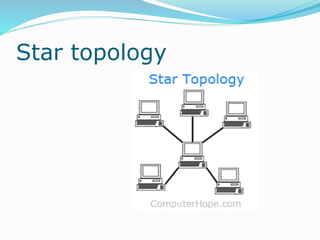
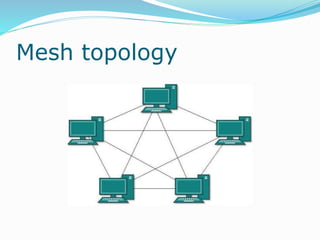
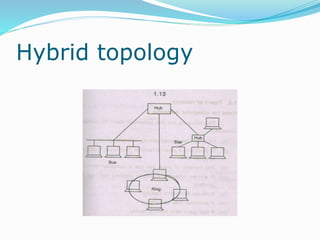
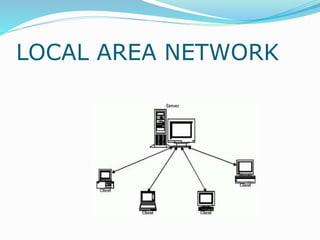
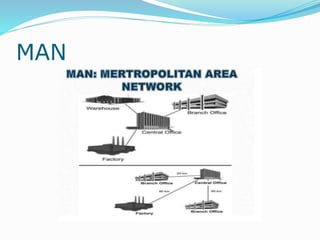
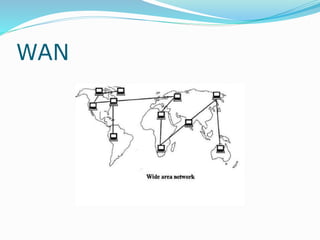
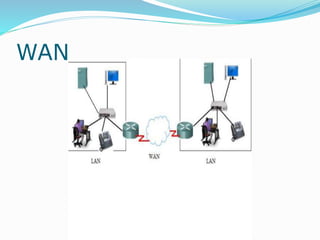
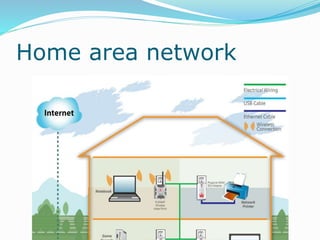
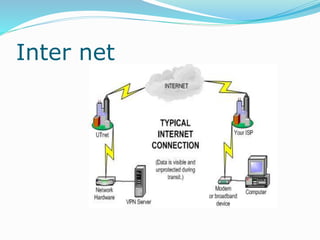
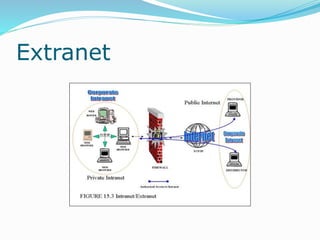
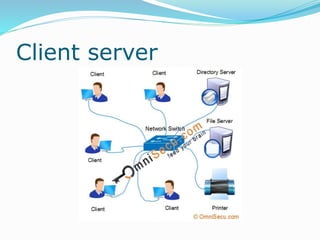
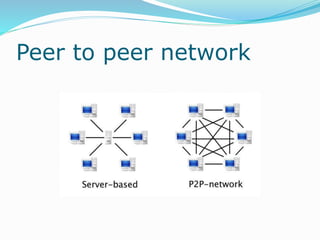
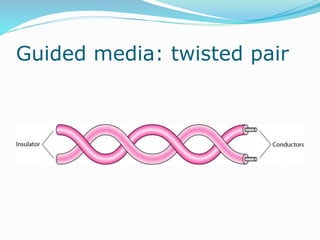
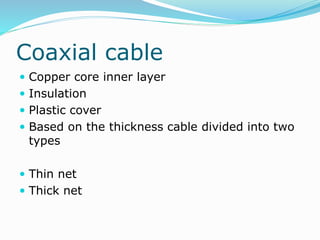
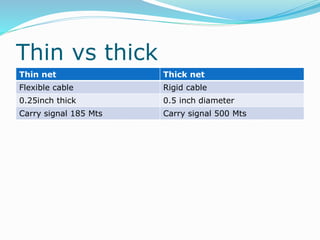
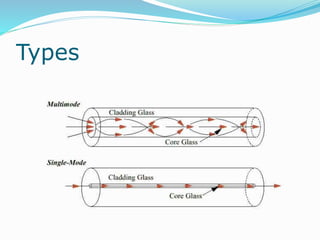
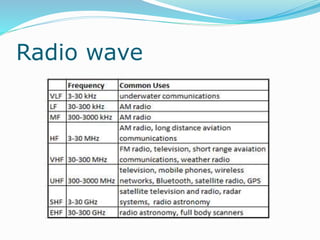
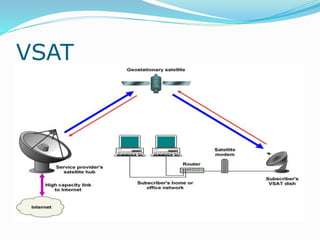
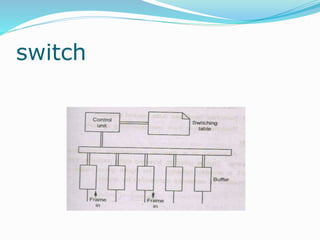
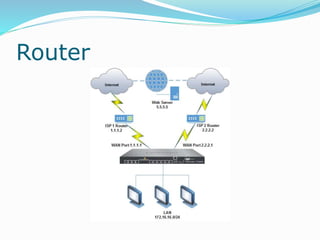
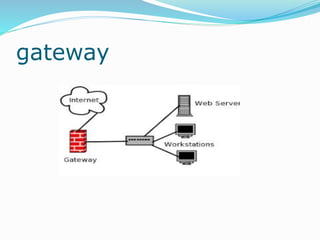
The document discusses various topics related to computer networks including network topologies (star, mesh, hybrid), transmission media (twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, radio waves, infrared), network devices (switches, routers, gateways), and standards (cable standards, types of switches, functions of routers and gateways). It provides information on LAN, MAN, WAN and other network types as well as guided and unguided transmission media.