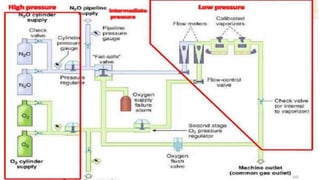
The document discusses the components and functioning of an anaesthesia work station's high pressure system. It describes the key components including gas cylinders, hanger yokes, cylinder pressure indicators, and pressure regulators. Gas cylinders contain medical gases at high pressure and have valves, handles, pressure relief devices, and markings. Hanger yokes orient and secure cylinders, providing a gas-tight seal. Cylinder pressure indicators display the pressure level in cylinders. Pressure regulators reduce the high cylinder pressure to a lower, constant pressure suitable for use in the anaesthesia machine.