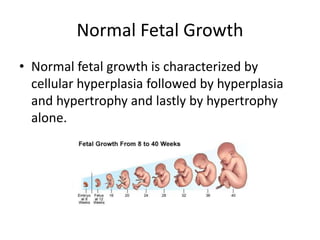
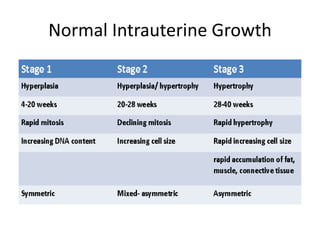
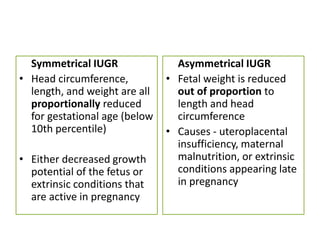
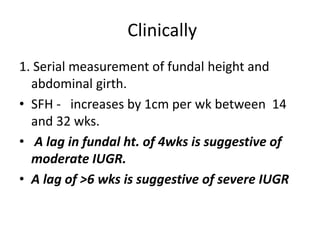
This document provides an overview of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). It defines IUGR as fetuses with an estimated fetal weight below the 10th percentile. The prevalence of IUGR is 3-10% of pregnancies and carries high risks of perinatal mortality and morbidity. Causes of IUGR include fetal, placental and maternal factors. Diagnosis involves serial ultrasounds to monitor fetal growth and Doppler studies of blood flow. Management focuses on treating any underlying conditions, fetal monitoring, and timely delivery once the fetus is mature. Strict surveillance of at-risk newborns is also needed due to complications of IUGR.