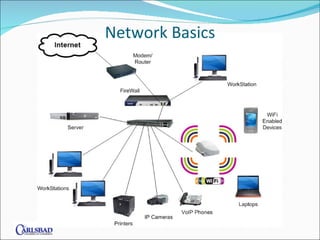
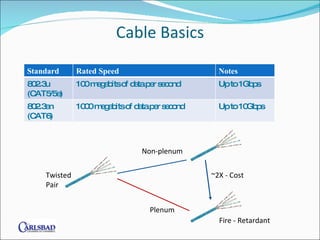
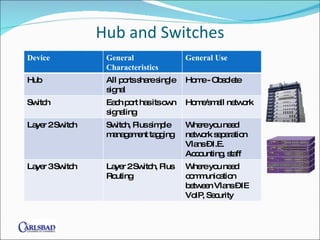
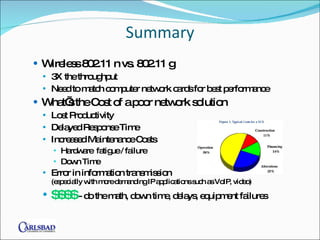
The document provides an overview of network basics, focusing on structured cabling, active components like hubs and switches, and wireless solutions. It compares different cable categories (Cat5/5e vs. Cat6) and their implications for speed, cost, and network performance, while also addressing the importance of selecting qualified installers and manufacturers. Additionally, it highlights the consequences of poor network solutions, including impact on productivity and equipment reliability.