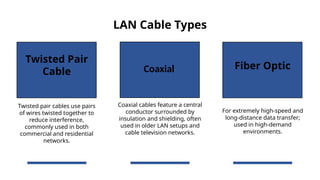
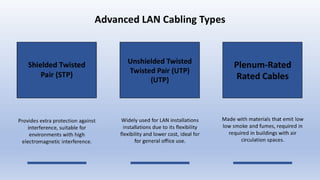
LAN Cabling: Installation & Maintenance Basics covers the fundamentals of Local Area Network (LAN) cabling, including cable types, connectors, wiring standards, and installation techniques. This topic explores best practices for setting up, testing, and troubleshooting network cables to ensure reliable data transmission. It is essential for students and professionals seeking skills in network infrastructure and maintenance.