This document discusses meteorological conditions and air pollution dispersion modeling in northern India. It makes three key points:
1) Meteorological conditions are the most critical factor for accurate air pollution dispersion modeling, as they define the movement and spread of pollutants in the atmosphere.
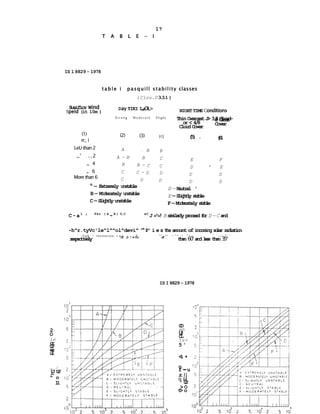
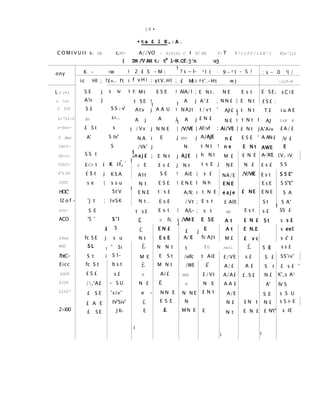
2) Common air pollution dispersion models use a Gaussian equation that requires meteorological data like wind speed, wind direction, and atmospheric stability to calculate pollution concentrations.
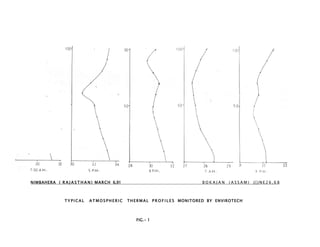
3) Thermal stratification and inversions in the lower atmosphere, especially ground-based inversions at night, significantly impact pollutant dispersion and must be understood and characterized for meaningful pollution modeling.