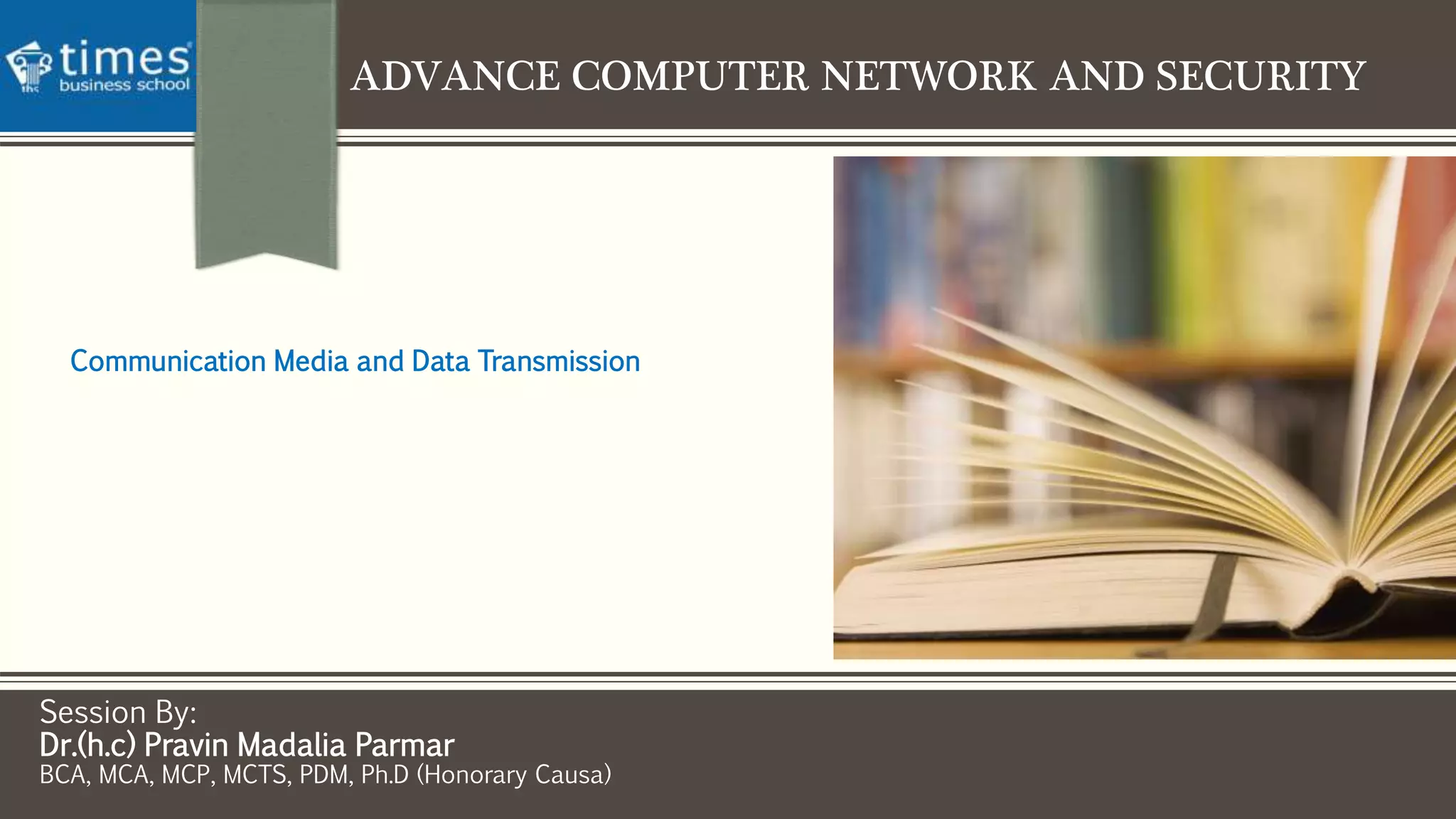
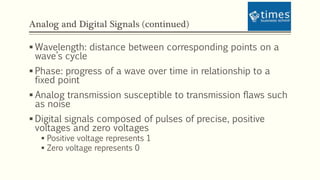
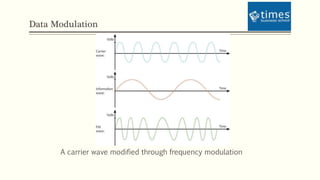
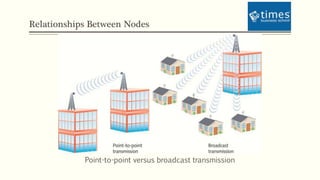
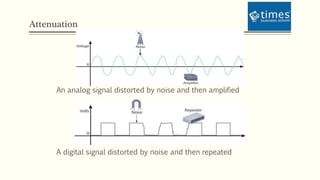
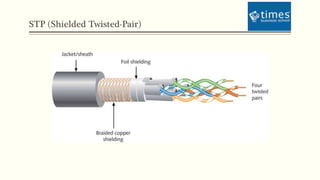
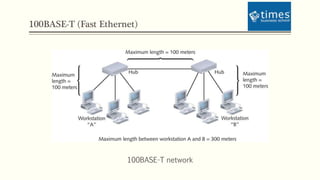
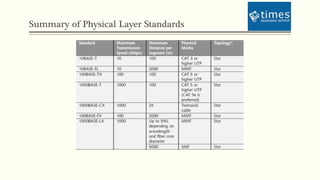
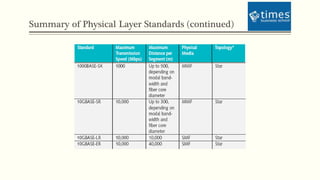
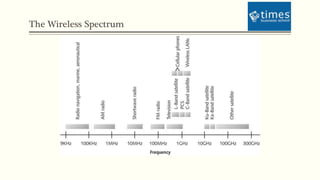
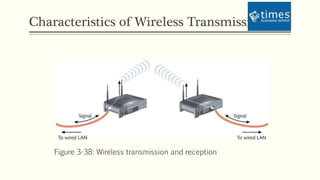
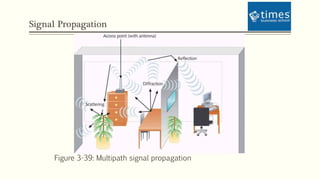
This document discusses communication media and data transmission. It covers topics such as analog and digital signals, transmission basics, networking media like coaxial cable, twisted-pair cable, fiber-optic cable, and wireless transmission methods. It compares different media types and provides an overview of concepts like throughput, bandwidth, latency, attenuation, and noise. It also discusses topics like data modulation, transmission direction, multiplexing, and the physical layer standards for Ethernet networks.