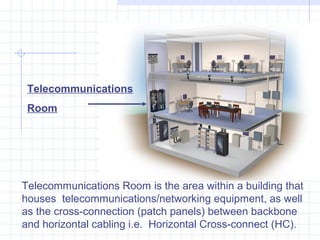
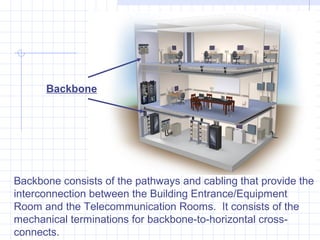
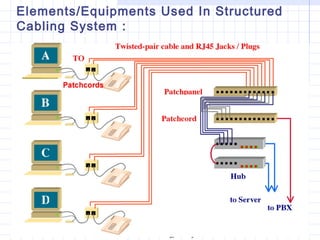
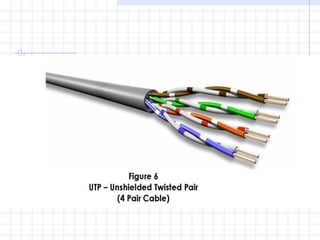
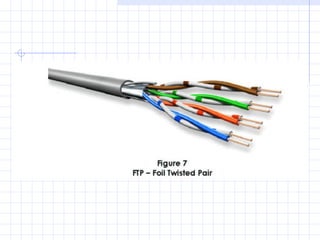
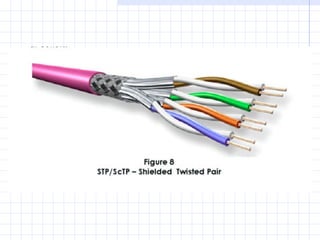
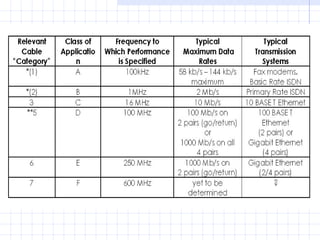
A structured cabling system integrates data, voice, video and management systems through a standardized infrastructure. It includes 6 sub-systems: building entrance, equipment room, telecommunications room, backbone cabling, horizontal cabling, and work areas. The telecommunications room houses networking equipment and cross-connects between backbone and horizontal cabling. Backbone cabling connects telecommunications rooms to the equipment room. Horizontal cabling extends from telecommunications rooms to work areas. A structured cabling system provides benefits like redundancy, ease of fault location and repair, flexibility, and long-term cost containment.