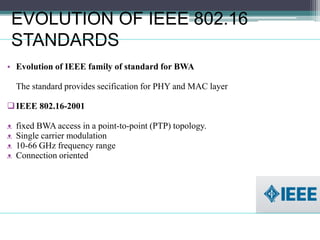
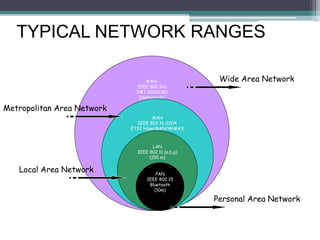
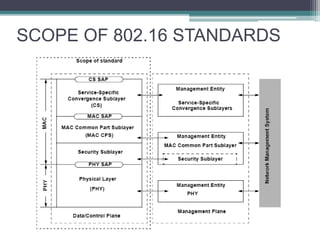
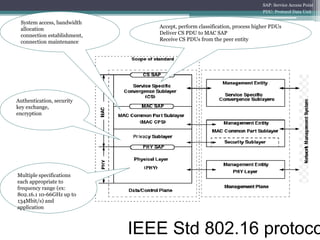
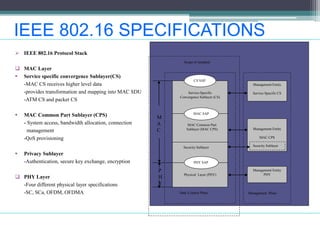
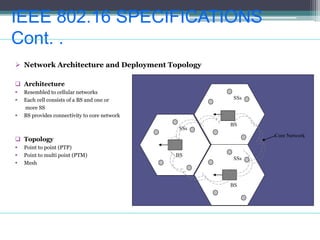
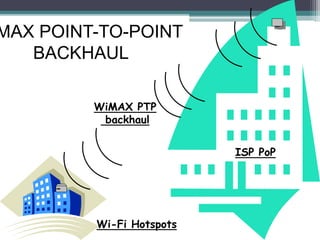
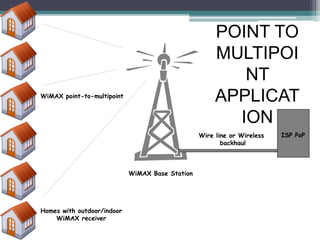
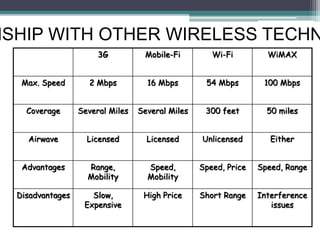
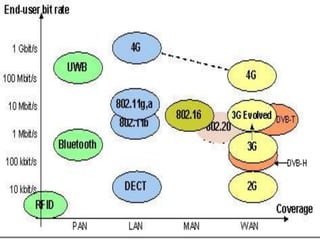
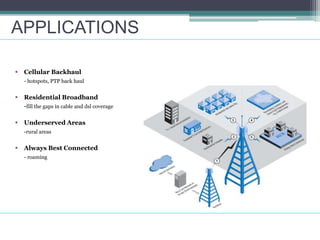
WiMAX is a wireless broadband technology that provides transmission of data using a wireless signal. It supports transmission of up to 30 miles for fixed users and 5-15 km for mobile users. The IEEE 802.16 standard defines the WiMAX technology specifications. It has evolved over time to support different frequencies and applications. WiMAX provides high-speed broadband access and can serve as a wireless alternative to cable and DSL networks. However, it requires line-of-sight and can be affected by interference or heavy rain. Potential applications include cellular backhaul, residential broadband access, and connectivity in underserved areas.