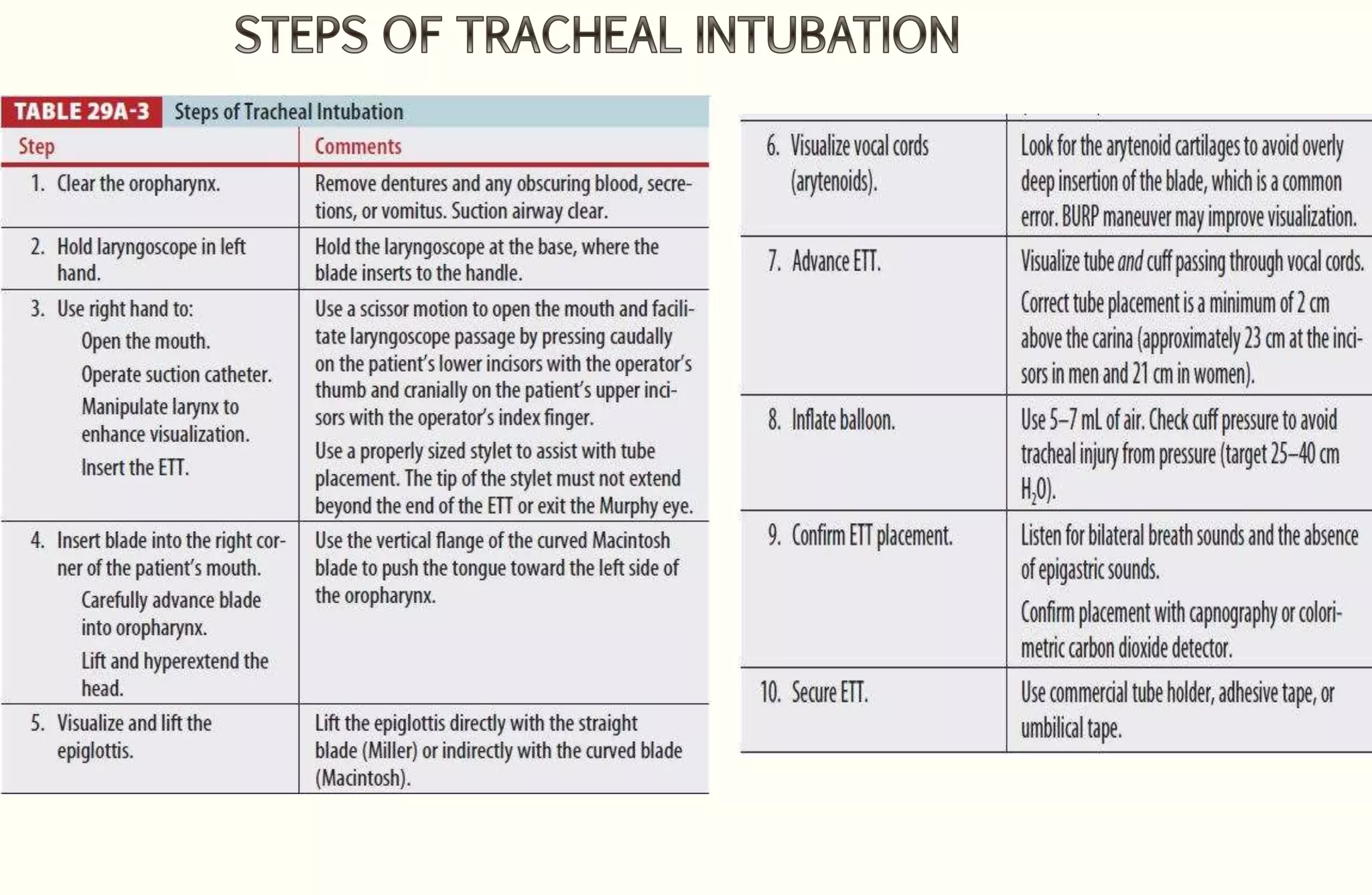
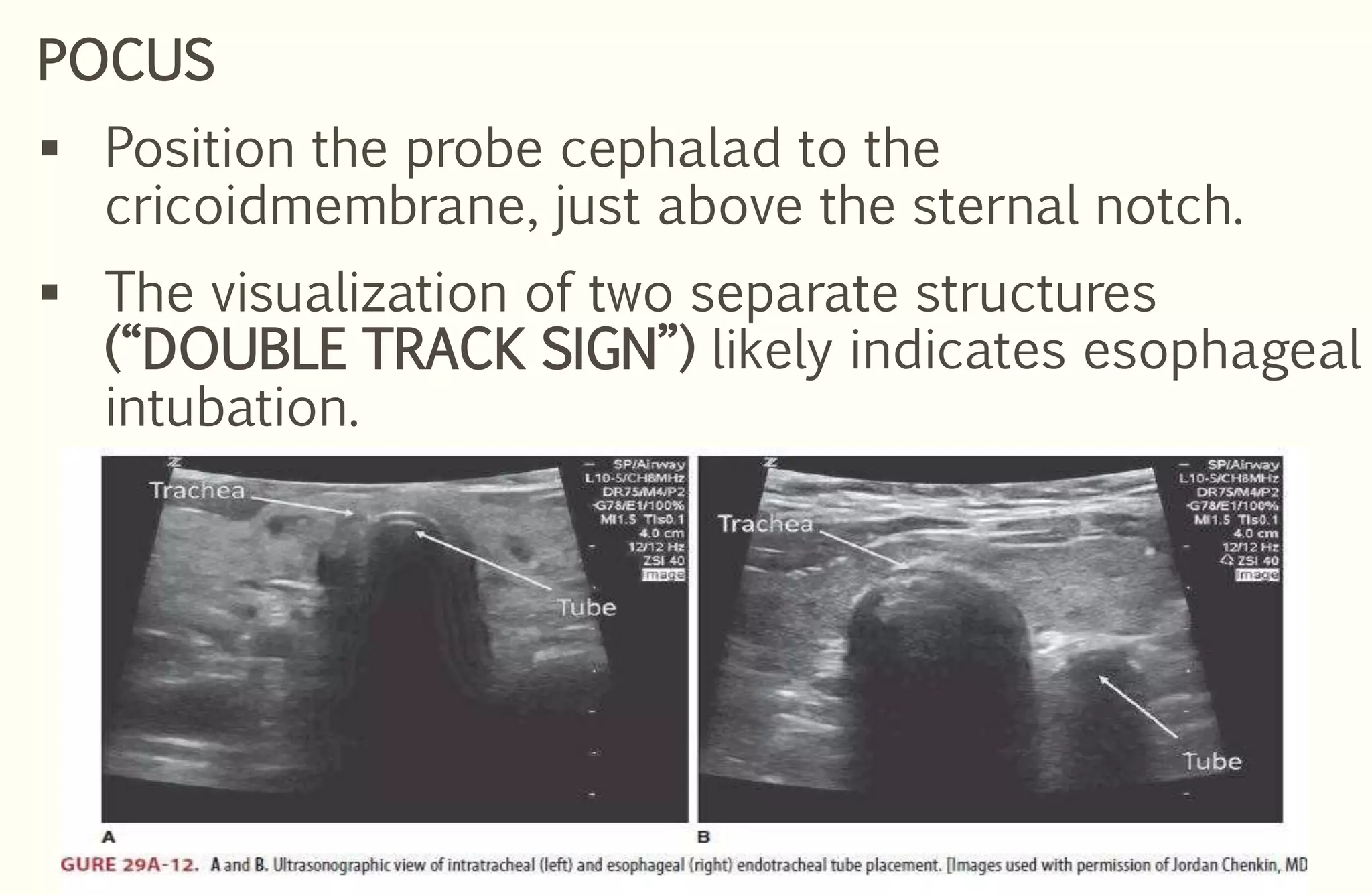
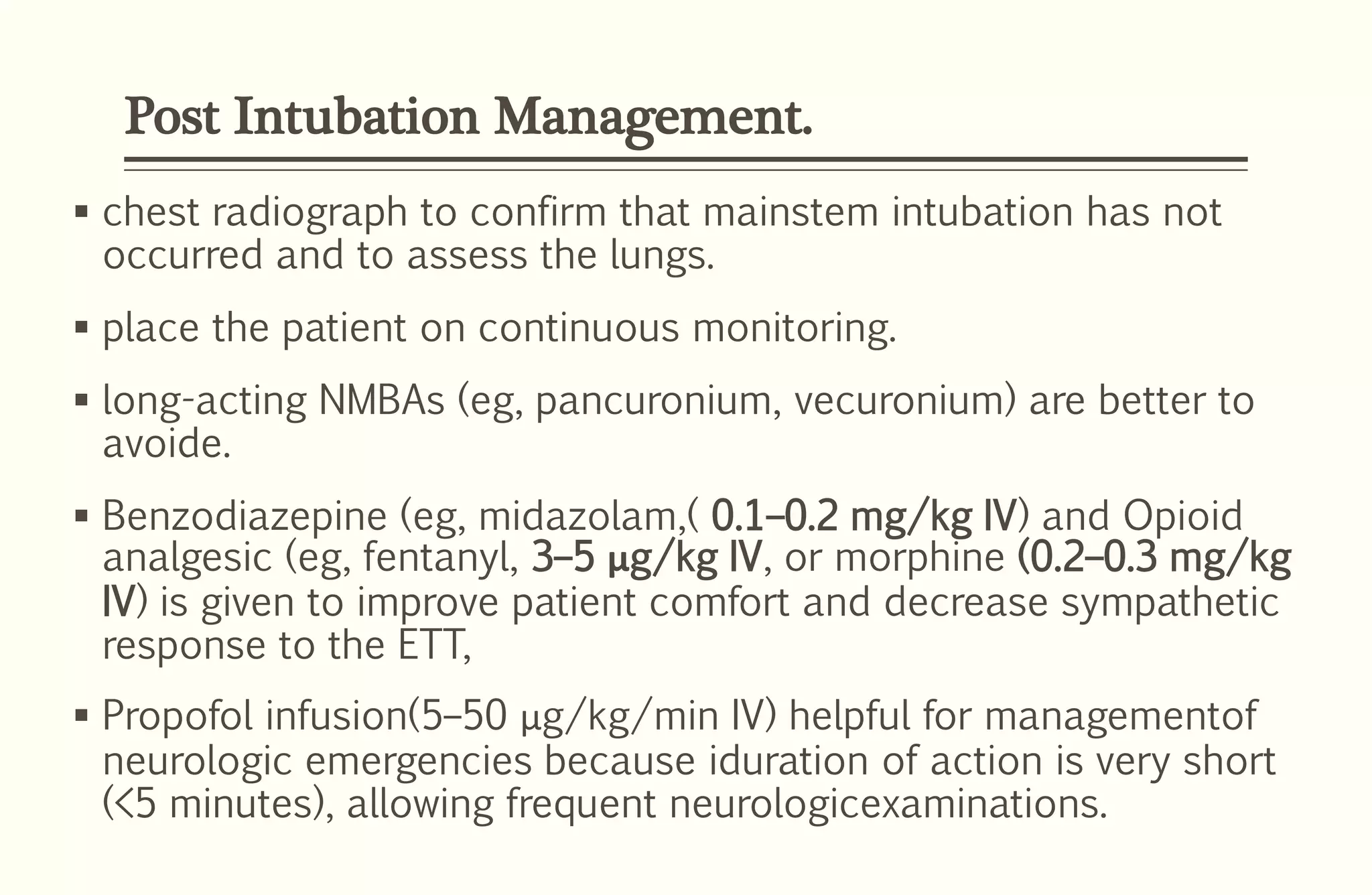
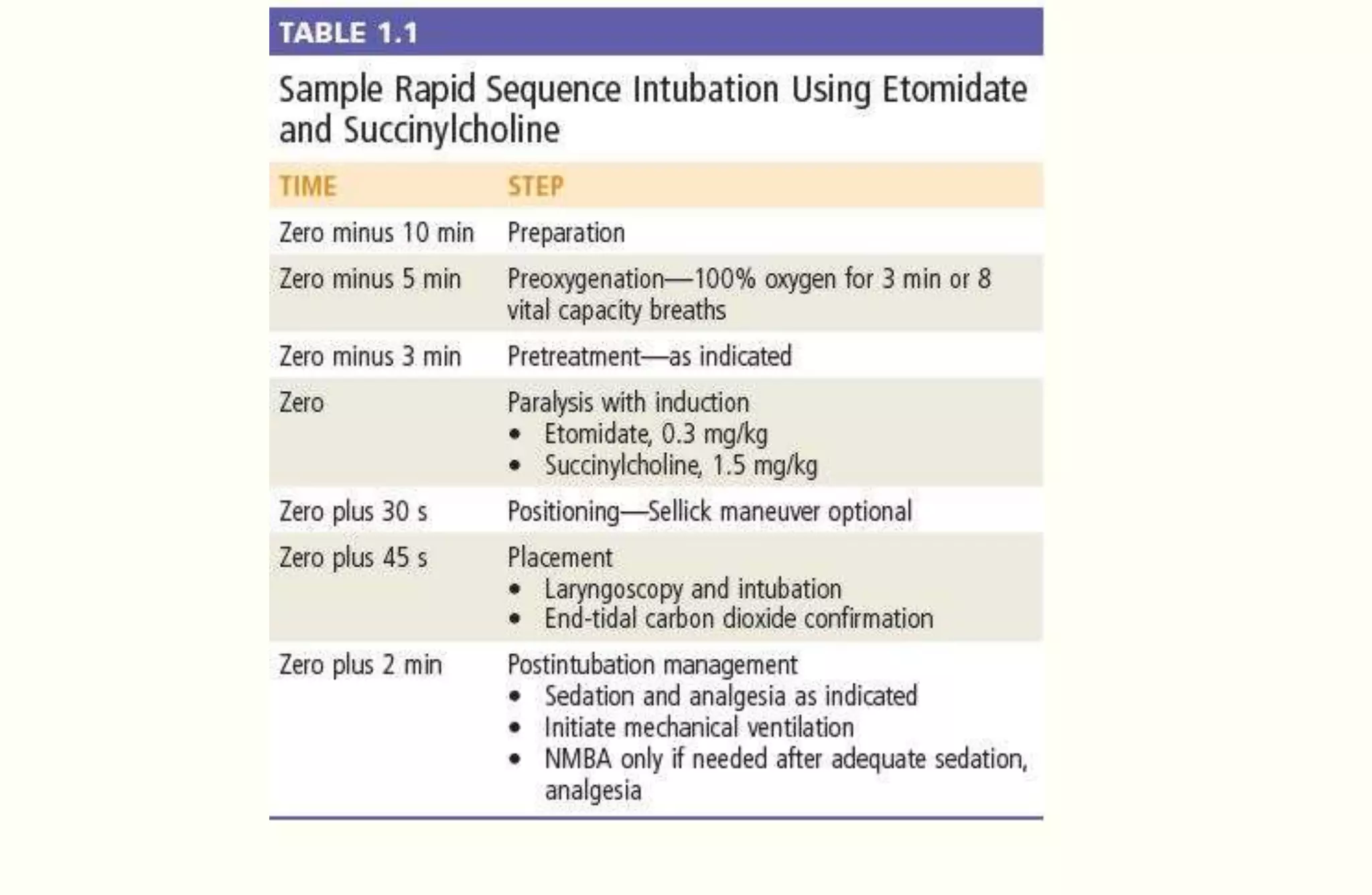
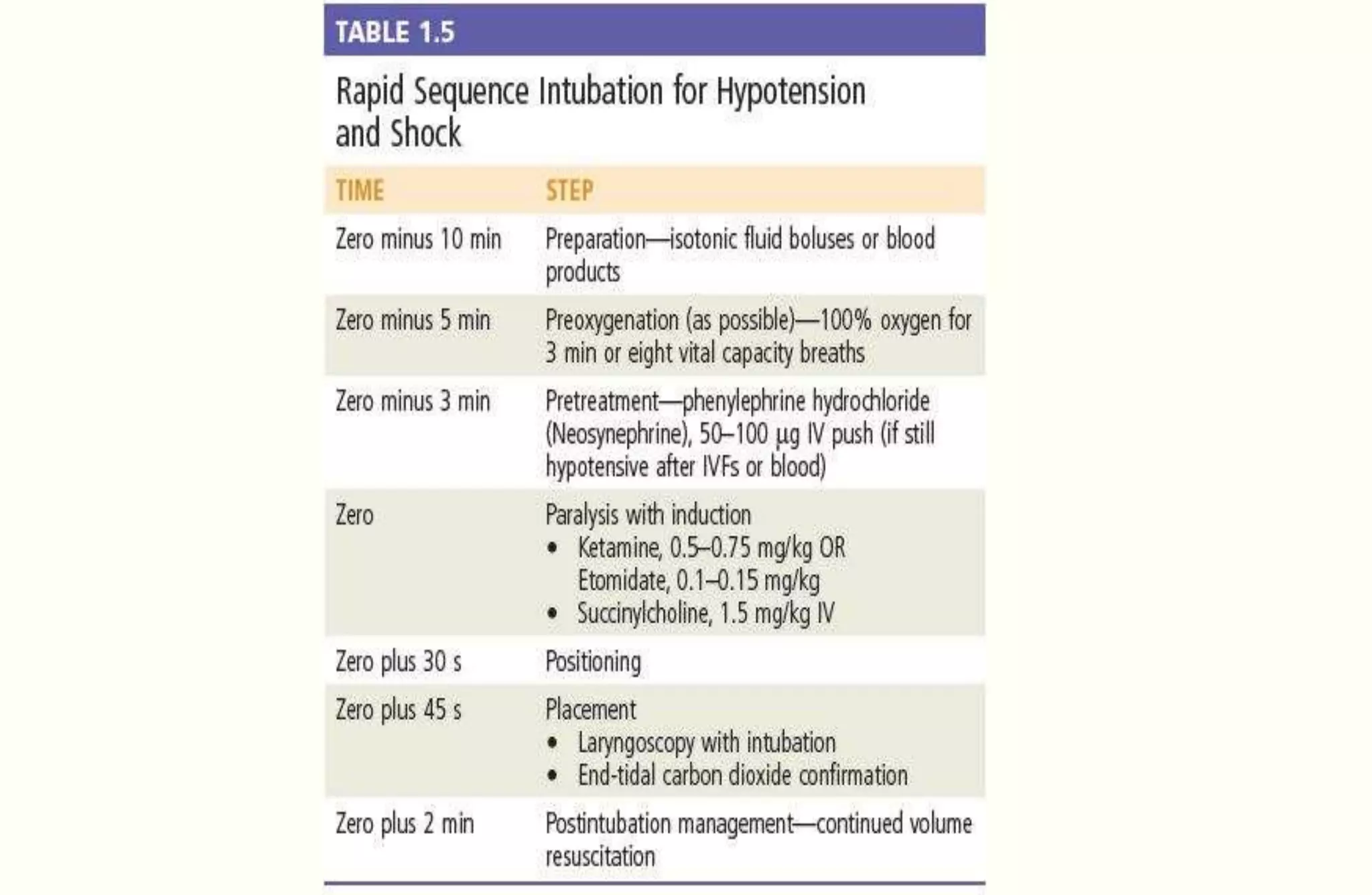
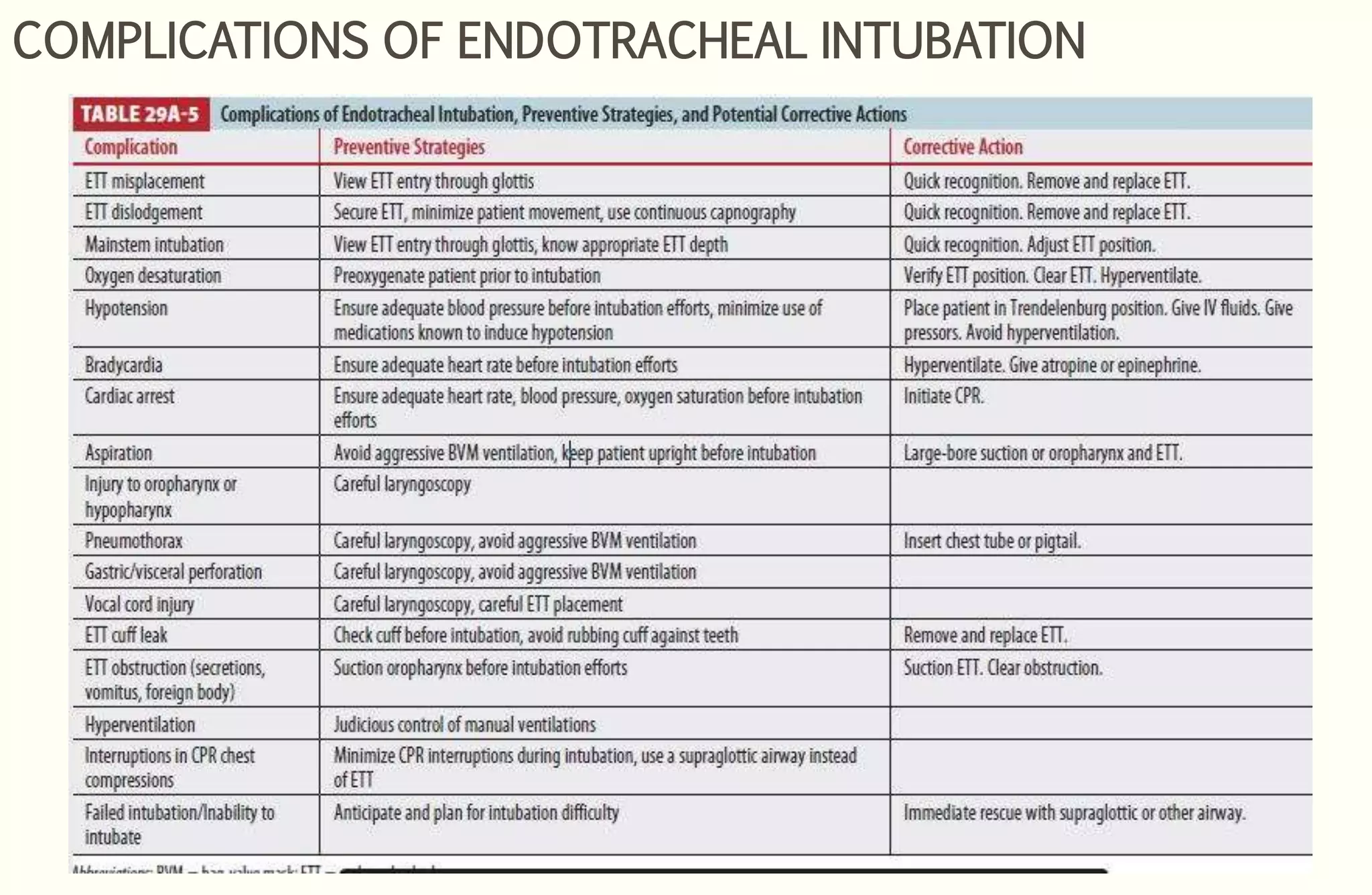
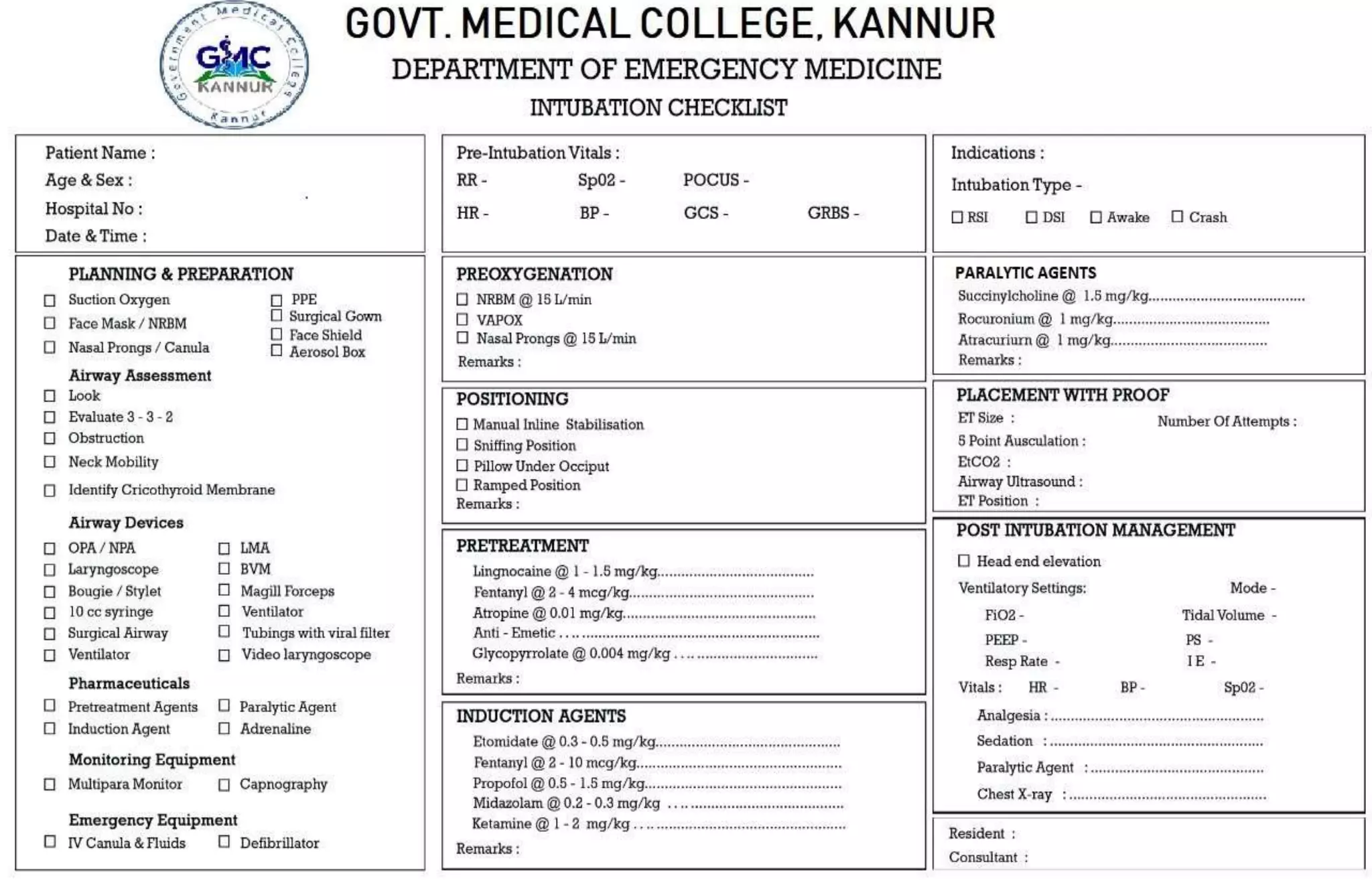
Rapid sequence intubation (RSI) involves the simultaneous administration of an induction agent and neuromuscular blocking drug to facilitate endotracheal intubation. It allows for increased success rates, decreased intubation times, and reduced risks of aspiration, hypoxia, and trauma. The key steps of RSI are preparation, preoxygenation, pretreatment, paralysis with induction, positioning, placement with proof of tube position, and post-intubation management. Confirmation of tube placement involves clinical assessment and mechanical methods like end-tidal CO2 monitoring and ultrasound. Complications can be minimized by adhering to the standardized RSI protocol.