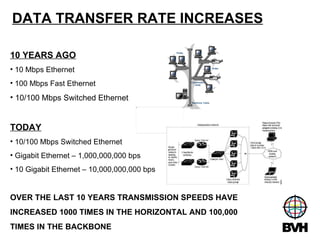
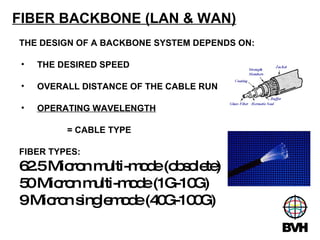
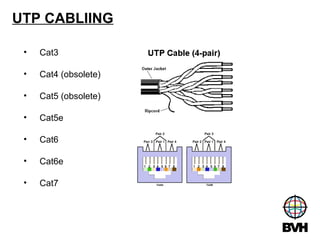
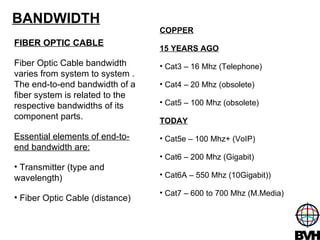
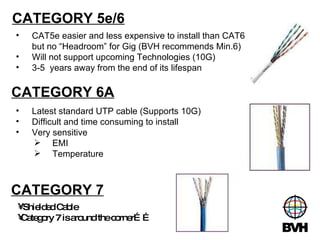
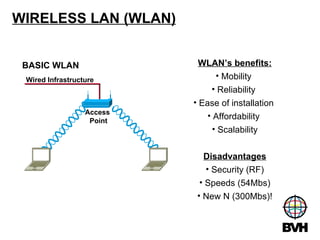
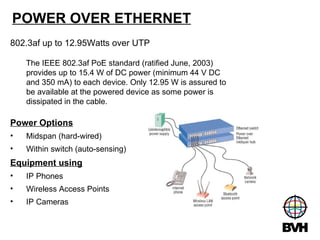
The document discusses several telecommunications associations and standards including TIA, EIA, BICSI and their roles in establishing standards. It also summarizes the key components and functions of an Entrance Facility (EF), Equipment Room (ER), and Telecommunications Room (TR). Additionally, it outlines how technologies like Gigabit Ethernet, VoIP, wireless networking, audiovisual systems, and Power over Ethernet have impacted cable infrastructure design by increasing bandwidth needs and requiring additional pathways, spaces and rack space. Careful planning of the cable infrastructure is necessary to allow future technologies to run seamlessly.