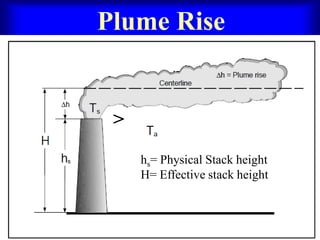
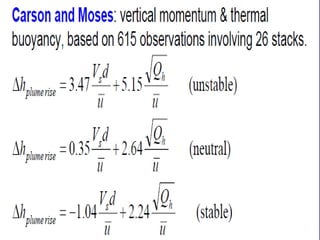
The document discusses plume rise in the context of air pollution, explaining that emitted gases from stacks mix with ambient air and rise due to their buoyancy and momentum. It details several formulas used to calculate plume rise, including the modified Carson and Moses formula and Briggs' formula, with specific coefficients based on stability conditions. Additionally, the document includes objective and theory questions pertaining to the topic of plume rise.




![2. Modified Carson and
Moses formula
0.5
h a.[(Vs .d ) / u ] b.[(Qh ) / u ]
Stability
Condition
a
b
Unstable
3.47
0.35
-1.04
5.15
2.64
2.24
Neutral
Stable
Prof S S Jahagirdar, NKOCET
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-18-131016035649-phpapp01/85/AIR-POLLUTION-CONTROL-L-18-7-320.jpg)

![4. Concave formula
1/ 2
h
h 2.71[Q
3/ 4
/u ]
It is modified by Thomas
h 4.71[Q
0.444
Prof S S Jahagirdar, NKOCET
/u
0.694
]
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-18-131016035649-phpapp01/85/AIR-POLLUTION-CONTROL-L-18-10-320.jpg)






