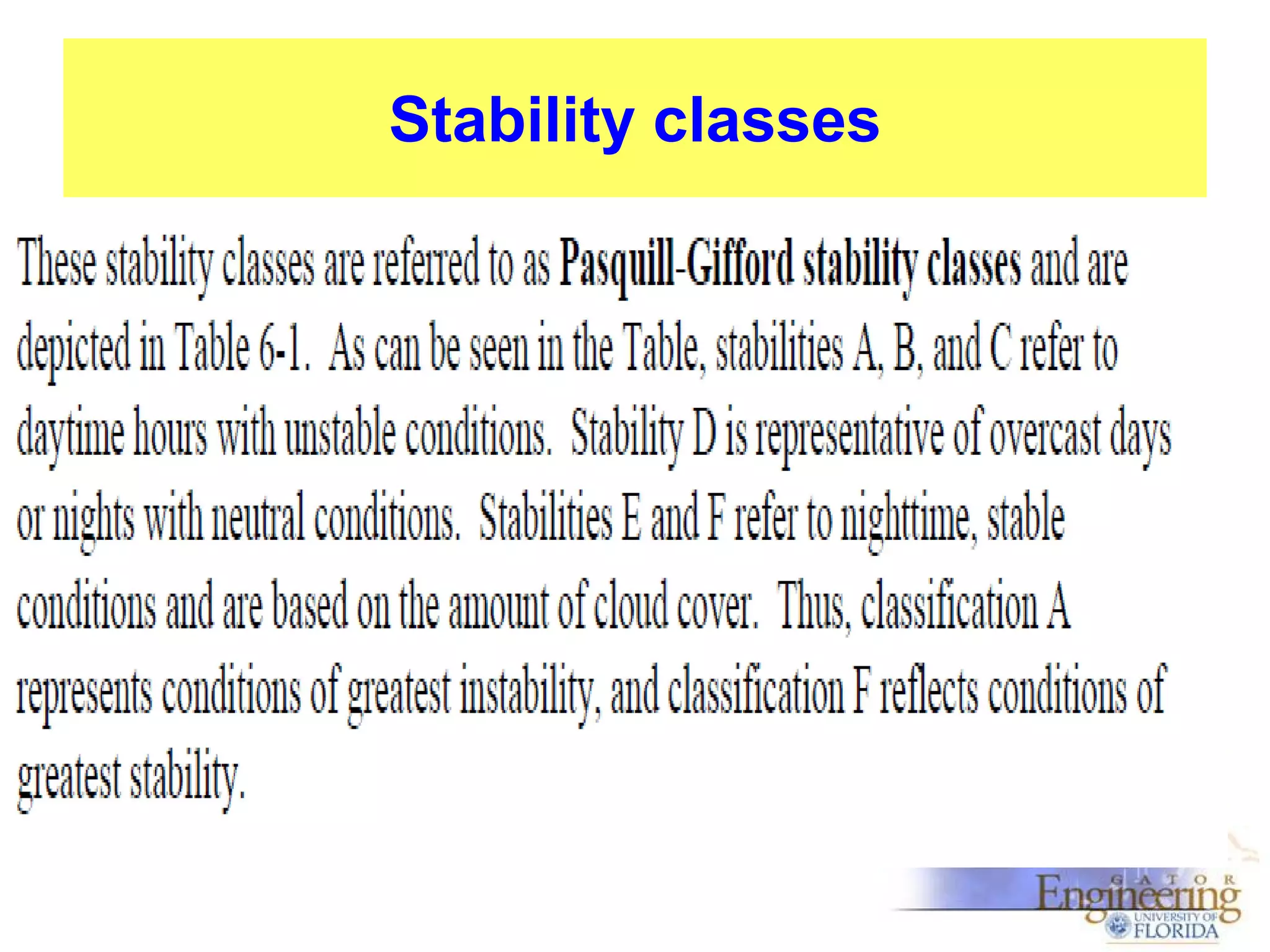
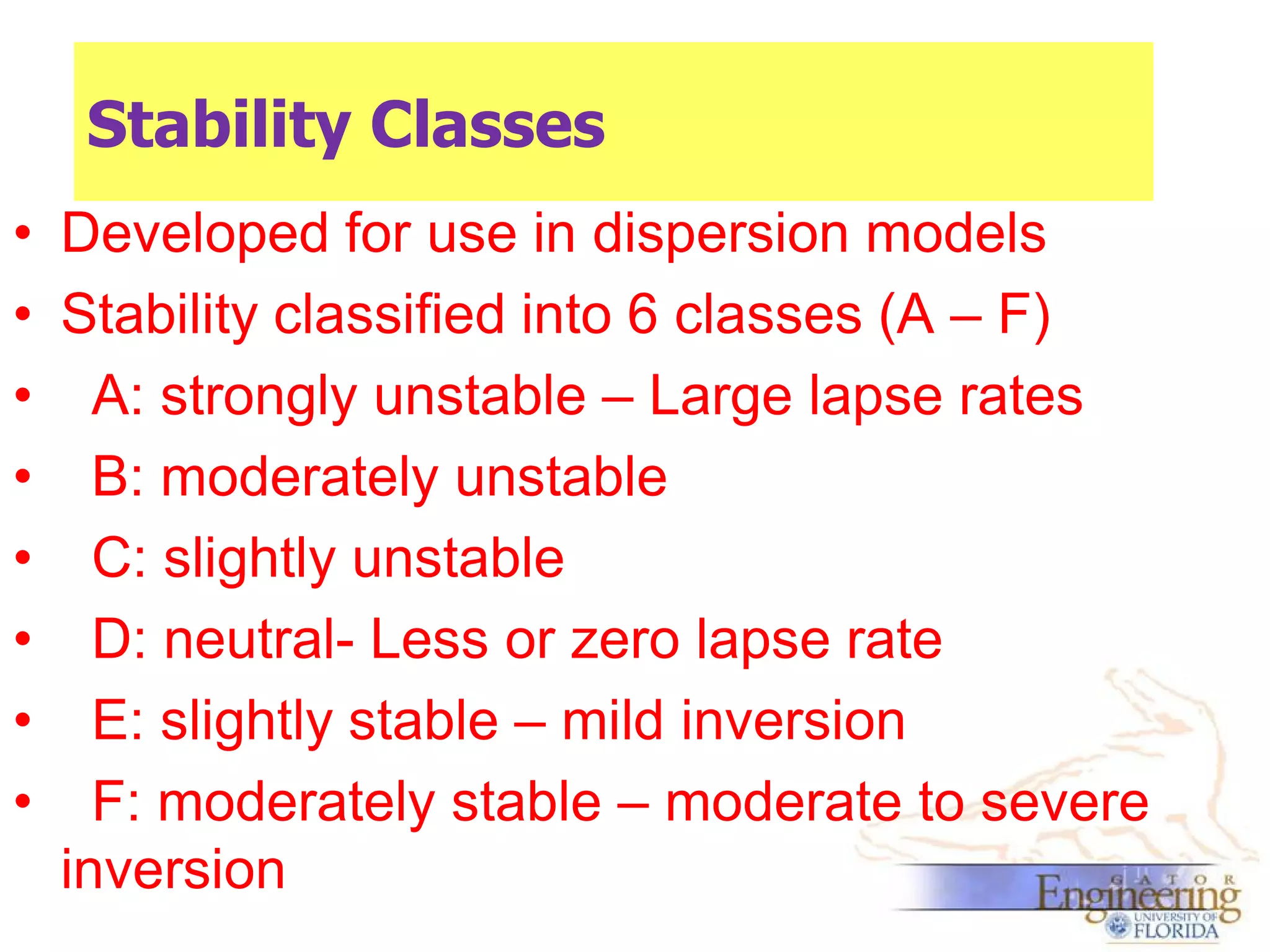
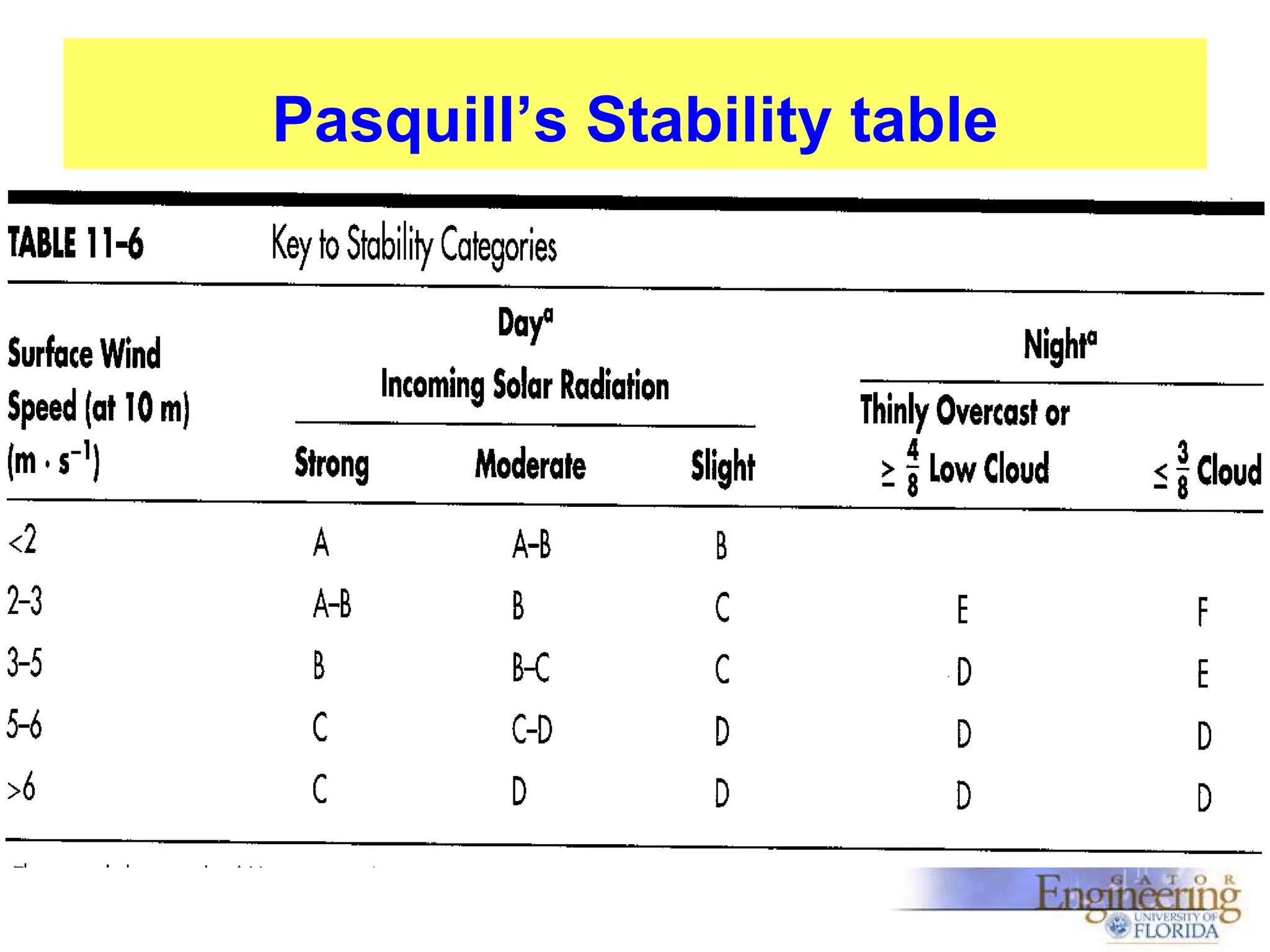
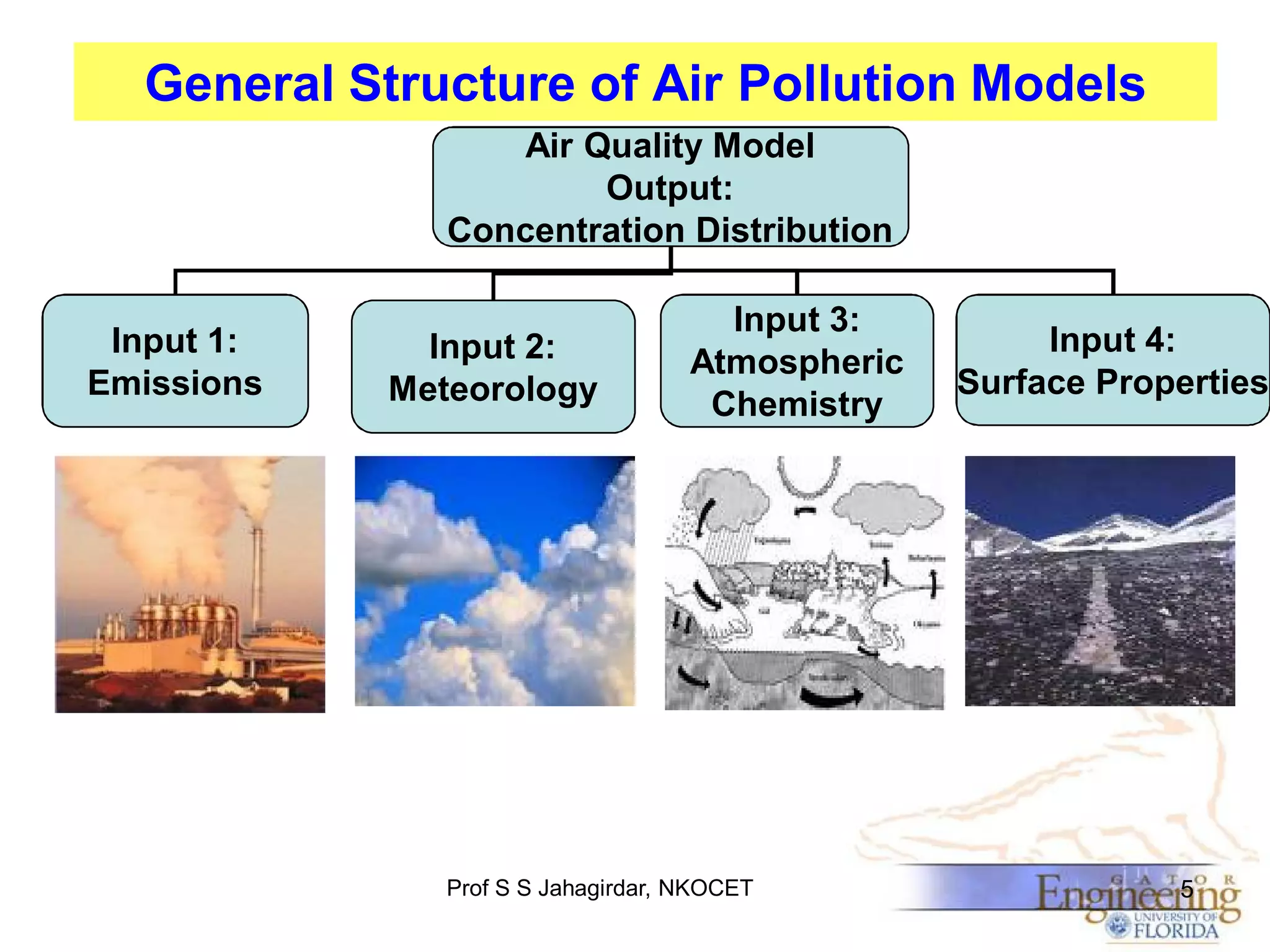
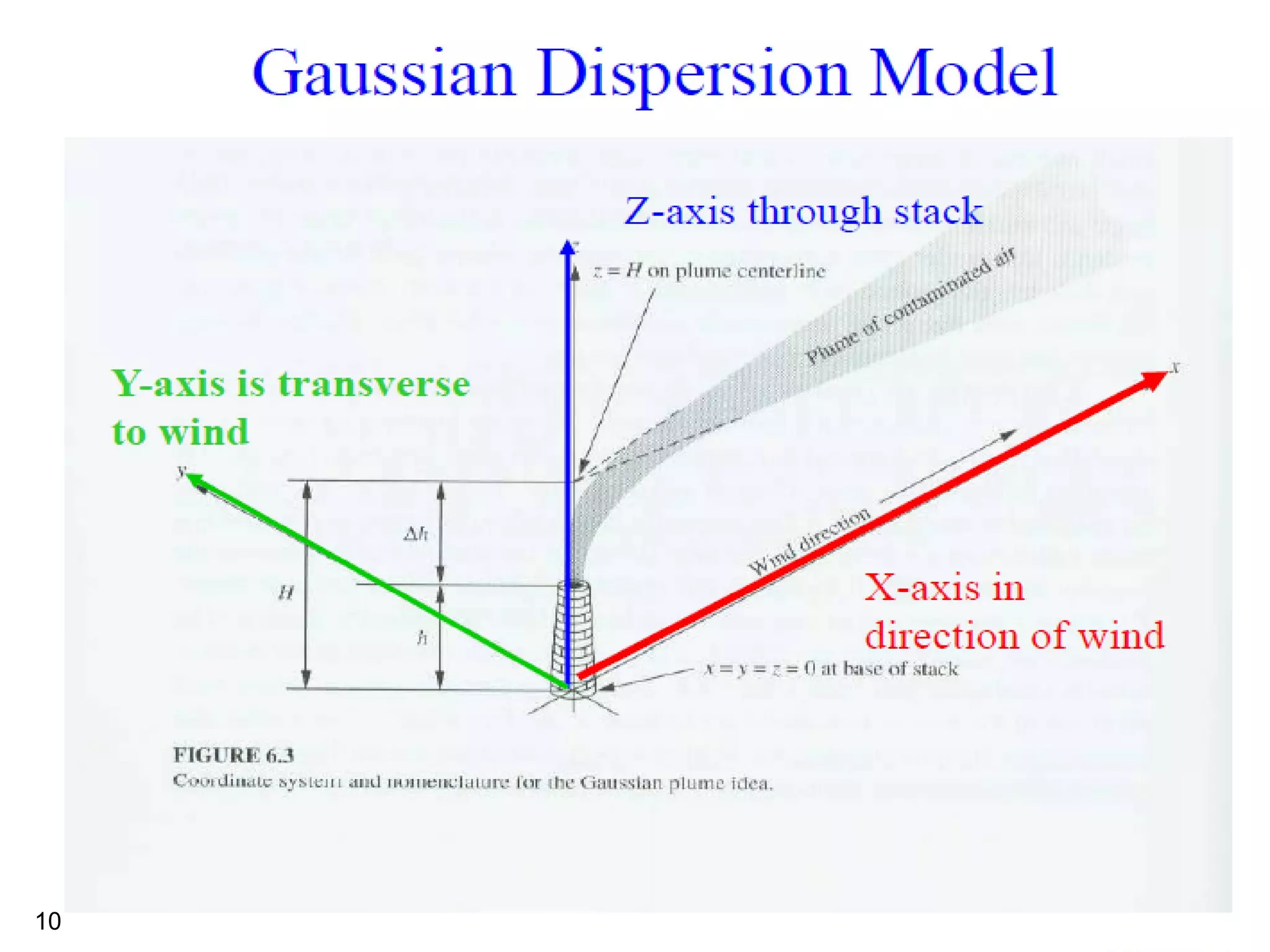
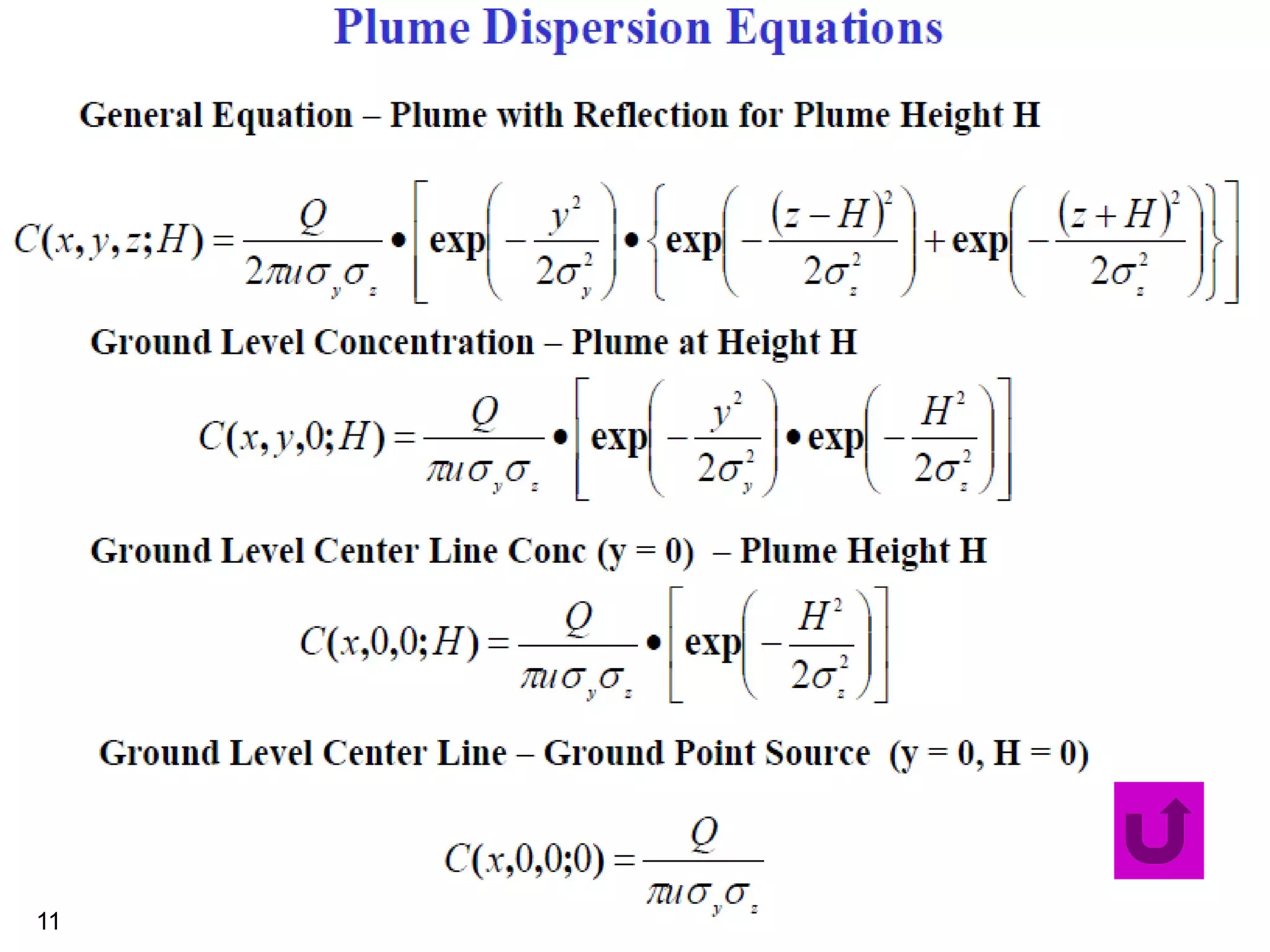
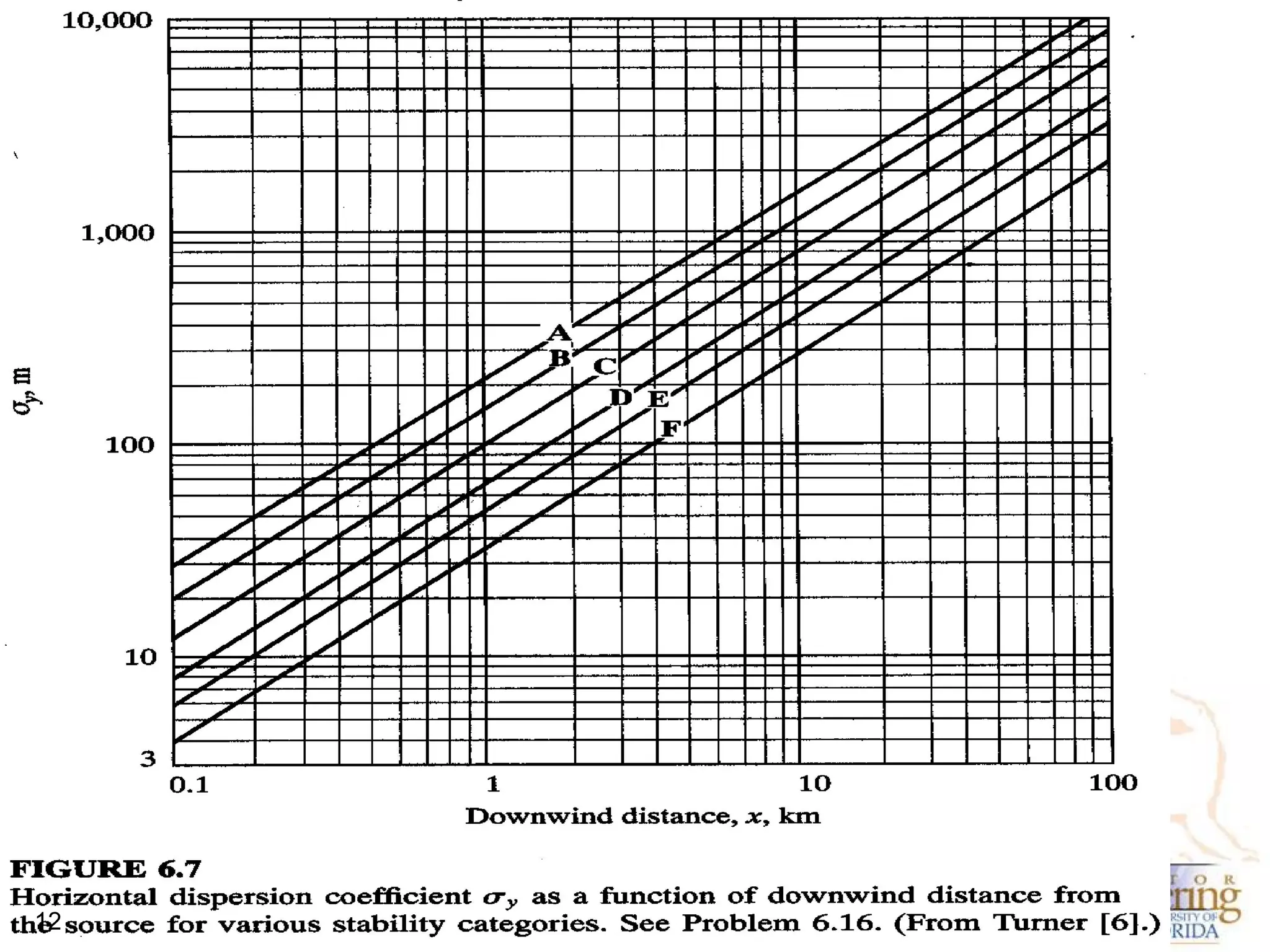
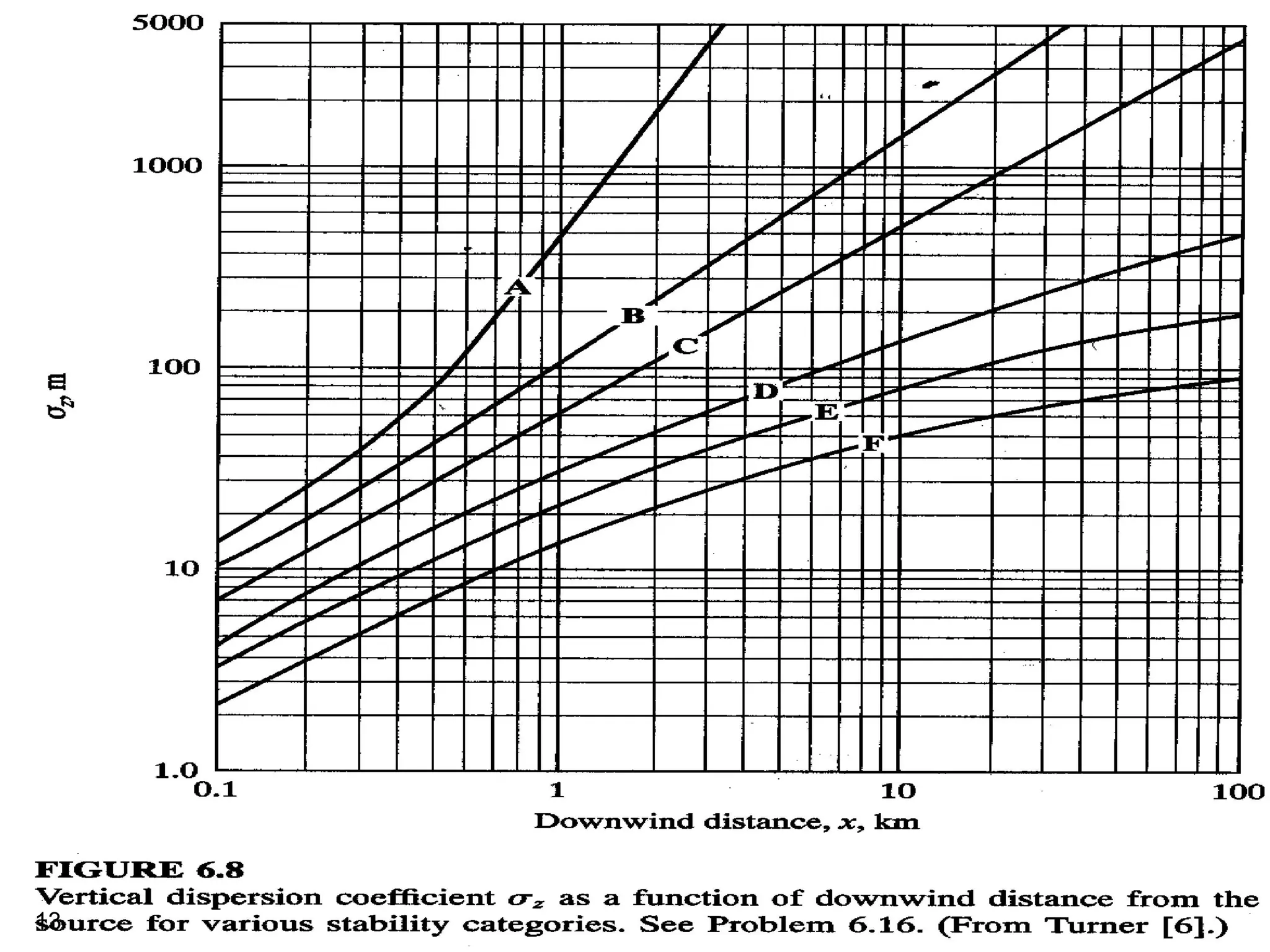
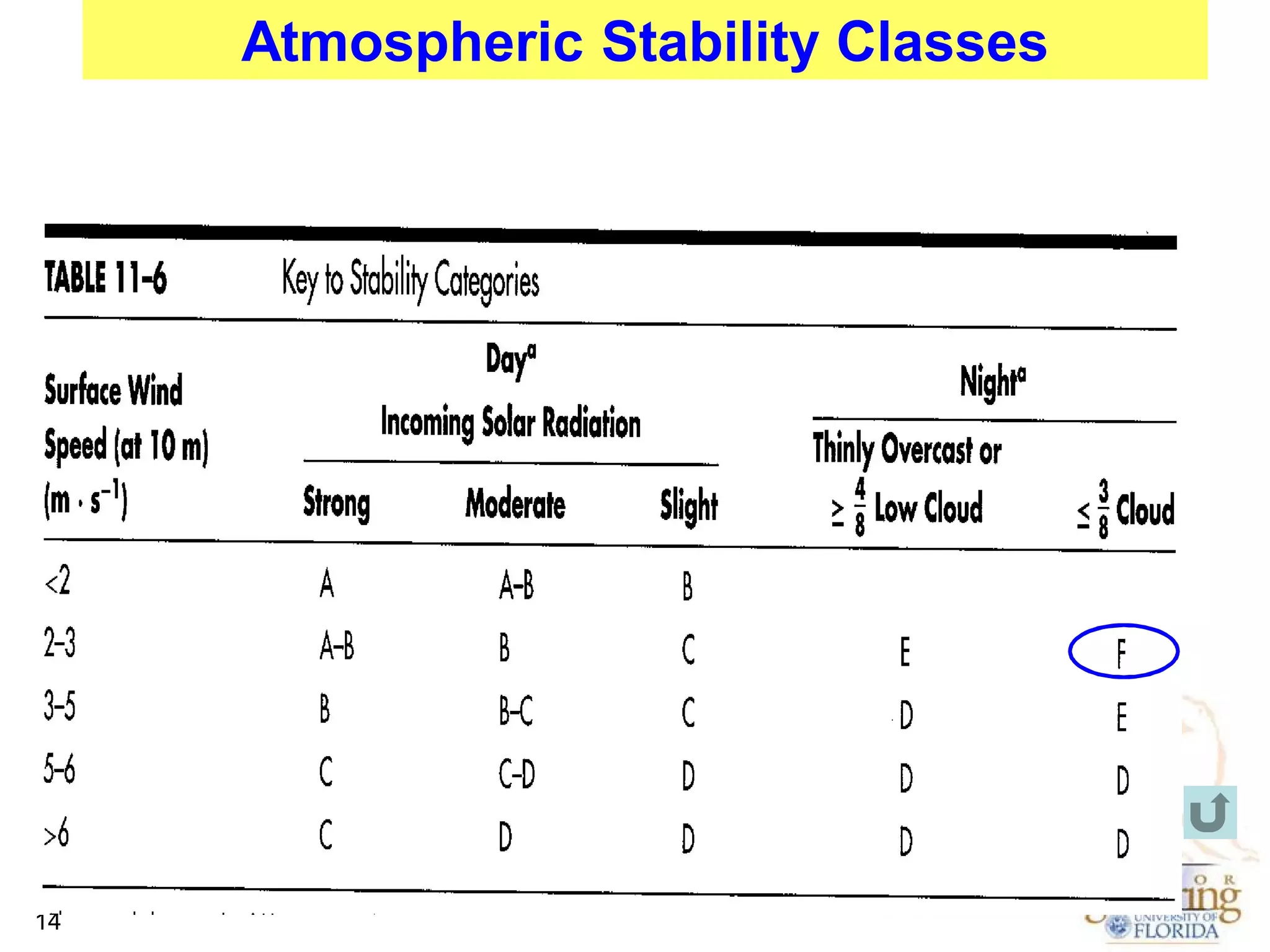
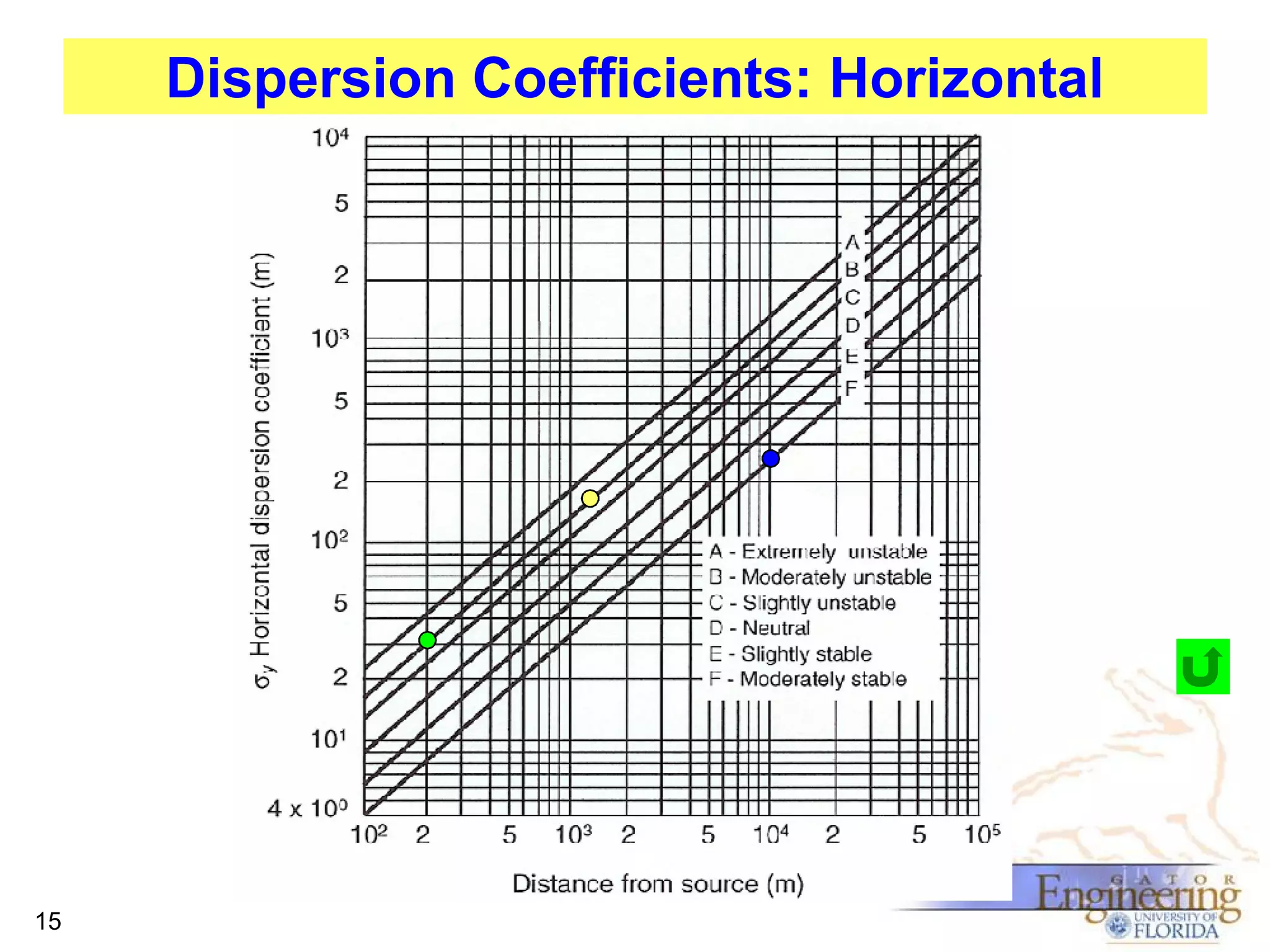
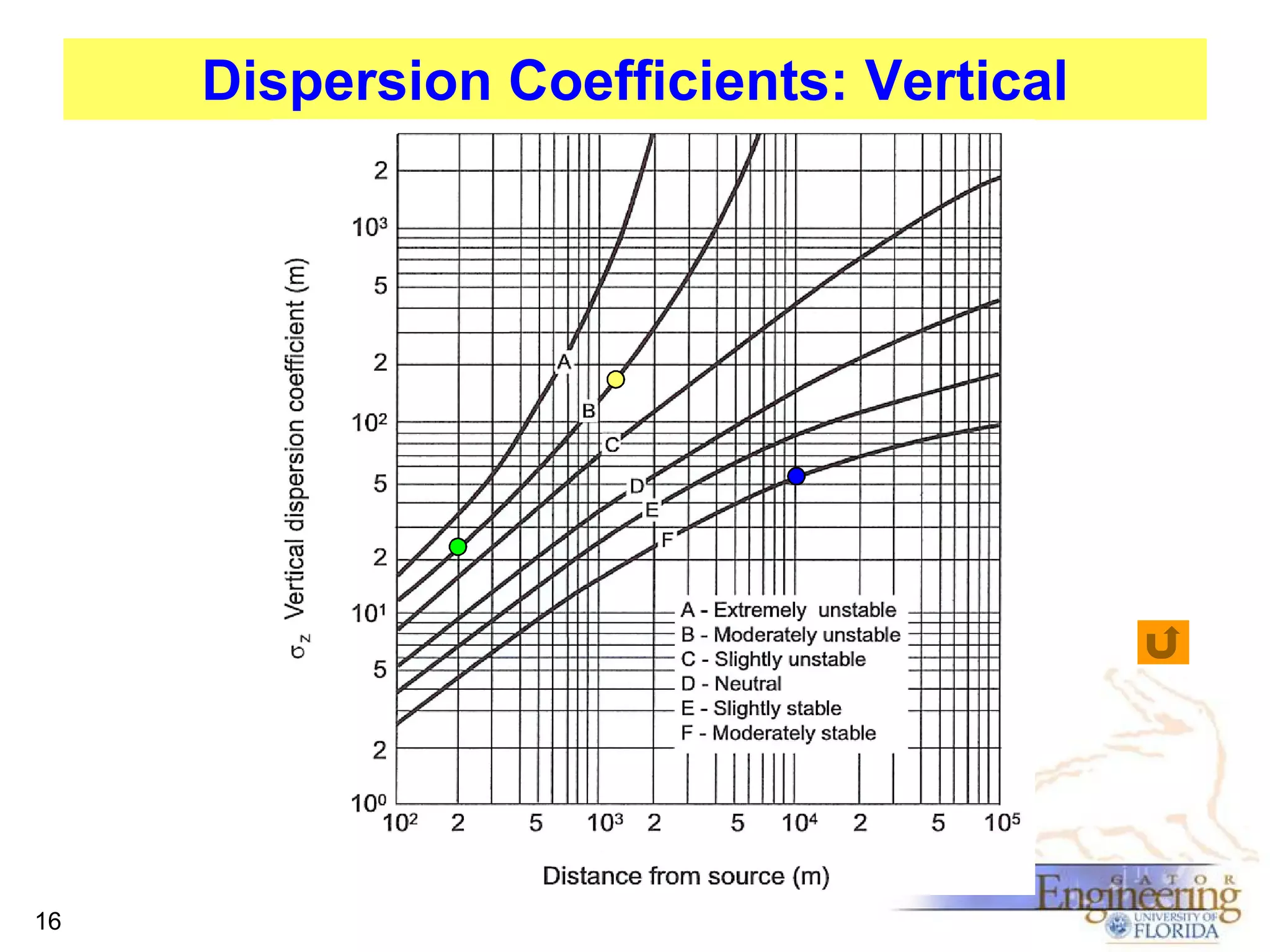
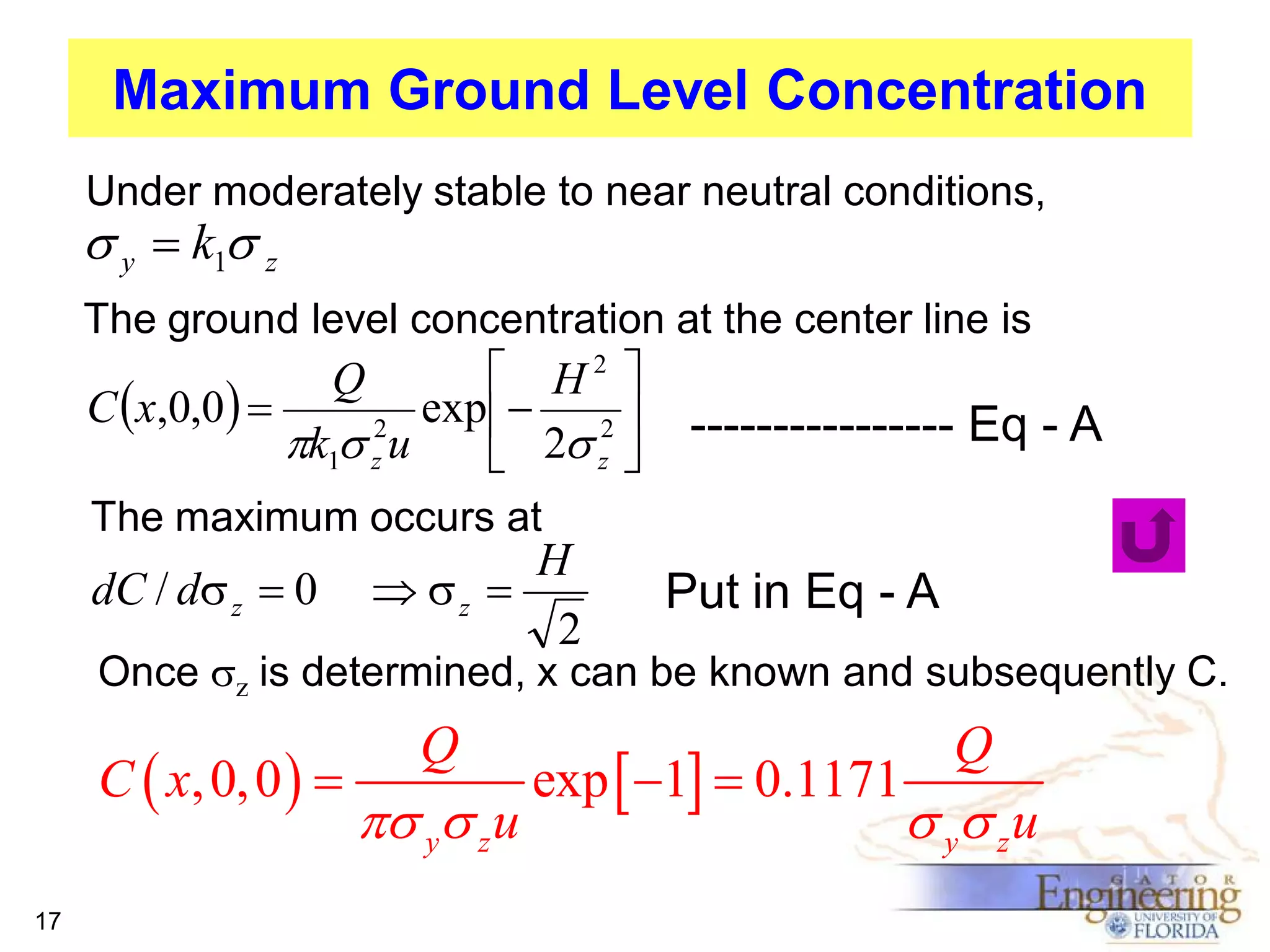
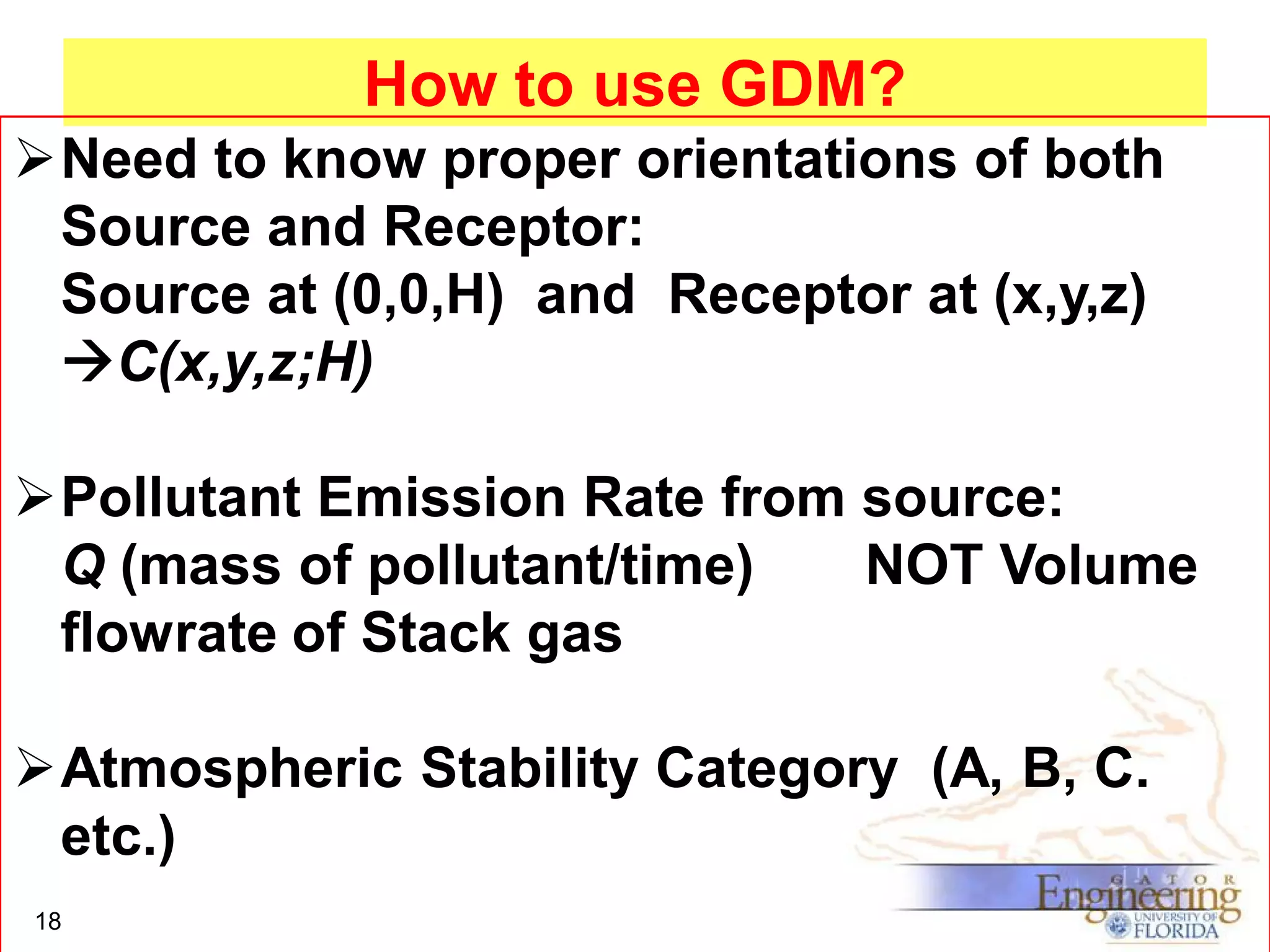
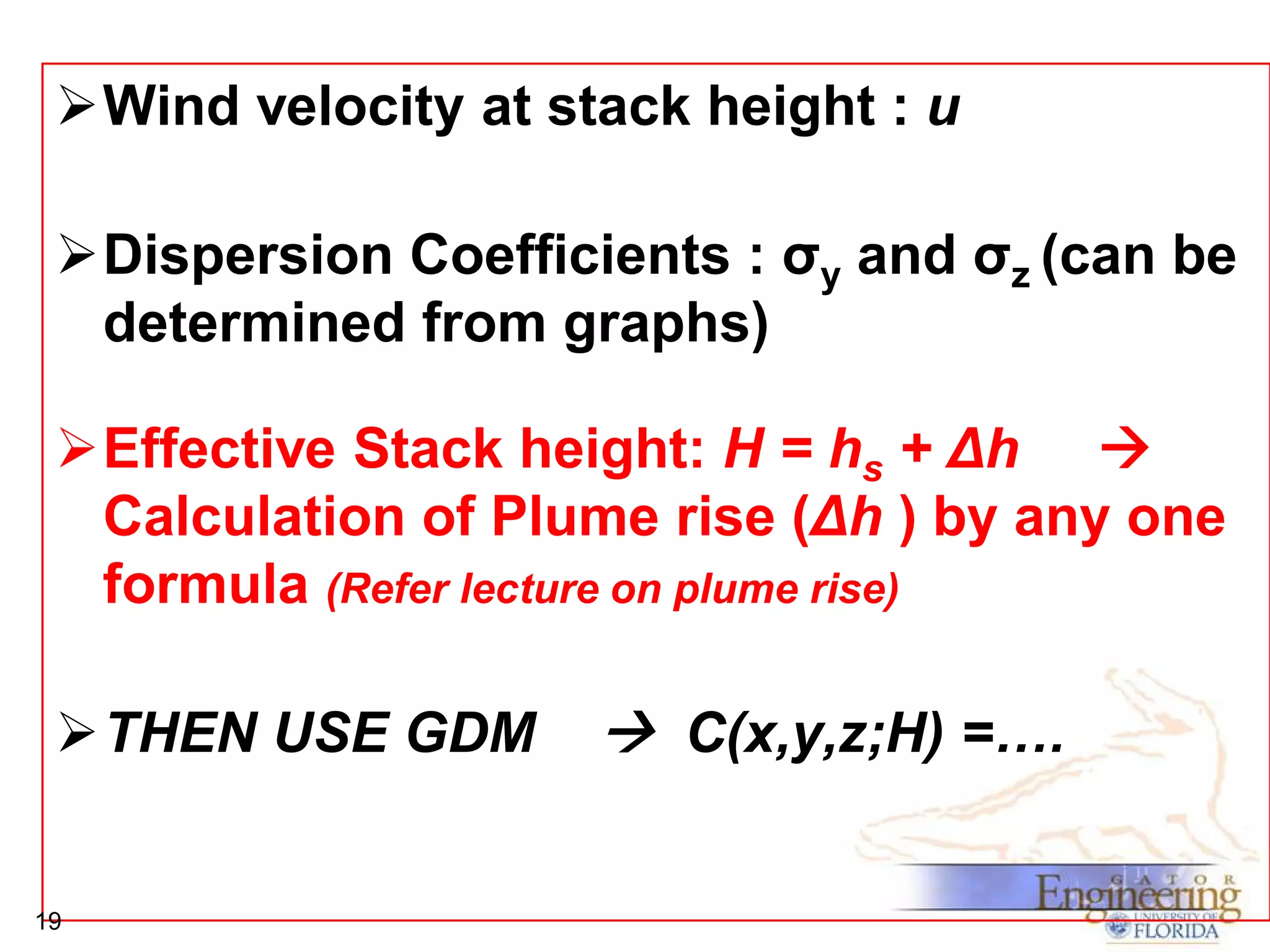
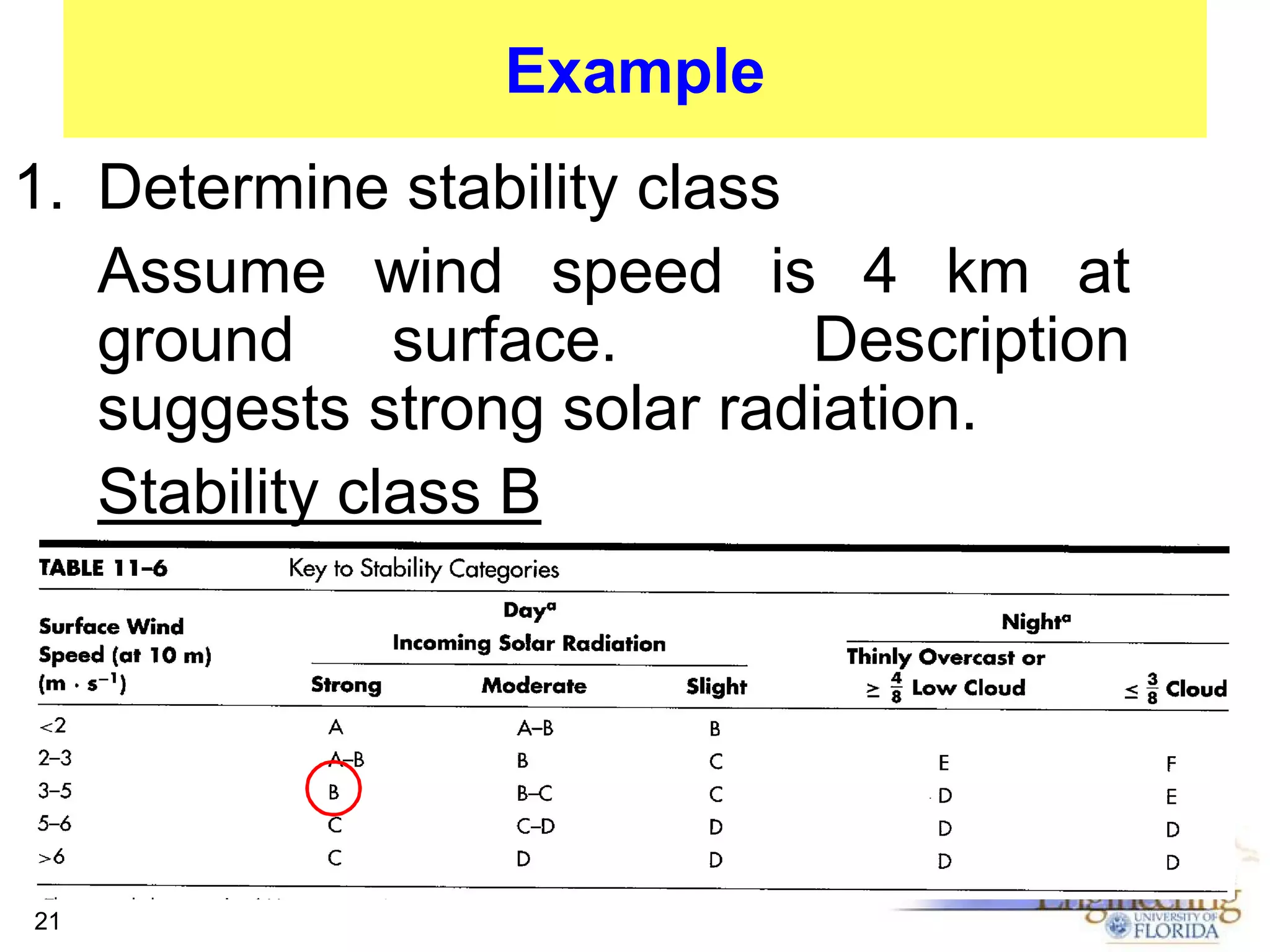
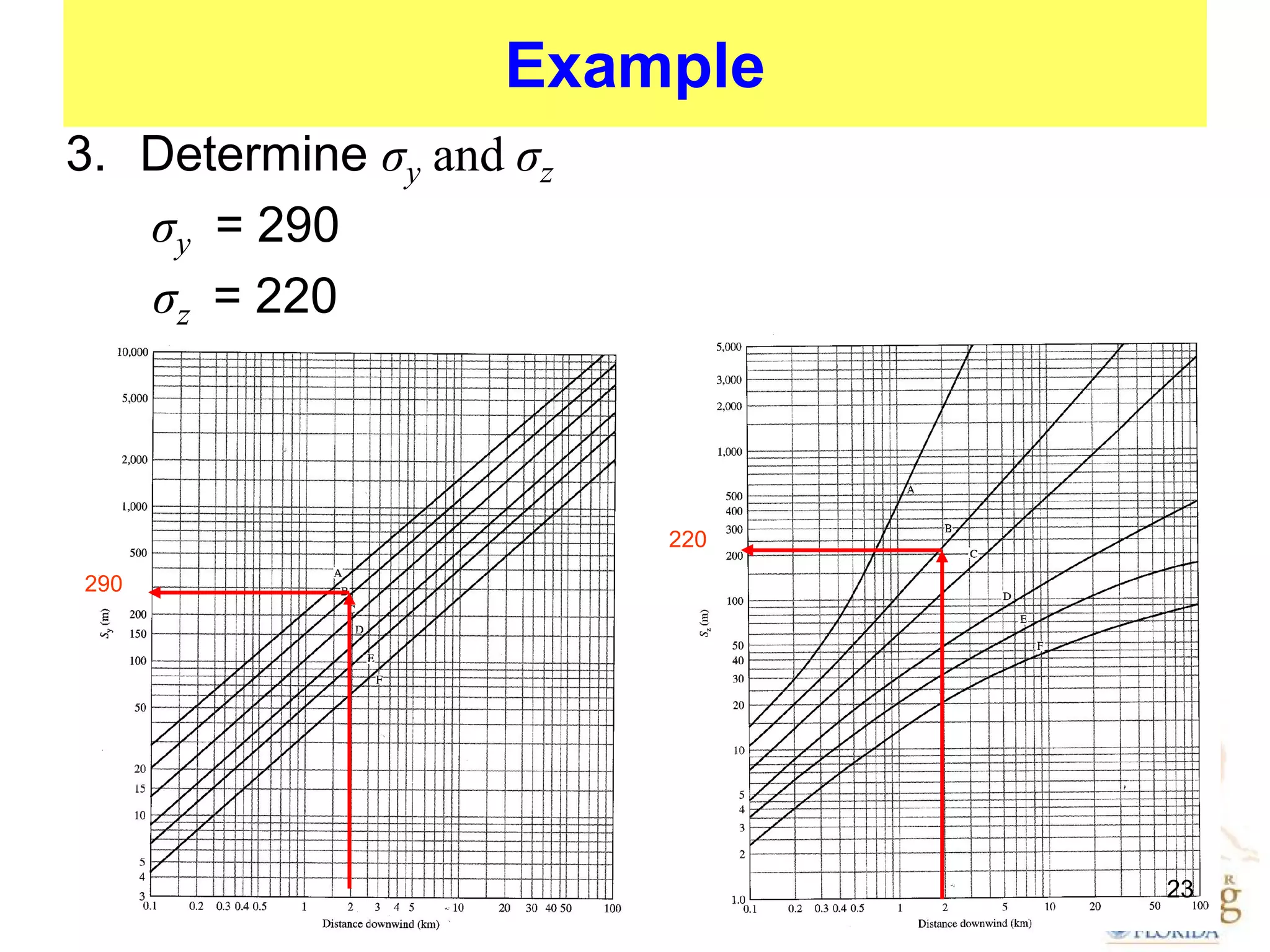
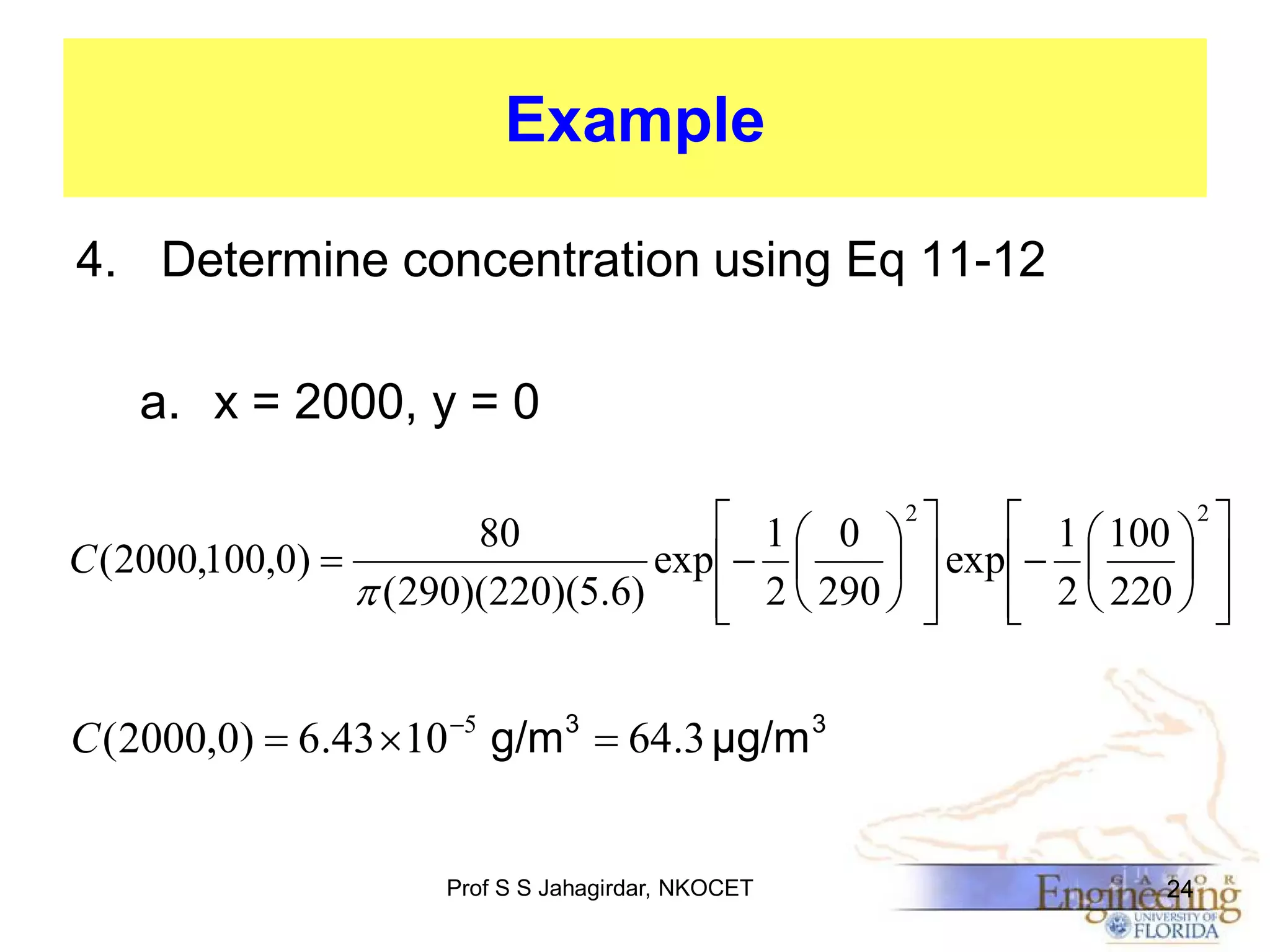
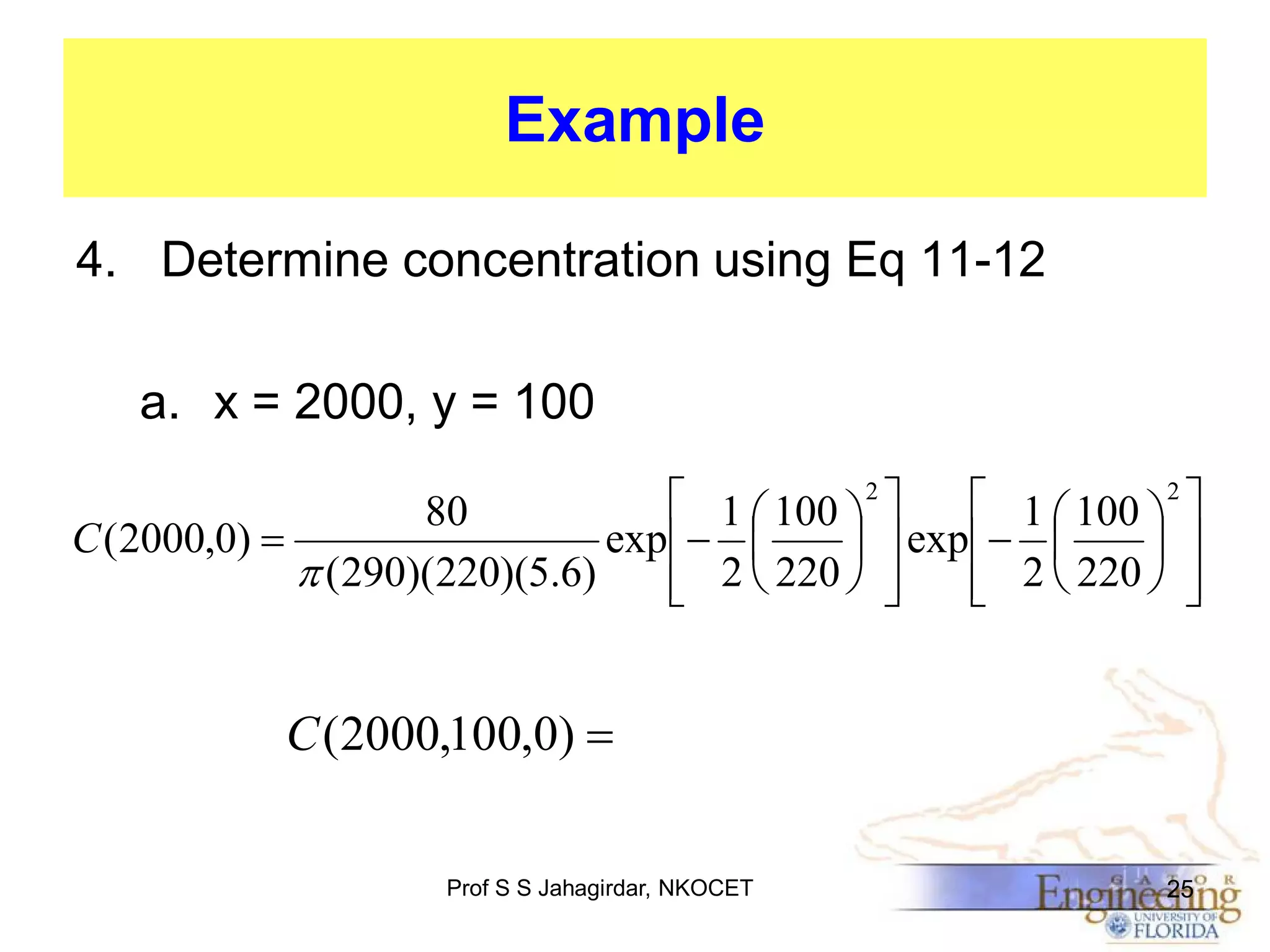
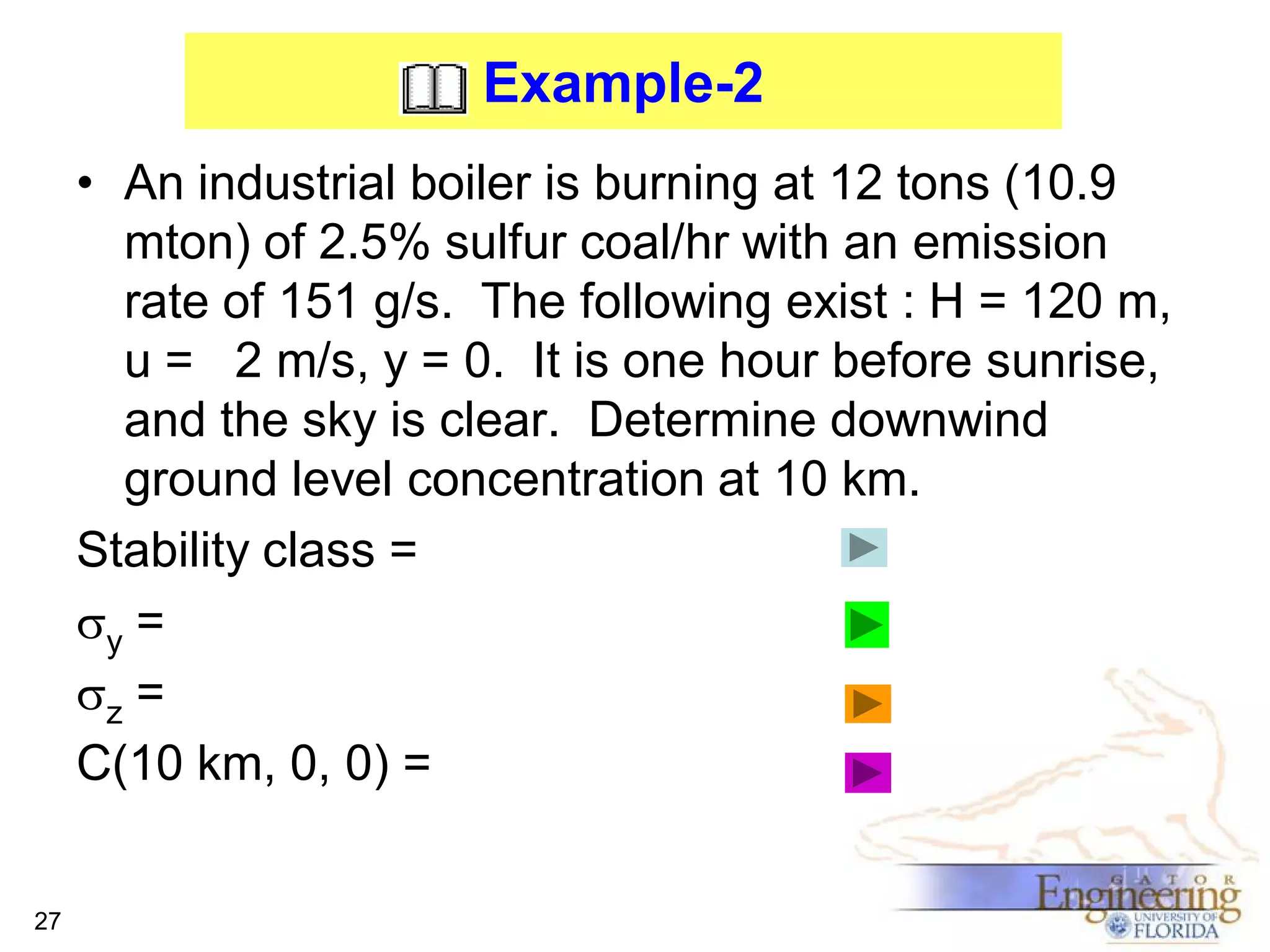
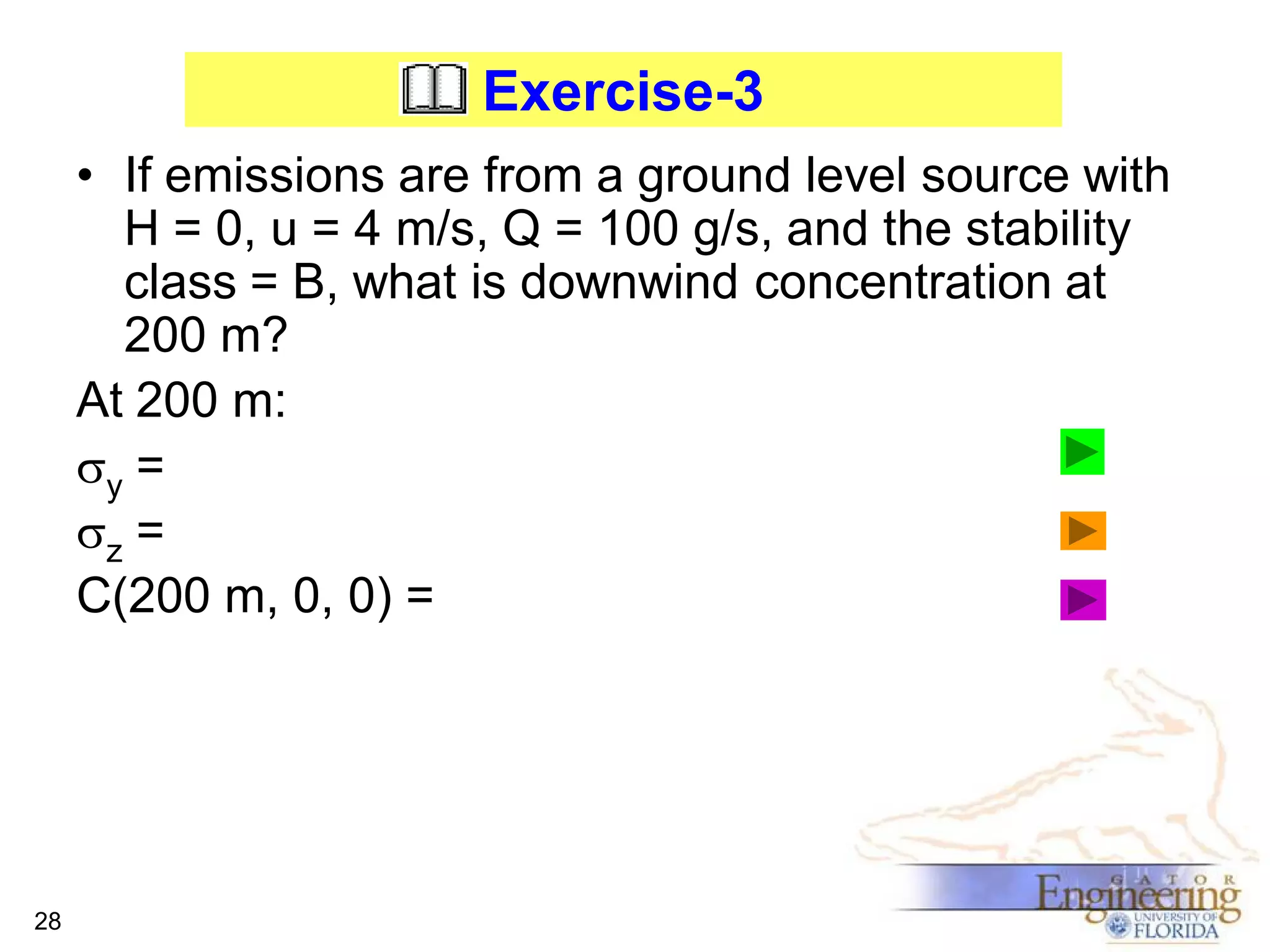
The document discusses the Gaussian Dispersion Model (GDM) used for predicting air pollution dispersion and its applications, including compliance monitoring and evaluating air quality standards. It outlines the stability classes, input parameters, model assumptions, and provides examples on how to use GDM effectively for predicting ground-level concentrations of pollutants. It concludes with exercises and theory questions to reinforce understanding of the concepts presented.